- What are Vault Secrets Engines?
- Generic vs. Cloud-Integrated Engines
- Enabling Engines with CLI
- Enabling Engines via UI
- Next Steps
What Are Secrets Engines?
Vault Secrets Engines enable integration with external platforms and back-end systems by generating dynamic secrets, certificates, encryption, and identity data. While Vault supports a wide range of cloud providers and services, this tutorial focuses on the core generic engines tested in the HashiCorp Certified Vault Operations Professional exam.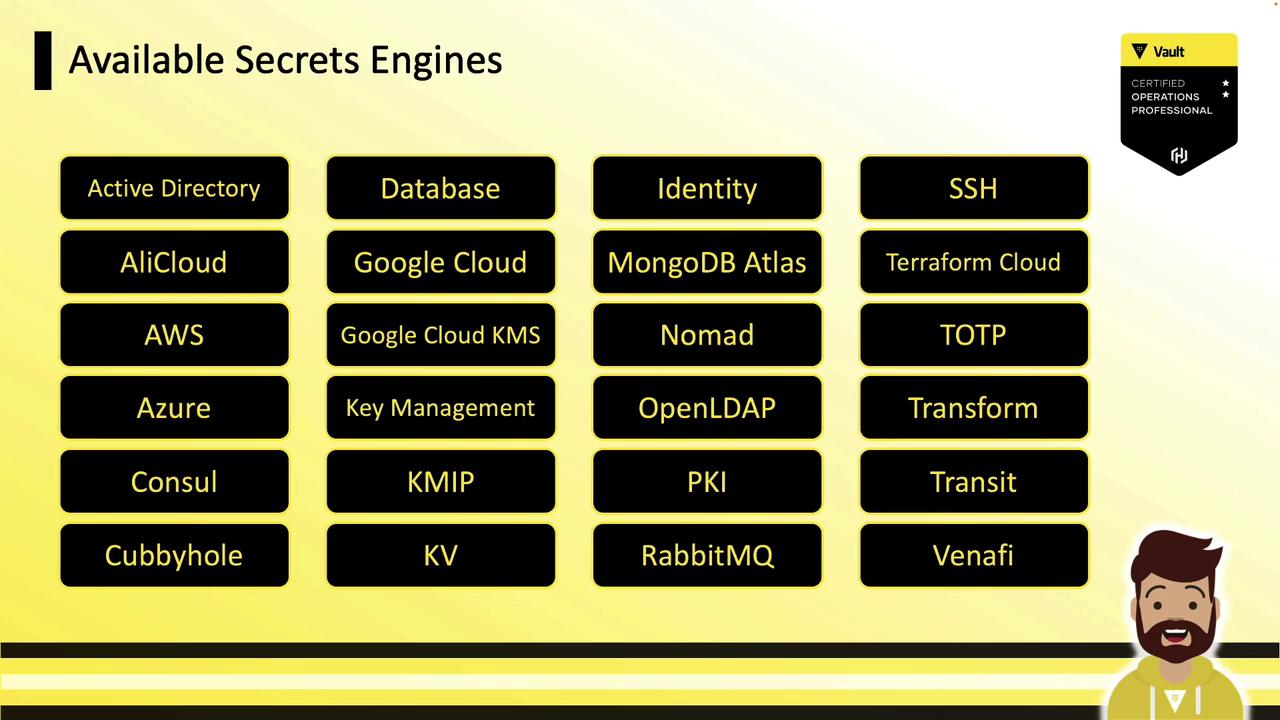
Generic Secrets Engines
Vault’s generic Secrets Engines do not require deep expertise in external platforms. These are commonly used across environments and covered in Vault certification:
| Engine | Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Database | Dynamic database credentials | 13+ platforms (MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, etc.) |
| KV (v1/v2) | Key/Value storage | v1 (simple) & v2 (versioned, metadata) |
| PKI | Certificate issuance & management | X.509/TLS certificates |
| Transit | Encryption-as-a-Service | Data encryption, auto-unseal |
| Cubbyhole | Per-token private secret storage | Enabled by default |
| Identity | Identity data storage | Enabled by default |
Enabling Secrets Engines
Engines can be enabled at a custom mount path using the Vault CLI, API, or UI. The UI offers a simple way to enable common engines, but some advanced configurations require CLI or API.
Use meaningful mount paths (e.g.,
prod-db/ or teams/cloud-kv/) to simplify management and auditing.Enable with Vault CLI
Thevault secrets command suite manages engine lifecycle:
enable: Mount a new enginedisable: Unmount an enginelist: View enabled enginesmove: Rename or relocate a mount pathtune: Adjust engine settings (TTLs, descriptions)
Sample Output
Ensure your Vault token has the
root policy or appropriate sys/mount and sys/cap capabilities to enable and configure Secrets Engines.Enabling Engines via UI
- Open the Vault UI and navigate to the Secrets tab.
- Click Enable New Secrets Engine.
- Select an engine type, configure the mount path and options, then click Save.
- For engines not fully supported in the UI, switch to the CLI or API for advanced settings.

Next Steps
Now that you’ve learned how to enable and manage Vault Secrets Engines, the next sections will dive deeper into configuring each engine:- Key/Value (KV) Secrets Engine
- Database Secrets Engine
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
- Transit Secrets Engine
- Identity and Cubbyhole Engines