Why Use Step Functions?
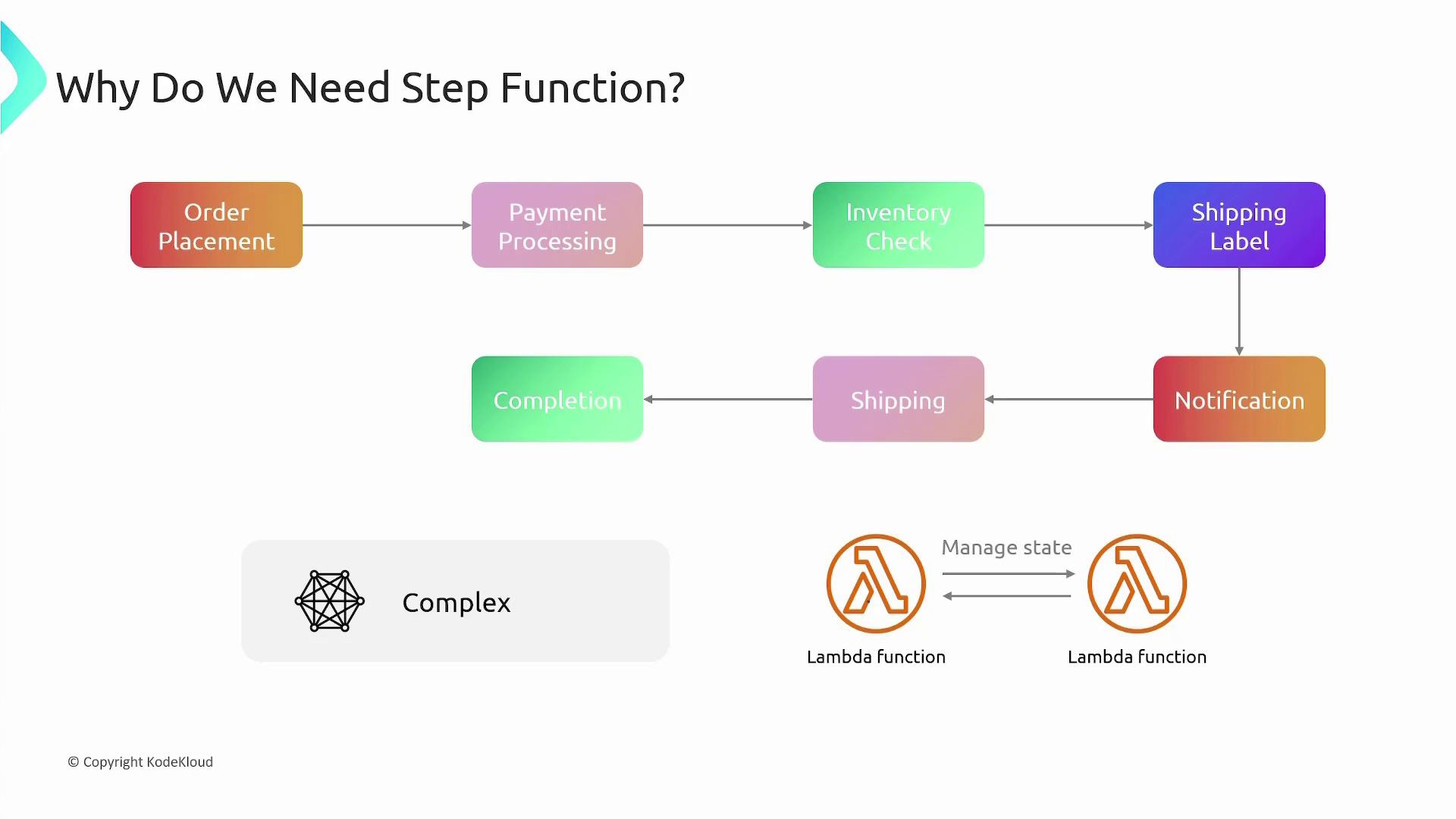
Imagine you are developing an e-commerce application responsible for processing orders. When a user places an order, a workflow is initiated that drives the process from order placement to fulfillment, shipment, and delivery. The overall workflow might involve the following steps:- Order Placement: Triggered when a customer places an order on the platform.
- Payment Processing: Validates and processes the payment.
- Inventory Check: Verifies product availability.
- Shipping Label Generation: Creates a shipping label after confirming inventory.
- Customer Notification: Sends order status updates and tracking information.
- Shipping: Prepares and dispatches the order.
- Order Completion: Marks the order as fulfilled in the system.
How AWS Step Functions Help
AWS Step Functions address these challenges by offering a visual and programmatic way to orchestrate workflows. They allow you to:- Define Each Step: Specify whether the step involves invoking a Lambda function, running an ECS task, or sending notifications via SNS.
- Visualize and Modify: Use a drag-and-drop GUI to easily visualize and adjust the workflow.
- Execute in Parallel: Run independent tasks simultaneously, such as payment processing and fraud detection.
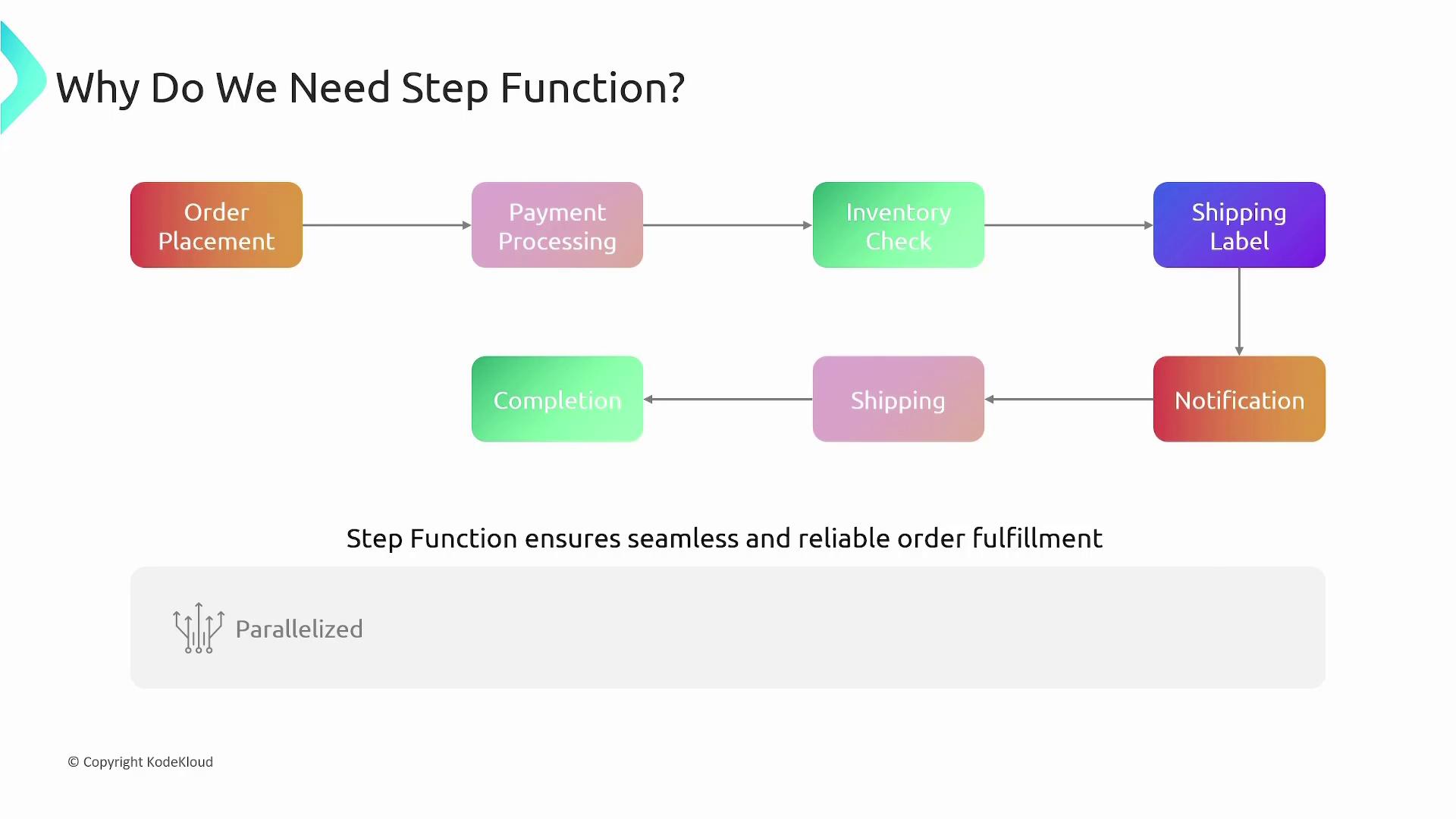
- Workflow Orchestration: Visually define, manage, and monitor workflows without embedding orchestration logic in your applications.
- Parallel Execution: Speed up processing with concurrent task execution.
- Error Handling: Automate exception management, retries, and escalation mechanisms.
- Visual Interface: Gain insights using the AWS console, which makes it easier for teams to understand workflow behavior.
- State Management: Seamlessly pass data between tasks, overcoming the stateless nature of Lambda functions.
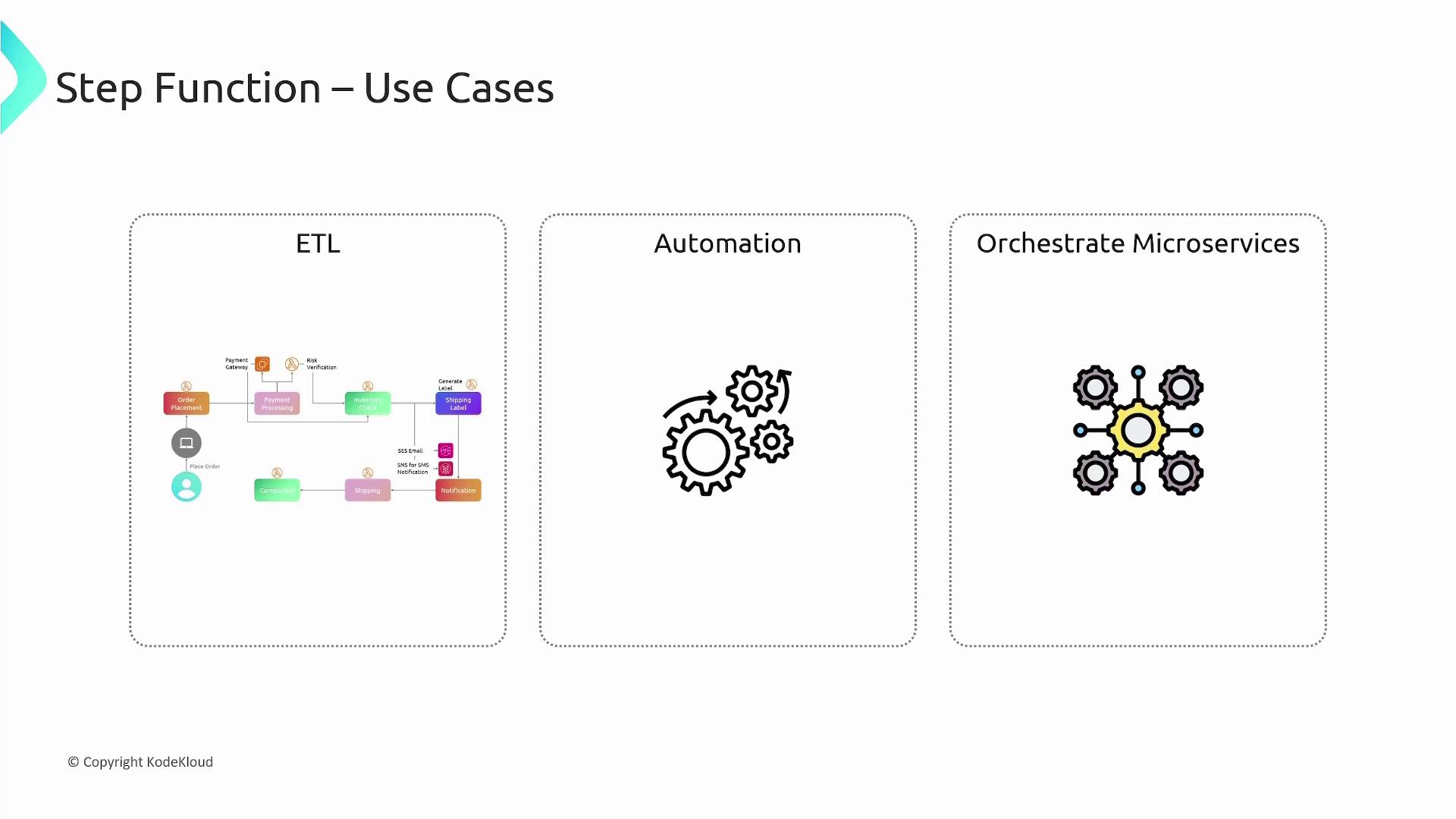
E-Commerce Order Processing with Step Functions
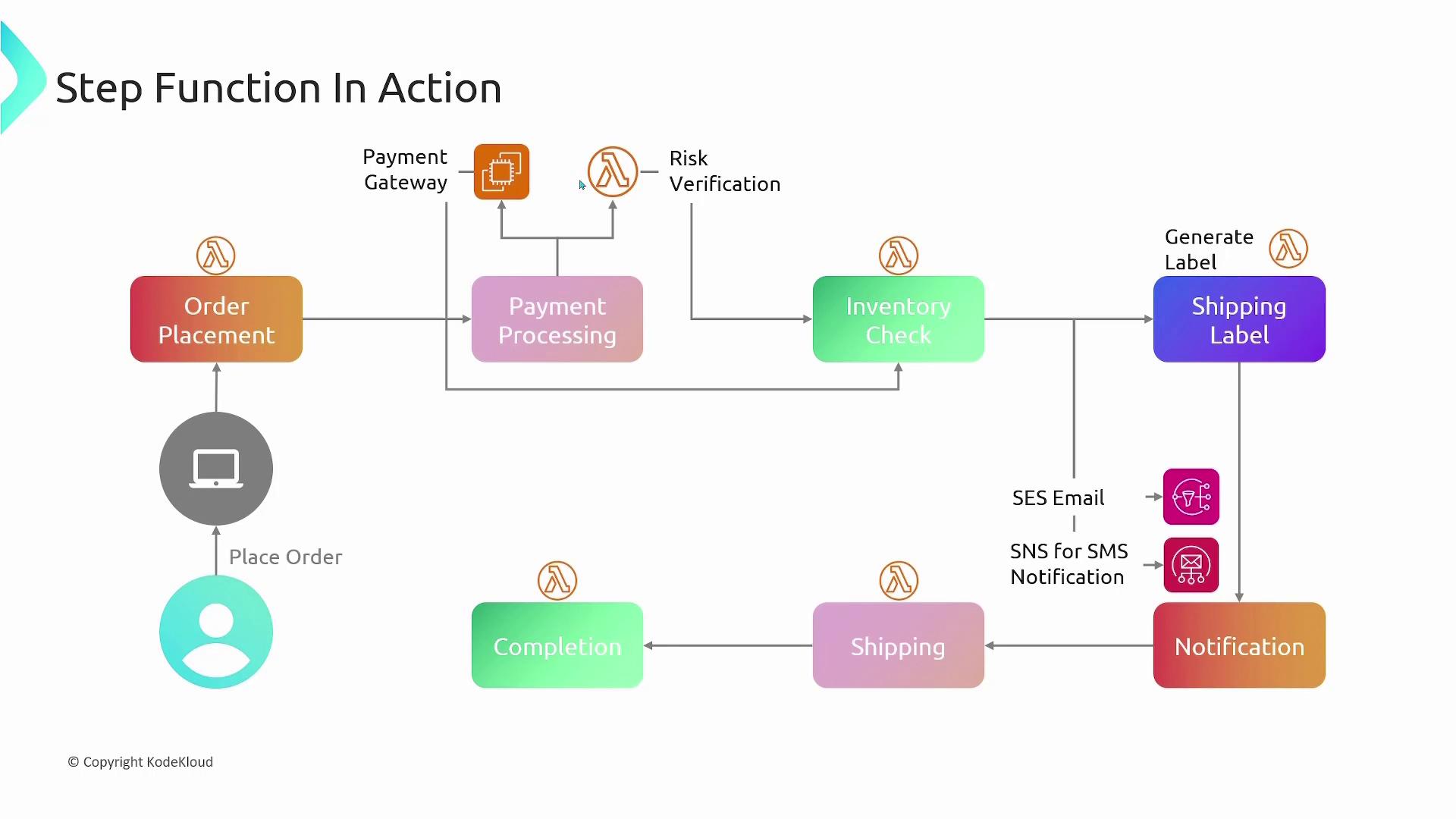
Let’s revisit the e-commerce order processing workflow and see how Step Functions can enhance it:- Order Placement: An event triggers the order placement Lambda function when a customer places an order.
- Payment Processing (Parallel Tasks):
- A task validates the payment using an external service running on an EC2 instance.
- Simultaneously, another task runs a fraud and risk detection Lambda function.
- Inventory Check: Once payment and fraud detection clear successfully, a Lambda function verifies product availability.
- Post-Inventory Actions (Parallel Tasks):
- One task generates the shipping label.
- Another task notifies the customer via SES (email) and SNS (SMS) with tracking details.
- Shipping: Initiates the shipment process.
- Order Completion: Updates the system to mark the order as complete.
Integrations and Use Cases
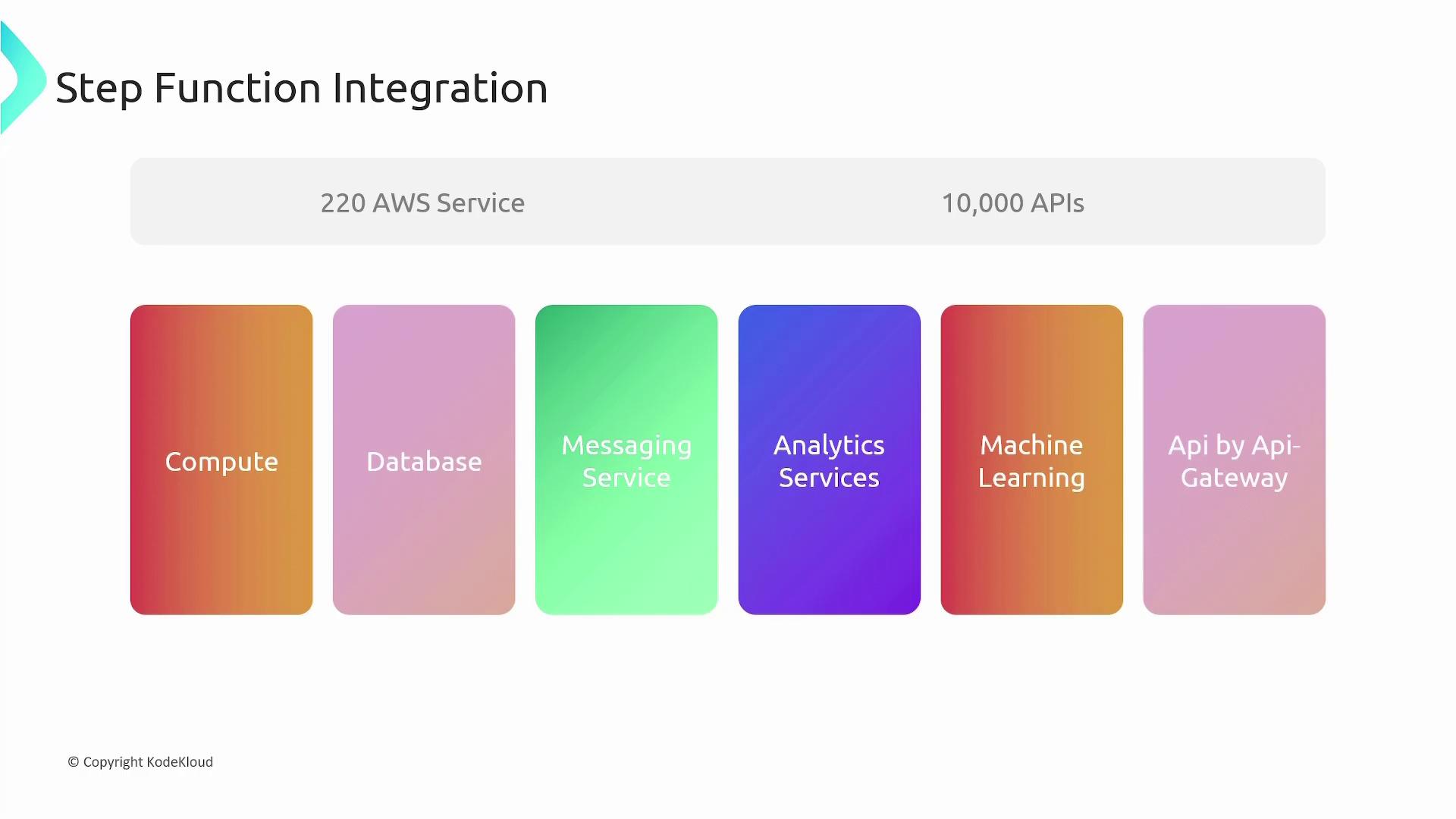
Step Functions integrate seamlessly with over 220 AWS services and more than 10,000 APIs. They work with services across various categories:| Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Compute | Lambda, ECS, EKS, AWS Fargate |
| Databases | DynamoDB and other data stores |
| Messaging | SNS, SQS |
| Analytics | Athena, AWS Batch, AWS Glue, EMR, Glue DataBrew |
| Machine Learning | SageMaker |
| API Management | API Gateway |
- Orchestrating multiple long-running ETL jobs.
- Automating security and IT service workflows with manual approval steps.
- Coordinating microservices to build responsive serverless applications.
Conclusion
By leveraging AWS Step Functions, you can break down complex workflows into manageable, modular tasks, simplify error handling, and benefit from a visual representation of your entire process. This approach leads to a more resilient and maintainable application architecture.For more information, check out the AWS Step Functions documentation and our serverless application guides.