AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
Design and Implement Infrastructure as Code IaC
Design and implement Azure Deployment Environments for on demand self deployment
In this guide, you’ll learn how to build scalable, secure, and automated Azure Deployment Environments—essential for DevOps professionals and candidates preparing for the AZ-400 certification exam. We’ll cover core concepts, deployment strategies, CI/CD setup, Infrastructure as Code, security best practices, and monitoring.
What Are Azure Deployment Environments?
Azure Deployment Environments are isolated, preconfigured resource groups and settings that streamline application rollout. They serve as reproducible “sandboxes” for development, testing, and production stages.
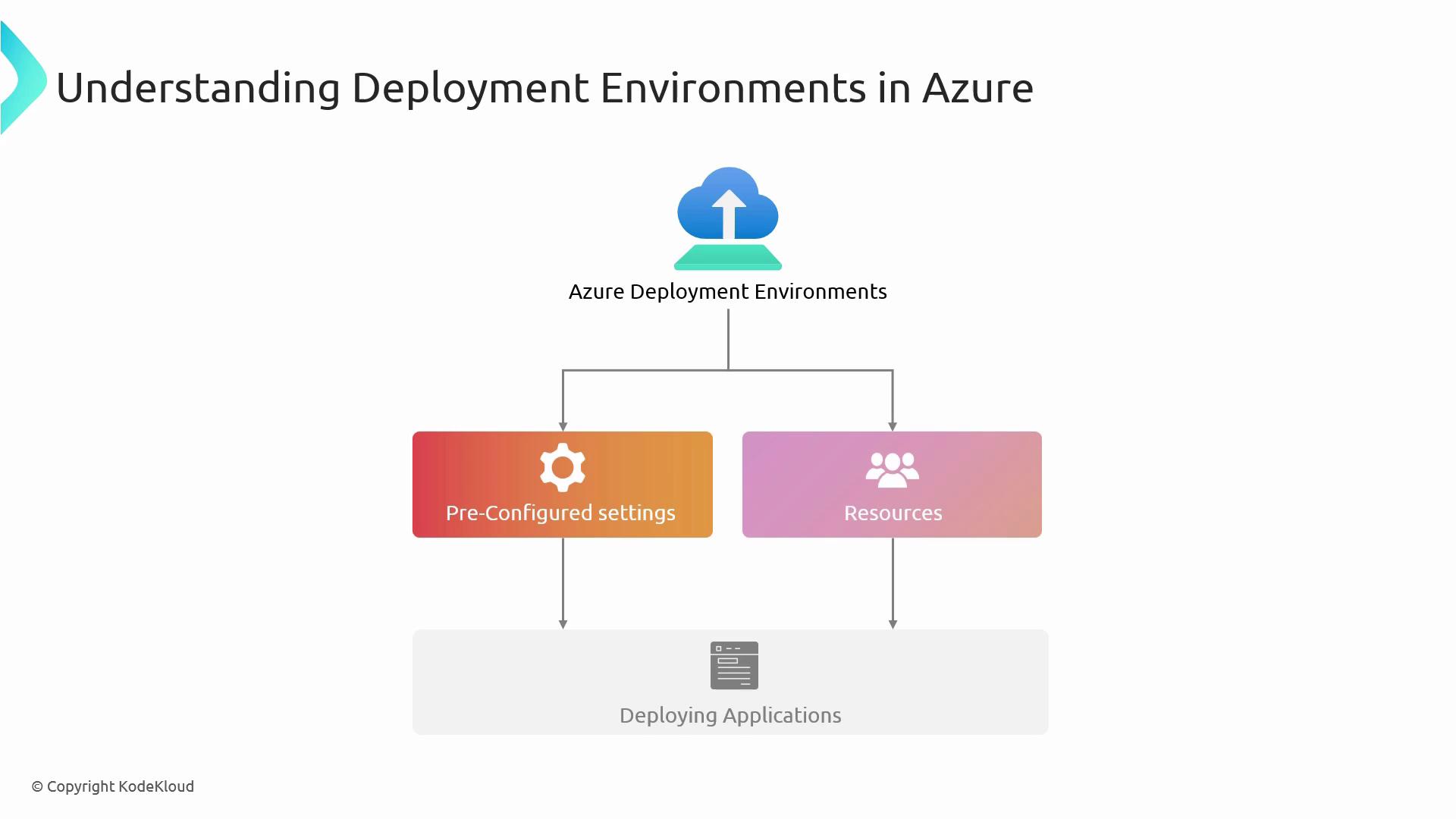
These environments integrate directly with your CI/CD pipelines, enabling automated builds, tests, and deployments.
By isolating each stage—Dev, QA, and Prod—you ensure consistent test results and minimize “it works on my machine” risks.
Common Deployment Strategies in Azure
Selecting the right deployment strategy helps balance risk, downtime, and user impact.
| Strategy | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Blue/Green | Two identical environments; switch production traffic on cutover | Zero-downtime upgrades |
| Canary | Roll out changes to a small subset of users before full release | Gradual feature validation |
| Rolling | Incrementally replace instances to minimize service disruption | Stateful or distributed applications |
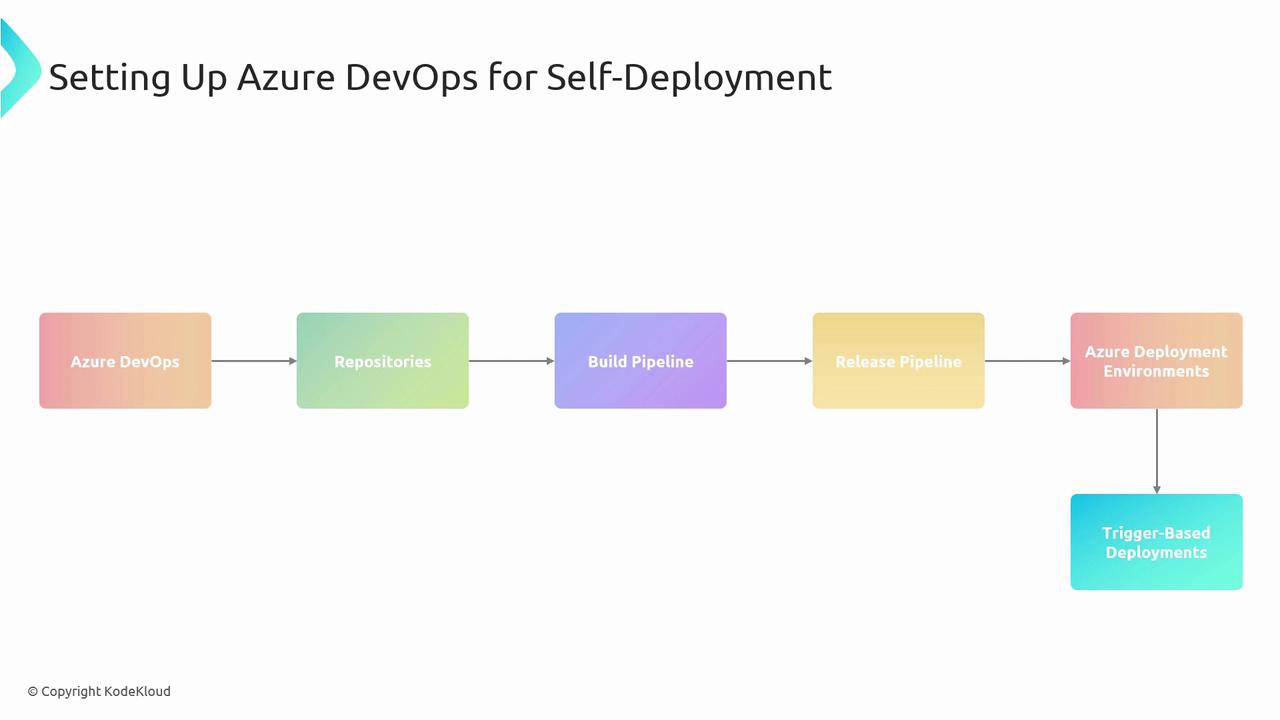
Setting Up Azure DevOps for Self-Deployment
To automate your pipeline end-to-end, combine these five key Azure DevOps components:
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Azure Repos | Host source code; enforce branch policies |
| Build Pipeline | Compile code, run unit tests, and produce build artifacts |
| Release Pipeline | Orchestrate deployments across Dev, Test, and Prod stages |
| Azure Deployment Environments | Map release stages to actual Azure resource groups |
| Triggers & Continuous Deployment | Automate pipeline start on commits or artifact availability |
Note
Ensure your Git branches follow a naming convention (e.g., feature/*, release/*) and enable pull-request policies to enforce code reviews.
Example YAML Snippet: Build Pipeline Trigger
trigger:
branches:
include:
- main
- release/*
pool:
vmImage: 'ubuntu-latest'
steps:
- task: UseDotNet@2
inputs:
packageType: 'sdk'
version: '6.x'
- script: dotnet build --configuration Release
Infrastructure as Code with ARM Templates
ARM templates let you define Azure resources declaratively in JSON or Bicep. Store these templates in your repo and deploy from your pipeline:
Warning
Keep sensitive values out of your template files. Use Azure Key Vault or pipeline variables with secret scopes for credentials and connection strings.
Security Considerations
Securing each Deployment Environment prevents misconfigurations and unauthorized access:
- Enforce the principle of least privilege with Azure RBAC.
- Automate policy compliance using Azure Policy.
- Monitor threats in real time via Azure Defender.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Proactive monitoring and regular upkeep ensure high availability and performance:
- Collect metrics and logs with Azure Monitor and Application Insights.
- Implement alerts on key performance indicators (CPU, memory, response time).
- Scale resources automatically with Azure Autoscale rules.
- Patch and update services on a regular schedule.
![]()
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content