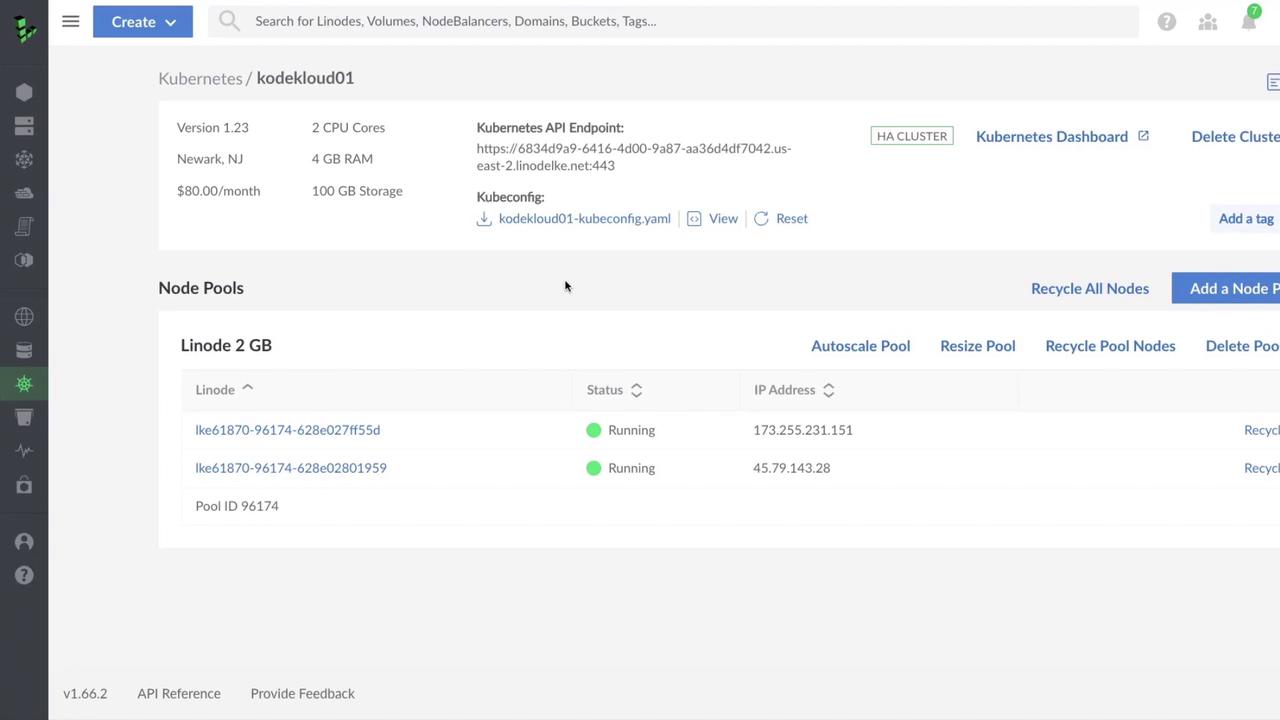
Exploring the LKE dashboard first gives you context on what happens behind the scenes when you later create and manage clusters.
Cluster Details
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Rename your cluster at any time for better identification. |
| Kubernetes Version | Shows the control plane version (e.g., v1.22). |
| Resources | Total CPU cores, RAM, and storage allocated. |
| Region | Data center location (e.g., us-east-1). |
| Price | Estimated monthly cost for the control plane and nodes. |
API Endpoint
LKE exposes your cluster’s API endpoint publicly. If you query it without valid credentials, you’ll see a 403 Forbidden error:Kubeconfig File
Download your cluster’s Kubeconfig from the dashboard and save it to~/.kube/config (or merge with your existing file). It includes:
- Certificate Authority data
- API server URL
- User credentials (token)
- Context settings
If your Kubeconfig is ever compromised, regenerate it immediately to revoke the old credentials.
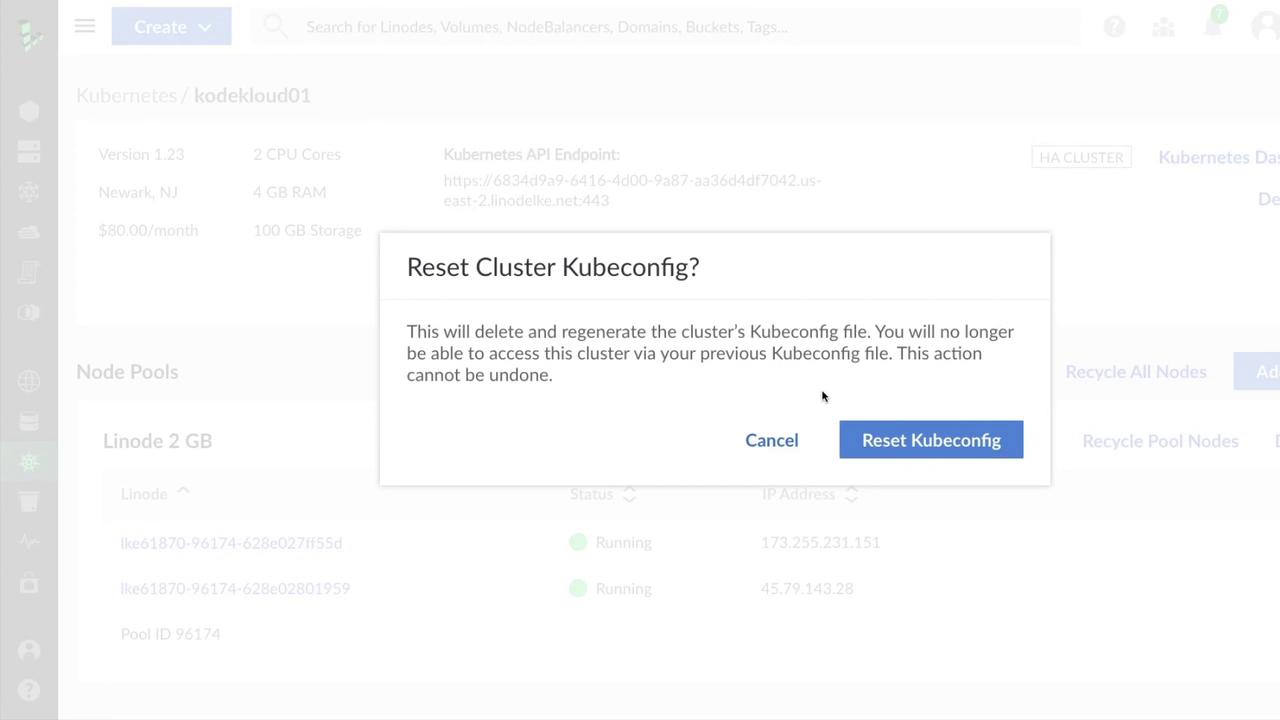
Kubernetes Dashboard & Node Pools
In the LKE dashboard, you’ll also find quick links for:- Accessing the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Managing cluster tags
- Deleting the entire cluster
- Recycle individual nodes or all nodes at once
- Enable autoscaling for dynamic scaling
- Resize node plans
- Delete individual nodes or entire node pools
- Create additional node pools
Links and References
Related Resources
| Resource | Purpose | Example Command |
|---|---|---|
| Pod | Basic unit of deployment | kubectl run nginx --image=nginx |
| Deployment | Managed pods with scaling | kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx |
| Service | Network access to pods | kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80 |
| NodePool | Worker node management | Configure via LKE dashboard or Terraform provider |