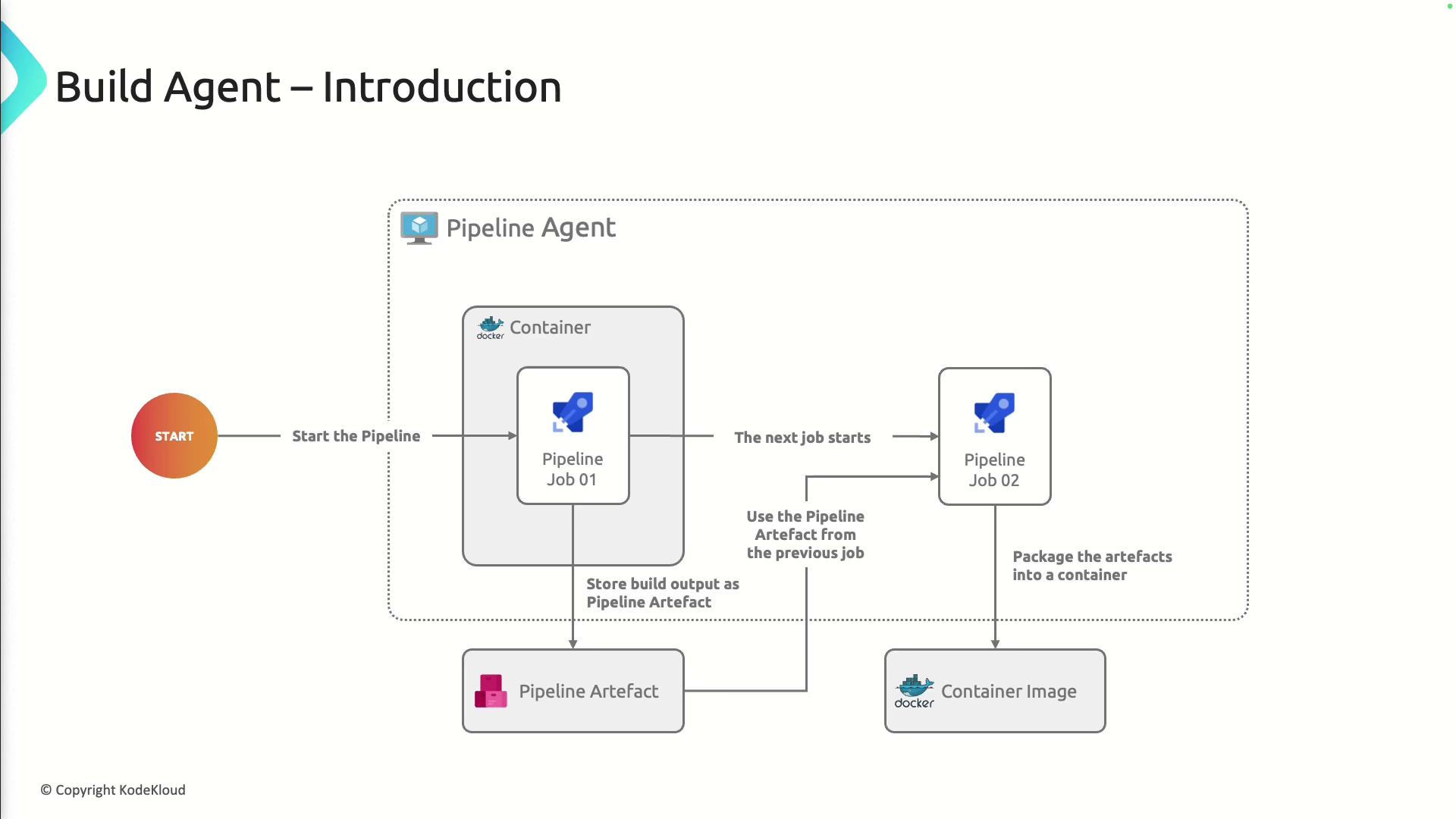
Typical Build and Deploy Workflow
A Build Agent executes each stage of your CI/CD pipeline:- Pipeline Trigger
- Checkout Source Code
- Run Build and Tests
- Publish Build Artifacts
- Package Artifacts (e.g., container images)
Automating these steps ensures consistent, repeatable deployments and reduces manual overhead.
Core Functions of a Build Agent
Build Agents are responsible for:- Cloning repositories (Git, TFVC, etc.)
- Executing build scripts (MSBuild, Maven, npm, etc.)
- Running automated tests
- Publishing artifacts to Azure Artifacts, GitHub Packages, or external feeds
- Deploying to target environments via tasks (e.g., ARM, Kubernetes)
Hosted vs. Self-Hosted Agents
Choose the right agent type based on your control, cost, and compliance needs:| Agent Type | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| Hosted Agent | Microsoft-managed with preinstalled tools and OS images | Quick start, no infrastructure overhead |
| Self-Hosted Agent | Customer-managed on VMs or on-prem servers | Custom dependencies, specific network access, cost optimization |

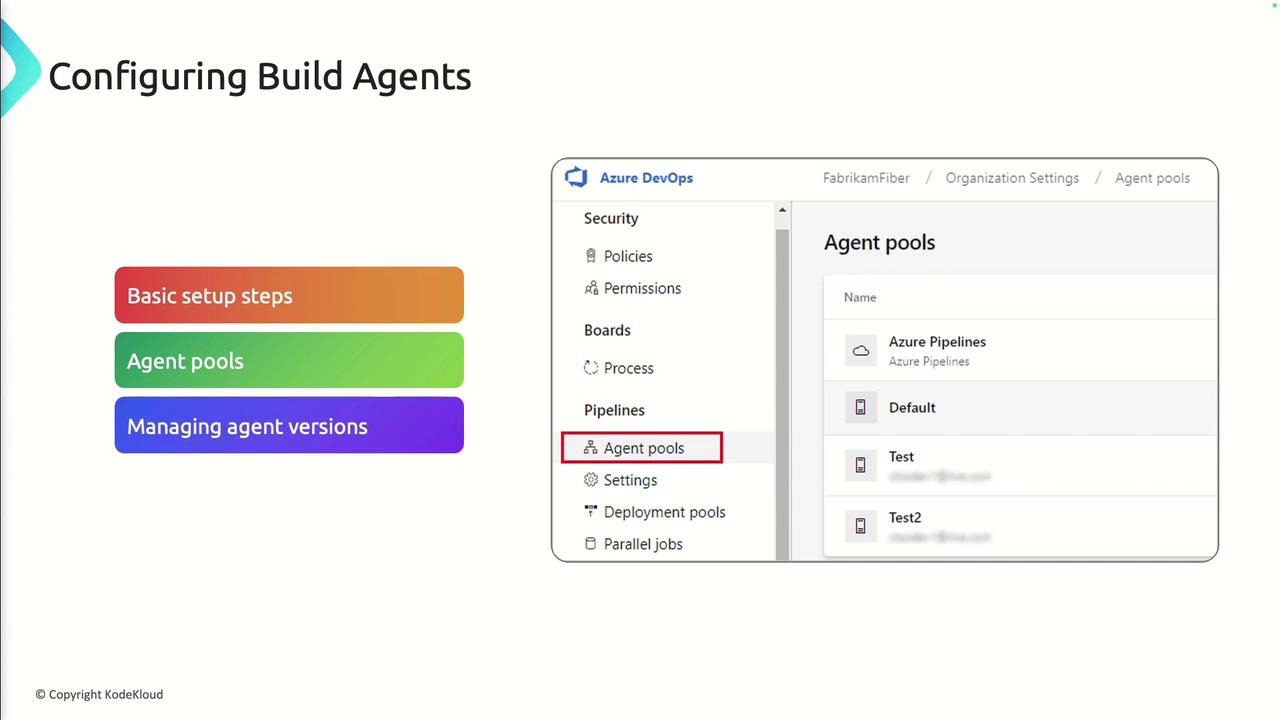
Configuring Build Agents
- Define Agent Pools
Use agent pools to group agents by environment or capability. - Install and Update Agents
For self-hosted agents, follow the Agent installation guide and keep the agent software updated. - Assign Permissions
Configure pool security to restrict who can queue pipelines or manage agents.
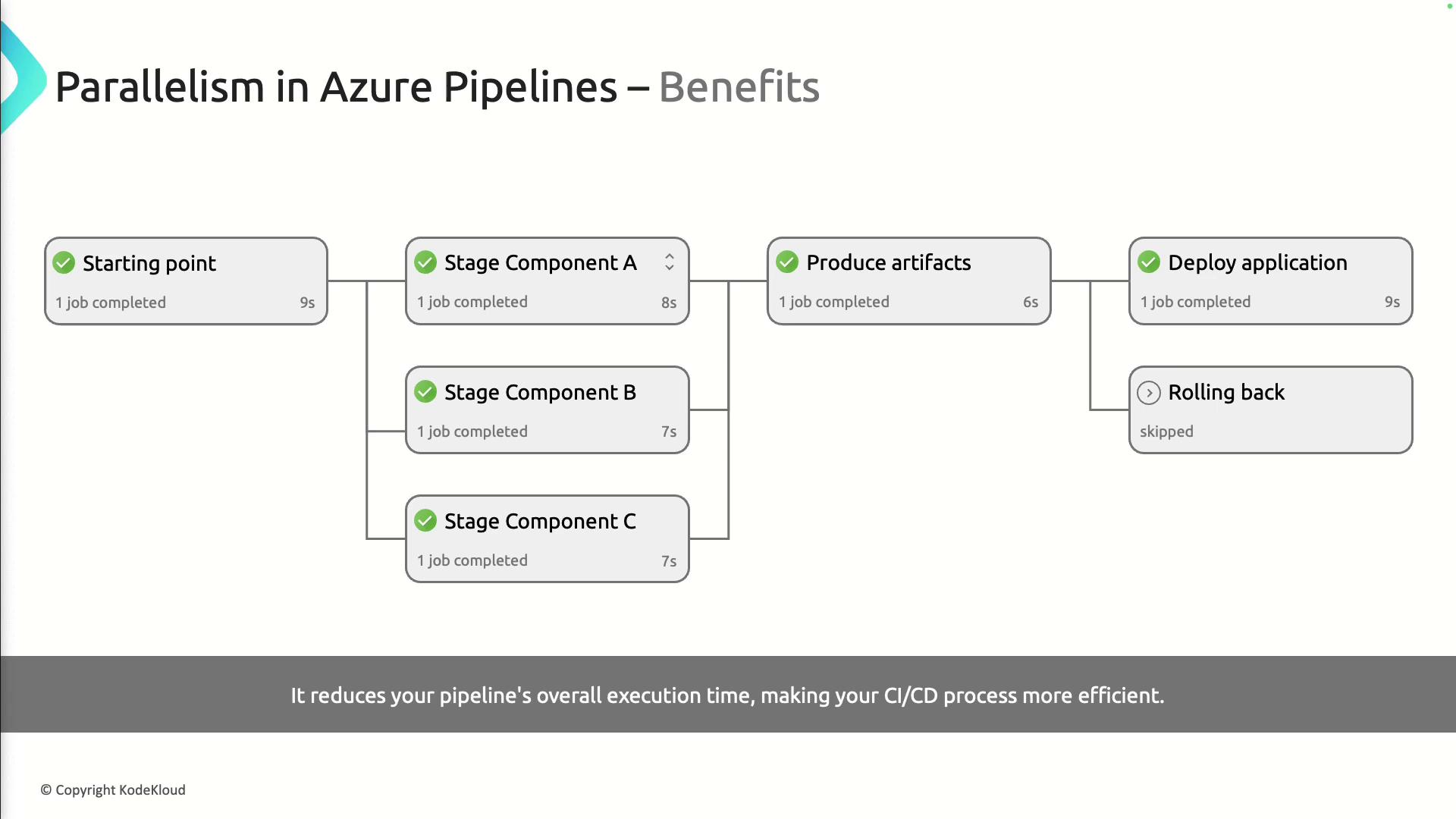
Enabling Parallelism
Parallel jobs run multiple pipeline stages or tasks at the same time, cutting down total execution time:- Sequential: A → B → C
- Parallel: A, B, and C run concurrently
Check your Azure DevOps plan for the number of parallel jobs included. Exceeding this limit will queue additional jobs and delay execution.
Best Practices for Parallel Builds
- Distribute test suites across multiple agents.
- Define dependencies with
dependsOnin YAML pipelines. - Use a matrix strategy to run combinations of environments in parallel:
- Monitor job durations to identify bottlenecks.
Optimizing Build Agents and Parallelism
Continuous improvement is key:- Monitoring and Scaling
Integrate with Azure Monitor to track agent performance and scale pool size dynamically. - Efficient Resource Allocation
Right-size VM SKUs for self-hosted agents; deallocate idle VMs when not in use. - Review and Refine
Regularly audit pipeline definitions, update agent versions, and tweak parallel strategies based on data.