Configuration Management in Azure
Configuration management ensures your Azure infrastructure remains consistent, reliable, and secure over time. Key benefits include:- Simplified administration and reduced human error
- Faster recovery and consistent rollback plans
- Predictable, repeatable deployments
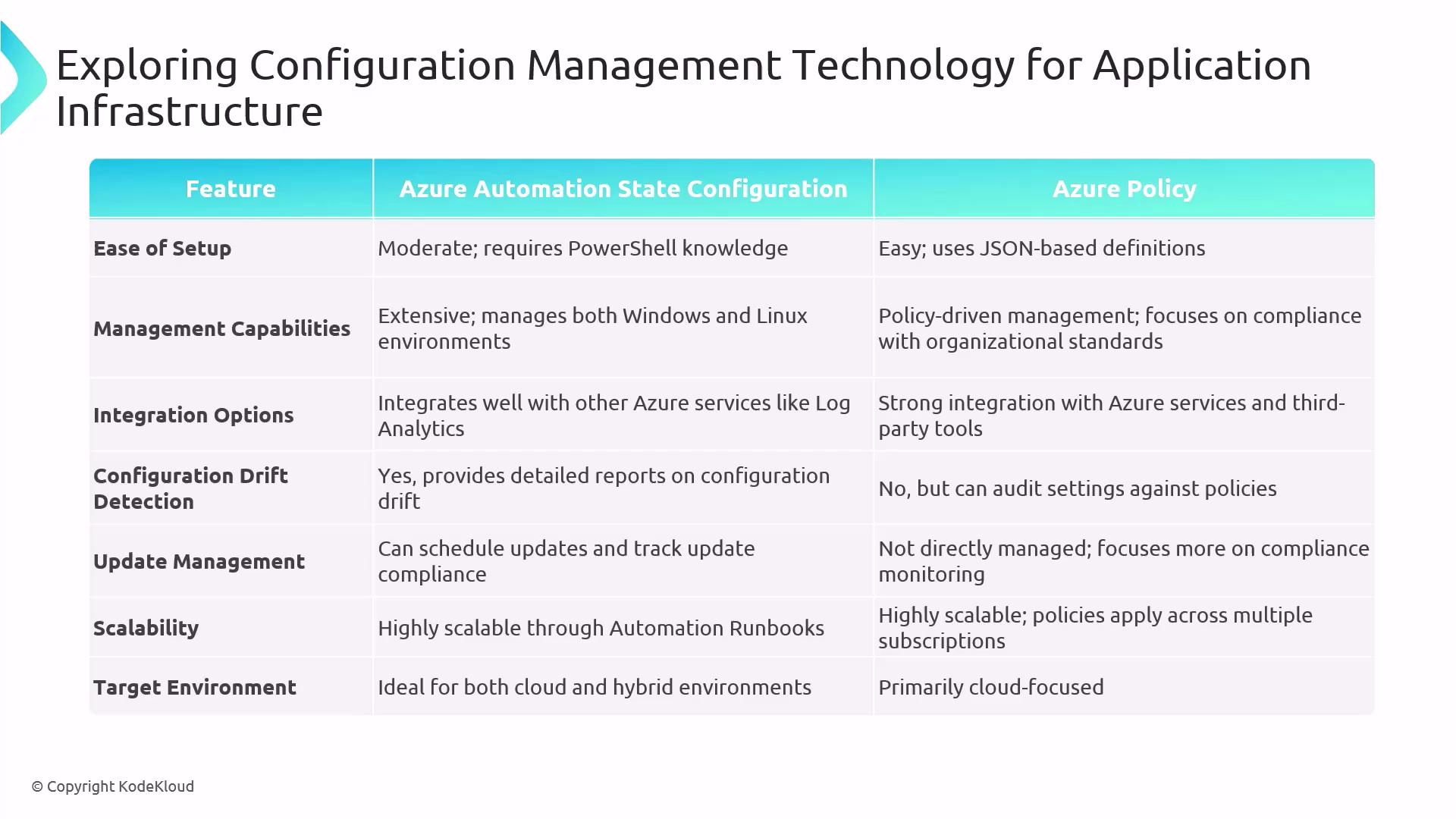
- Azure Automation Desired State Configuration (DSC): Comprehensive machine configuration management.
- Azure Policy: Lightweight governance and compliance enforcement.
Misconfiguring Azure Policy assignments can block resource provisioning. Always test policies in non-production scopes first.
Best Practices for Configuration Management
Integrating these practices helps maintain a secure, compliant Azure environment:Storing your configuration scripts and policy definitions in Git ensures traceability and team collaboration.
- Use version control (Git) for all automation scripts and DSC modules
- Conduct regular audits to detect drift and unauthorized changes
- Continuously refine your processes to adapt to new compliance standards

Desired State Configuration (DSC) and Related Tools
Azure Automation DSC lets you declare and enforce the state of your VM configurations at scale. Complementary tools include:- Azure Resource Manager (ARM): Deploy and manage resources using declarative JSON templates.
- Bicep: A concise DSL that simplifies authoring and maintaining ARM templates.
- Azure Automanage Machine Configuration: Automates best practices and configuration across Azure VMs.
| Tool | Purpose | Documentation |
|---|---|---|
| Azure Automation DSC | Machine configuration | DSC Overview |
| Azure Policy | Compliance and governance | Policy Overview |
| Azure Resource Manager (ARM) | Declarative resource deployment | ARM Templates |
| Bicep | Simplified ARM authoring | Bicep Docs |
| Azure Automanage Machine Configuration | VM configuration automation | Automanage |
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Strategy
Implement a scalable IaC approach to manage Azure resources through versioned code, testing, and automation:- Source Control Integration
- Keep ARM, Bicep, and Terraform definitions in Git repositories for traceability.
- Automated Testing
- Use CI/CD pipelines (e.g., Azure Pipelines, GitHub Actions) and testing frameworks (e.g., Pester, Terratest).
- Deployment Automation
- Provision resources reliably with Terraform, ARM, or Bicep at scale.

| Step | Description | Tooling |
|---|---|---|
| Version Control | Track and review IaC code changes | GitHub, Azure Repos |
| Testing | Validate templates and modules before deployment | Pester, Terratest, Azure Pipelines |
| Deployment | Automate provisioning and updates | Terraform, ARM, Bicep |
| Monitoring | Ensure resource health and compliance over time | Azure Monitor, Application Insights |
Azure Deployment Environments and Strategies
Designing multiple deployment stages and release strategies helps minimize risk and improve reliability:| Environment | Purpose | Recommended Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Development | Feature development and unit tests | Feature branches, dev resource groups |
| Testing | Integration and acceptance testing | CI pipelines, automated tests |
| Staging | User acceptance and validation | Blue/Green or Canary deployments |
| Production | Live customer workloads | A/B testing, Canary rollouts |
- Azure DevOps Self-Deployment: Standardize pipelines for consistent releases across environments.
- Deployment Strategies: Implement Blue/Green, Canary, or A/B testing for controlled rollouts.
- Monitoring & Maintenance: Leverage Azure Monitor and Application Insights for real-time telemetry and alerts.
We look forward to seeing you in the next lesson!