AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
Design and Implement Deployments
Application deployment using Containers Binaries and Scripts
In this guide, you’ll learn three primary methods for deploying applications in Azure—containers, binaries, and scripts. Whether you’re preparing for the AZ-400 exam or optimizing production pipelines, understanding these strategies ensures reliable, repeatable deployments.
What Is Application Deployment in Azure?
Application deployment means packaging and configuring your code so it runs reliably in Azure. Core tasks include:
- Managing dependencies
- Configuring environment settings
- Integrating with services like networking, databases, and monitoring
Deployment Workflow
Every deployment pipeline typically follows three stages:
- Build
Compile source code, bundle libraries, and generate artifacts. - Test
Execute automated tests to validate functionality and catch regressions. - Install
Deploy artifacts to your Azure environment (e.g., App Service, Kubernetes, VMs).
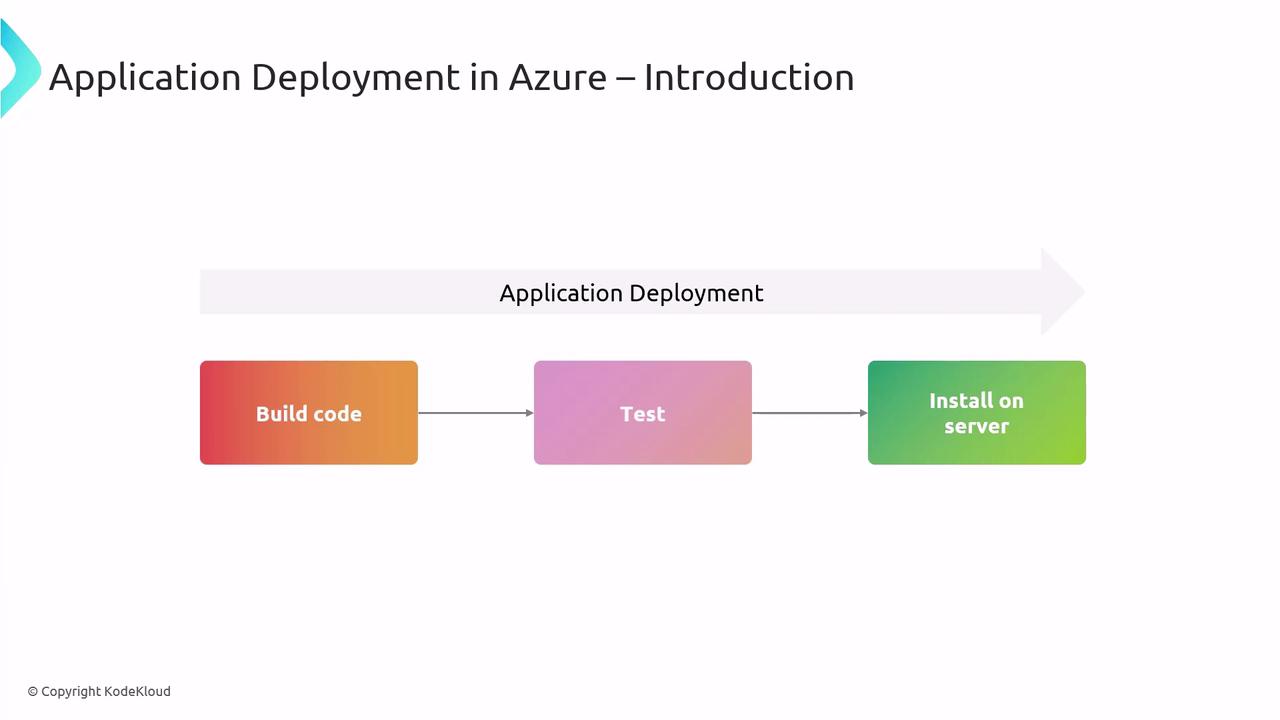
Understanding this three-step flow is essential for both exam success and real-world delivery.
Deploying with Containers
Containers package your application code, dependencies, and configuration into lightweight, portable units. This approach guarantees consistent behavior across every environment.
Key Benefits
- Consistency Across Environments
Identical runtime from local dev to production. - Scalability
Spin up multiple container instances on demand. - Isolation
Processes run in separate namespaces, reducing conflicts.

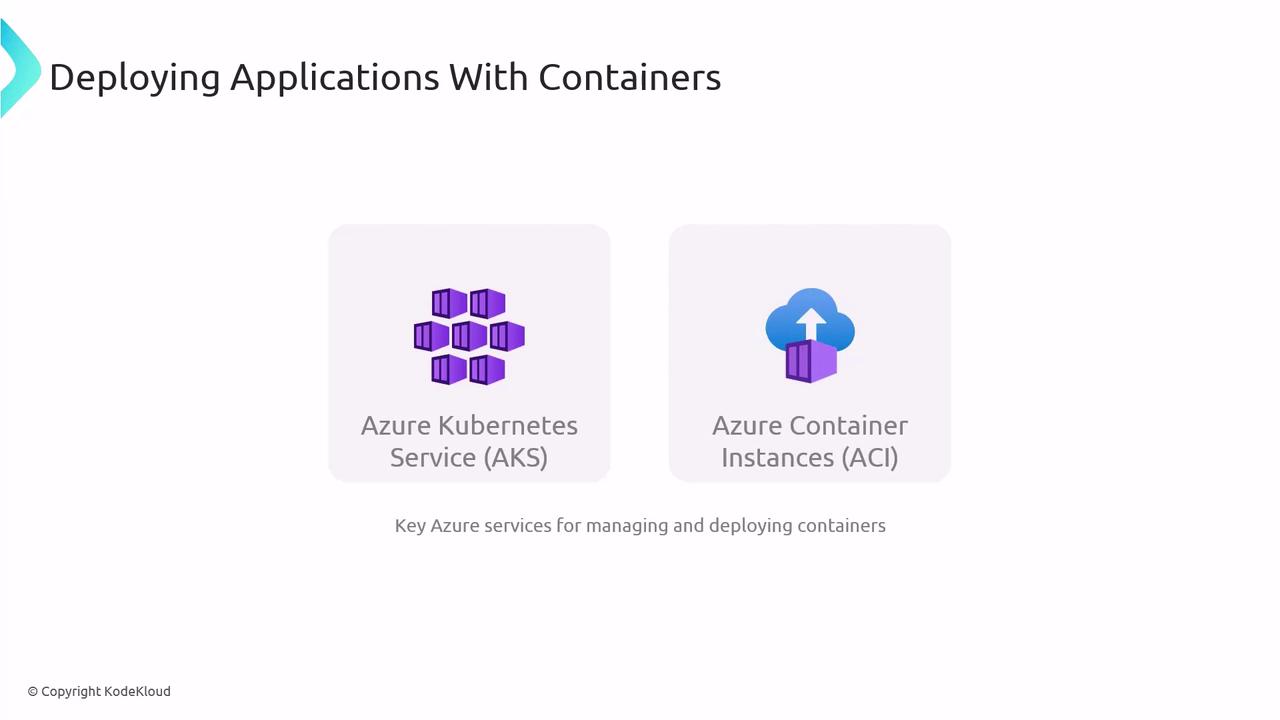
Azure Container Services
Azure offers two main container hosting options:
| Service | Description | Ideal Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) | Managed Kubernetes cluster for advanced orchestration | Production microservices with high availability |
| Azure Container Instances (ACI) | Serverless containers without VM management | On-demand tasks, dev/test environments |
Note
Use ACI for simple, burstable workloads and prototyping. Choose AKS for production-grade orchestration, autoscaling, and complex networking.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
AKS simplifies Kubernetes deployment in Azure. Key features include:
- Integrated CI/CD
Connect with Azure DevOps or GitHub Actions for automated pipelines. - Security
Leverage network policies, Azure Active Directory integration, and role-based access control. - Monitoring
Built-in support for Azure Monitor and Log Analytics.
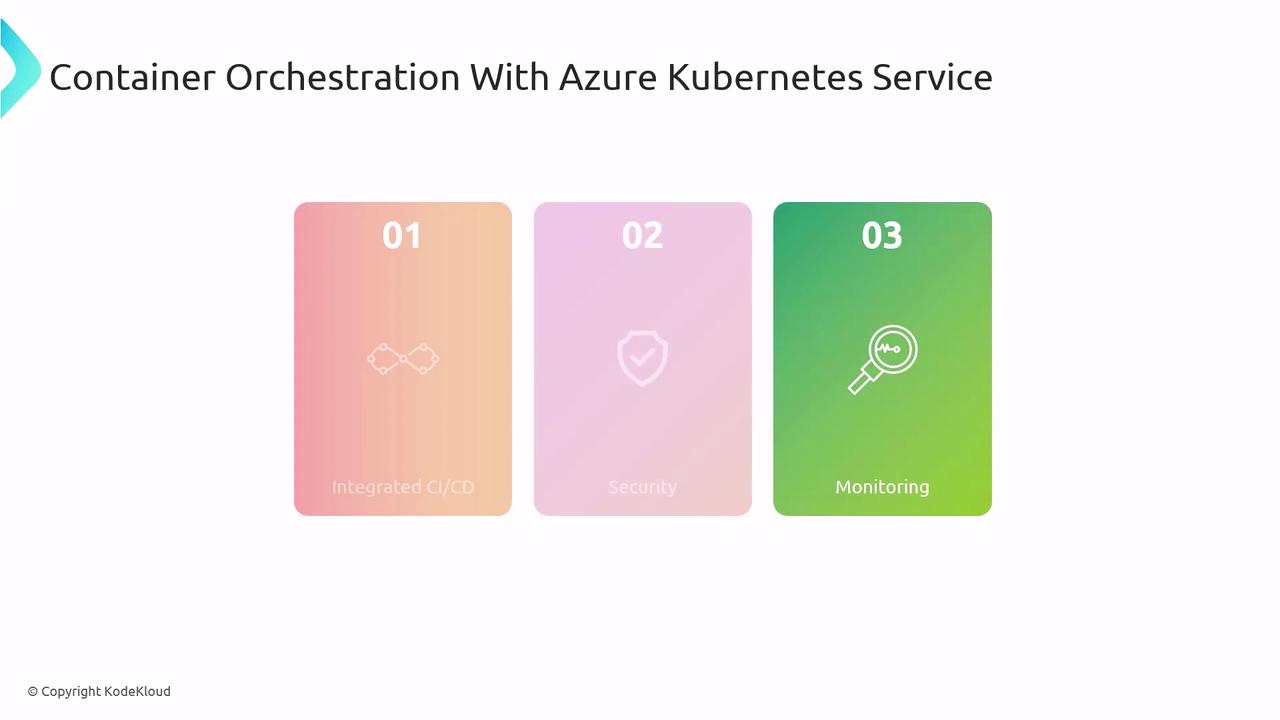
Mastering AKS fundamentals is critical for the AZ-400 exam and for running resilient container workloads.
Deploying with Binaries
Binaries are compiled executables that run directly on the host OS. Azure App Service abstracts infrastructure so you can deploy these executables as a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS).
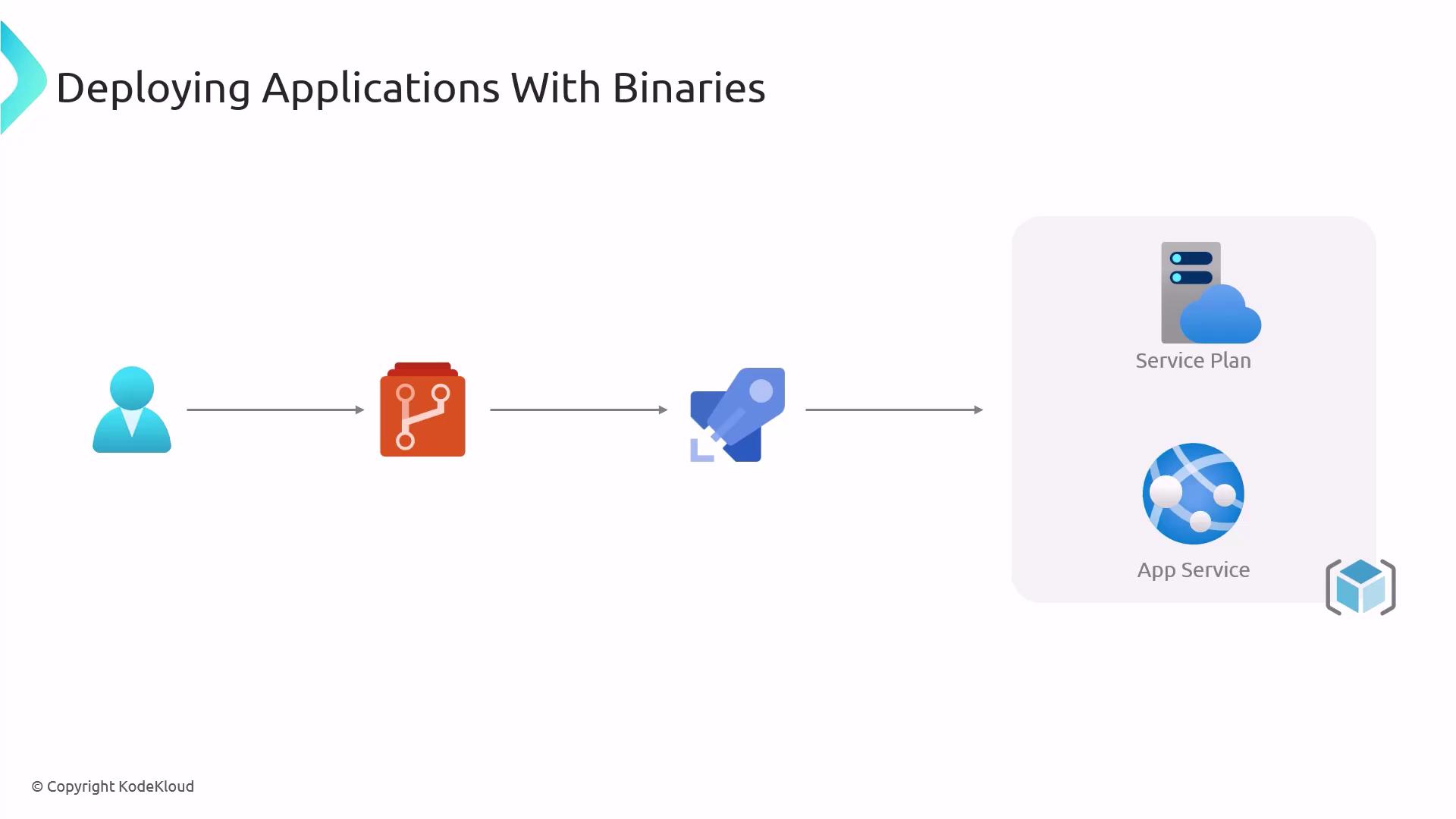
Typical Binary Deployment Flow
- Developer commits code to a Git repository.
- CI pipeline compiles source into binaries.
- Deployment pipeline pushes binaries to Azure App Service.
- App Service host runs the application.
App Service Deployment Methods
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| FTP / Web Deploy | Upload binaries or web projects directly to the server. |
| Docker Container | Host container images on App Service for PaaS simplicity. |
Note
For Linux-based executables, consider Docker deployment on App Service to leverage container isolation and portability.
Scripted Deployments
Automating Azure resource provisioning and application deployment with scripts guarantees repeatable, versioned environments.

Azure supports two primary scripting tools:
Both integrate seamlessly into CI/CD pipelines for full infrastructure-as-code workflows.
Sample Azure CLI Deployment Script
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# Log in to Azure
az login
# Variables
RG_NAME="MyResourceGroup"
LOCATION="eastus"
PLAN_NAME="MyAppServicePlan"
APP_NAME="MyWebApp"
# Create a resource group
az group create --name $RG_NAME --location $LOCATION
# Create an App Service plan
az appservice plan create \
--name $PLAN_NAME \
--resource-group $RG_NAME \
--sku S1 \
--is-linux
# Create a Web App
az webapp create \
--resource-group $RG_NAME \
--plan $PLAN_NAME \
--name $APP_NAME \
--runtime "DOTNET|6.0"
# Deploy code (assuming a local folder named 'publish')
az webapp deploy \
--resource-group $RG_NAME \
--name $APP_NAME \
--src-path "./publish"
Warning
Store your service principal credentials or managed identity settings securely. Avoid hardcoding secrets in scripts.
Understanding script-based deployments is vital for automating infrastructure and passing the AZ-400 exam.
Links and References
- AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- Azure Container Instances (ACI)
- Azure App Service
- Azure DevOps Services
- Azure CLI Documentation
- Azure PowerShell Documentation
Watch Video
Watch video content