AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
Design and Implement Infrastructure as Code IaC
Azure Automation State Configuration
Azure Automation Desired State Configuration (DSC) is a powerful service for defining, deploying, and enforcing system configurations at scale. By authoring PowerShell-based DSC scripts, you can automate consistency checks and drift correction across Azure and on-premises environments—eliminating manual errors and saving operational time.
Key Benefits
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Centralized Management | Single pane of glass to manage DSC configurations across subscriptions and regions. |
| Automatic Drift Correction | Continuous monitoring with automatic remediation of configuration drift. |
| Detailed Compliance Reporting | Out-of-the-box dashboards and logs to track node compliance over time. |
Scenario: Enforce Software on Multiple Windows VMs
In this walkthrough, we'll ensure a scheduled PowerShell task is installed and maintained on several Azure Windows VMs using Azure Automation DSC.
Prerequisites
- Azure subscription with contributor or automation operator role
- Azure VM Agent installed on each target VM
- Az.Automation PowerShell module installed locally
Warning
Before registering VMs for DSC, ensure the Azure VM Agent is up to date. Without it, DSC cannot communicate with the Automation account.
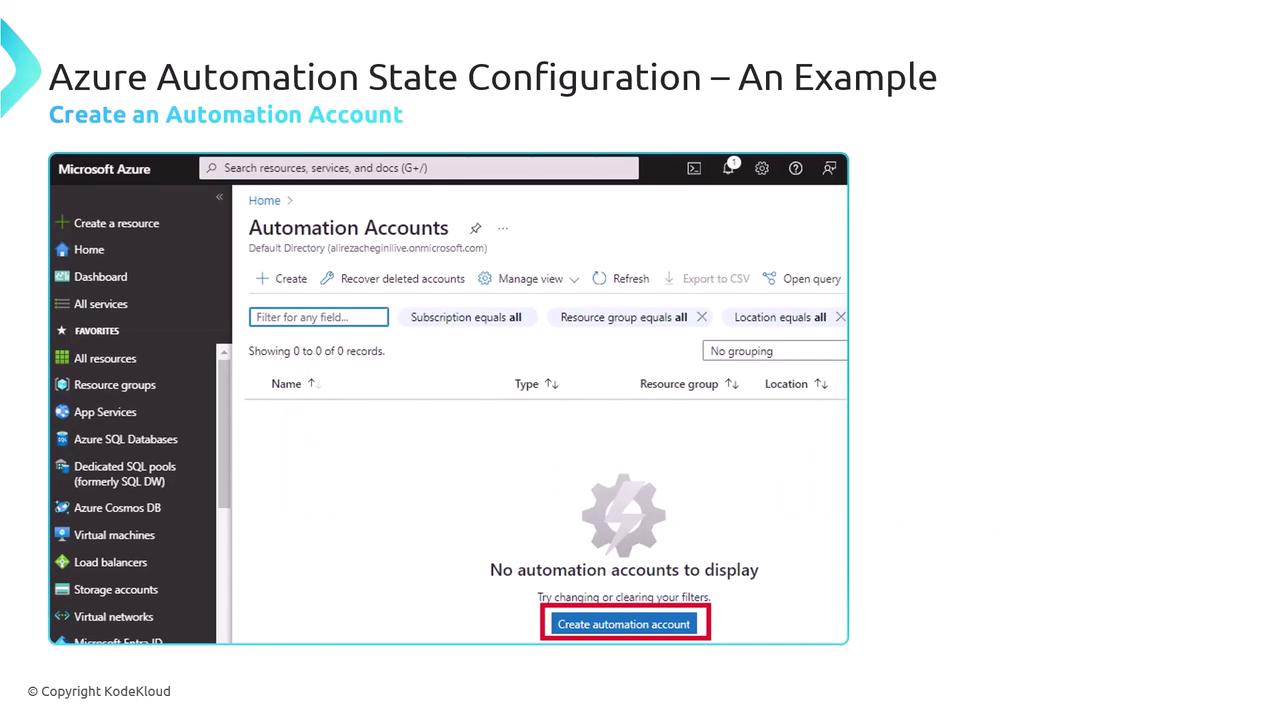
Step 1: Create an Automation Account
Your Automation Account is the central hub for DSC configurations, runbooks, and assets.
- In the Azure portal, search for Automation Accounts.
- Click + Create, fill in the name, resource group, and region.
- Review and Create.
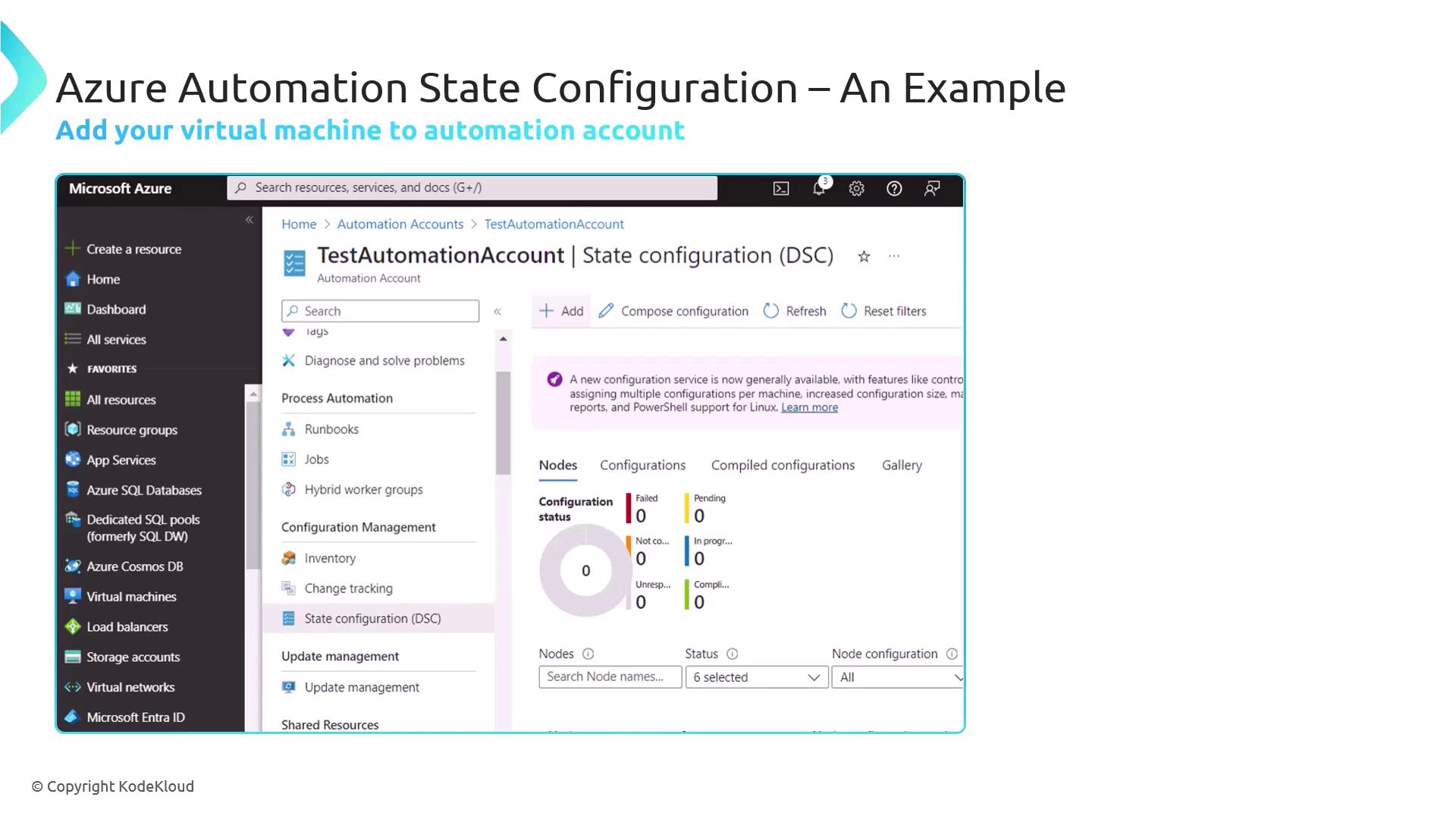
Step 2: Register Your VM as a DSC Node
Once the Automation Account is active, add your Windows VM as a DSC node.
- Navigate to State Configuration (DSC) > Nodes.
- Click Add > Azure VM.
- Select your subscription, resource group, and VM.
- Configure:
- Refresh Frequency: Interval for DSC pull (e.g., 30 minutes)
- Configuration Mode:
ApplyAndAutoCorrectorApplyAndMonitor
On the registration settings page, enter the Registration Key, Node Configuration Name, and Refresh Interval.
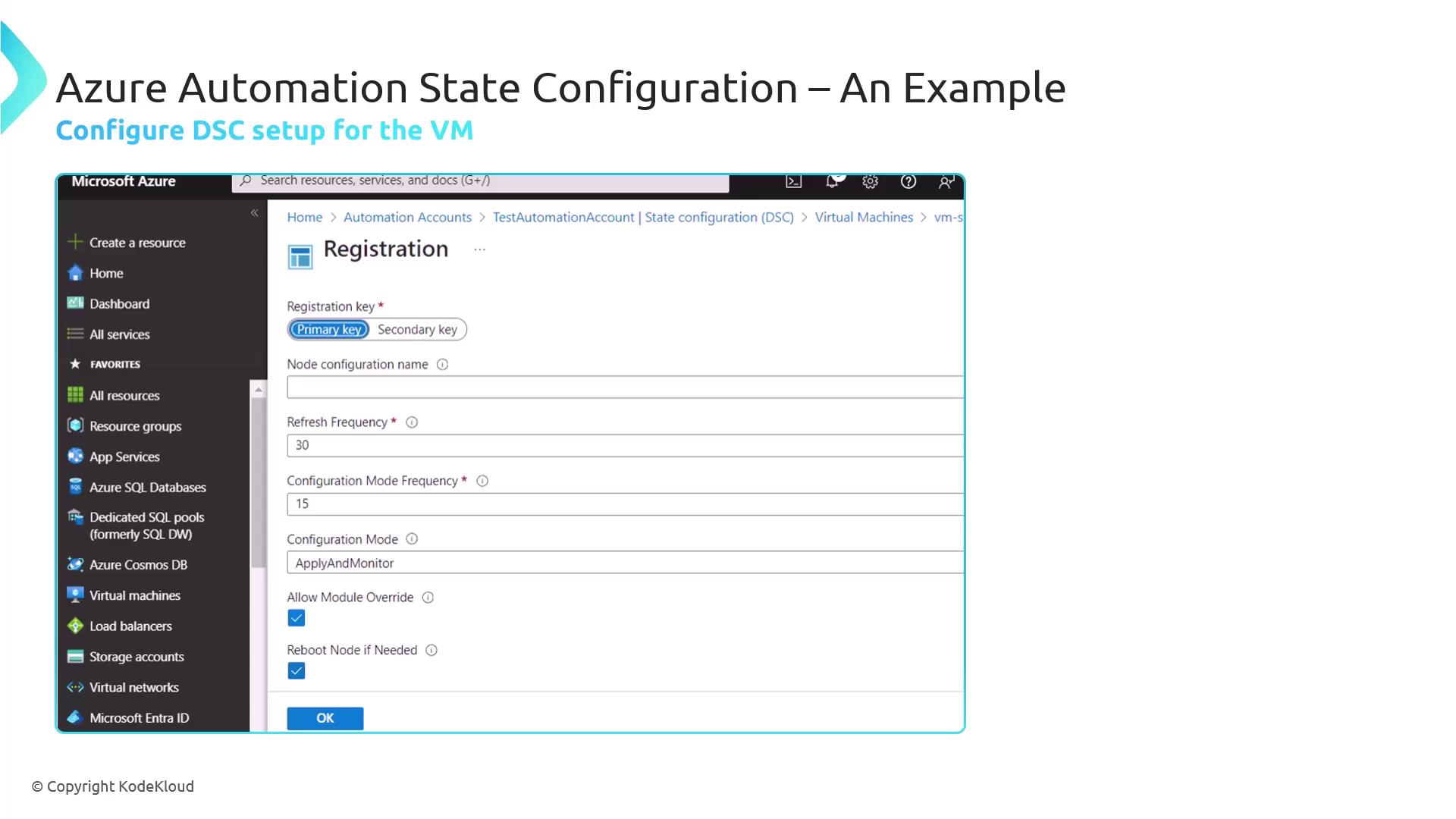
After registration, the VM appears in the DSC Nodes view marked Compliant (no custom configurations yet).
Step 3: Author and Import Your DSC Configuration
Define a DSC configuration that schedules a PowerShell task to run daily at midnight and repeat every 15 minutes for 8 hours.
Configuration ScheduledTaskDaily {
Node 'localhost' {
ScheduledTask ScheduledTaskDailyAdd {
TaskName = 'Test task Daily'
TaskPath = 'MyTasks'
ActionExecutable = 'C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe'
ScheduleType = 'Daily'
DaysInterval = 1
RepeatInterval = '00:15:00'
StartBoundary = '2023-10-01T00:00:00'
RepeatDuration = '08:00:00'
}
}
}
# Compile the configuration to a local folder
ScheduledTaskDaily -OutputPath "$env:Temp\DSC"
Note
Ensure you include StartBoundary and RepeatDuration when you need the schedule to span a specific time window.
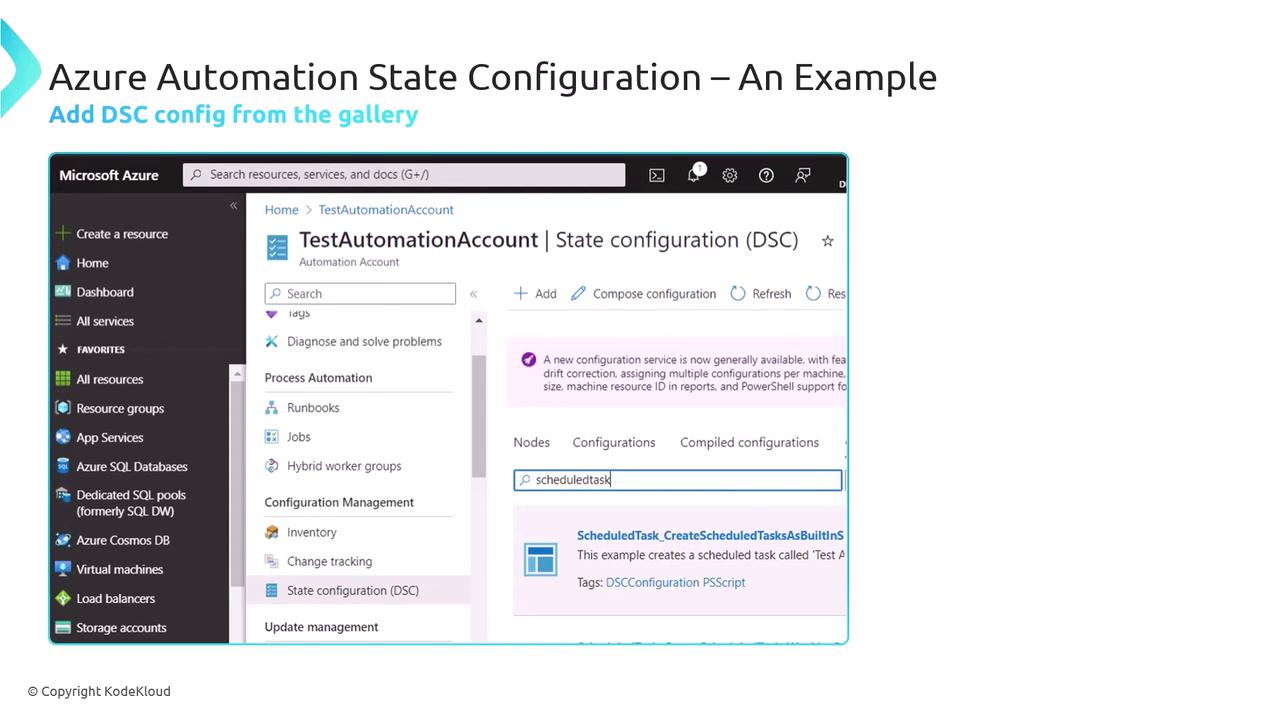
- In the portal, go to State Configuration (DSC) > Configurations.
- Click Add, upload the compiled
.moffile from"$env:Temp\DSC". - Confirm and Save.
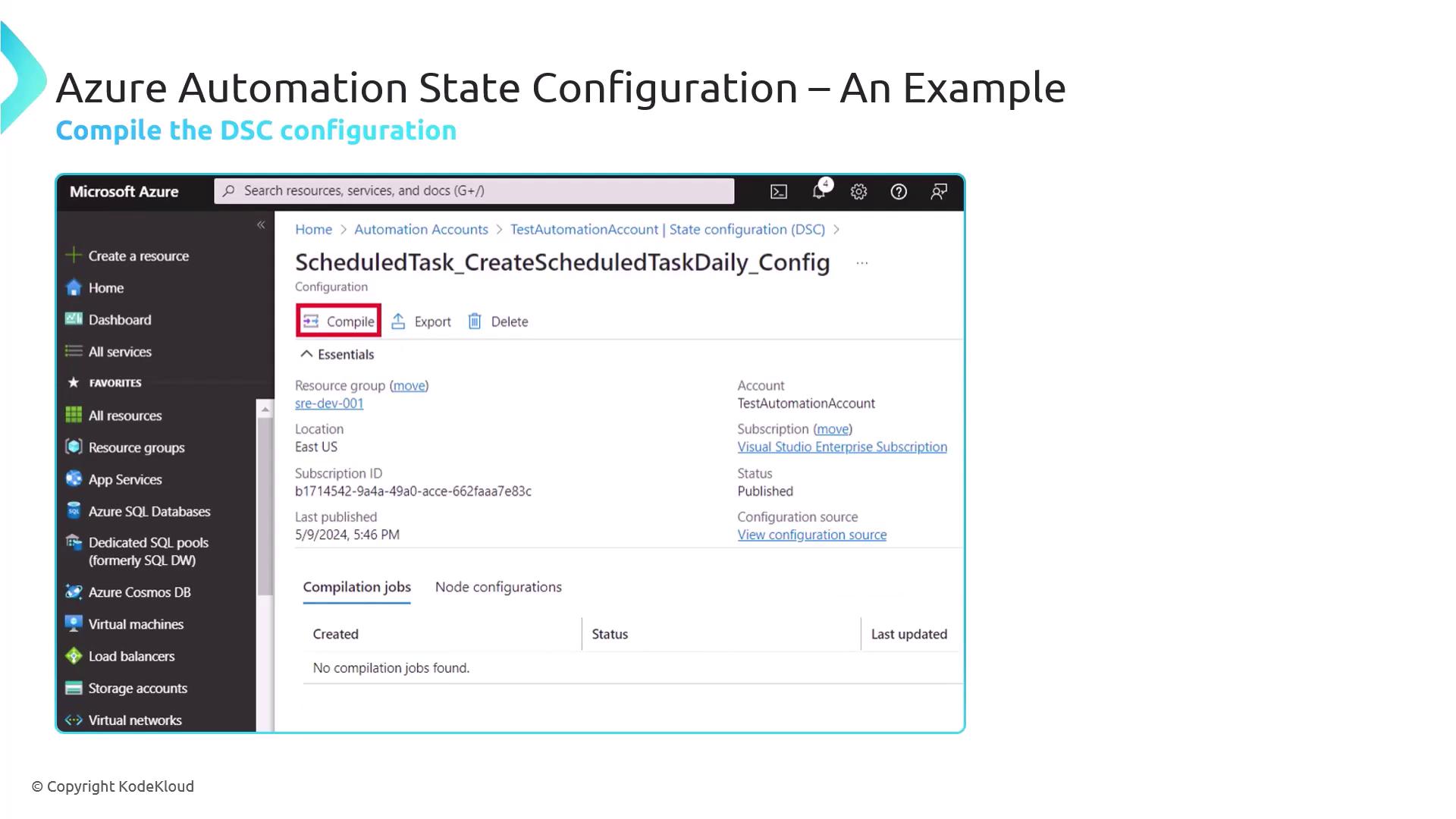
Compile status will appear in Configuration Versions.
Step 4: Assign the Configuration to the VM
Apply the new DSC configuration to your node:
- Under State Configuration (DSC) > Nodes, select your VM.
- Click Assign Node Configuration.
- Choose the
ScheduledTaskDailyconfiguration version and OK.
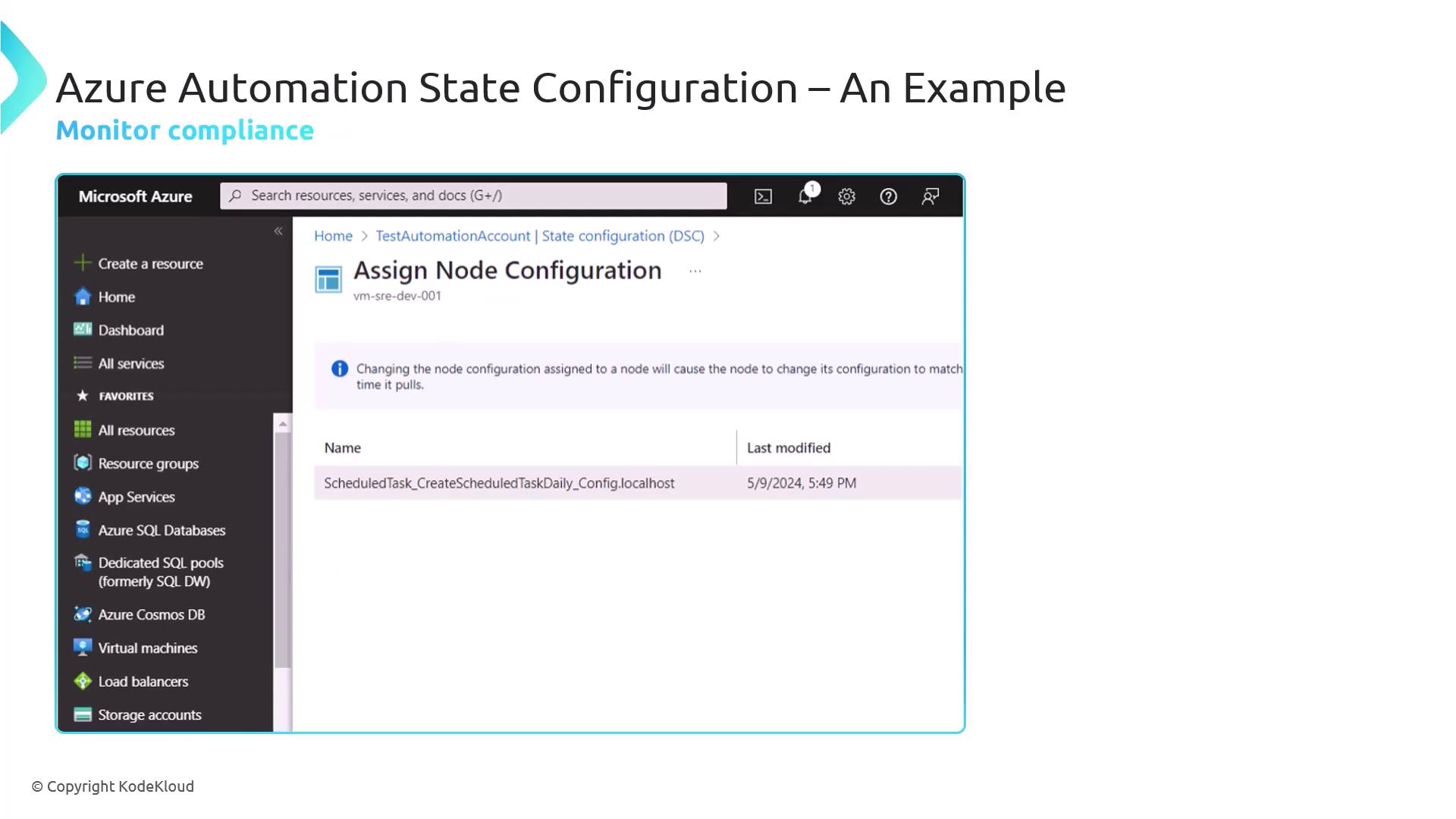
- The node will show Noncompliant until DSC applies your settings.
- After successful application, it returns to Compliant, indicating the scheduled task is in place.
Links and References
- Azure Automation DSC Overview
- PowerShell ScheduledTask DSC Resource
- Az.Automation PowerShell Module
- Azure Virtual Machine Agent
Watch Video
Watch video content