AWS Solutions Architect Associate Certification
Introduction
Why AWS Solutions Architecture Certification and what is a solutions architect
Welcome back, future AWS Solutions Architect Associate professionals. In this article, we explore the benefits of the AWS Solutions Architect Associate (SAA) certification and clarify the role of a Solutions Architect. This discussion focuses on the Associate-level certification and details how the role differentiates itself from other IT and cloud positions.
We will cover: • The rationale for the SAA certification
• An overview of the Solutions Architect role
• Sample exam questions you might encounter
AWS Exam Landscape Overview
The AWS exam progression starts from the AWS Cloud Practitioner (CLF-C02) foundational level—depicted as a black hexagon—and moves upward through Associate-level exams. The Solutions Architect exam, the focus of this article, is one of these key tracks. Other Associate-level certifications include the AWS Certified Developer - Associate exam and certifications addressing operational roles, eventually leading to Professional and Specialty exams. The difficulty scaling moves from black to blue, then to teal green, and finally to purple for deep-dive specialties.
Exam Retirement Notice
One of the current exams is scheduled for retirement in April of this year. Although it is included for historical context, AWS will soon replace it with a new exam format.
While the foundational level no longer demands prior cloud experience, it is recommended that candidates have one to two years of hands-on experience in roles such as Solutions Architect, Developer, or SysOps Administrator. AWS suggests that for some certifications, three to five years of relevant experience may be beneficial.
AWS Solutions Architect Associate Certification at a Glance
The AWS Solutions Architect Associate certification emphasizes a solid understanding of AWS services without requiring coding or operational tasks. Its primary focus is on evaluating how solutions can enhance security, optimize performance, and improve cost-efficiency within AWS environments.

This certification is uniquely designed to ensure that you can design solutions which integrate AWS services effectively. It is important to note that the Solutions Architect Associate role is distinct from positions such as Enterprise Architect or other specialized architect roles.
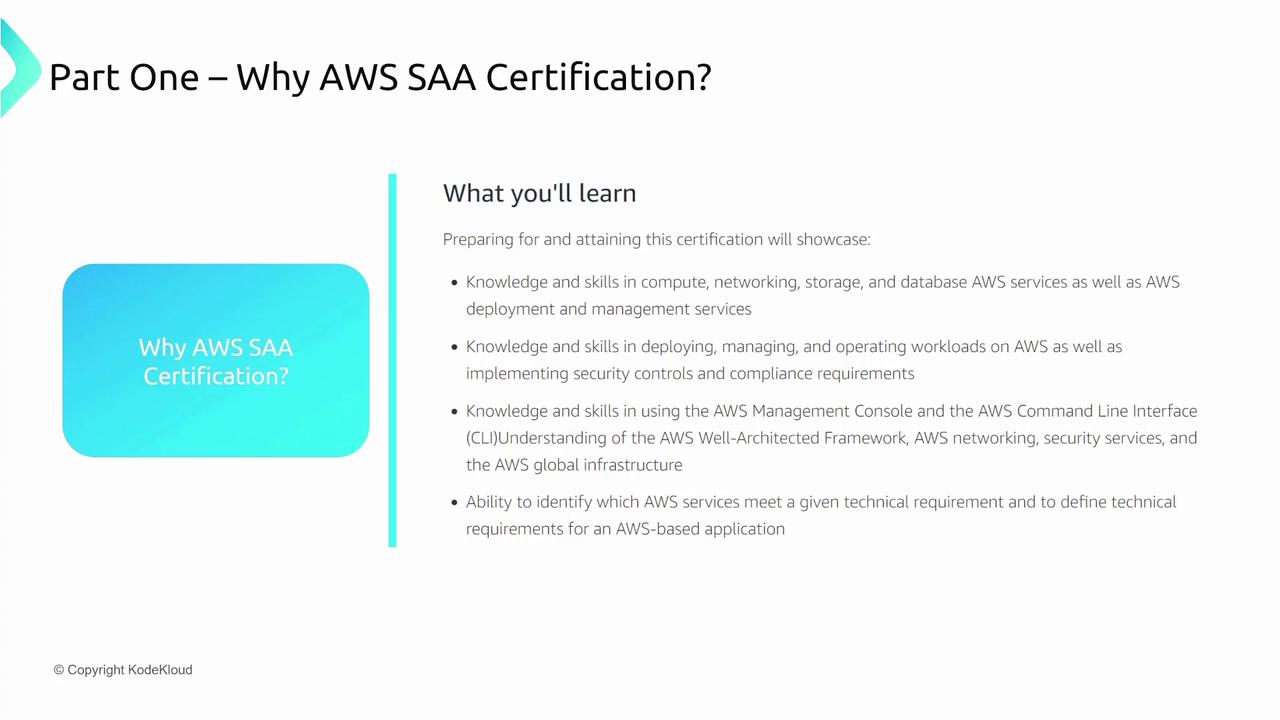
Who Should Consider the SAA Certification?
If you are seeking comprehensive exposure to core AWS services—whether you work in development, operations, machine learning, or security—this certification is an excellent starting point. It covers a broad spectrum of topics including compute, networking, storage, databases, deployment management, and migration services. Mastery of the AWS Well-Architected Framework and a solid understanding of the AWS global infrastructure are key to your success.

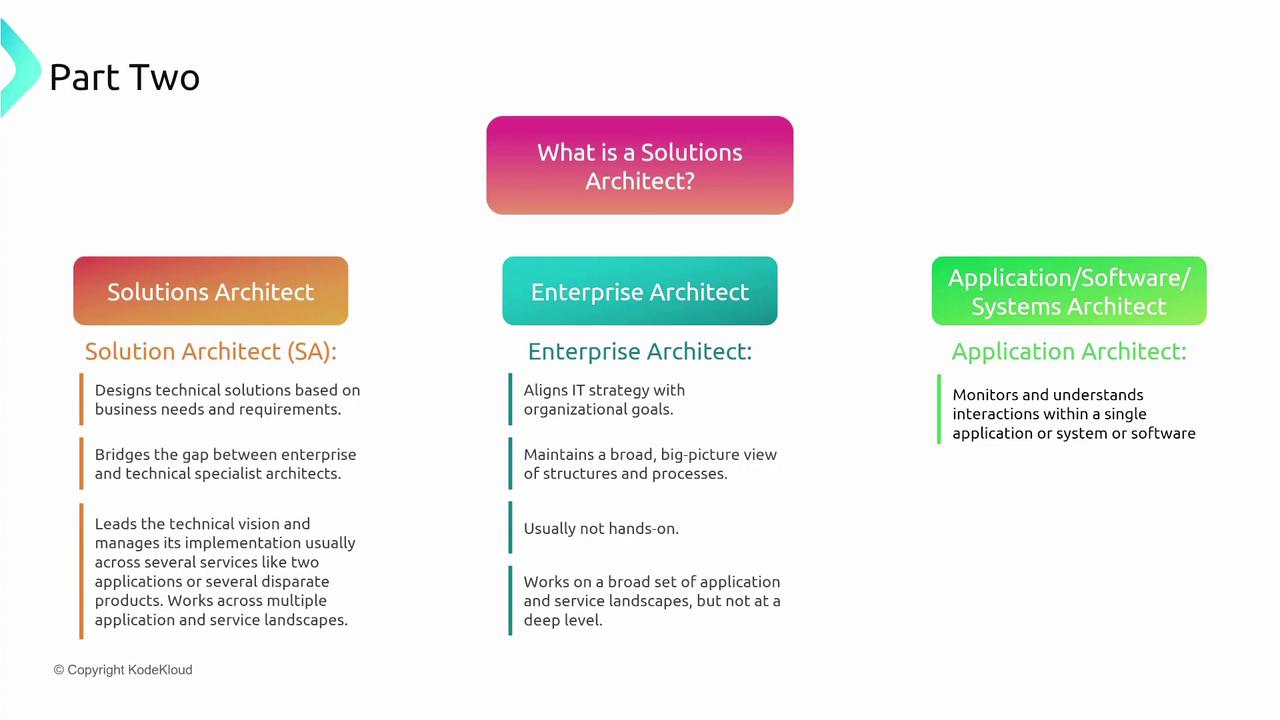
What Is a Solutions Architect?
A Solutions Architect designs technical solutions that meet detailed business requirements by integrating multiple AWS services. This role acts as a bridge between enterprise-level strategy and hands-on technical details. For instance, while a Python software developer concentrates on application development, or an enterprise architect focuses on policy and strategic governance, a Solutions Architect ensures cohesive integration across systems and services.
In contrast:
- An Enterprise Architect holds a strategic outlook across an organization’s entire IT ecosystem.
- An Application Architect is focused on a singular product or service.
Solutions Architects work closely with both roles to ensure that technical designs align with broader business objectives.
Exam Format and Example Questions
The AWS Solutions Architect Associate exam (SAA-C03) comprises about 65 scenario-based questions over a two-hour duration. The exam evaluates your ability to design multi-service solutions rather than merely testing memorized facts.
Below are sample questions that reflect the scenario-based problem-solving you can expect:
Example Question 1
A company operates a public-facing three-tier web application in a VPC spanning multiple availability zones. The application tier’s Amazon EC2 instances are in private subnets and need to download software patches from the internet while remaining inaccessible directly from the internet. Which actions should be taken? (Select two.)
To meet these requirements:
- Configure a NAT gateway in a public subnet, as NAT gateways must reside in public subnets to function as internet proxies.
- Create a custom route table for the private subnets with a route that directs outbound traffic to the NAT gateway.
Using an Elastic IP or placing a NAT instance in a private subnet would not fulfill the requirements. The correct answers are options A and B.

Example Question 2
A Solutions Architect is tasked with devising a cost-saving strategy for Amazon EC2 instances that do not need to operate during a two-week company shutdown. The instances store data in memory, which must be preserved during downtime. Which feature of EC2 allows this?
Hibernation is the feature that preserves instance memory during shutdowns. The recommended solution is to use instance hibernation, making option C the correct answer.

Example Question 3
A company needs to run a monitoring application on an EC2 instance within a VPC. The instance is accessed via its private IPv4 address. The challenge is to quickly redirect traffic to a standby EC2 instance if the primary application fails. Which solution best supports an active/passive setup?
Two solutions include: • Attaching a secondary Elastic Network Interface (ENI) with the private IP address to the primary instance and transferring the ENI to the standby instance upon failure. • Associating an Elastic IP address with the primary instance’s network interface and re-associating it with the standby when necessary.
While both options are viable, the ENI solution (option C) is preferred as it maintains the configuration within the private subnet, avoiding exposure of a public IP address.
Example Question 4
An analytics company is setting up a web analytics service that requires each user's webpage to include a JavaScript script for making authenticated GET requests to the company’s S3 bucket. To ensure the script functions correctly across domains, what is the optimal solution?
The recommended approach is to provide users with a pre-signed URL. This URL includes authentication tokens with an expiration timer, allowing secure, authenticated GET requests without additional configuration.

Summary
The AWS Solutions Architect Associate certification stands out as the most popular AWS Associate-level credential. It prepares you to build comprehensive, multi-service technical solutions that align with business needs. Unlike the enterprise architect, who maintains a broad strategic view, or the application architect, focused solely on a single product, a Solutions Architect bridges these roles by integrating multiple services seamlessly.
Key exam topics include:
- Designing custom route tables for VPCs
- Exploring connectivity options like VPC peering and transit gateways
- Implementing best practices across various AWS services

By mastering these concepts, you will be better prepared to succeed on the AWS Solutions Architect Associate exam and excel as a Solutions Architect—the technical professional who bridges enterprise strategy with detailed system implementation.
I'm Michael Forrester. Thank you for reading. If you have any questions, please join our AWS courses Slack channel. Otherwise, I look forward to seeing you in the next lesson.
Watch Video
Watch video content