AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
Design and Implement a Strategy for Managing Sensitive Information in Automation
Implement and manage secrets keys and certificates by using Azure Key Vault
Azure Key Vault is a centralized solution for securely storing and managing secrets, cryptographic keys, and certificates in Azure. It helps enforce access policies, integrate with DevOps workflows, and maintain compliance with regulatory standards.
Table of Contents
- Overview
- Core Features
- Managing Secrets
- Managing Cryptographic Keys
- Managing Certificates
- Authentication and Authorization
- Access Policies
- Monitoring and Logging
- DevOps and CI/CD Integration
- Automation
- Best Practices
- Demo: Creating and Managing Secrets
- References
Overview
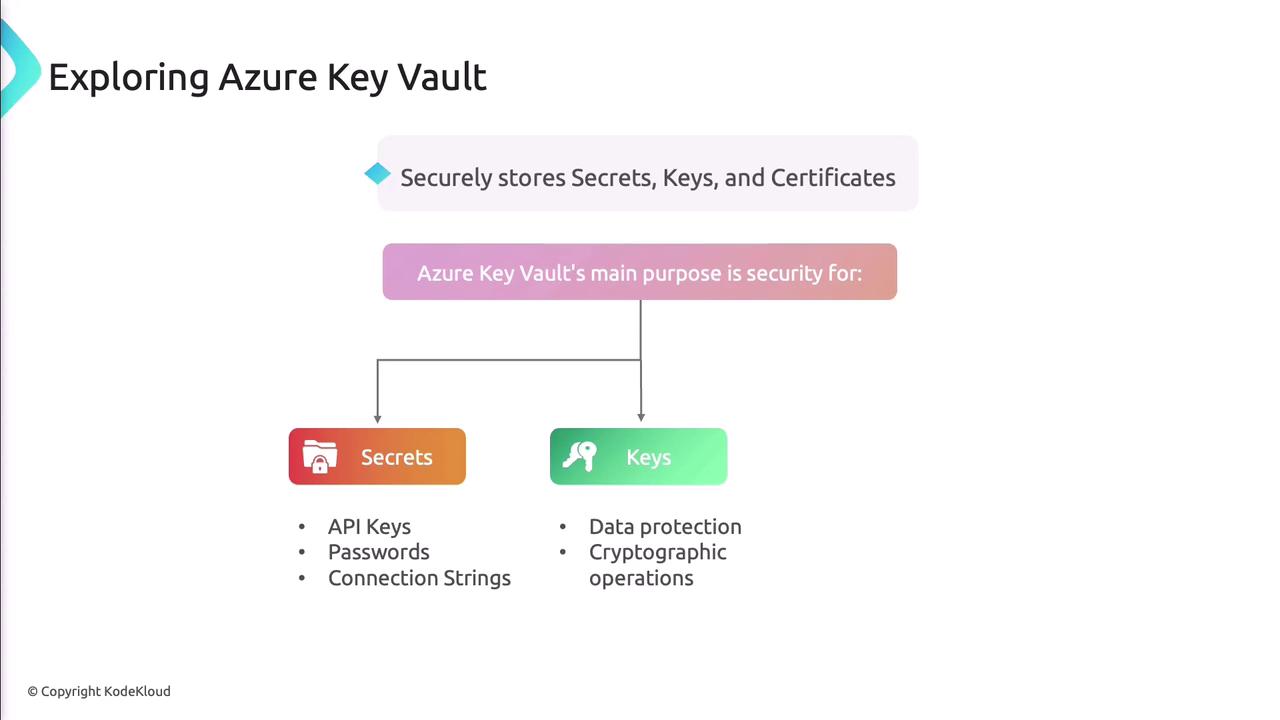
Azure Key Vault streamlines security operations by centralizing storage for secrets, keys, and certificates. It offers:
- Secure secret, key, and certificate storage
- Hardware Security Module (HSM) protection
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) with Azure Active Directory
- Comprehensive logging via Azure Monitor and Azure Security Center
- Automated key rotation and certificate renewal
Core Features
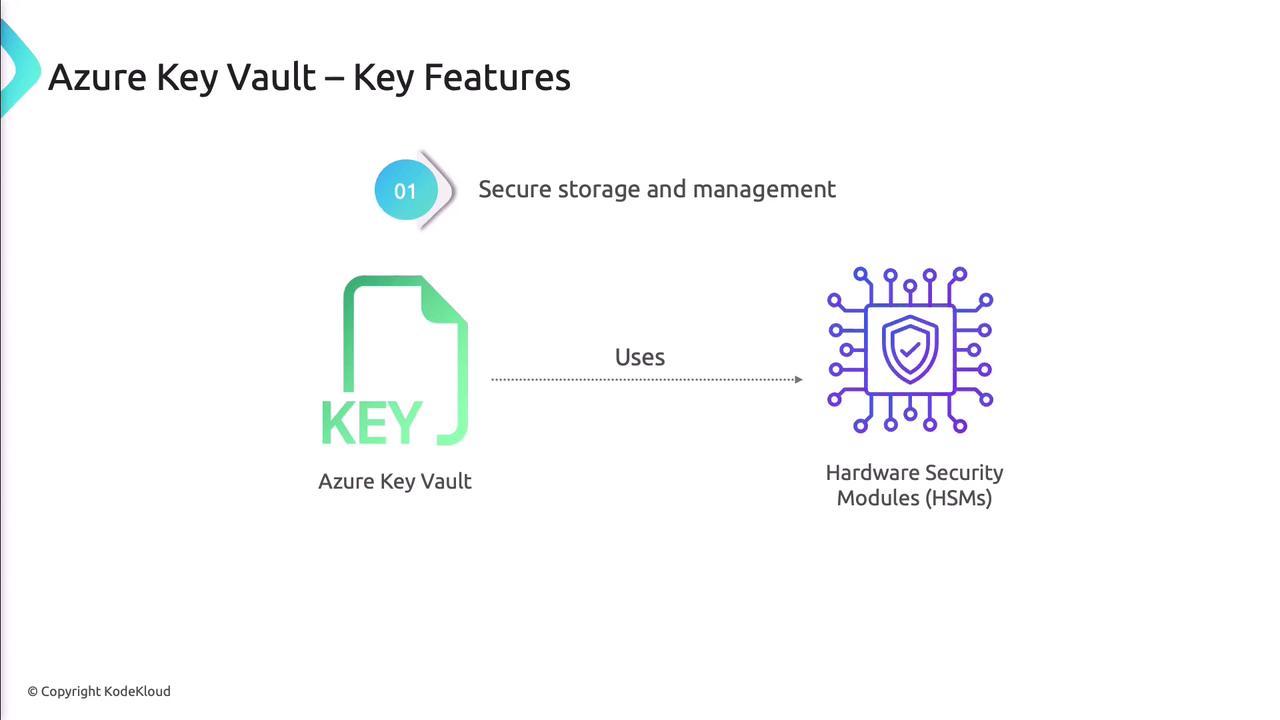
Secure Storage and Management
Azure Key Vault uses certified Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) to protect your data.
Note
Choose the Standard or Premium tier to leverage HSM-backed key protection.
Access Control
Integrate with Azure Active Directory to apply RBAC, granting least-privilege access to secrets, keys, and certificates.
Logging and Monitoring
Stream diagnostic logs to Azure Monitor and Security Center to audit every operation and maintain compliance.
Managing Secrets
Secrets include API keys, passwords, and connection strings needed at runtime.
Common Use Cases
| Scenario | Description |
|---|---|
| Database connection strings | Secure credentials for web apps |
| API keys for external services | Protect third-party service tokens |
| Application configuration parameters | Secure feature flags and configuration values |
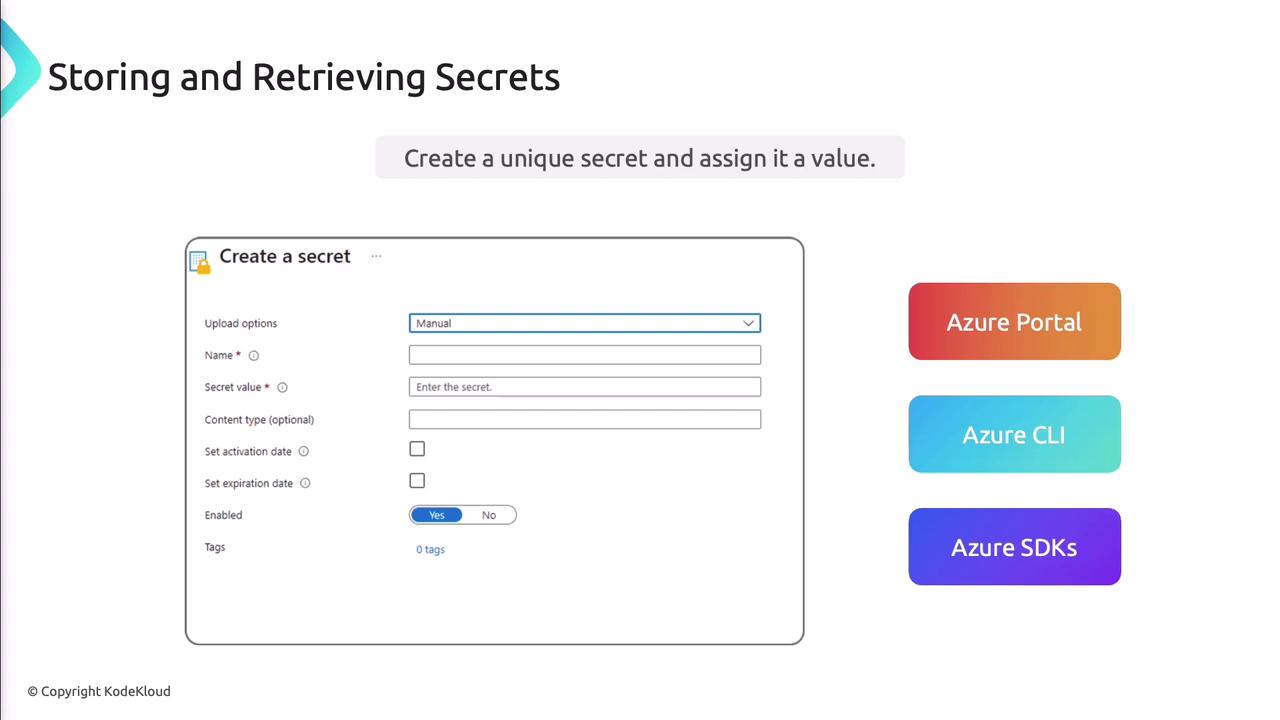
Create a Secret
You can use the Azure Portal, CLI, or SDKs.
Azure CLI example:
az keyvault secret set \
--vault-name MyKeyVault \
--name "api-token" \
--value "mySecretValue"
Retrieve a Secret
az keyvault secret show \
--vault-name MyKeyVault \
--name "api-token"
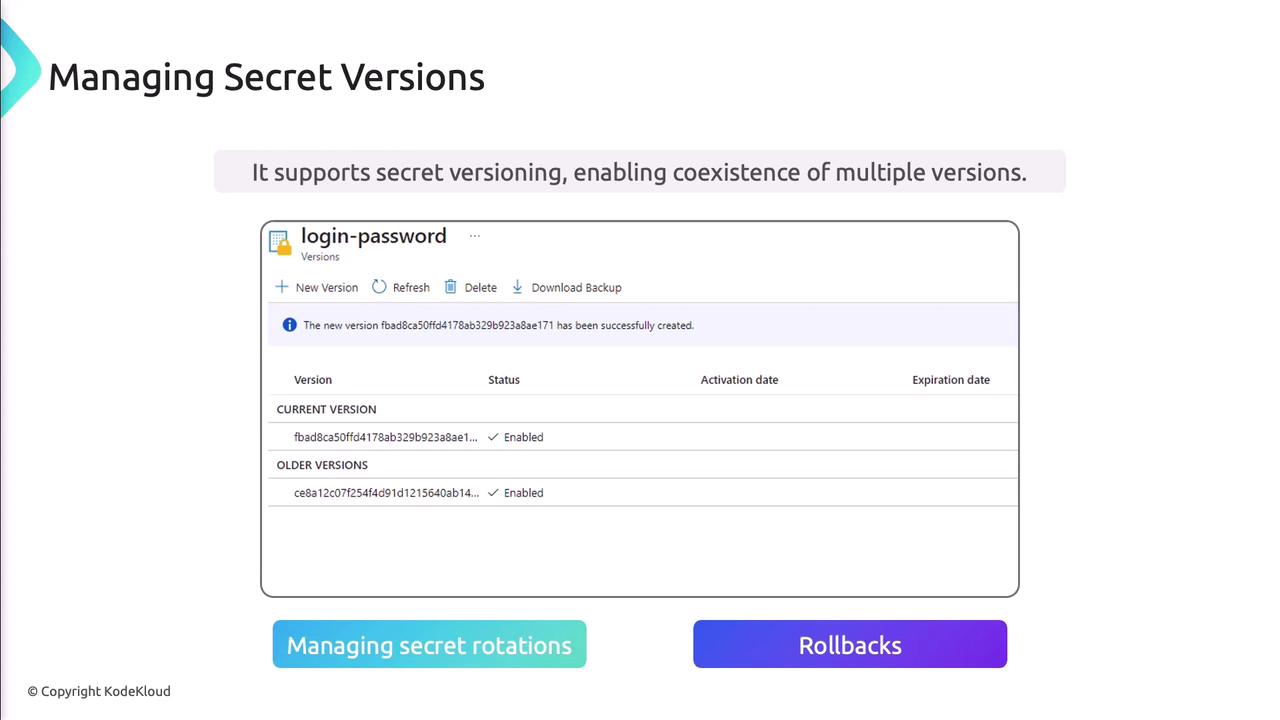
Secret Versioning
Azure Key Vault retains previous versions, supporting rotation and rollback.
Managing Cryptographic Keys
Support for RSA and Elliptic Curve keys enables encryption, decryption, signing, and verification.

Generate a Key (Azure CLI)
az keyvault key create \
--vault-name MyKeyVault \
--name "myRSAKey" \
--kty RSA \
--size 2048
Key Rotation and Expiration
Automate rotation to minimize risk by defining policies.
az keyvault key rotation-policy update \
--vault-name MyKeyVault \
--name "myRSAKey" \
--expires "P90D" \
--lifetime-actions "[{'trigger':{'lifetimePercentage':85},'action':{'type':'Rotate'}}]"
Managing Certificates
Azure Key Vault handles SSL/TLS, client authentication, and code-signing certificates.
Certificate lifecycle: issuance, renewal, and revocation.
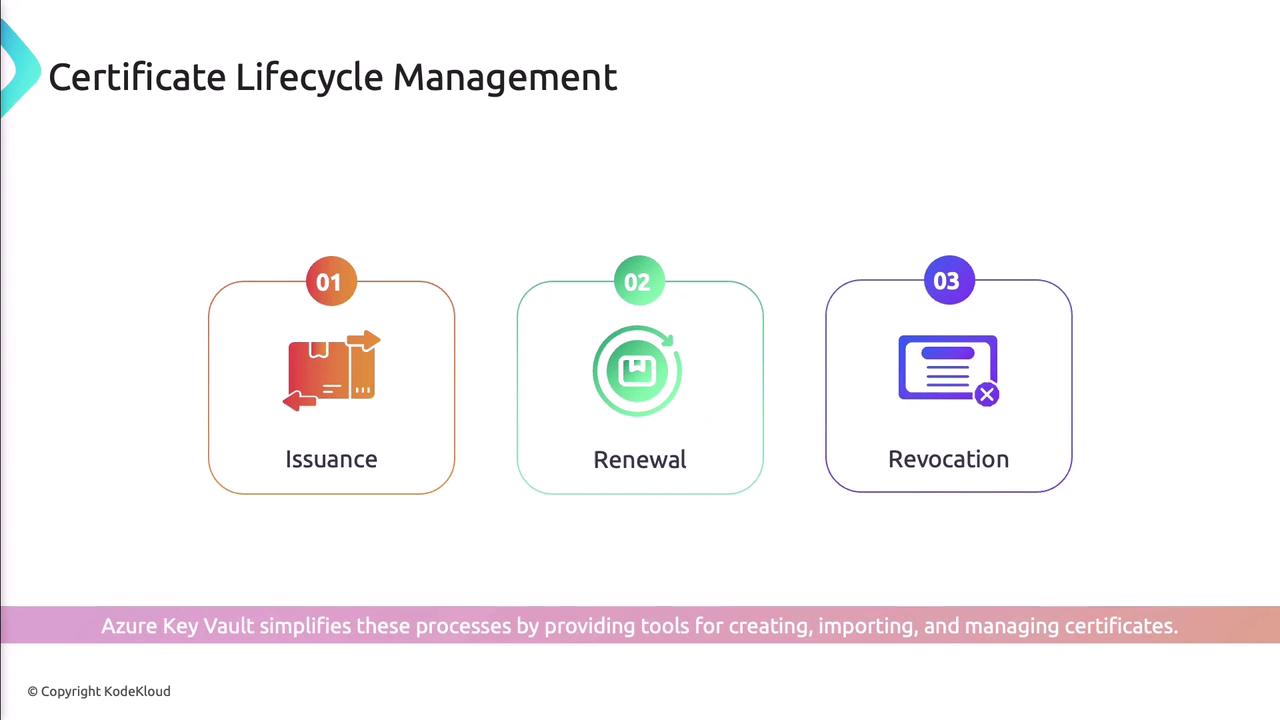
Automatic renewal prevents disruptions by integrating with certificate authorities.
Authentication and Authorization
Azure Active Directory manages authentication, while RBAC defines authorization for vault objects.
Common roles: Owner, Contributor, Reader.
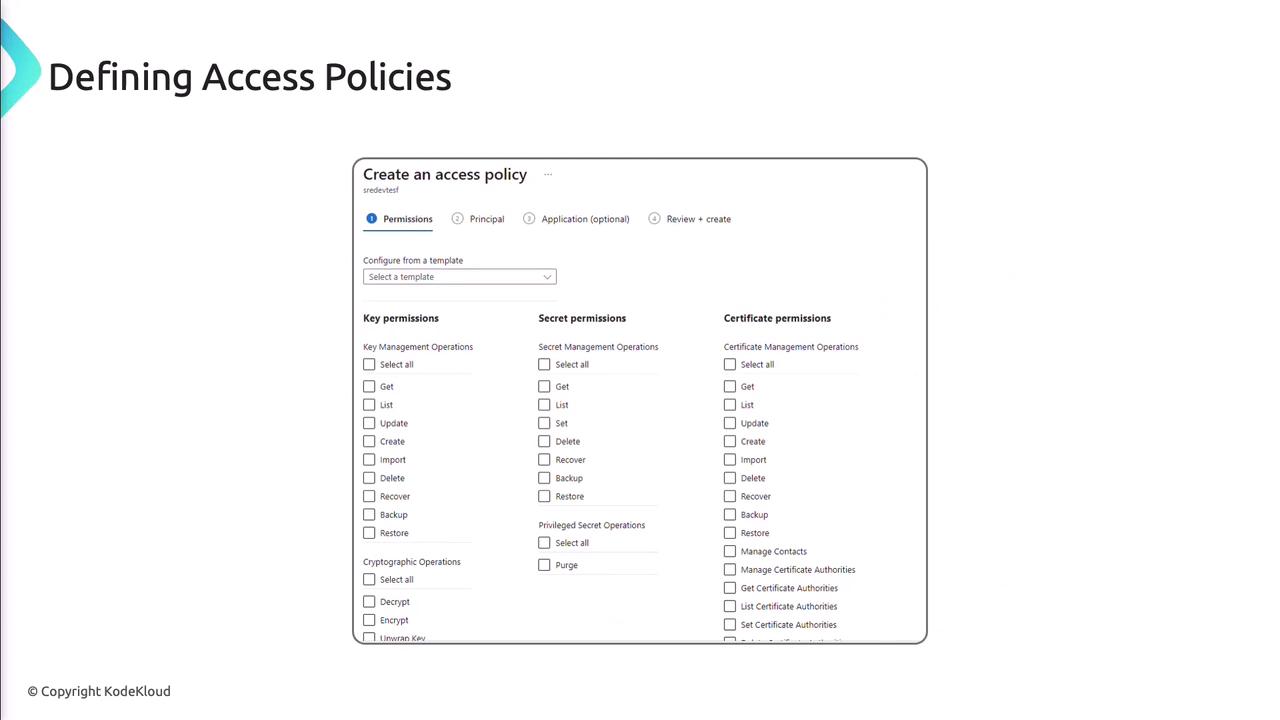
Access Policies
Fine-grained permissions can be assigned for secrets, keys, and certificates via portal, CLI, or PowerShell.
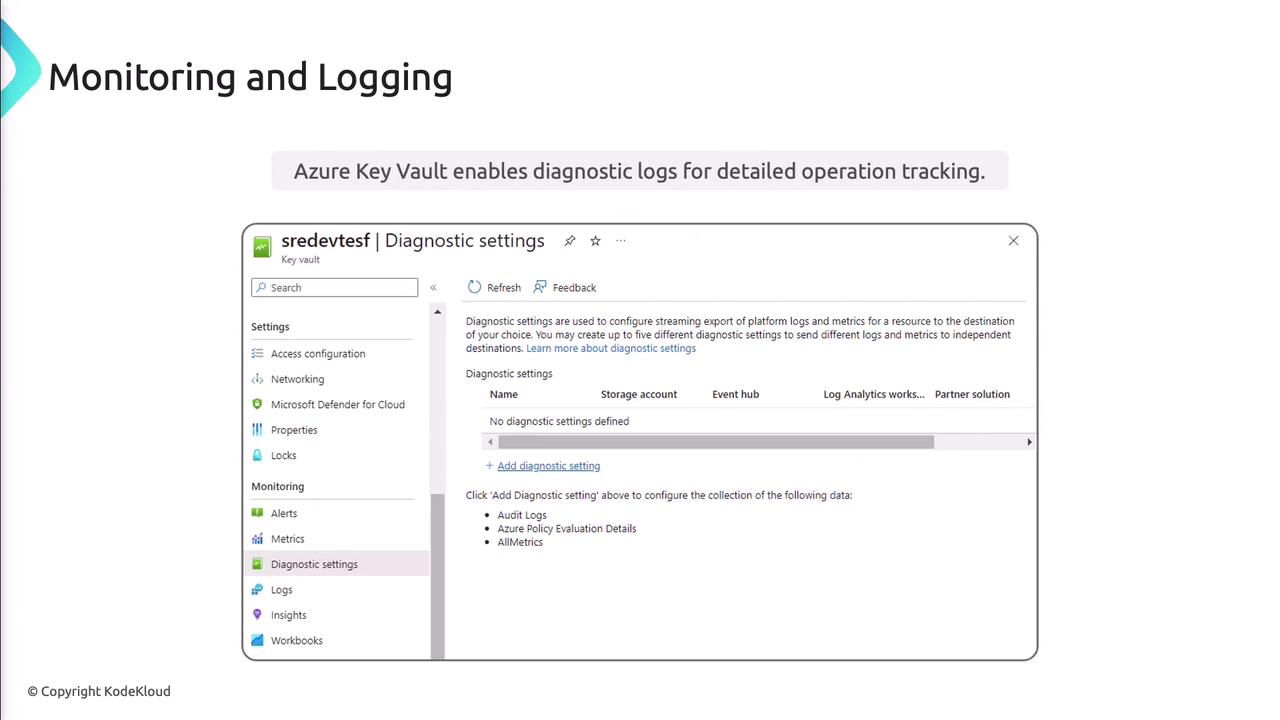
Monitoring and Logging
Enable diagnostic logging to capture vault operations and feed them into Azure Monitor for alerts and dashboards.
DevOps and CI/CD Integration
Retrieve secrets dynamically in build and release pipelines. Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions, and Jenkins all support Key Vault integration.

Applications authenticate to Key Vault using managed identities or service principals.
Automation
Automate routine tasks—rotation, renewal, and policy updates—using Azure Automation, Logic Apps, or PowerShell.

Best Practices
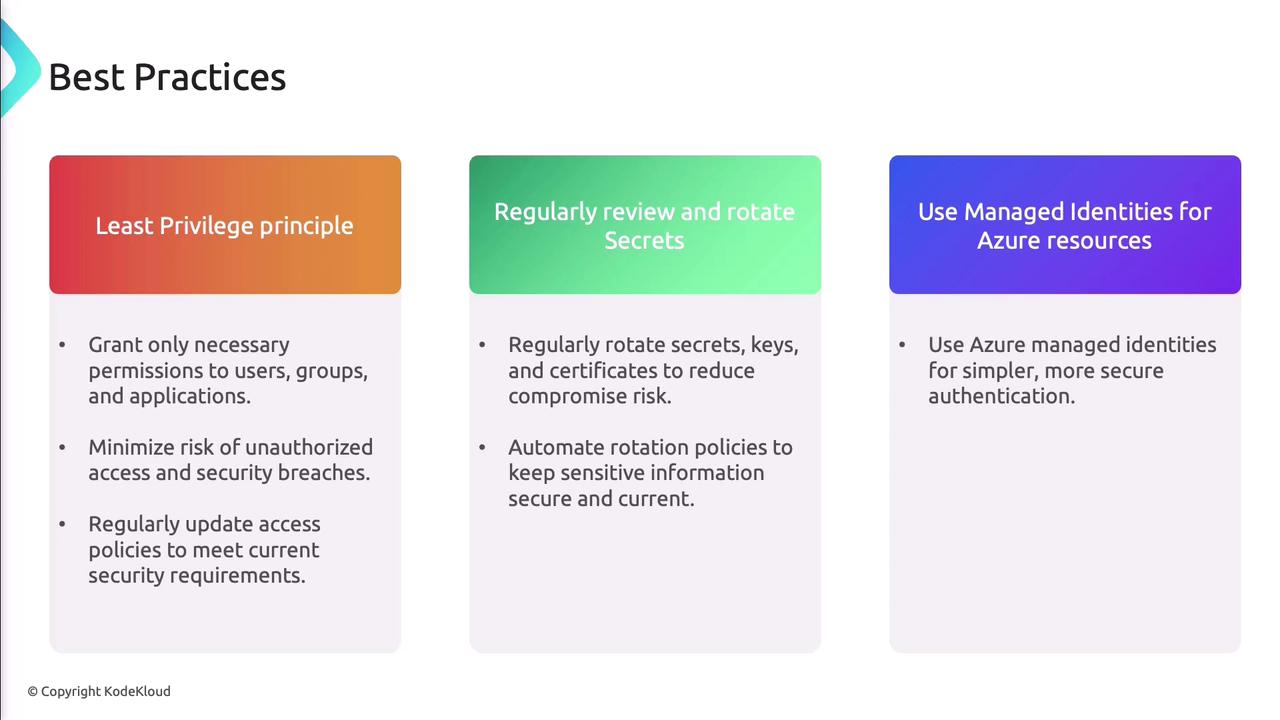
- Apply the principle of least privilege.
- Regularly review and update access policies.
- Rotate secrets, keys, and certificates on a schedule.
- Use managed identities to avoid credential leaks.
Warning
Deleting a Key Vault or disabling critical secrets is irreversible. Always back up before removal and test in a non-production environment.
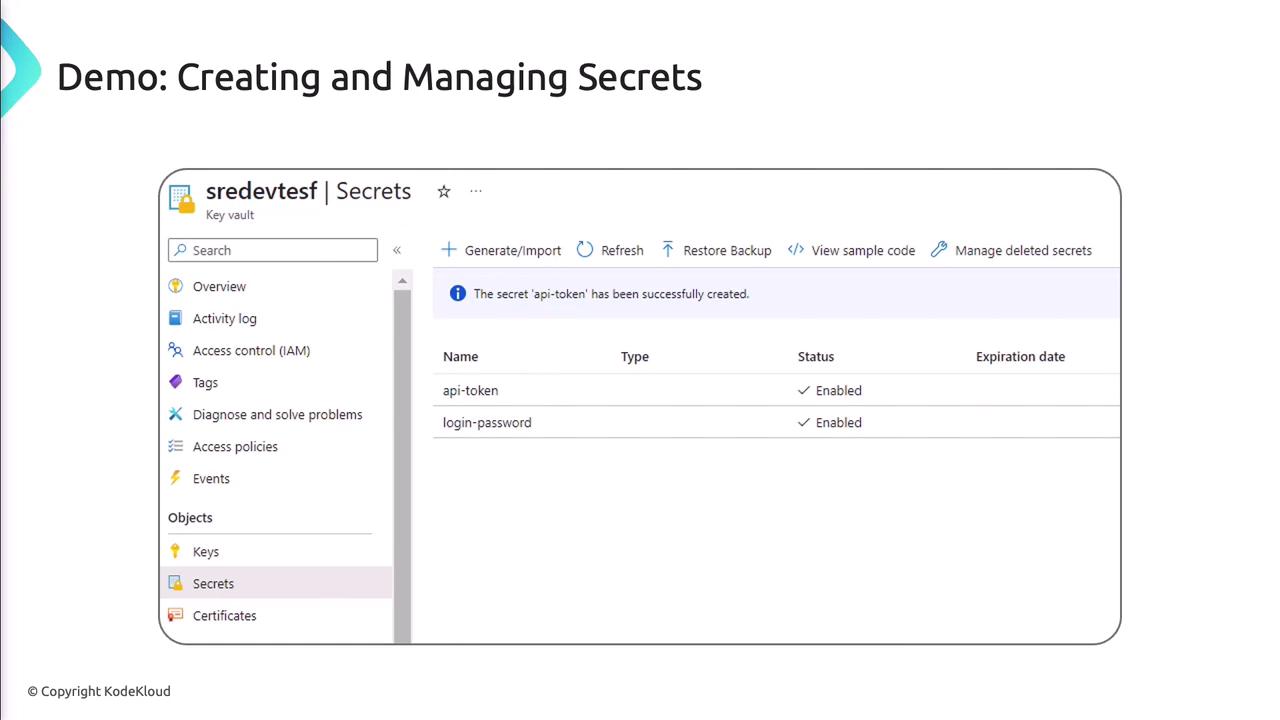
Demo: Creating and Managing Secrets
- In the Azure Portal, go to your Key Vault and select Secrets.
- Click Generate/Import, provide a name and value, then click Create.
- To view or rotate, select the secret and choose New Version.
References
Watch Video
Watch video content