Dependency Scanning Tools
Azure Pipelines offers a range of extensions and tasks for open-source and commercial scanners. Below is a quick comparison:| Tool | Database Type | Integration | Key Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| WhiteSource Bolt | Proprietary OSS DB | Extension / Task | Severity reports & remediation |
| Snyk | Community & Commercial | Task + Policy Check | Fix suggestions & policy alerts |
| OWASP Dependency Check | NVD & Community | CLI task | CVE-based findings & CSV/HTML |
WhiteSource Bolt
Automated open-source vulnerability analysis with continuous database updates. Generates severity-ranked reports, displays affected components, and recommends fixes. Integrates as a build or release task in Azure Pipelines.
Snyk
Real-time monitoring of dependencies for known vulnerabilities. Provides actionable remediation advice—package updates, code patches, or workarounds. Embeds into your pipeline to enforce policy-based blocking of risky dependencies.
OWASP Dependency Check
Open-source scanner that compares project libraries against the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) and community feeds. Integrates via CLI or pipeline task to automate periodic scans and produce standardized reports.
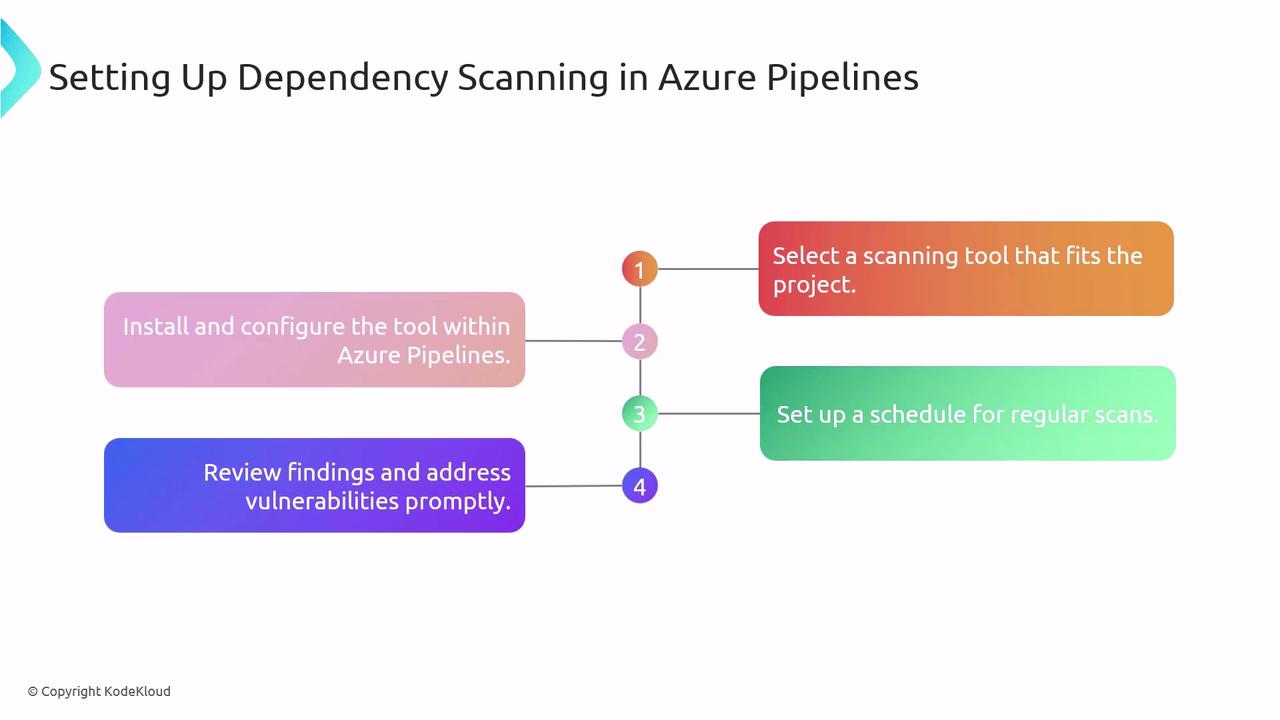
Setting Up Dependency Scanning in Azure Pipelines
- Select the scanner that best fits your tech stack and reporting needs.
- Install or add the extension/task to your pipeline YAML or Classic editor.
- Configure authentication and project settings (API tokens, project keys).
- Schedule scans on every build, nightly run, or on-demand.
- Review findings and automate work items for high-severity issues.
Automate recurring scans—even if dependencies haven’t changed—to catch newly disclosed vulnerabilities.
Security scanning targets code and infrastructure weaknesses—identifying injection flaws, insecure configurations, and runtime threats before deployment.
- Code analysis for SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), insecure patterns
- Infrastructure audits of cloud resources, container images, IaC templates
Security Scanning Tools
| Tool | Focus | Scan Types | Integration |
|---|---|---|---|
| SonarQube | Code Quality & SAST | Vulnerabilities, Debt | Marketplace Task |
| Aqua Security | Container & Runtime | Image & Config scans | CLI / Task |
| Fortify | SAST & DAST | Static & Dynamic | REST API / Task |
SonarQube
Analyzes code for security vulnerabilities (e.g., XSS, SQL injection), code smells, duplication, and complexity. Quality gates enforce blocking builds until issues are resolved.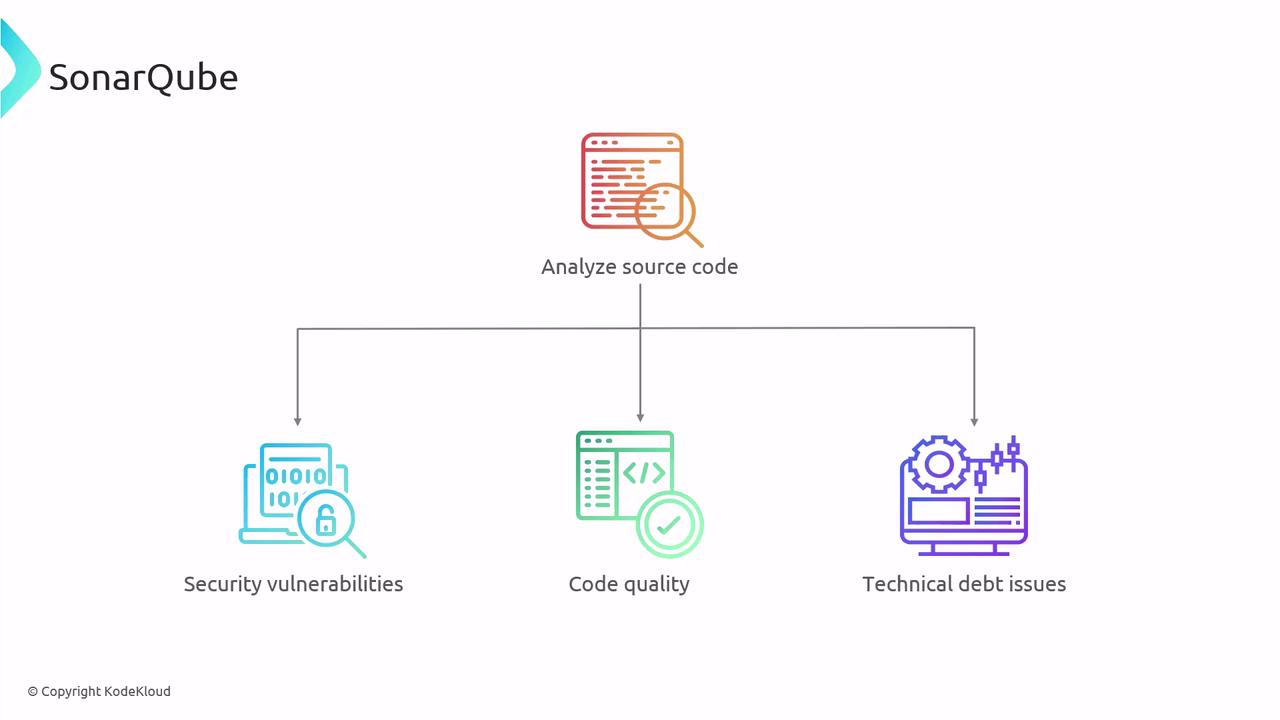
Aqua Security
Specializes in container image security—scanning during build, pre-push, and at runtime for vulnerabilities, malware, and misconfigurations. Ideal for AKS and Kubernetes pipelines.
Fortify
Combines static application security testing (SAST) with dynamic analysis (DAST). Static scanning finds code-level flaws; dynamic scanning probes a running application for runtime issues.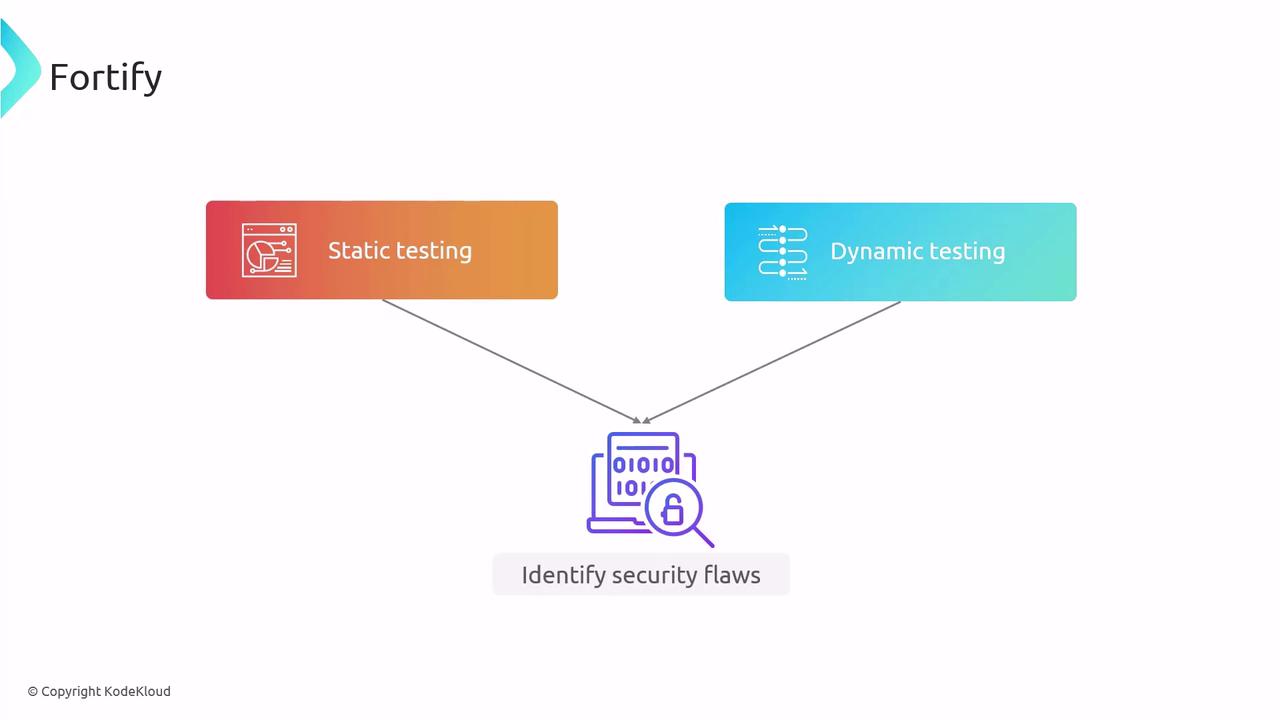
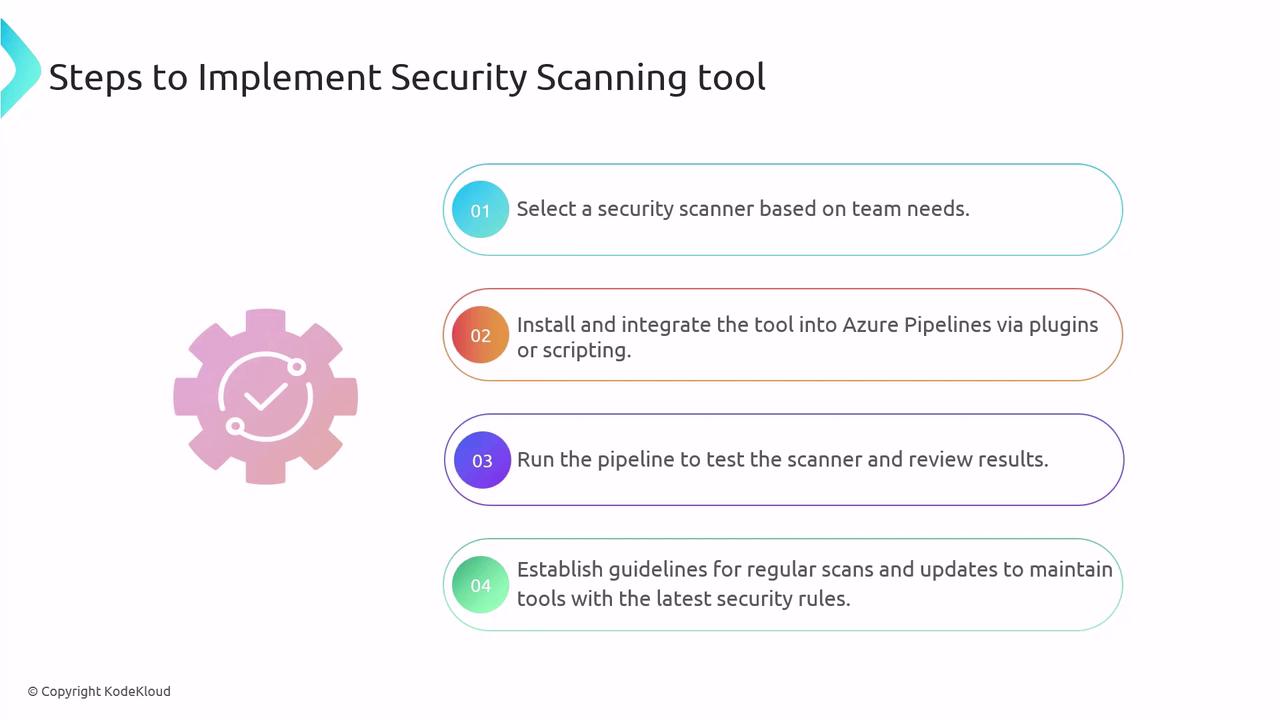
Implementing a Security Scanner in Azure Pipelines
- Choose a scanner based on supported languages and vulnerability focus.
- Add the respective task or script to your YAML pipeline.
- Configure credentials, endpoints, and thresholds.
- Run the pipeline, analyze scan output, and triage issues.
- Automate periodic scans and keep scanner definitions up to date.
Example: SonarQube Integration
- Select your SonarQube edition (Community or Developer).
- Provision and configure the SonarQube server.
- In Azure DevOps, install the SonarQube extension.
-
In your pipeline YAML:
- Define quality gates in the SonarQube dashboard to fail on critical issues.
Continuous dependency and security scanning is a DevSecOps imperative. Automate both open-source component checks and code/infrastructure vulnerability scans to:
- Catch issues earlier and reduce remediation costs
- Enforce policy gates to prevent insecure releases
- Maintain an audit trail of findings and fixes
