AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
Implement Security and Validate Code Bases for Compliance
Understand SQL Injection Attacks
SQL Injection (SQLi) is one of the most critical security vulnerabilities for any application that interacts with a relational database. In this guide, we dive into what SQL Injection is, how attackers exploit it, and the best practices to defend against it—particularly in a cloud environment using Azure SQL Database.
Scenario: The Wish List Feature
Imagine an e-commerce platform where your product manager, Alex, wants users to build custom wish lists by submitting their own SQL queries. While this feature sounds innovative, allowing end users to run arbitrary database queries can open the door to SQL Injection.
Note
Never trust user input for query construction. Even developers can introduce vulnerabilities if input isn’t handled correctly.
Threat Landscape Overview
In a typical cloud-native setup:
- Users browse and submit requests via the application front end.
- The application connects to an Azure SQL Database.
- Developers may also have administrative access for troubleshooting.
- Azure’s built-in features like Auditing and Advanced Data Security provide monitoring and alerts.
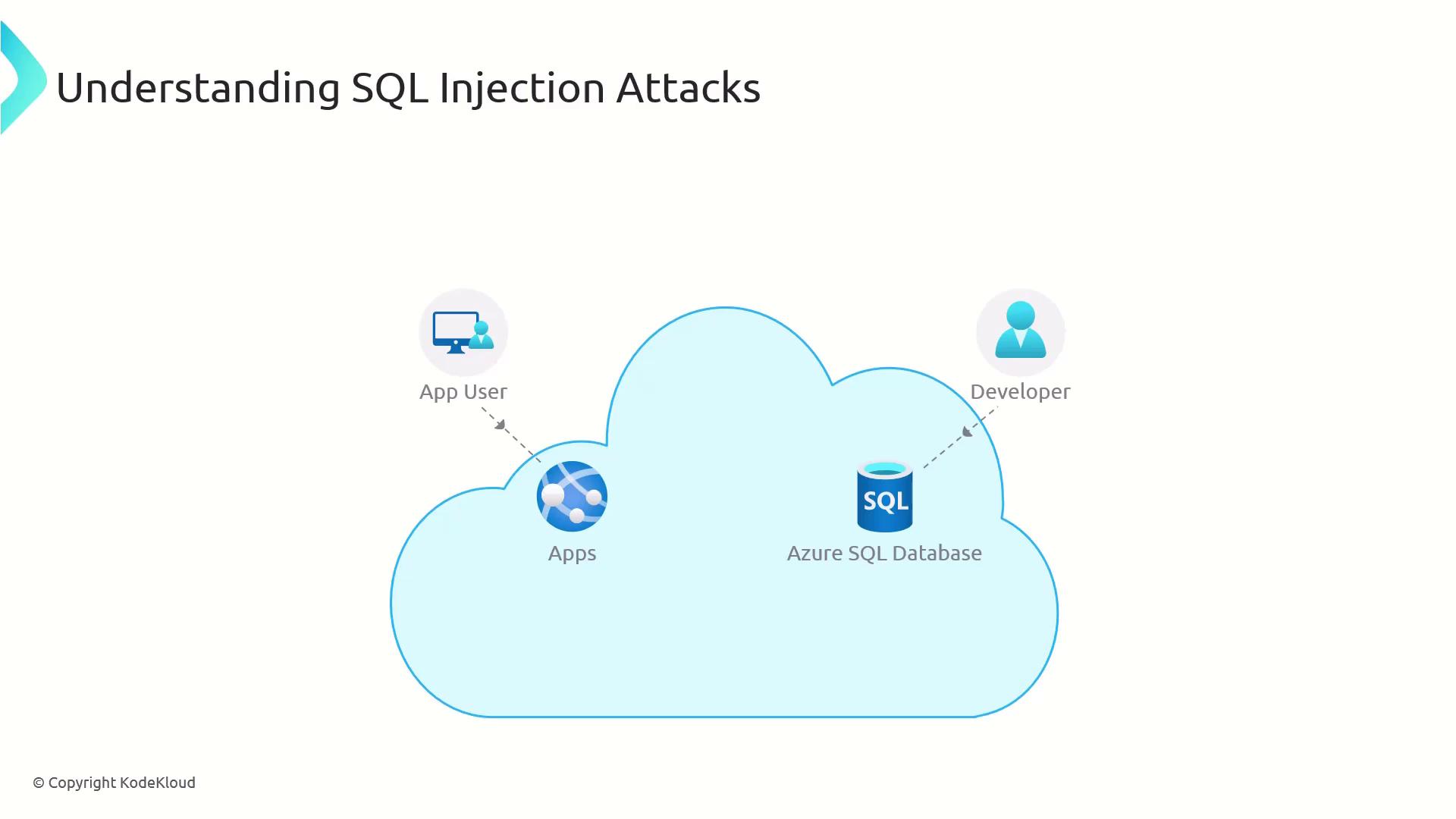
Although Azure can detect suspicious activities, the primary defense against SQLi must be built into your application code.
Key Elements at a Glance
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Underlying Risk | How unvalidated input allows malicious SQL to slip through. |
| Attack Anatomy | Step-by-step flow of a typical SQLi exploit. |
| Proactive Defenses | Coding and configuration practices to block SQLi. |
1. Underlying Risk
When you concatenate user input directly into SQL statements, you risk letting malicious actors inject additional SQL commands. Our “custom wish list” scenario is a prime example—every new feature that executes raw queries increases your attack surface.
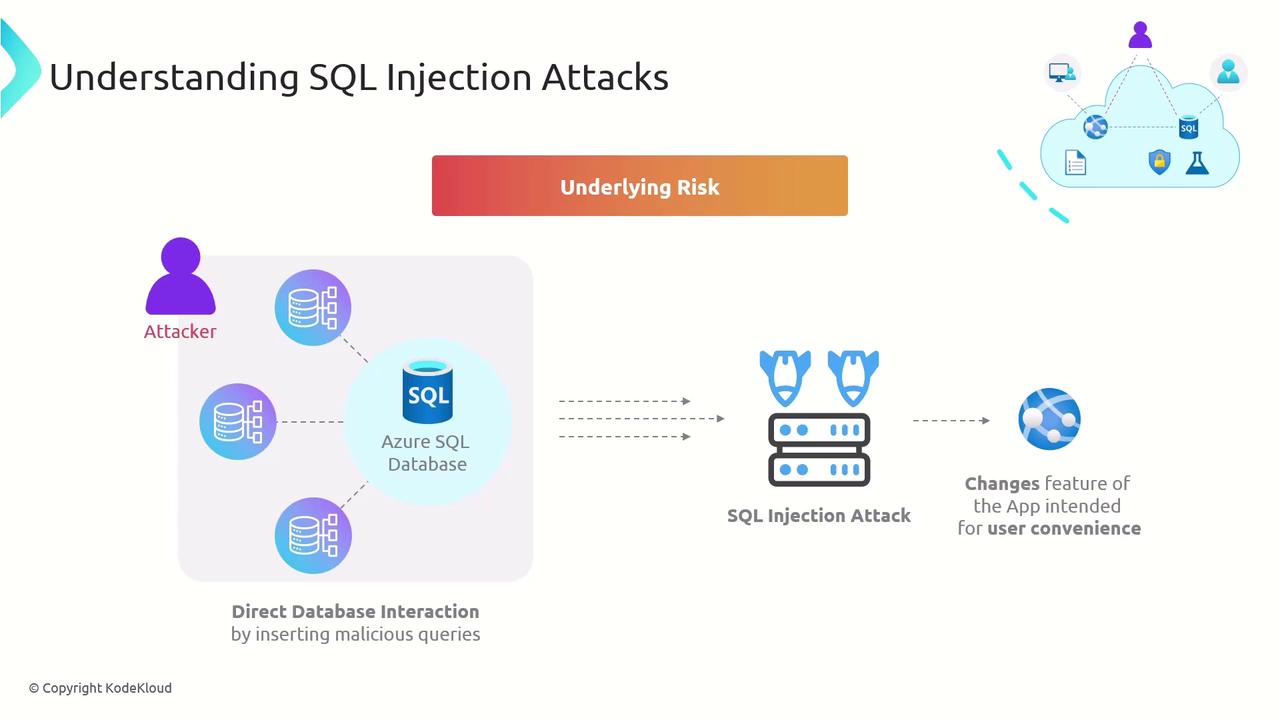
If inputs aren’t validated or sanitized, an attacker could:
- Retrieve sensitive data (e.g., user credentials).
- Modify or delete records.
- Escalate privileges for full database control.
2. Anatomy of a SQL Injection Attack
Let’s walk through a typical SQLi exploit:
- Identify a Vulnerable Input
The attacker locates a form field or URL parameter that reflects input directly into a query. - Craft Malicious Payload
They append SQL syntax—e.g.,'; DROP TABLE Orders; --—to the input. - Execute via the Application
The back-end builds a query string by concatenation and sends it to the database. - Database Runs the Injected SQL
The server interprets the injected commands as part of the original query.
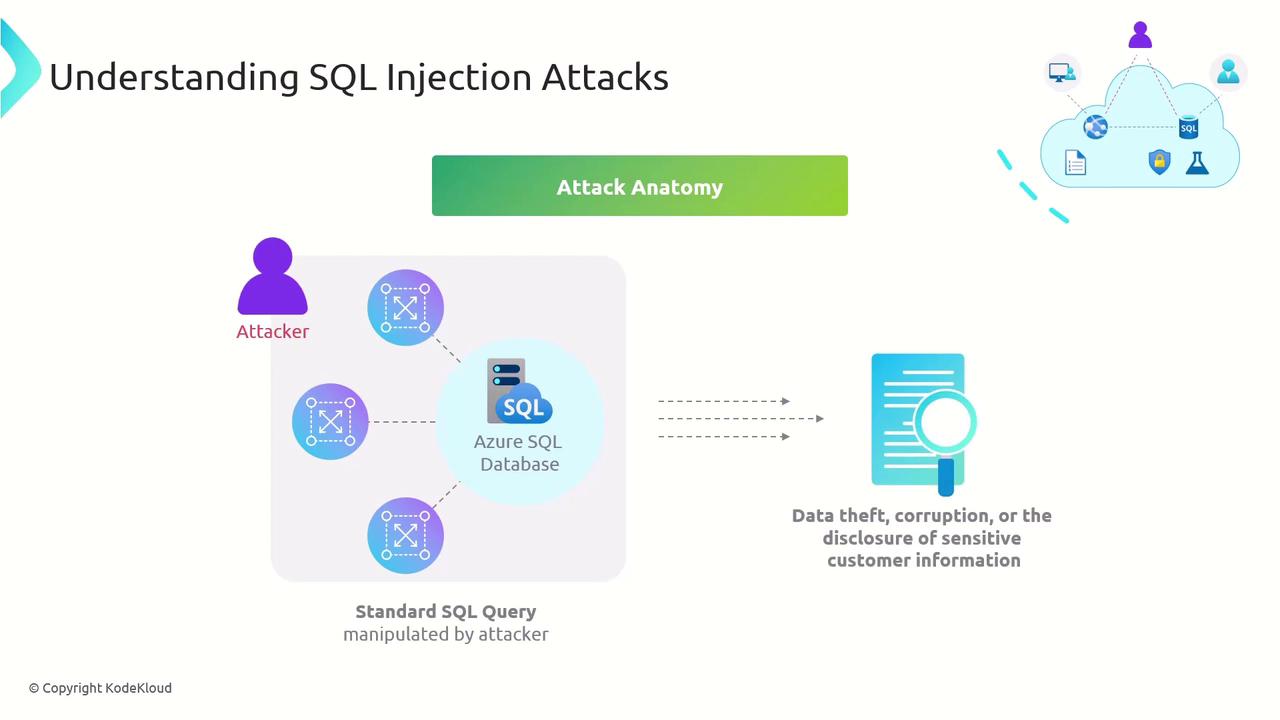
Impact: Data theft, corruption, or even full admin takeover of the database—resulting in regulatory fines, reputational damage, and financial loss.
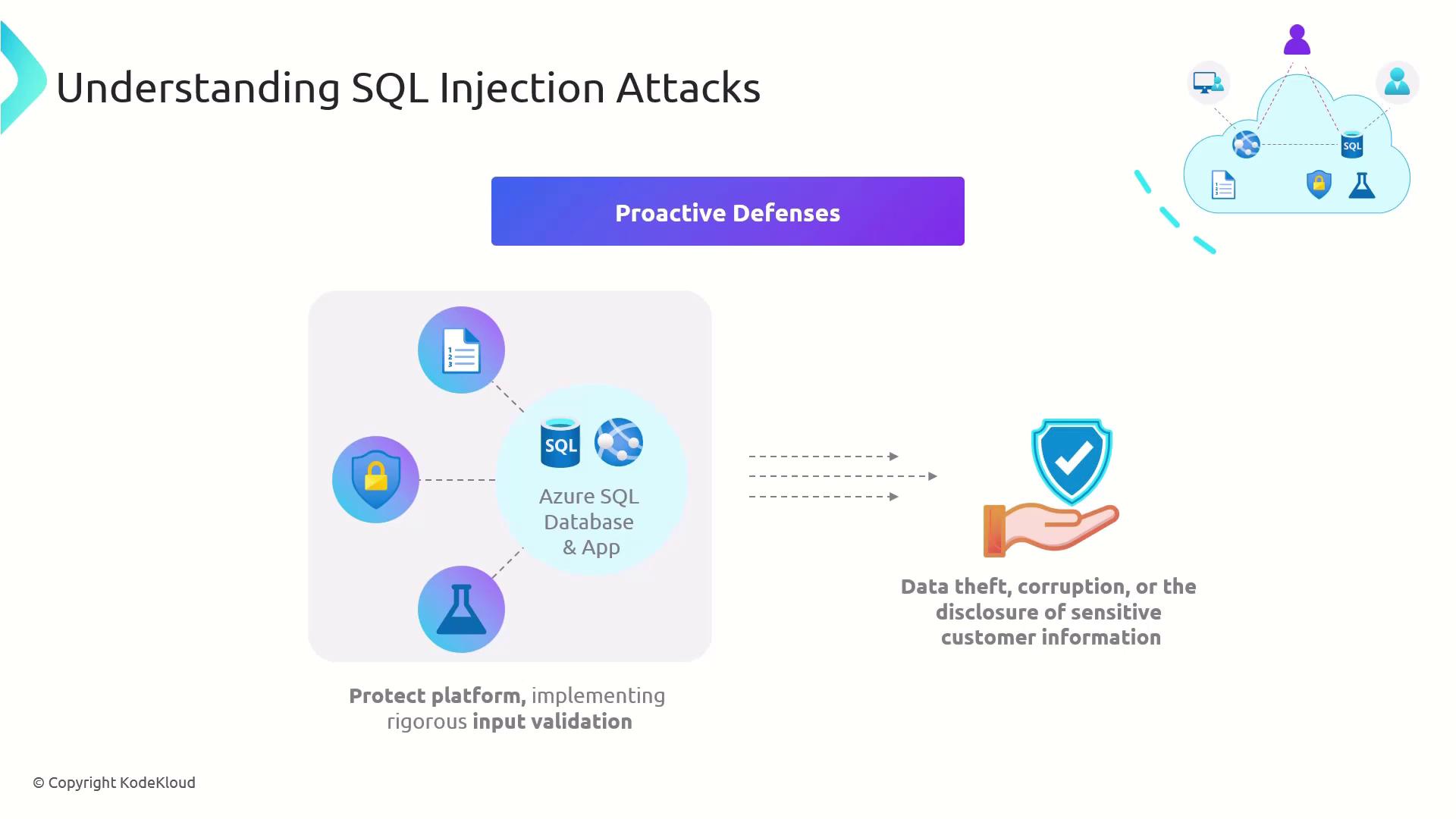
3. Proactive Defenses
A multi-layered approach is essential. The following strategies are proven to reduce SQLi risk:
| Defense Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Input Validation & Sanitization | Enforce strict patterns and reject unexpected characters on both client and server sides. |
| Parameterized Queries / Prepared Statements | Use bind variables so data never merges with SQL commands. |
| Stored Procedures | Encapsulate SQL logic in DB-residents procedures with controlled interfaces. |
| Principle of Least Privilege | Assign each application account the minimum permissions needed. |
| Security Audits & Testing | Employ automated scanners, manual code reviews, and penetration tests regularly. |
Warning
Skipping proper testing can leave hidden SQLi vectors. Integrate security checks into your CI/CD pipeline.
By embedding these practices into your development lifecycle, you ensure robust protection against SQL Injection—and safeguard your data, your customers, and your organization.
References
- OWASP SQL Injection Cheat Sheet
- Azure SQL Database Auditing
- Azure SQL Database Advanced Data Security
- Kubernetes Basics
Watch Video
Watch video content