AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
Work with Azure Repos and GitHub
Working with Git locally
In this guide, you’ll master the core Git workflows for local development: initializing repositories, configuring identity, staging and committing changes, branching and merging, and cloning from remote hosts like GitHub and Azure Repos. We’ll also explore graphical tools in Visual Studio Code, Visual Studio, and GitHub Desktop.
1. Configure Your Identity
Before you make any commits, set up your name and email. These values appear in each commit’s metadata.
git config --global user.name "Jeremy Morgan"
git config --global user.email "[email protected]"
Note
Use --global to apply settings across all repositories on your machine. To override identity per-repo, omit --global and run the commands inside the repository directory.
2. Initialize a Git Repository
Create and enter a new project folder:
PS C:\Users\jeremy\Projects> mkdir my-project PS C:\Users\jeremy\Projects> cd my-projectInitialize Git:
git initOutput:
Initialized empty Git repository in C:/Users/jeremy/Projects/my-project/.git/Create a file and check status:
echo "Hello Git!" > hello.txt git statusYou should see
hello.txtlisted as an untracked file.Stage and commit:
git add hello.txt git commit -m "Initial commit: add hello.txt"Review your commit history:
git log --oneline --decorateExample output:
395883b (HEAD -> master) Initial commit: add hello.txt
Common Git Commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| git init | Create a new local repository |
| git status | Show untracked, staged, and modified files |
| git add <file> | Stage changes for the next commit |
| git commit -m "message" | Save staged changes with a commit message |
| git log --oneline --graph | View a condensed, graphical commit history |
3. Branching and Feature Workflows
Create and switch to a new branch:
git branch feature/1900 git checkout feature/1900Output:
Switched to branch 'feature/1900'Update
hello.txtto:Hello Azure Repos!Stage and commit your change:
git status git add hello.txt git commit -m "Update greeting for Azure Repos"
- Visualize the branch history:
Output:git log --oneline --graph --decorate --all* 7c4495d (HEAD -> feature/1900) Update greeting for Azure Repos | * 395883b (master) Initial commit: add hello.txt |/
4. Merging Changes Back into Master
Switch to master and merge:
git checkout master
git merge feature/1900
You’ll typically see a fast-forward merge:
Updating 395883b..7c4495d
Fast-forward
hello.txt | 1 +
Verify the merged content:
Get-Content .\hello.txt
# Output: Hello Azure Repos!
5. Cloning a Remote Repository
5.1 From GitHub
- On GitHub New Repository, create my-cool-project (private), initialize with a README.
Clone via HTTPS:
git clone https://github.com/YourUser/my-cool-project.gitAdd, commit, and push a file:
cd my-cool-project echo "Hello world" > hello.txt git add hello.txt git commit -m "Add hello.txt" git push origin mainYou’ll now see
hello.txtin your GitHub repo.
5.2 Using Visual Studio Code
Open the cloned folder in VS Code. The Source Control view shows your changes:
5.3 Inside Visual Studio
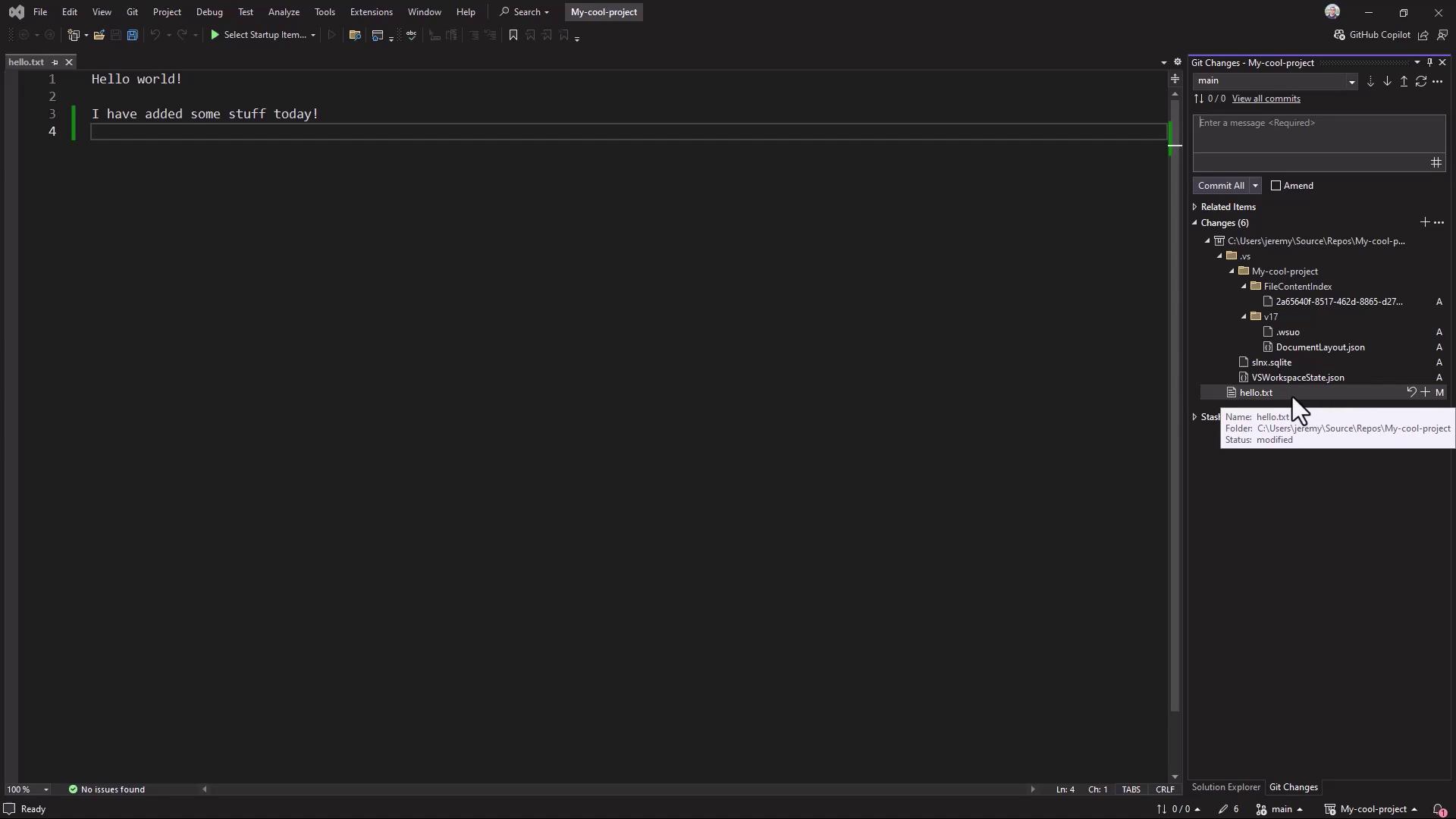
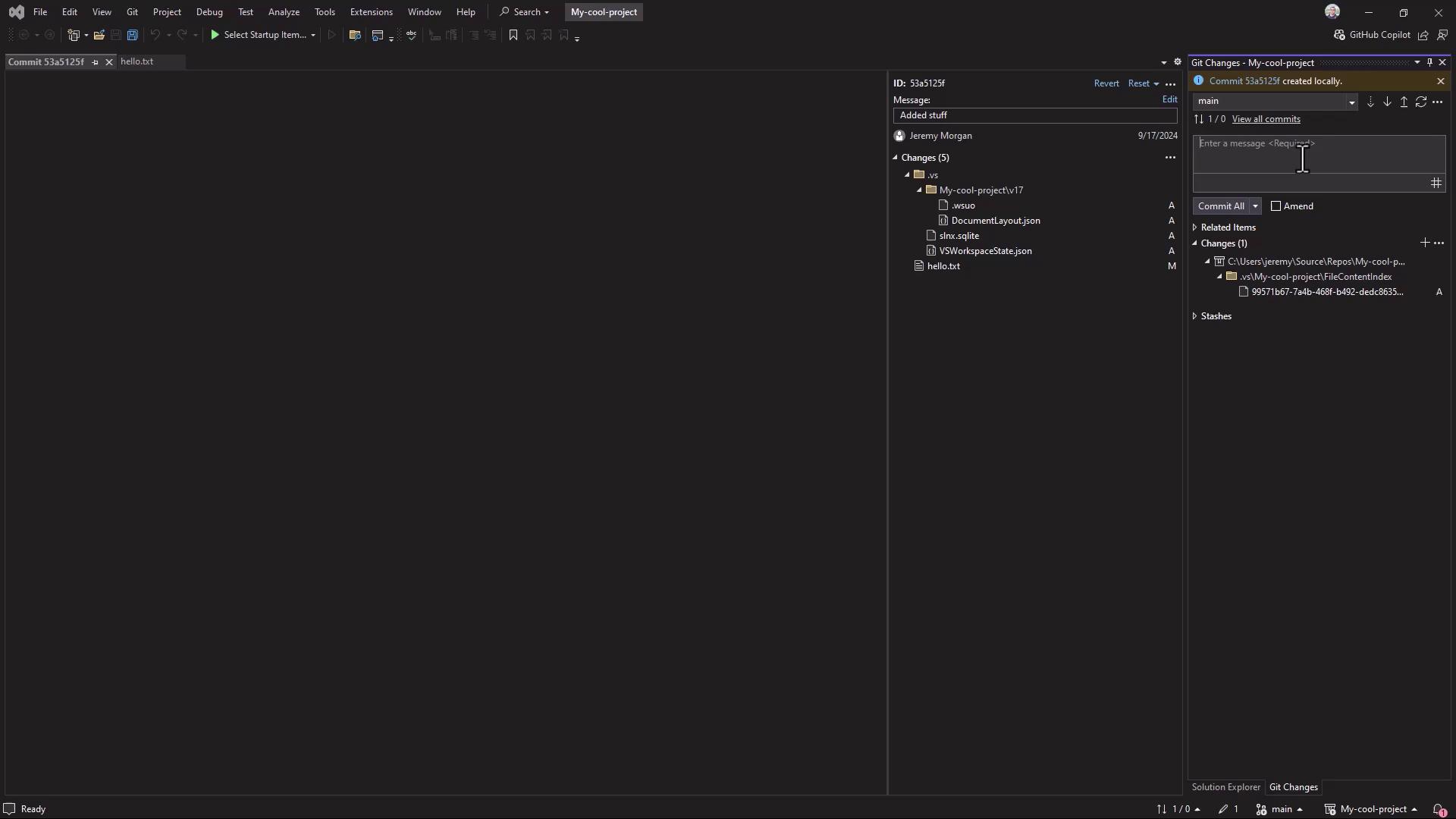
In Visual Studio, use the Git Changes window to stage, commit, and push:
5.4 Cloning from Azure Repos
PS C:\Users\jeremy\Projects> mkdir azure-test
PS C:\Users\jeremy\Projects> cd azure-test
PS C:\Users\jeremy\Projects\azure-test> git clone https://[email protected]/KodeKloudDemo/KodeKloud%20Hotel/_git/SmartHotel360
6. GUI Client: GitHub Desktop
GitHub Desktop provides an intuitive interface for cloning, committing, and pushing. After installing and signing in, configure your identity:
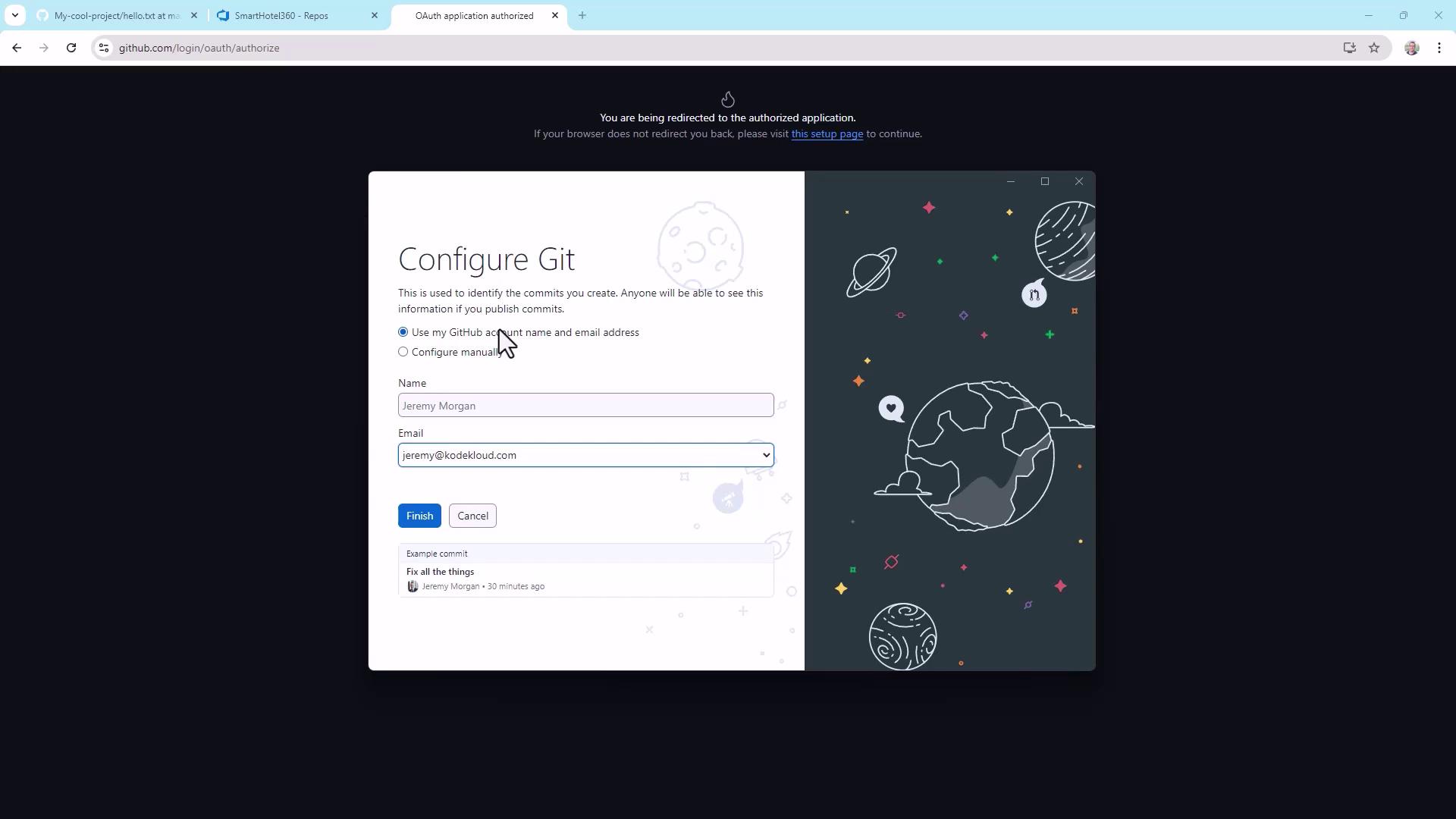
Clone your repo and open it in VS Code. When prompted:
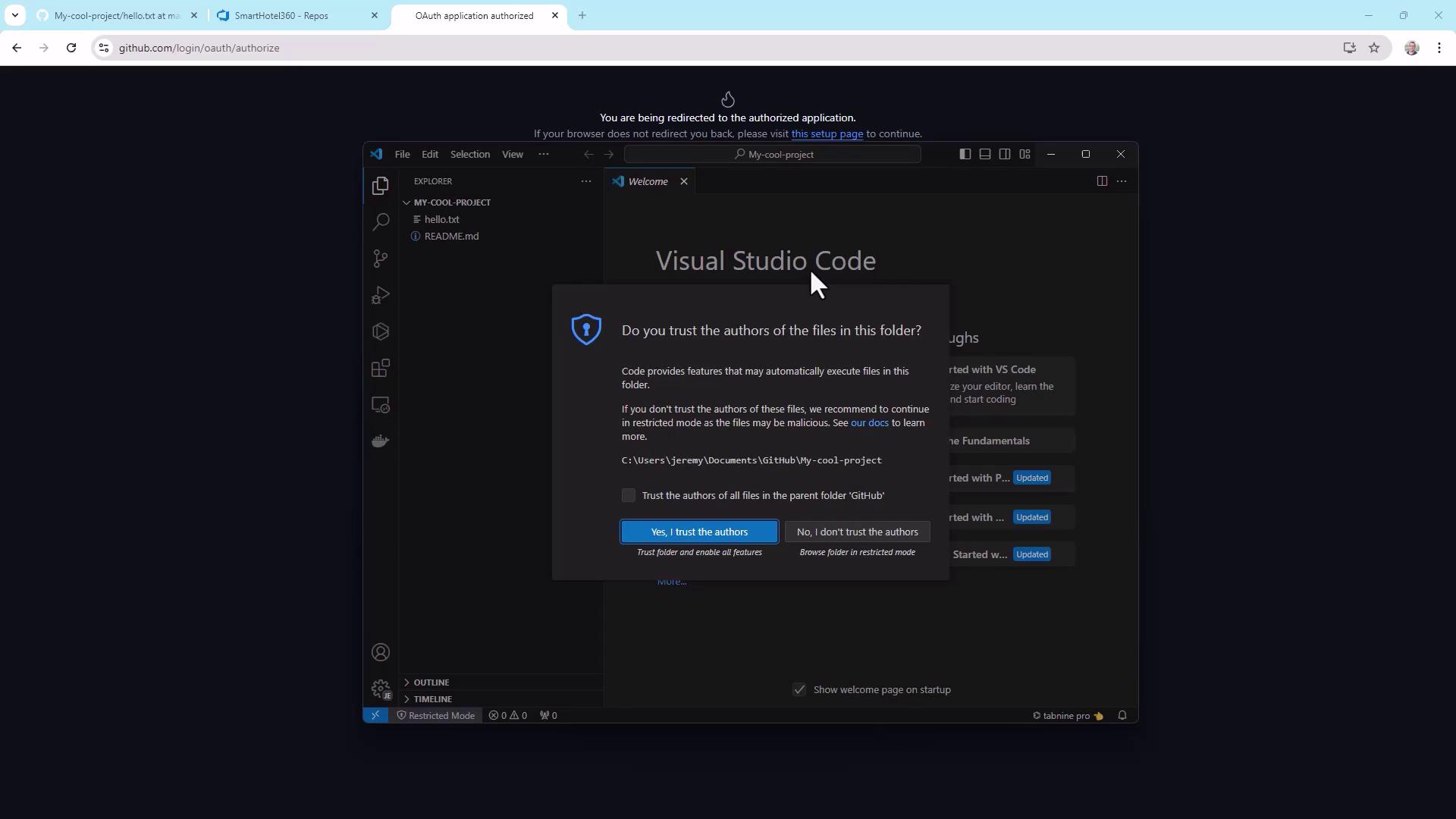
Warning
Only trust workspaces you recognize. Untrusted code can run arbitrary scripts on your machine.
Summary
You now know how to:
- Configure Git identity
- Initialize, stage, and commit a repository
- Create, switch, and merge branches
- Clone and contribute to remote repositories
- Use GUI tools like VS Code, Visual Studio, and GitHub Desktop
With these skills, you’re ready to collaborate efficiently across any Git-based project.
References
Watch Video
Watch video content