HashiCorp Certified: Vault Operations Professional 2022
Configure Access Control
Control Group
Control groups provide an extra layer of approval for sensitive Vault paths, requiring designated approvers to explicitly authorize each request. This feature is covered in the Vault Certified Operations Professional exam and can be useful when you need multi-party approval on top of ACL and Sentinel policies.
Note
Control groups are rarely used in production environments but are essential for high-security workflows and exam preparation.
What Are Control Groups?
By default, Vault evaluates:
- The token’s attached ACL policies
- Any Sentinel policies applied to the token or path
With a control group configured on a path, Vault enforces a third requirement: an explicit approval step from one or more designated identity groups before returning secrets.

Control Group Factors
You can define control group requirements in:
- ACL policies
- Sentinel policies
Currently, the only supported factor is an Identity Group, which specifies both the list of approvers and the number of required approvals.
| Factor Type | Description | Example Use |
|---|---|---|
| Identity Group | Approver group names and approval count | Require 2 approvals from account-managers |
Require 1 approval each from account-managers and security-team |

Control Group Workflow
When a control group is applied, Vault follows this sequence:
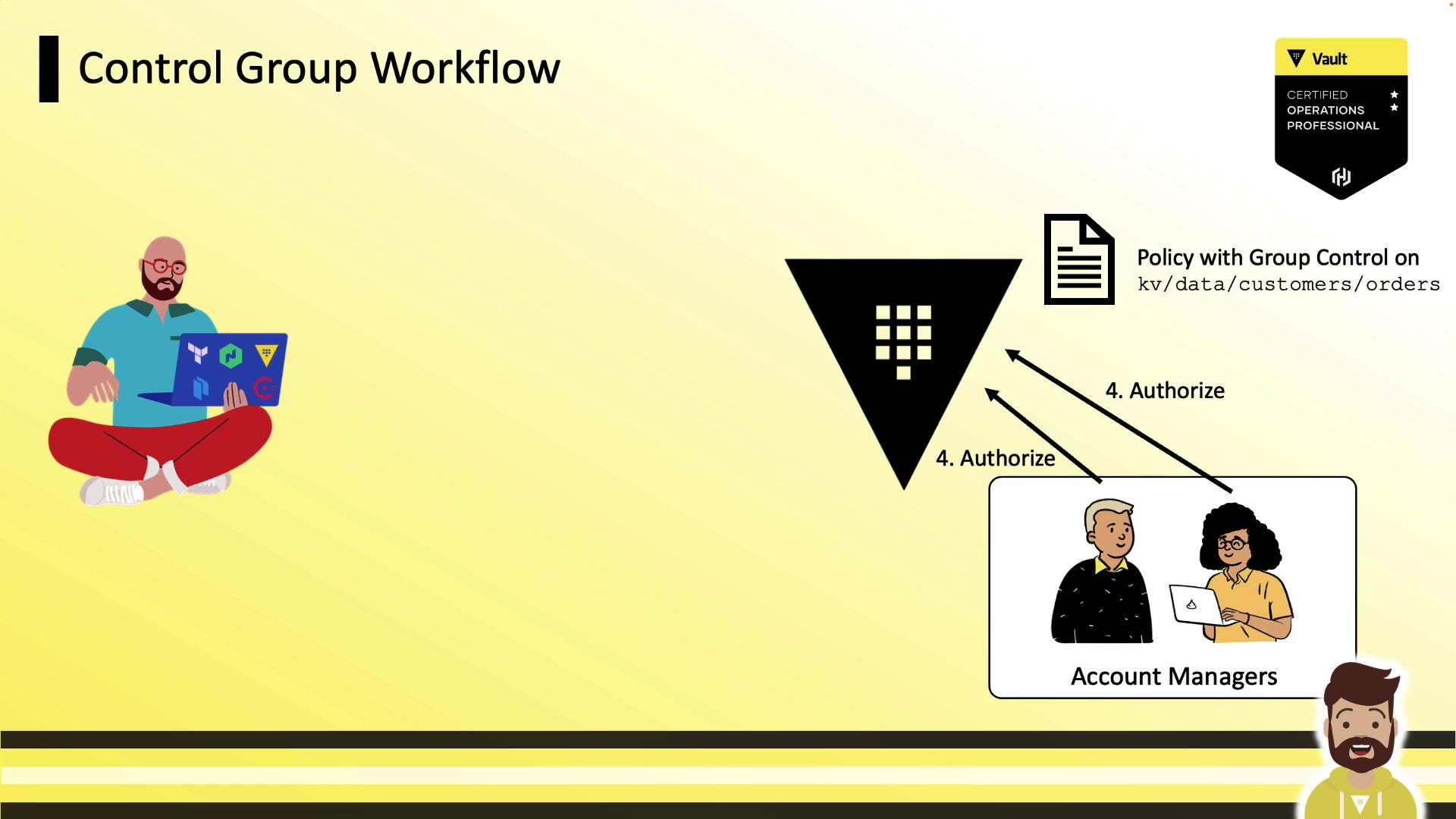
- Client requests a secret at the protected path.
- Vault returns a wrapping token instead of the secret.
- Client shares the wrapping token’s accessor with the approvers.
- Approvers submit the accessor back to Vault to authorize the request.
- Once all approvals are met, the client runs
vault unwrapto retrieve the secret.
1. Client Receives a Wrapping Token
A standard read on a protected path yields wrapping info:
{
"wrap_info": {
"token": "hvs.CAESIPvNkRgluUVNT_ccLsm6aZ-",
"accessor": "cql9n3r4kMeIQZekoLrMWMWN",
"ttl": 300
// ...
}
}
The client then forwards the accessor to the designated approvers.
2. Approvers Authorize the Request
Approvers log in (CLI or UI) and run:
vault write sys/control-group/authorize accessor="cql9n3r4kMeIQZekoLrMWMWN"
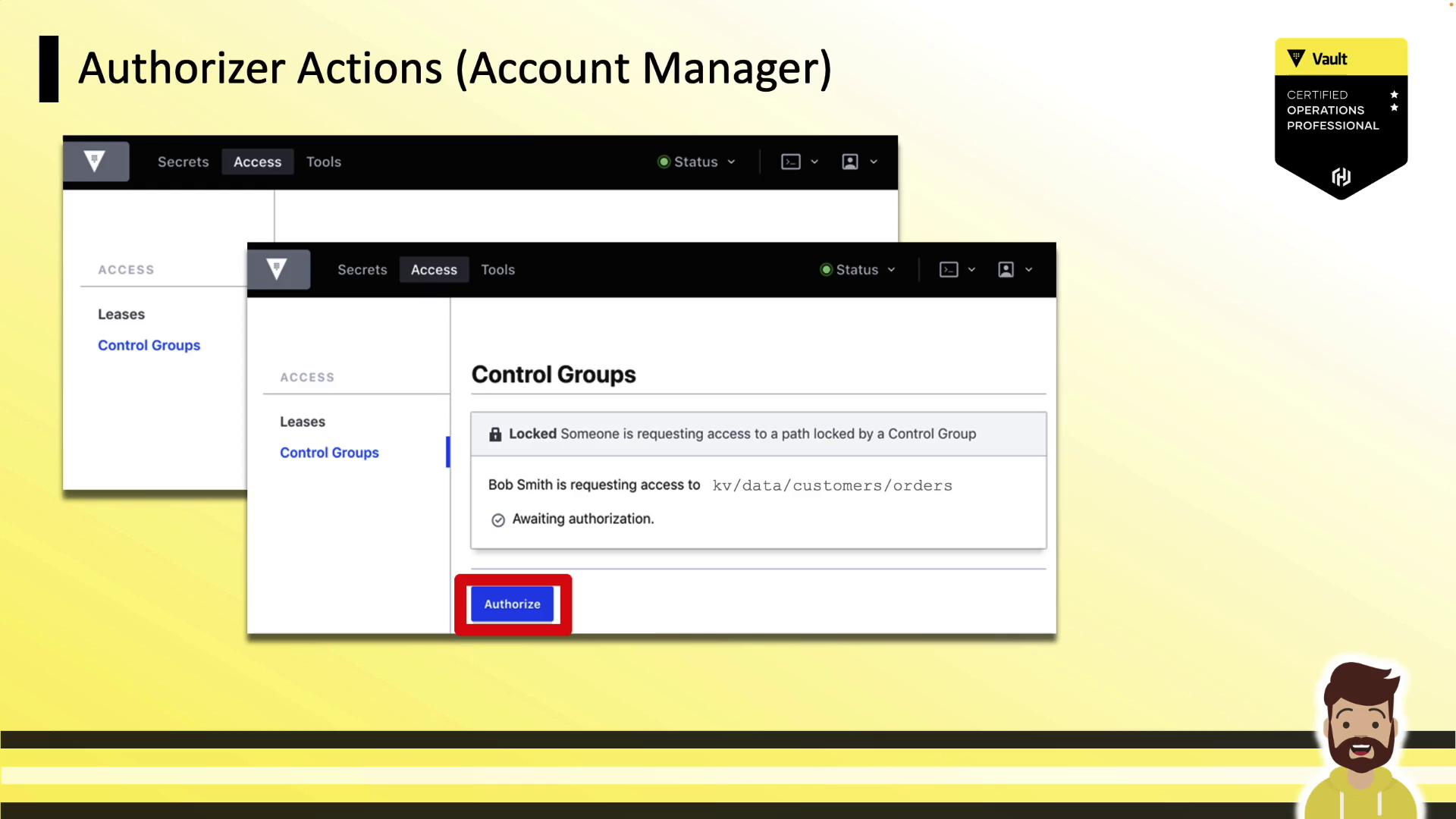
If the policy requires multiple sign-offs, Vault waits until all approvals are recorded:
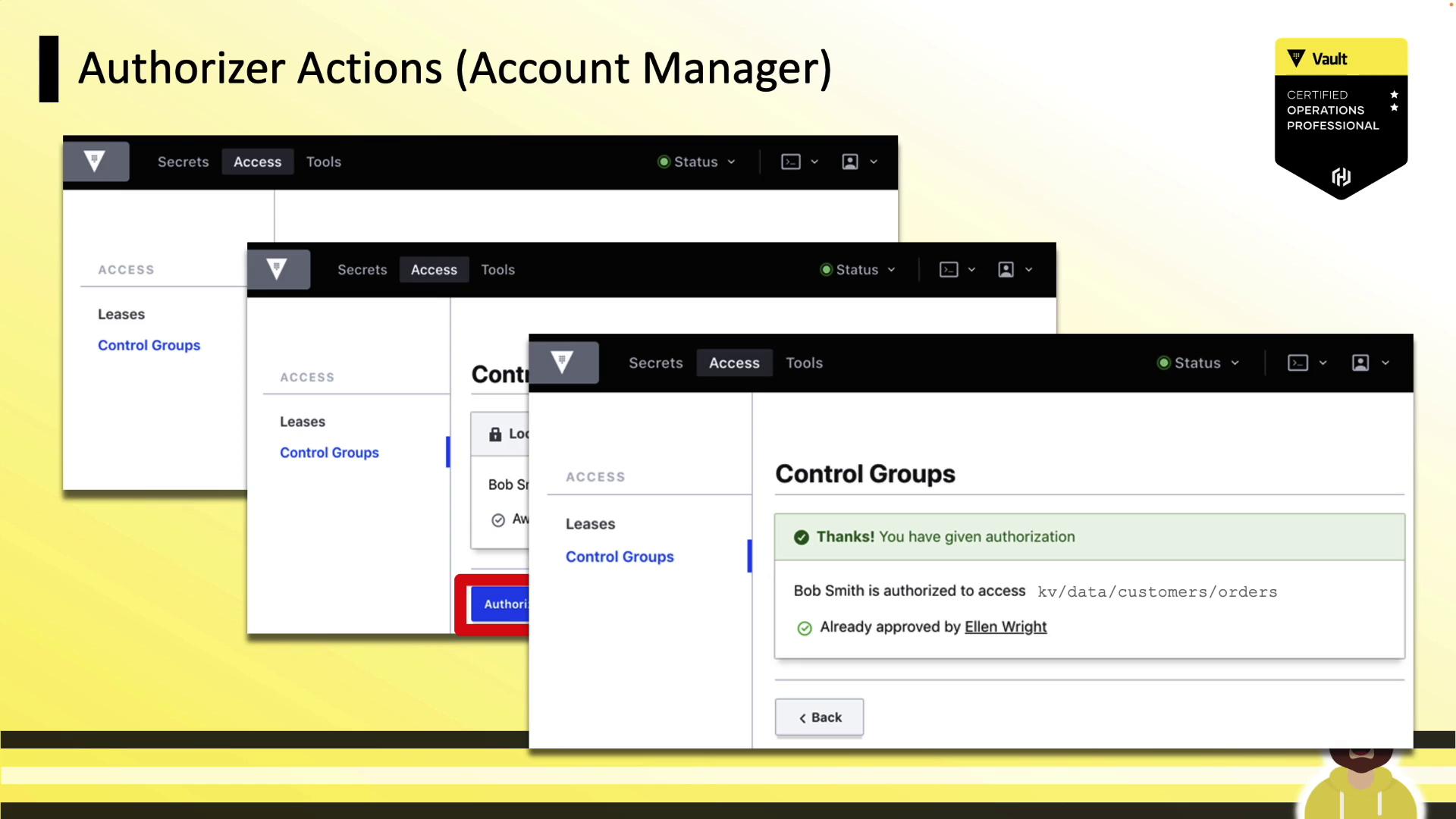
3. Client Unwraps the Secret
After approvals:
vault unwrap hvs.CAESIPvNkRgluUVNT_ccLsm6aZ-
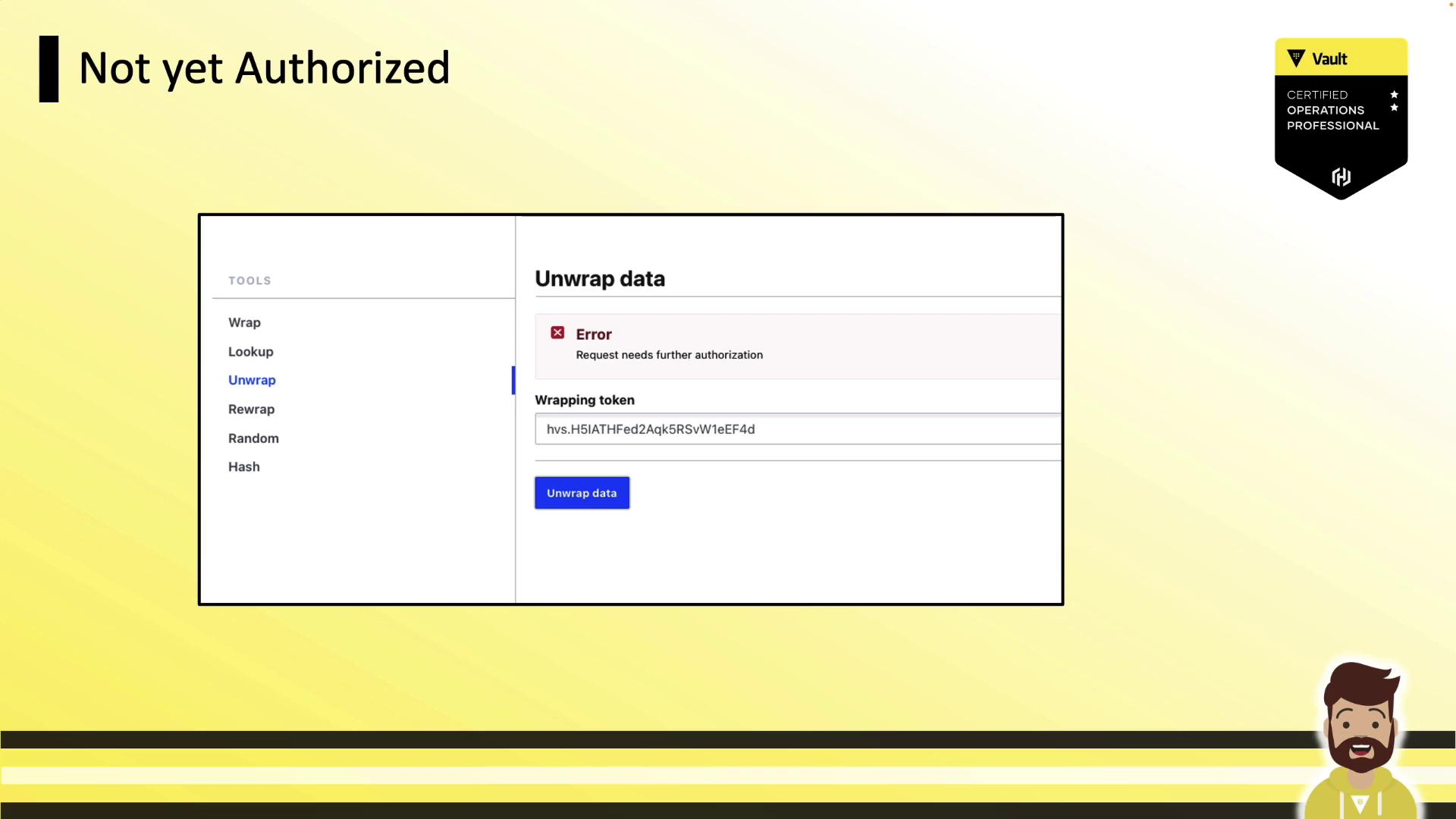
If approvals are missing, unwrap returns an error:
Defining Control Groups in ACL Policies
The following ACL policy requires two approvals from the account-managers group on path kv/data/customers/orders:
path "kv/data/customers/orders" {
capabilities = ["read"]
control_group = {
factor "acct_manager" {
identity {
group_names = ["account-managers"]
approvals = 2
}
}
}
}
You can add multiple factor blocks or specify multiple group_names for more complex authorization schemes.
Defining Control Groups in Sentinel Policies
Control groups can also be enforced in Sentinel as an External Governance Policy (EGP). This example requires at least two approvals from account-managers:
import "controlgroup"
control_group = func() {
numAuthzs = 0
for controlgroup.authorizations as authz {
if "account-managers" in authz.groups.by_name {
numAuthzs = numAuthzs + 1
}
}
return numAuthzs >= 2
}
main = rule {
control_group()
}
Deploy this Sentinel policy to enforce the same approval workflow on your protected path.
Demo: Control Groups in Action
Authenticate with a token that has a control-group policy:
vault login hvs.CAESIA7Y-LwSxnE926onQwdxlUF7w7KJ5-Request the secret:
vault kv get kv/customers/ordersShare the
wrapping_accessorwith approvers and await authorization.Unwrap the token once all approvals are in place:
vault unwrap hvs.H5IATHFed2Aqk5RsW1eEF4d
Conclusion
Control groups add a mandatory multi-party approval step on top of standard ACL and Sentinel policies. While the only supported factor today is an identity group, mastering control groups is crucial for sensitive workflows and the Vault Certified Operations Professional exam.
References
Watch Video
Watch video content