AWS Solutions Architect Associate Certification
Designing for Cost Optimization
Cost Optmization Concepts with Various AWS Services
Welcome to today's lesson presented by Michael Forrester. In this session, we explore AWS cost optimization strategies, including licensing options, reservation models, savings plans, ROI/TCO analysis, and billing tools. This guide is structured for clarity and SEO optimization, complete with diagrams to illustrate each concept.
Licensing Options for AWS Services
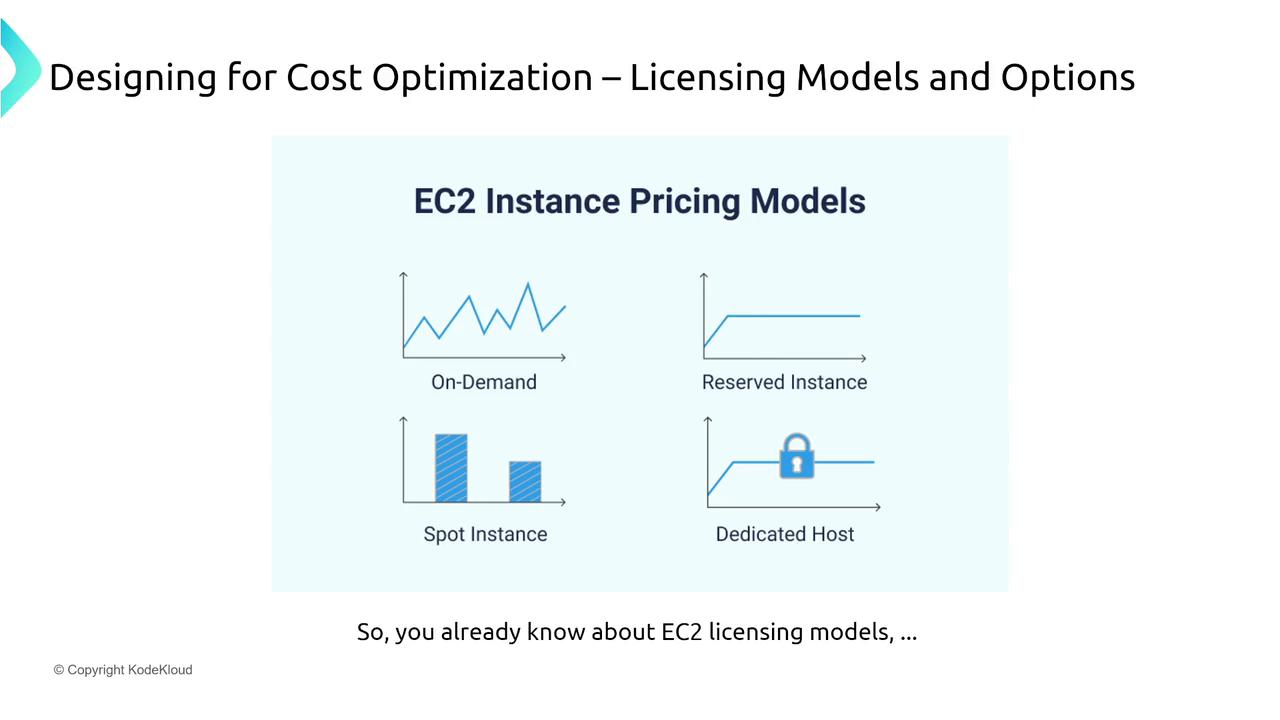
AWS provides several pricing models to help you optimize costs for services such as Amazon EC2:
On-Demand Pricing:
Pay the fixed hourly rate (e.g., $1 per hour) with no long-term commitment. This option offers maximum flexibility for dynamic workloads.Reserved Instances:
Commit to a one- or three-year term, which significantly reduces the hourly rate (for example, from $1 to 70 cents per hour). This model is ideal for steady-state or predictable workloads.Dedicated Hosts:
Reserve complete physical servers at a higher cost (e.g., $20 per hour). This option provides enhanced security and compliance by isolating your instances on dedicated hardware.Spot Instances:
Utilize excess AWS capacity at a much lower price (around 50% of the on-demand rate). These instances are best suited for non-critical, interruptible workloads such as batch processing or reporting, as they can be reclaimed by AWS with a two-minute warning.
The diagram below visualizes these various EC2 instance pricing models as part of AWS cost optimization strategies:
Reserved Instance Variations
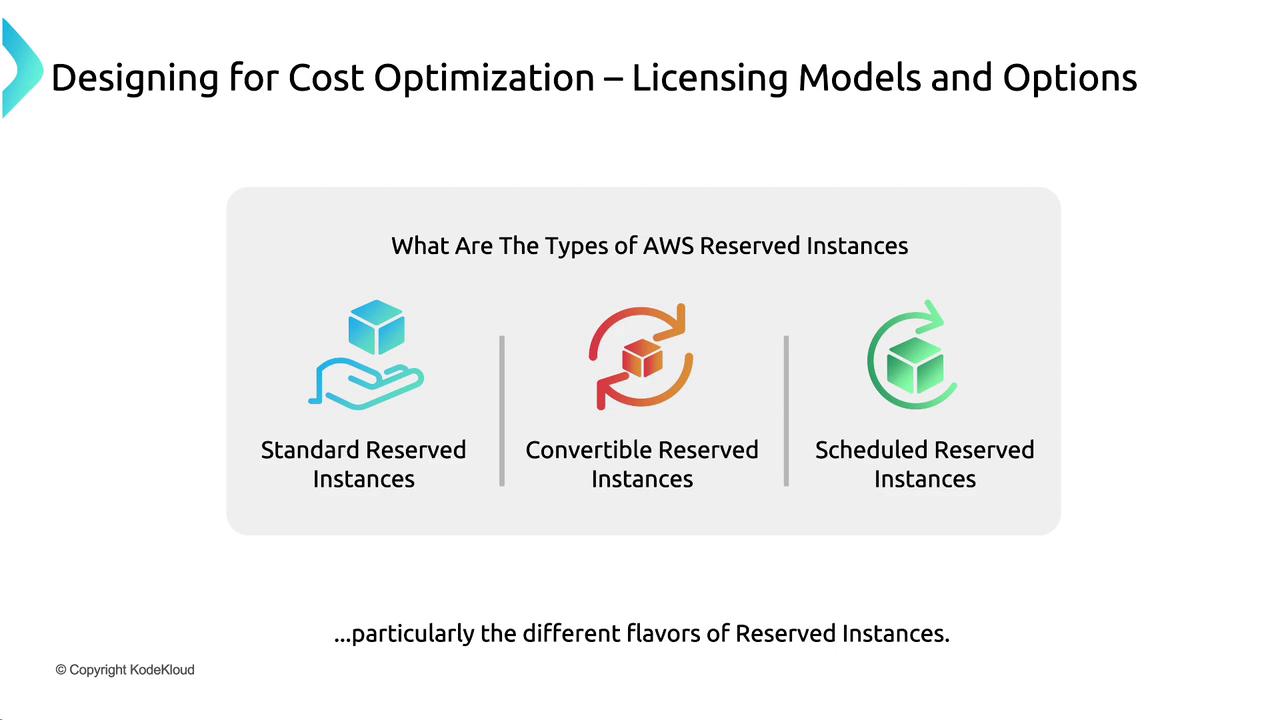
Reserved Instances offer different types of commitments to suit varying business needs:
Standard Reserved Instances:
Offer the highest discounts (up to 66% off) in exchange for a strict one- or three-year commitment. An example is reserving a Red Hat Linux M5 XL instance in a specific availability zone (e.g., Virginia) to achieve maximum savings.Convertible Reserved Instances:
Provide flexibility by allowing changes in instance types, operating systems, or locations as your requirements evolve.Scheduled Instances:
Reserve capacity during predetermined time periods (for instance, extra web servers during business hours, Monday through Friday from 8 a.m. to 8 p.m.), rather than a continuous 24/7 commitment.
The following image outlines these different types of Reserved Instances:
Savings Plans
AWS offers Savings Plans as another layer of cost optimization:
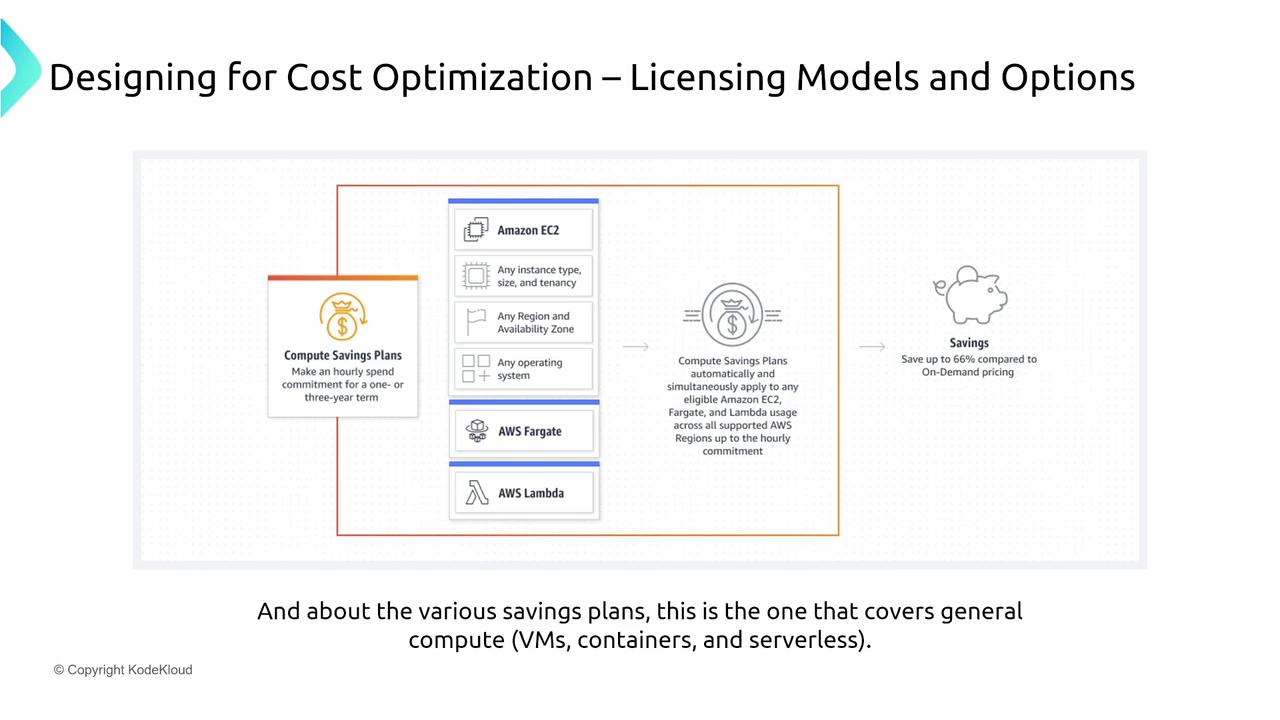
Compute Savings Plans:
These plans offer discounted rates across services such as EC2, AWS Fargate, and AWS Lambda. By committing to a specific spend—turning $10,000 into an effective $30,000 usage bucket over one or three years—you can secure substantial discounts.Note
AWS Fargate is integrated with ECS and EKS rather than being a standalone service.
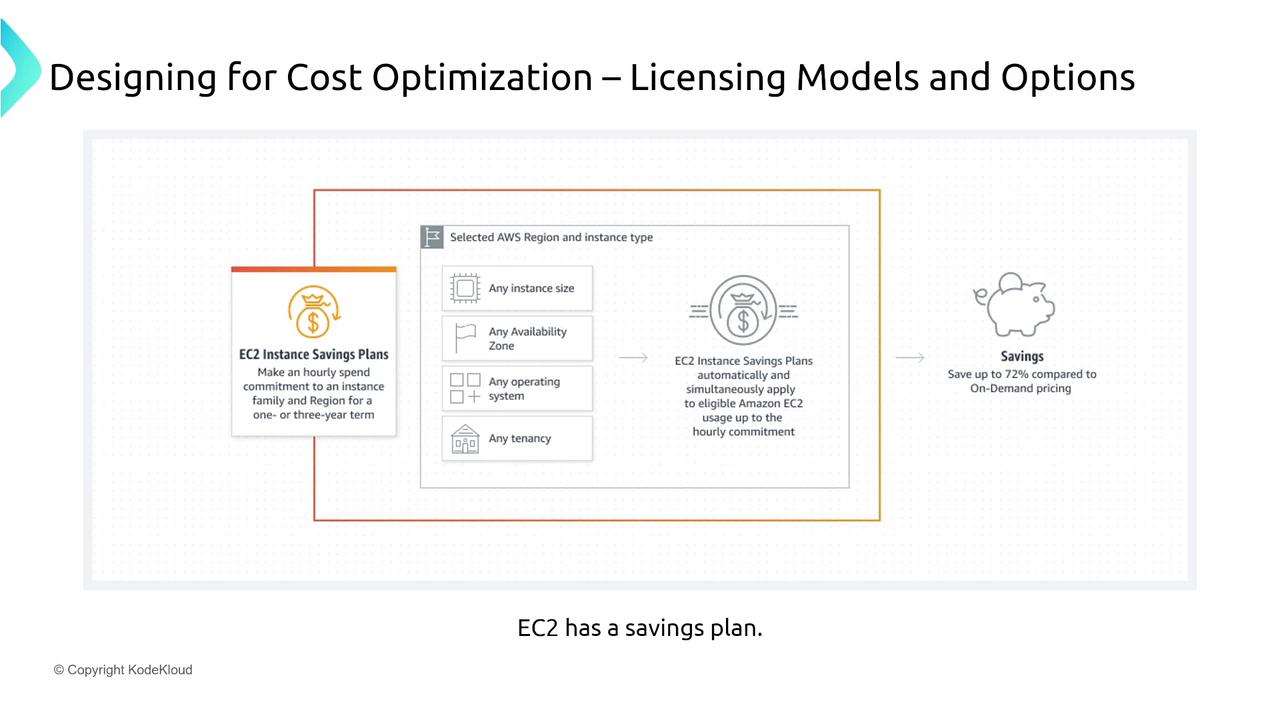
EC2 Instance Savings Plans:
Focus exclusively on virtual machine usage and can save up to 72% with a three-year commitment and partial upfront payment.SageMaker Savings Plans:
Tailored for machine learning workloads, these plans can offer up to 64% discounts, which is critical considering the high compute requirements of ML applications.
The diagram below highlights Compute Savings Plans covering multiple services (Virtual Machines, Fargate, and Serverless):
Additionally, consider the specific advantages of EC2 Instance Savings Plans:
For machine learning applications, the SageMaker Savings Plans provide targeted benefits:
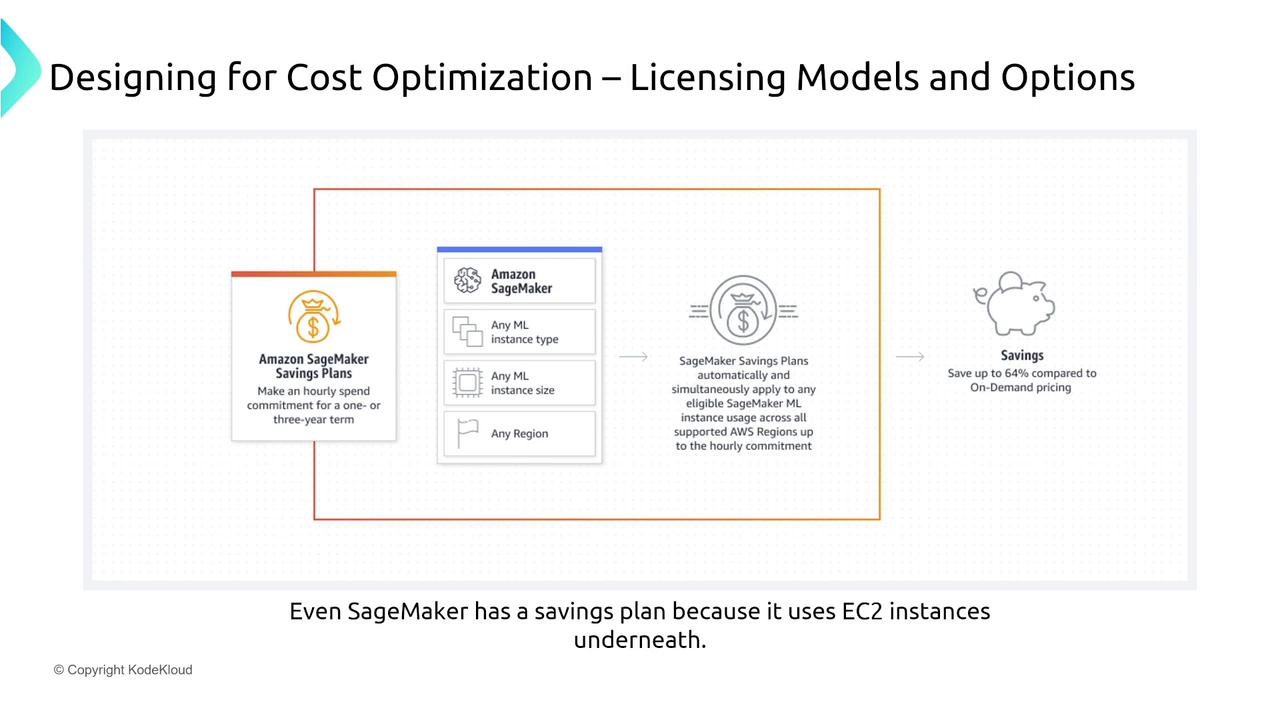
Reservations Beyond Compute
Reservations are available for numerous other AWS services to maximize cost savings:
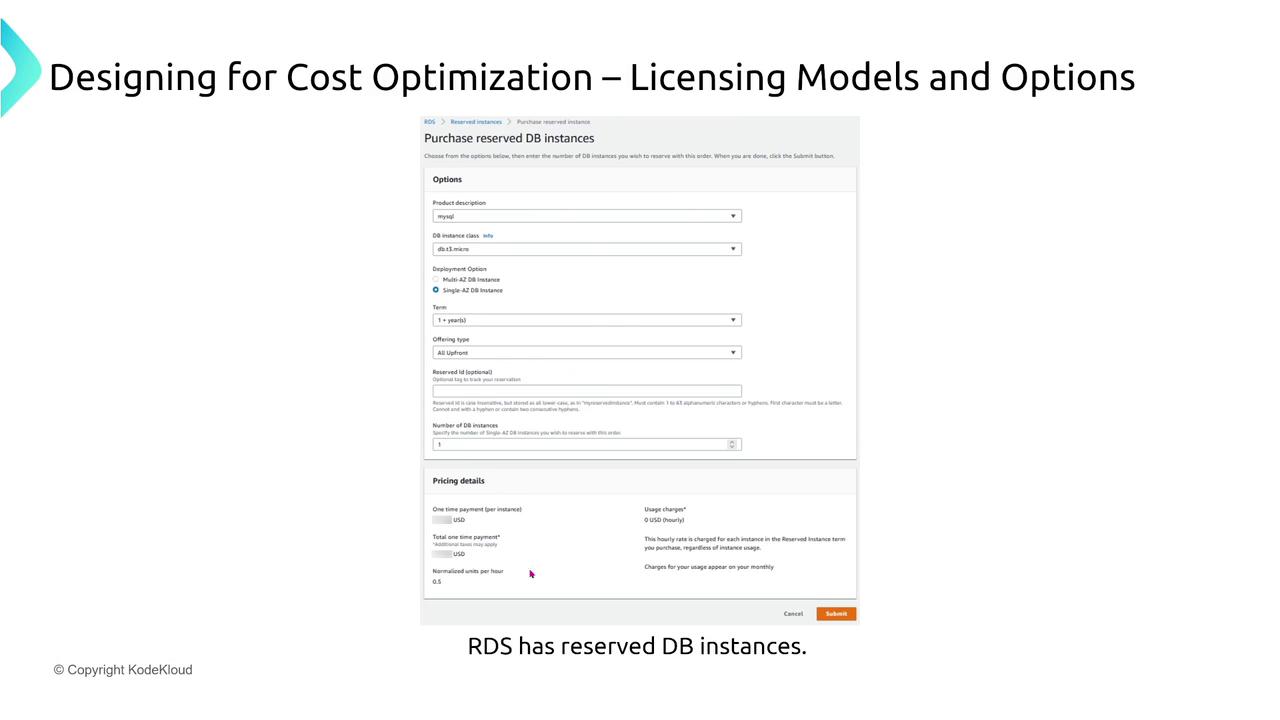
Amazon RDS:
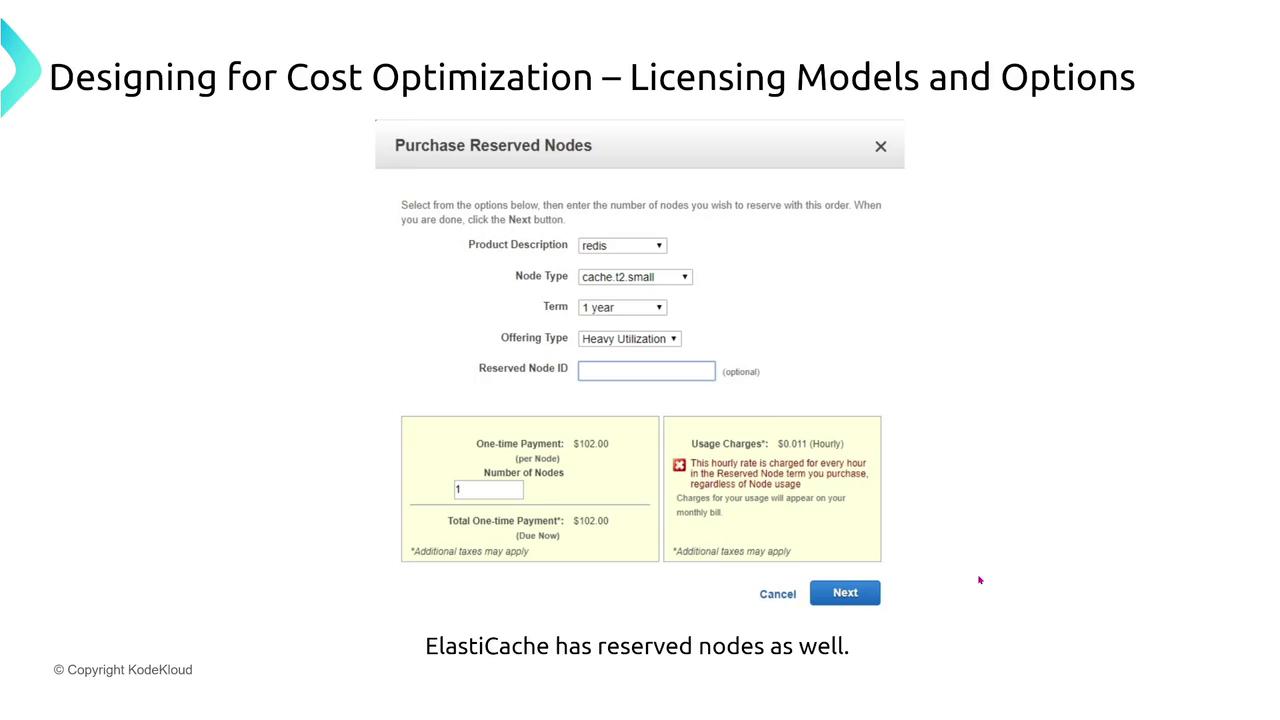
Reserve database instances (e.g., a MySQL T3 micro) for one or three-year periods to reduce long-term deployment costs.ElastiCache:
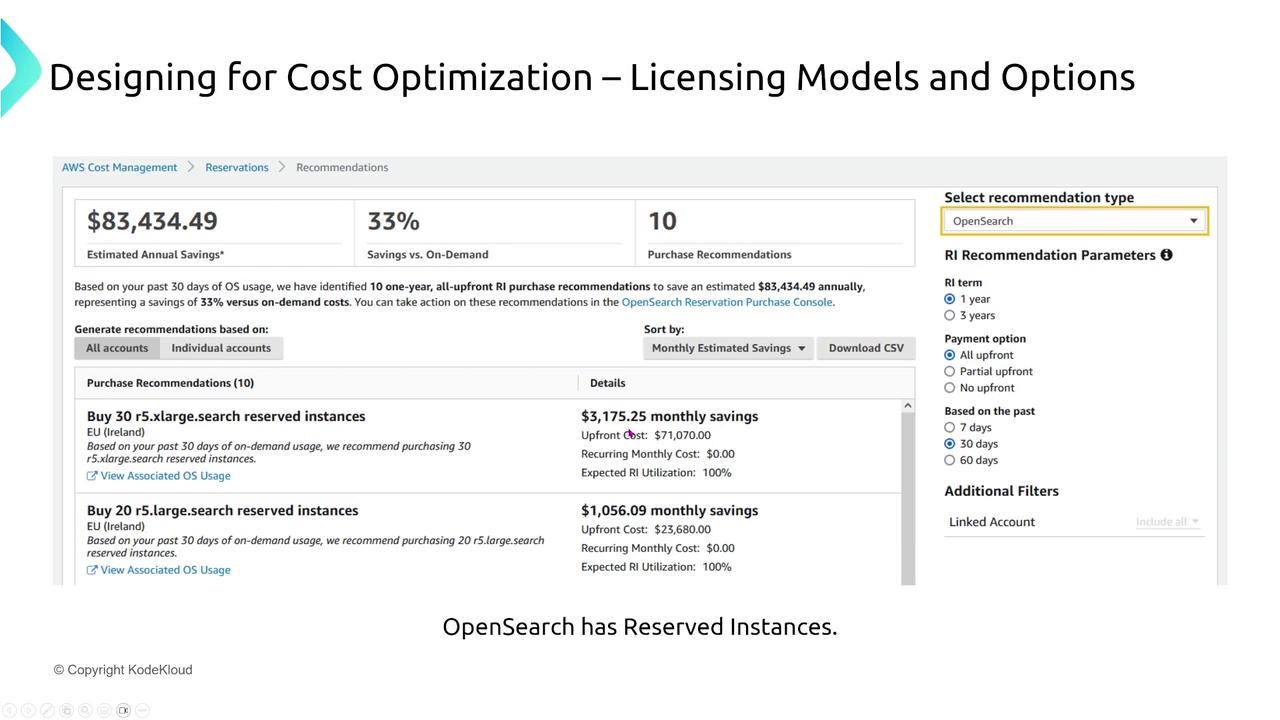
Reserve cache nodes (for instance, a T2 small node for one year) to lower caching service expenses.OpenSearch:
Utilize reserved capacity options similar to those for virtual machines, unlocking significant discounts.Redshift:
Switch from on-demand pricing (approximately $76,000 per year) to reserved nodes, potentially saving over 30%—tens of thousands of dollars.DynamoDB:
Even as a serverless service, you can reserve read/write capacity units for predictable workloads.CloudFront:
Leverage bundled cost-saving options, including CloudFront Functions and Lambda@Edge.
The image below summarizes the reservation options available across AWS services:

Additional images provide further insight into the reservation purchasing process:
The following diagram demonstrates AWS Cost Management recommendations for OpenSearch reservations:
For Redshift, the reserved node configuration screen highlights significant cost reductions:

CloudFront’s bundled saving options are depicted in the image below:
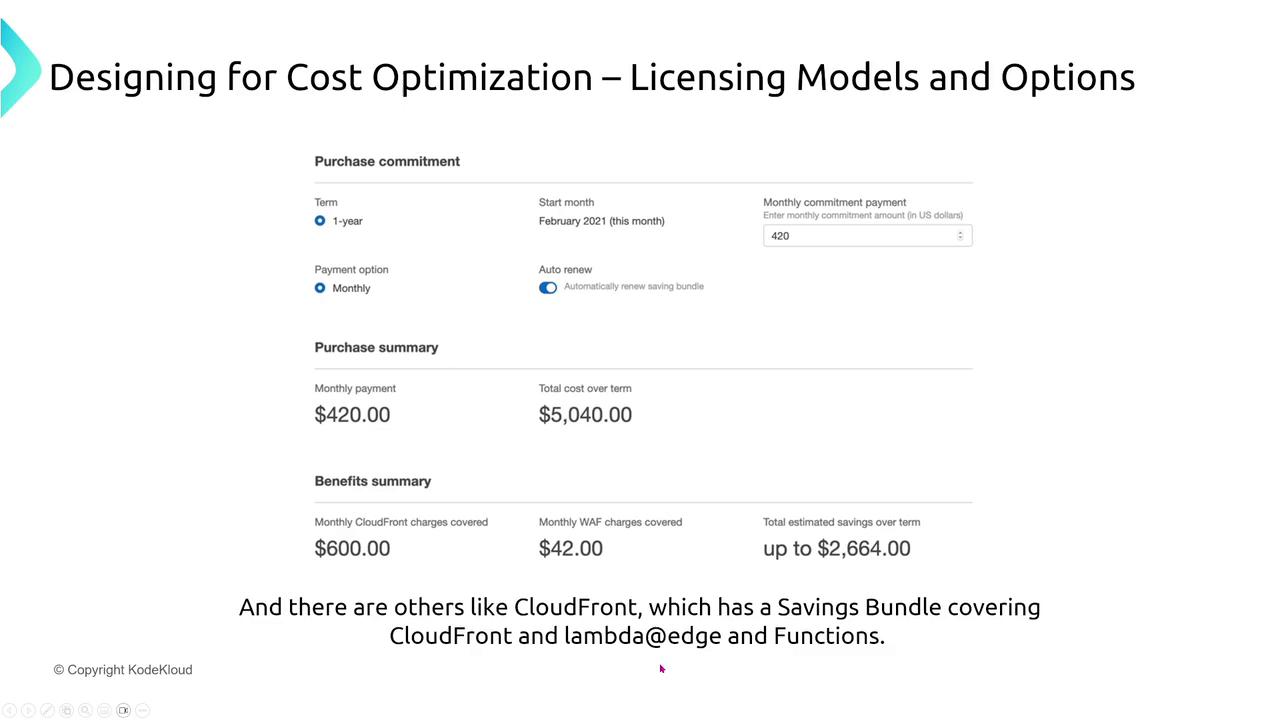
If additional discounts are needed beyond the public options, consider exploring enterprise agreements with your AWS representative.
ROI and Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Cost optimization extends beyond pricing models—it also involves a deeper understanding of the financial impact through ROI and TCO analysis.
Return on Investment (ROI)
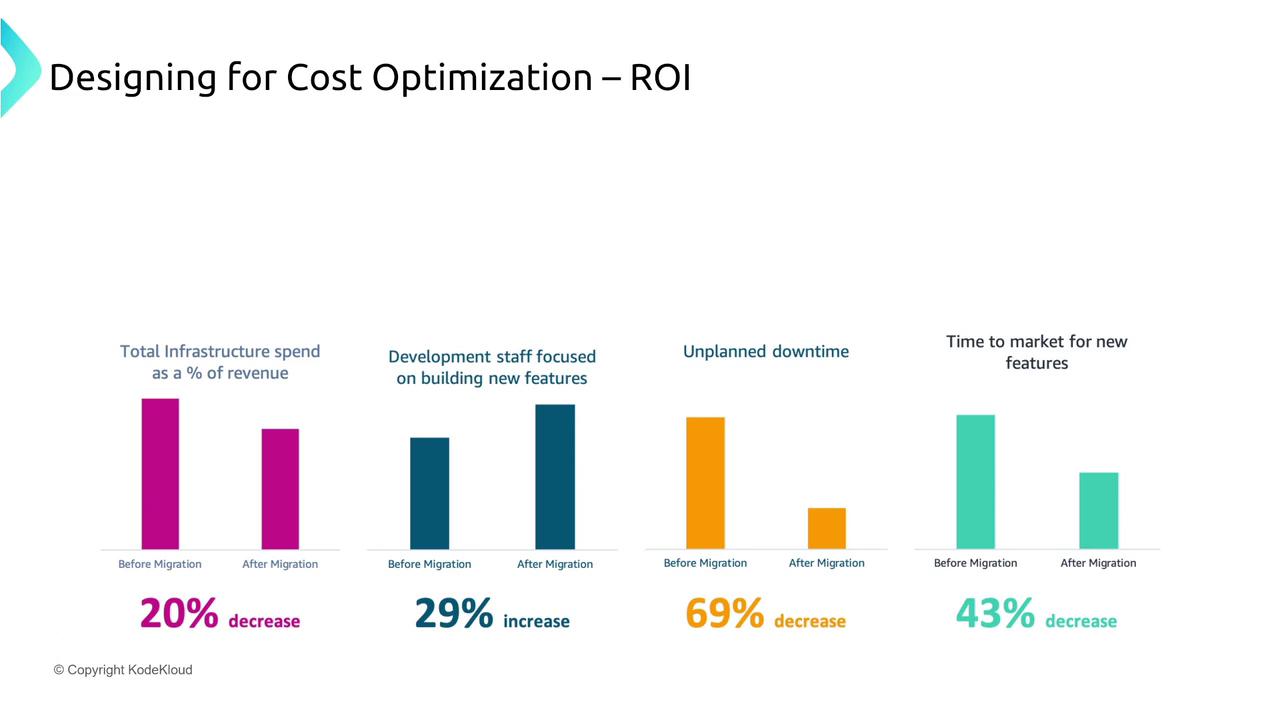
ROI measures whether each dollar spent on AWS delivers more value through benefits such as reduced downtime, faster time-to-market, and lower infrastructure expenses as a percentage of revenue. The bar chart below illustrates the positive impact of migration on key cost metrics:
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
TCO factors in both direct and indirect costs, including labor, maintenance, compliance, and potential disruptions. For example, while AWS may offer lower direct costs (e.g., $30 per month vs. $100 on-premises), the associated intangible benefits—such as increased uptime, reduced labor expenses, and an enhanced focus on innovation—are equally important.
The diagram below summarizes the ROI benefits and key advantages offered by AWS:

Another image compares the TCO between on-premises and AWS solutions, emphasizing the value of considering both tangible and intangible costs:

AWS Billing Tools
Effectively managing billing is critical for optimizing your AWS spending. AWS offers several tools that cater to different aspects of cost management:
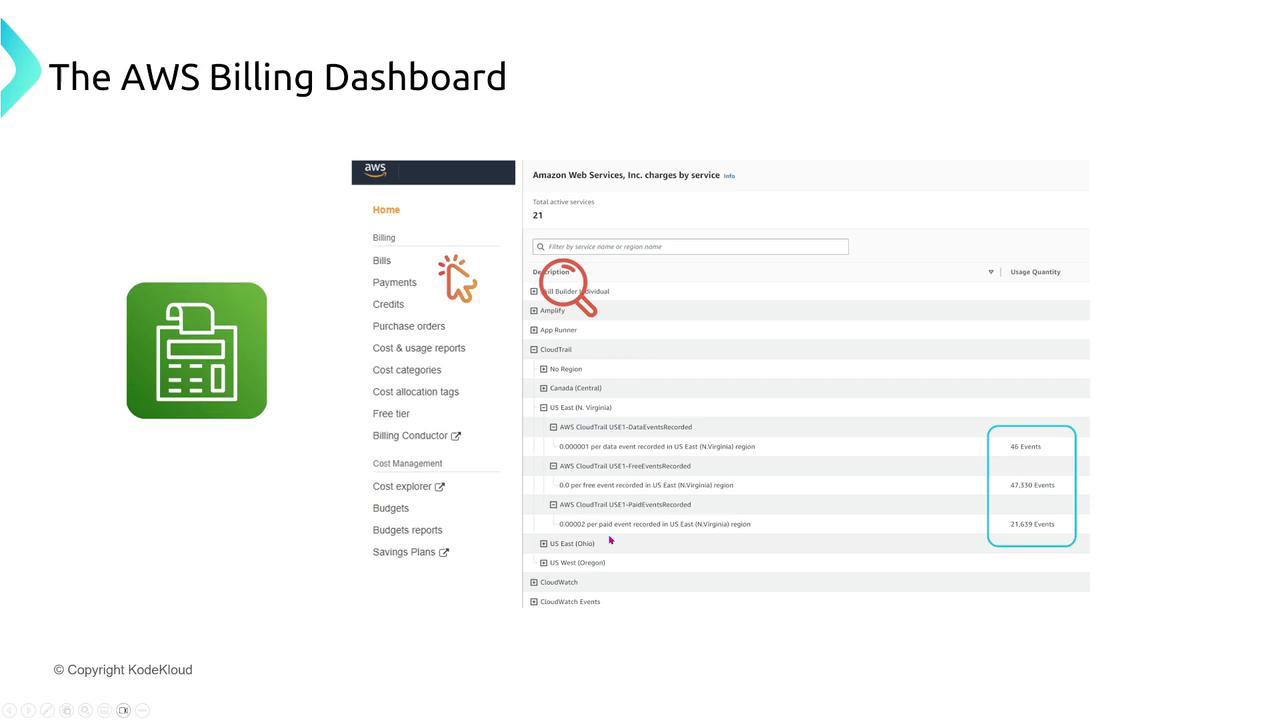
Billing Dashboard
The Billing Dashboard is an intuitive interface that presents cost details by service, region, and usage. It offers a comprehensive overview of your spending without requiring custom visualization.
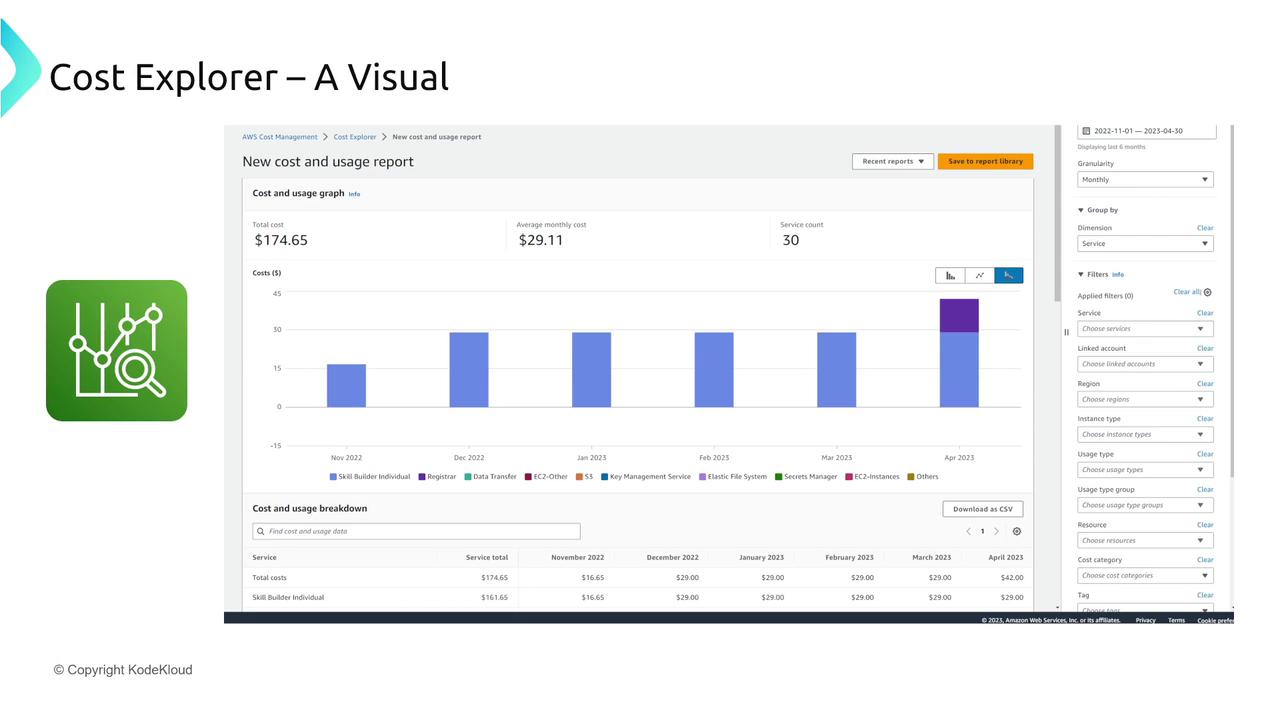
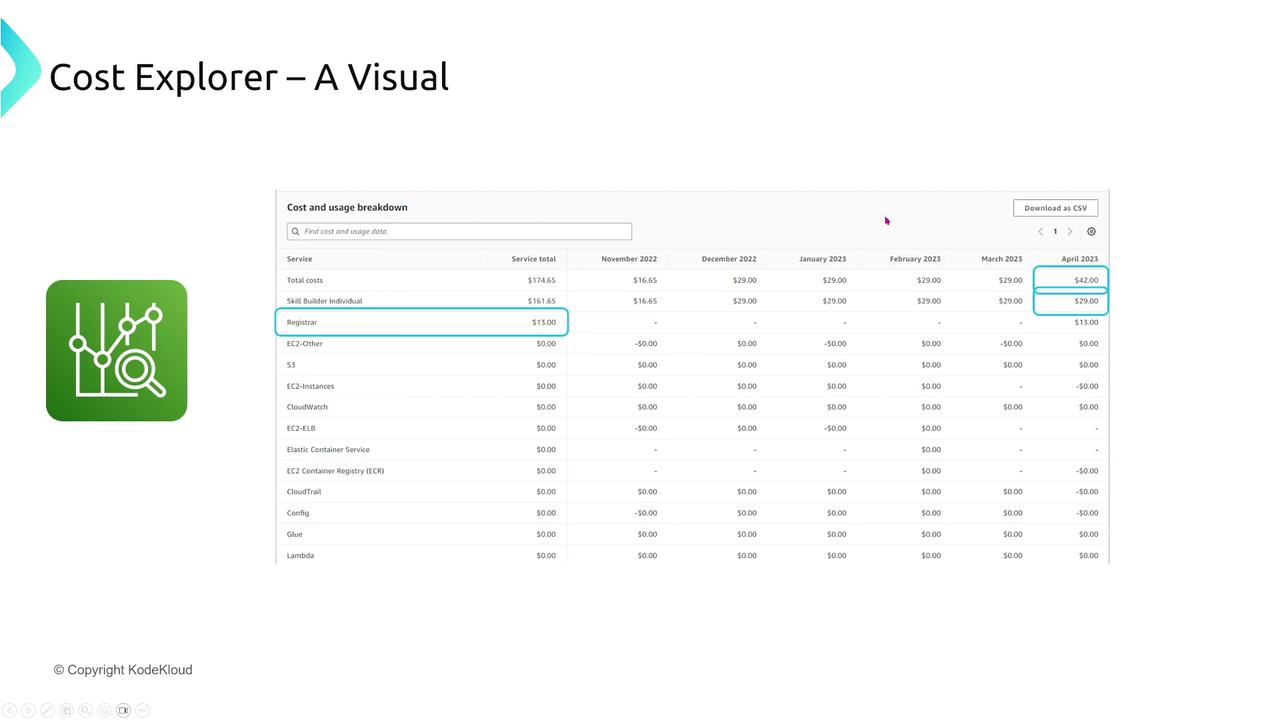
Cost Explorer
Cost Explorer provides interactive, visual presentations of your spending data. Filter and chart cost data by dimensions such as usage types, locations, and accounts. It also offers CSV export options for detailed analysis.
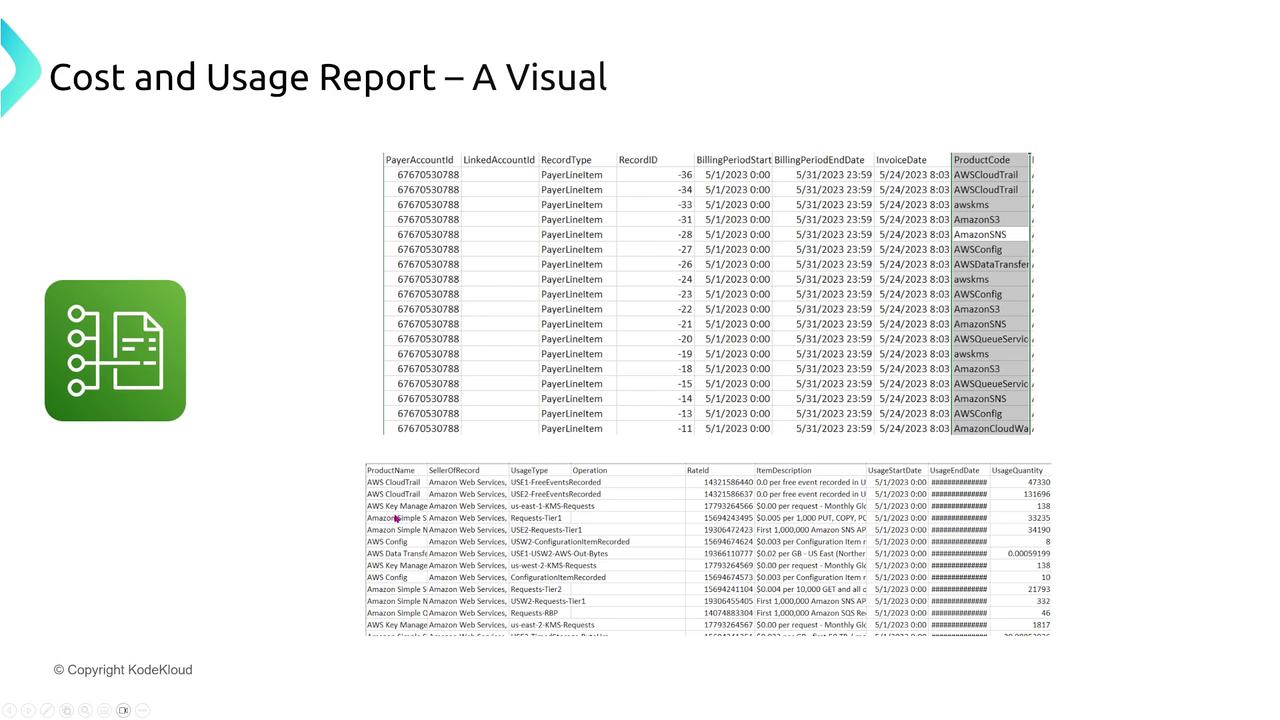
Cost and Usage Report
For granular monitoring, the Cost and Usage Report provides detailed data in CSV format to an S3 bucket. Analyze the report further using tools such as Athena or QuickSight.
AWS Budgets
AWS Budgets allow you to set spending limits, track usage by service or account, and trigger automated actions when thresholds are met (for example, sending notifications or even halting instance launches).
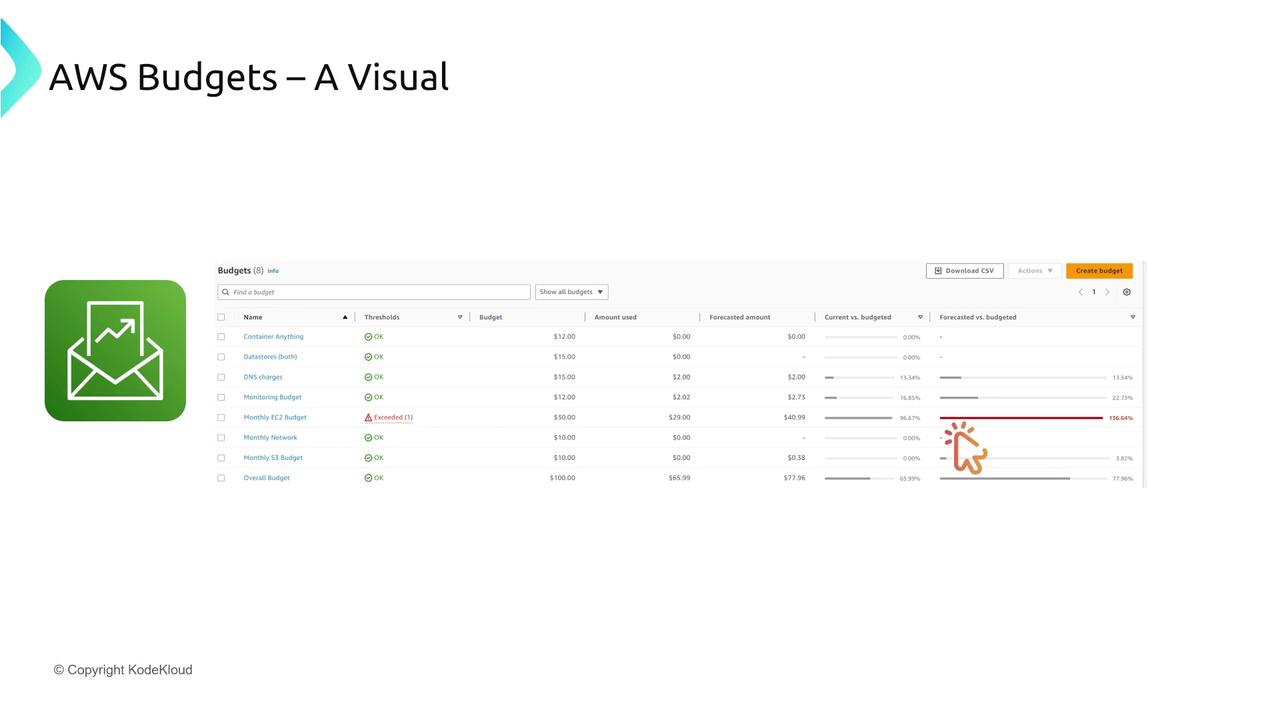
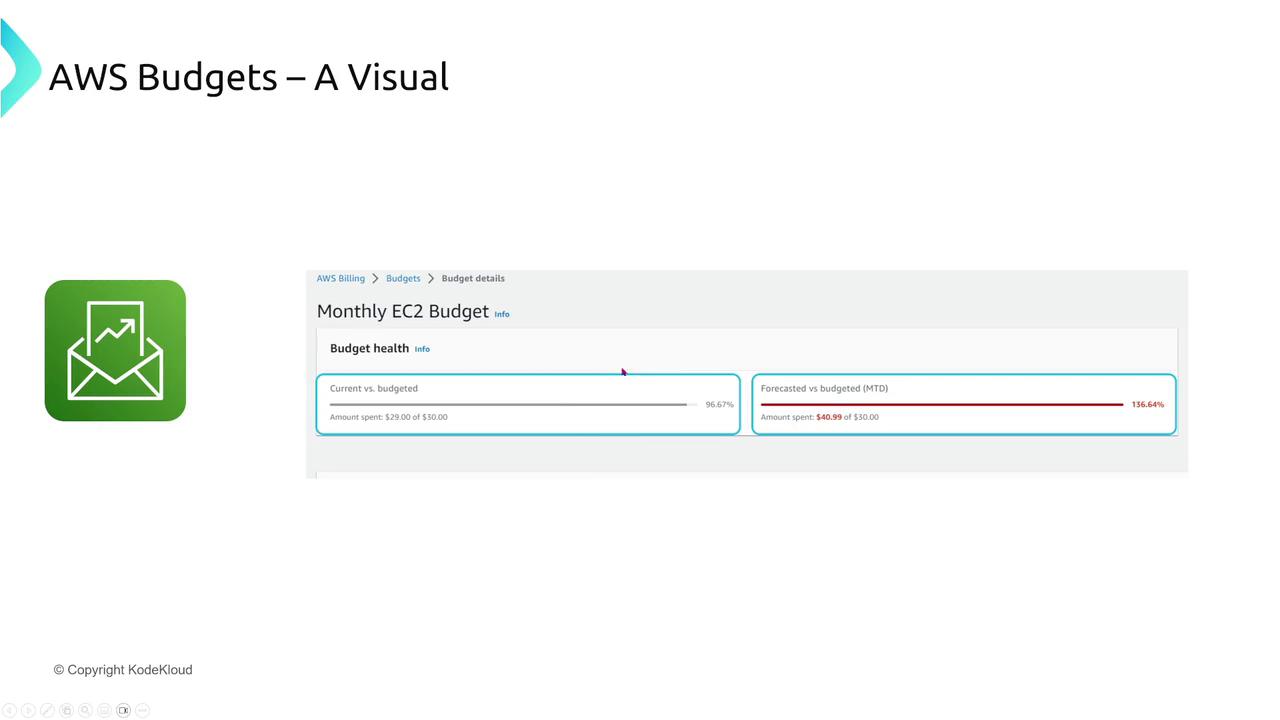
Summary
In this lesson, we covered a comprehensive overview of AWS cost optimization strategies:
- Licensing models including On-Demand, Reserved Instances (Standard, Convertible, Scheduled), Spot Instances, and Dedicated Hosts.
- Savings Plans across Compute (covering EC2, Fargate, and Lambda), EC2-specific plans, and SageMaker options.
- Reservations for services beyond compute, such as RDS, ElastiCache, OpenSearch, Redshift, DynamoDB, and CloudFront.
- The importance of evaluating ROI and TCO, factoring in both tangible and intangible benefits like improved uptime and reduced labor costs.
- AWS billing tools including the Billing Dashboard, Cost Explorer, the Cost and Usage Report, and AWS Budgets to monitor and control expenditure.
Tip
For further reading on AWS cost optimization strategies, check out the AWS Cost Management Documentation.
Keep these concepts in mind as exam questions frequently focus on cost and billing management. If you have any questions or need further assistance, feel free to reach out via the forums at [email protected].
Happy learning and best of luck on your AWS certification journey!
Watch Video
Watch video content