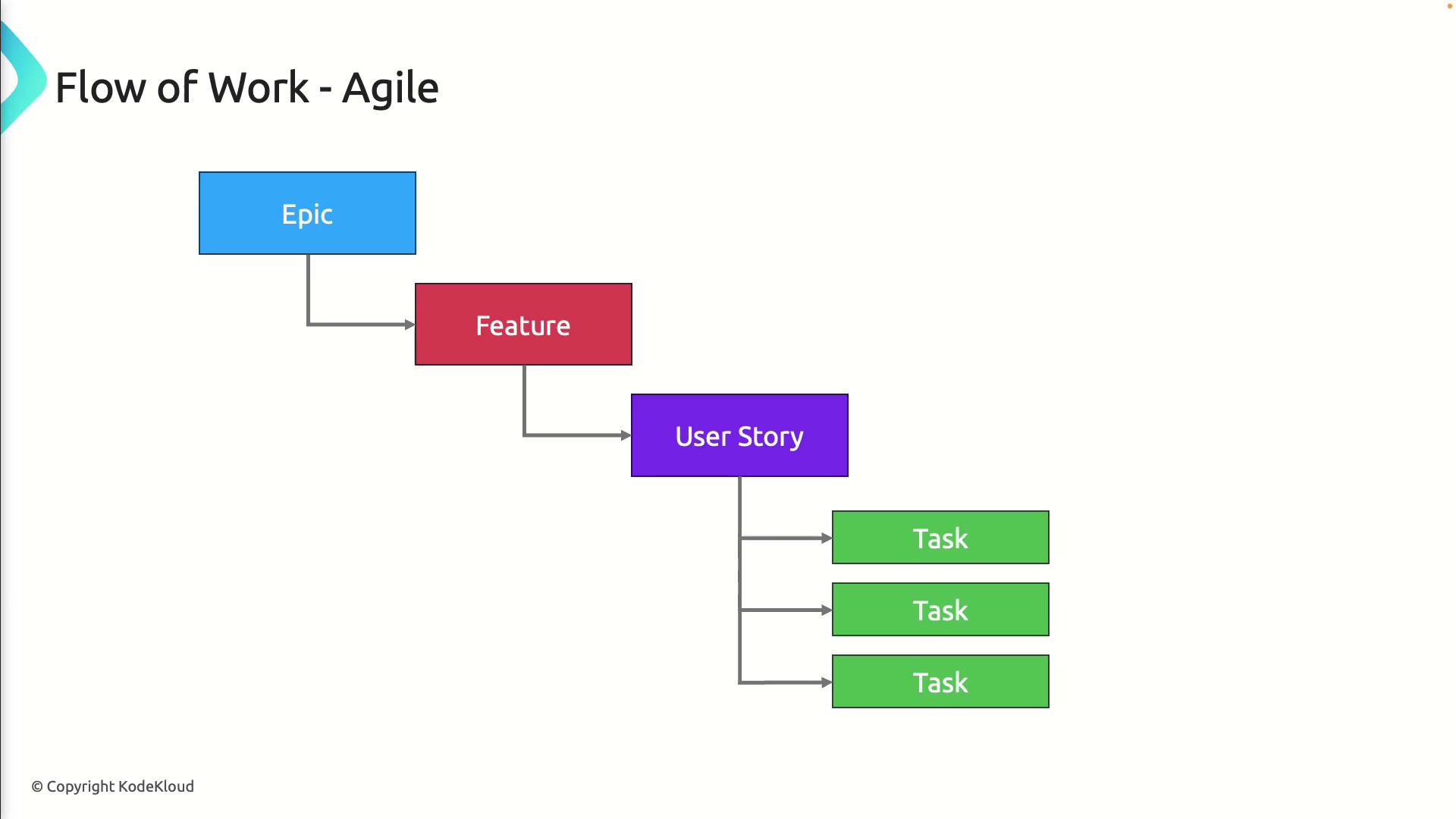
1. Work Item Hierarchy
At the highest level, Agile work is organized into backlog items:- Epic
Captures a large business goal or feature set, managed in the Portfolio Backlog. - Feature
Breaks an Epic into smaller, demonstrable capabilities. - User Story
Defines a user-centric requirement in the Product Backlog. - Task
Specifies individual development or testing actions.
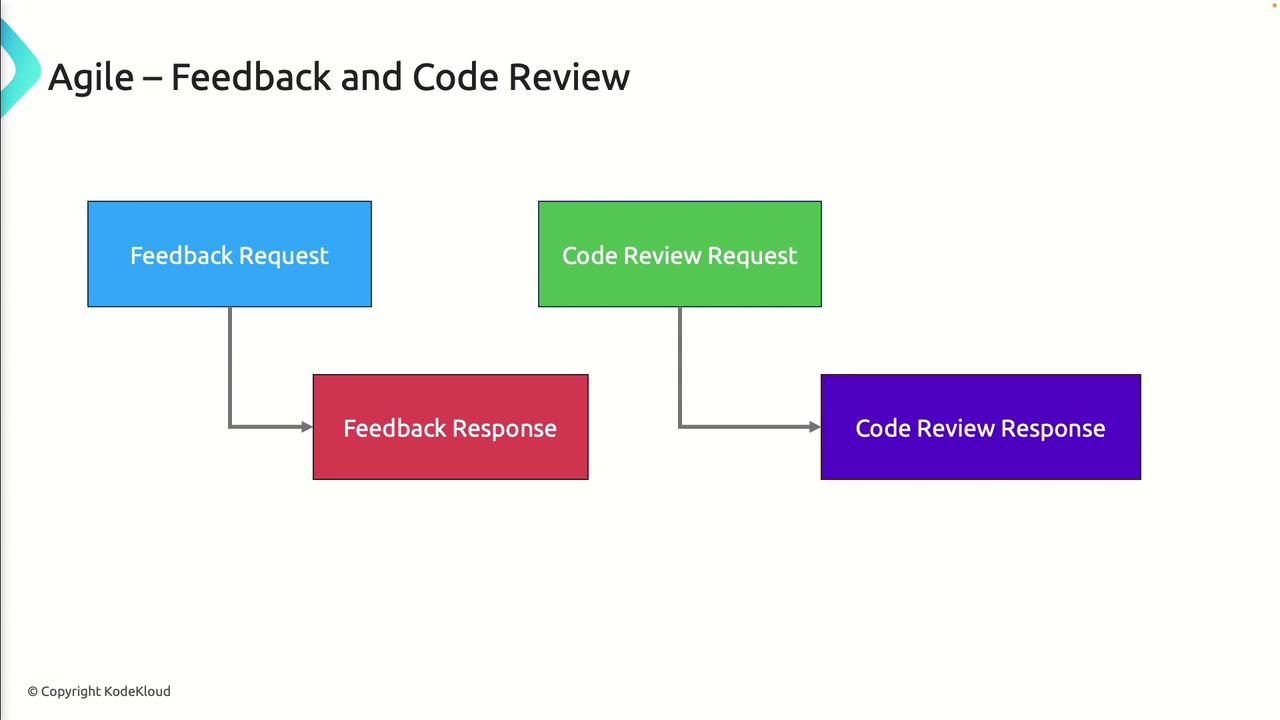
2. Feedback and Code Review Process
Agile emphasizes continuous feedback. The typical sequence is:- Feedback Request: Developer asks stakeholders to validate functionality.
- Feedback Response: Stakeholders provide comments or approvals.
- Code Review Request: Developer submits a pull request or merge request.
- Code Review Response: Peers review, comment, approve, or request changes.
Regular code reviews not only catch defects early but also promote shared knowledge and consistency across the codebase.
3. Testing Structure
Agile testing is layered to ensure coverage from strategy down to individual scenarios:| Level | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Test Plan | Overall scope, objectives, and entry/exit criteria | Regression and performance plan |
| Test Suite | Group of related test cases | Authentication suite |
| Test Case | Detailed steps, inputs, and expected results | Login with valid credentials |
Failing to update shared steps when workflows change can cause multiple tests to break simultaneously. Review shared steps regularly.

4. Issue and Bug Tracking
Work items for defects and tasks help teams triage and resolve problems efficiently:| Work Item Type | Purpose | Typical Workflow |
|---|---|---|
| Issue | General task or improvement | New → Active → Resolved → Closed |
| Bug | Defect needing a fix | New → Active → Resolved → Closed |
5. Work Item States
All Agile work items move through these standard states:- New: Item is created and awaiting grooming.
- Active: Work is in progress.
- Resolved: Development or testing is complete—pending review.
- Closed: Item is accepted and done.
- Removed: Item is discarded or deemed obsolete.

6. End-to-End Workflow
- Planning
Define User Stories, acceptance criteria, and test strategy. - Backlog Management
Prioritize Epics and Features, estimate effort, and assign items. - Development & Review
Implement Tasks, request feedback, submit pull requests, and address review comments. - Testing
Execute test cases, reuse shared steps, and update test suites. - Bug/Issue Resolution
Triage reported defects, assign to developers, and verify fixes. - Closure
Move completed items to Closed or remove obsolete ones.