In this guide, you’ll learn how to install the Blue Ocean plugin in Jenkins, create and configure a multibranch pipeline with its graphical editor, archive build artifacts, publish JUnit reports, and view results both in Blue Ocean and the classic UI. Each step includes screenshots to illustrate the workflow.
1. Install the Blue Ocean Plugin
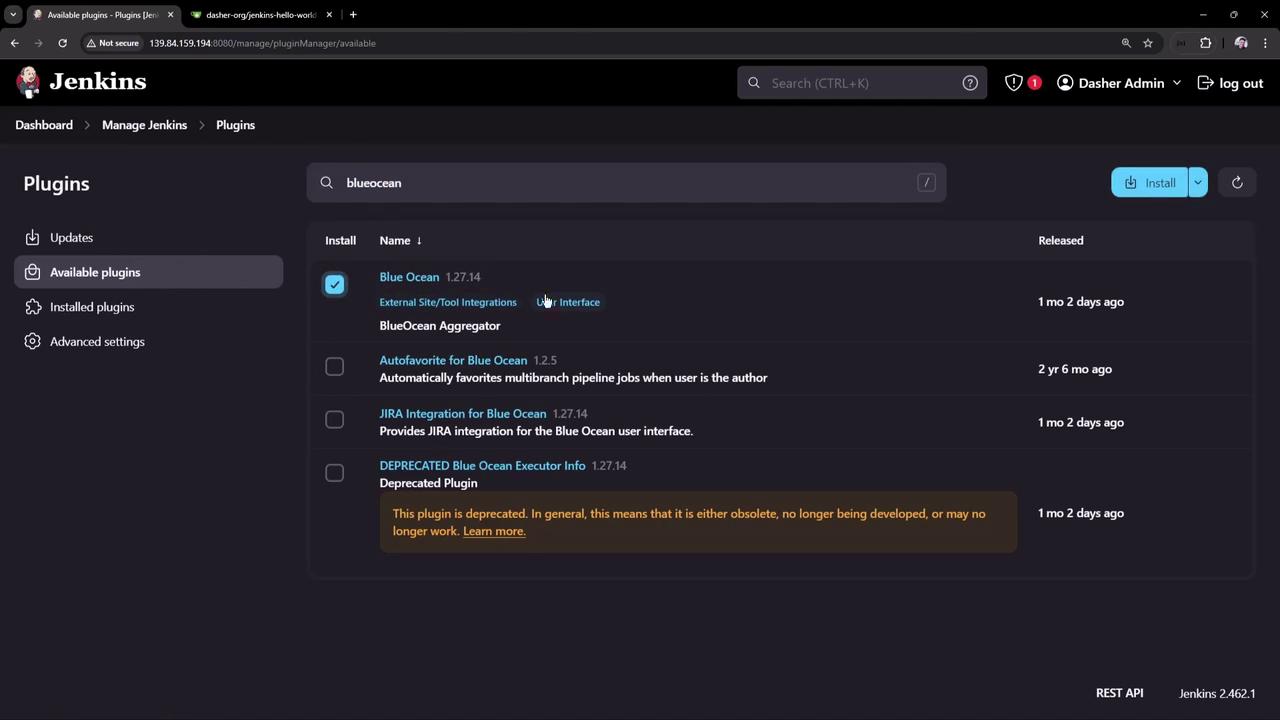
Navigate to Manage Jenkins → Plugin Manager → Available .
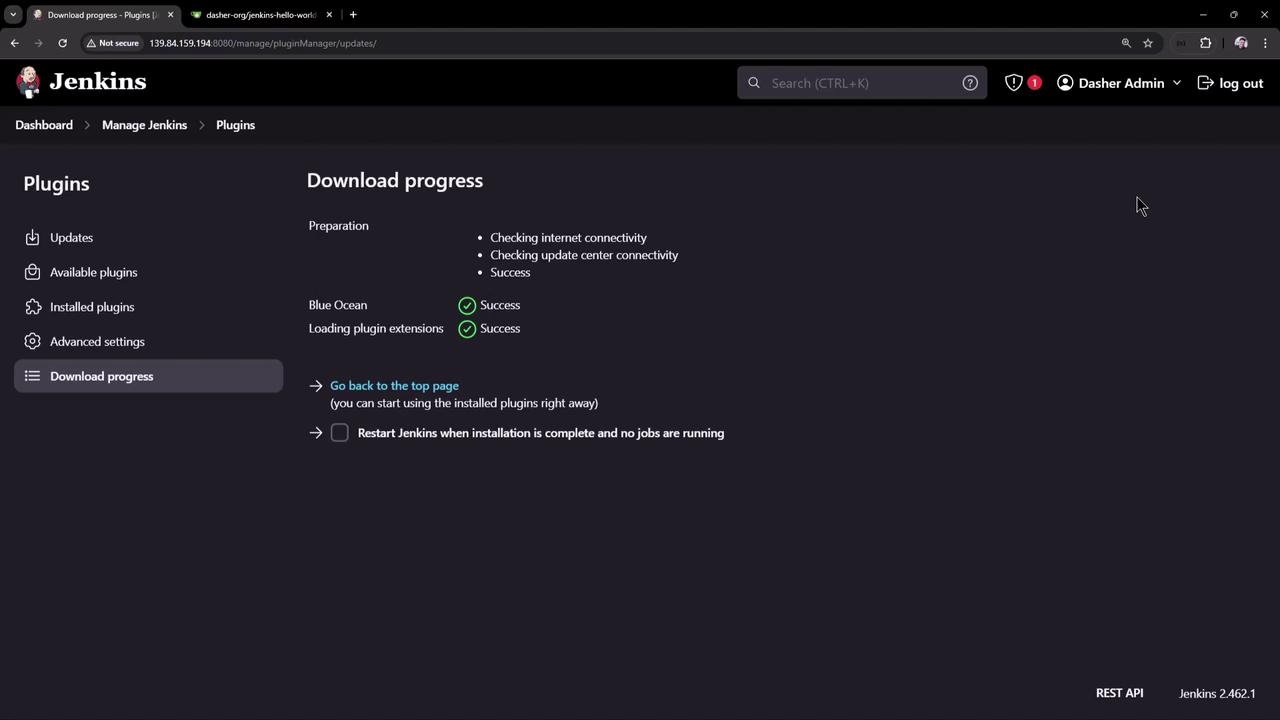
Search for blueocean , select the plugin bundle, and click Install without restart .
Blue Ocean requires Jenkins 2.x and the Pipeline plugin. Ensure your instance meets these prerequisites before installation.
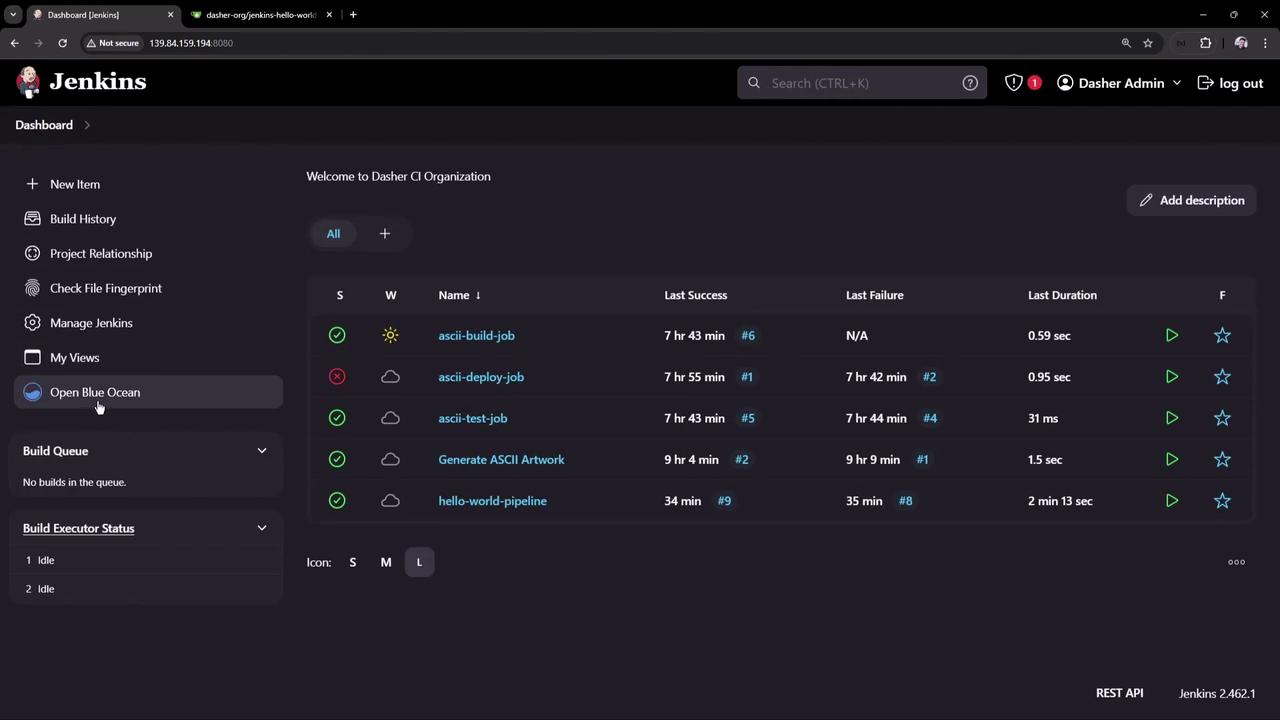
After installation, return to the dashboard. You should see Open Blue Ocean in the sidebar.
2. Launch Blue Ocean and Create a New Pipeline
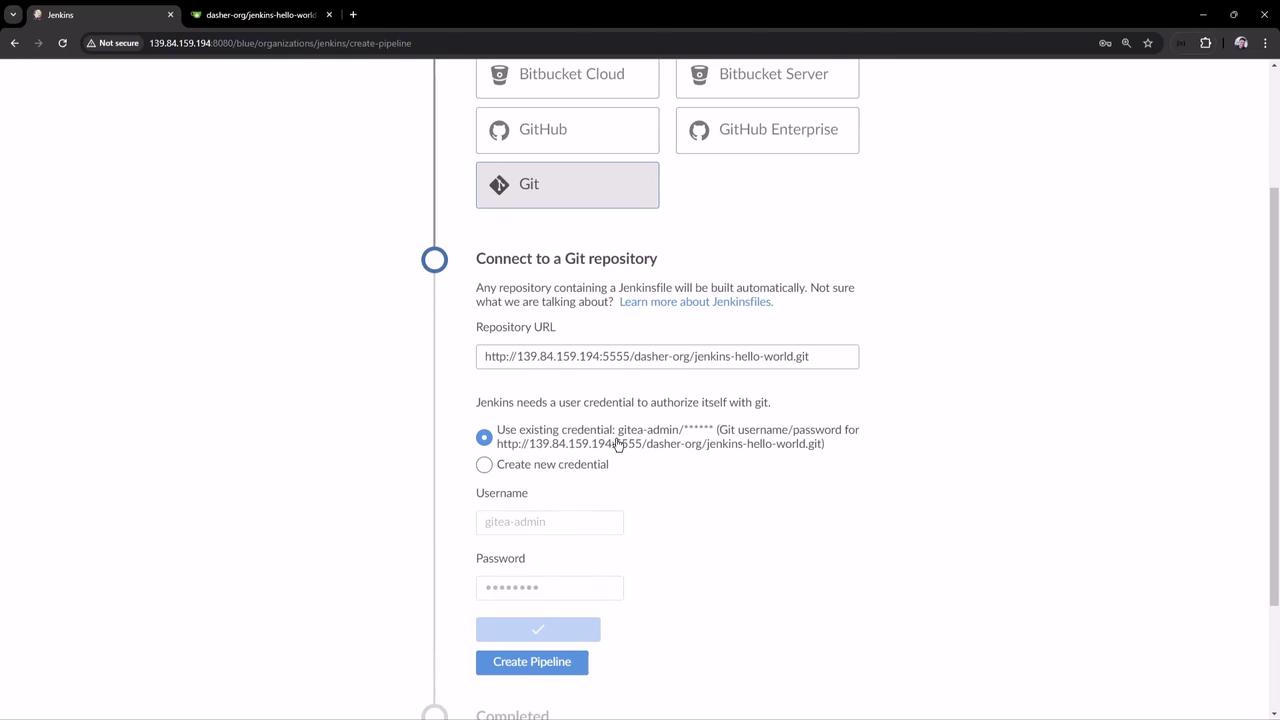
Click Open Blue Ocean → New Pipeline .
Select Git , enter your repository URL, and add credentials if needed.
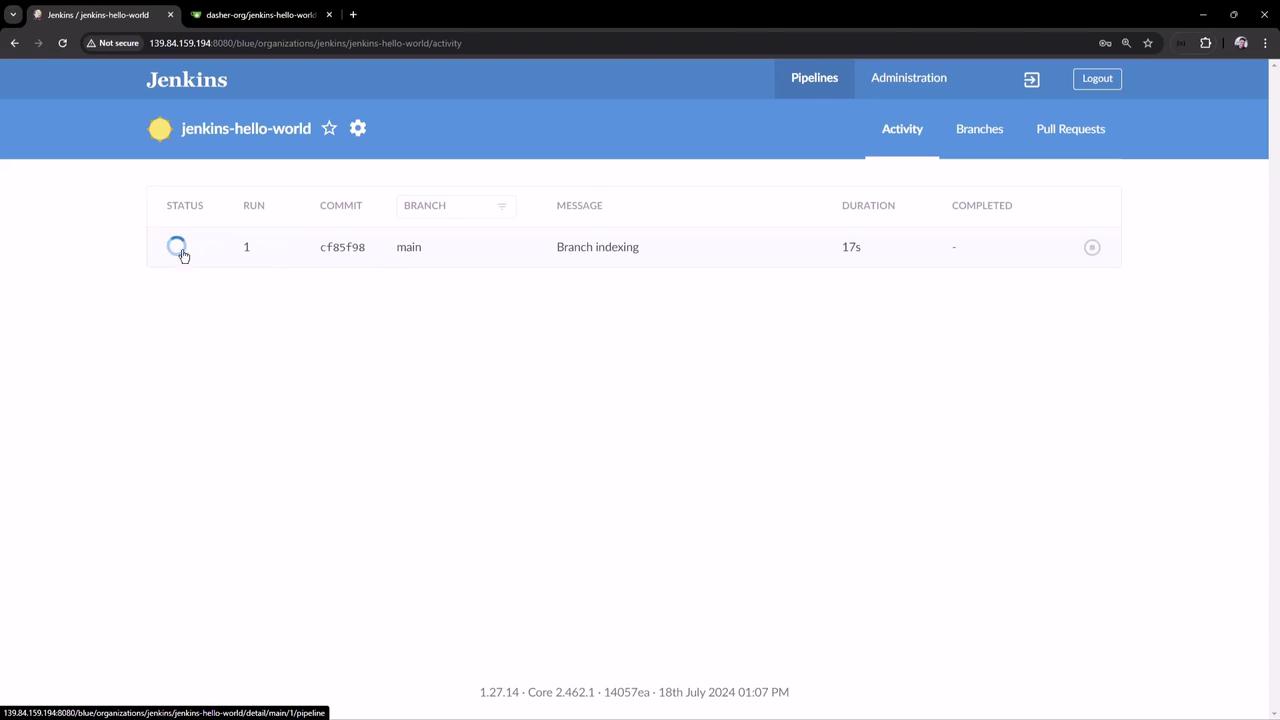
Blue Ocean will scan branches for a Jenkinsfile and automatically trigger the pipeline if found.
Once branches are indexed and a run starts, you’ll see the activity feed:
3. Example Jenkinsfile and Stage Overview Below is the sample Jenkinsfile stored in your repository. It defines three key stages:
pipeline { agent any tools { maven 'M398' } stages { stage( 'Echo Version' ) { steps { sh 'echo Print Maven Version' sh 'mvn -version' } } stage( 'Build' ) { steps { sh 'mvn clean package -DskipTests=true' } } stage( 'Unit Test' ) { steps { script { for ( int i = 0 ; i < 60 ; i ++ ) { echo " ${ i + 1 } " sleep 1 } } sh 'mvn test' } } } }
Stage Name Purpose Commands Echo Version Display Maven environment details mvn -versionBuild Compile and package the app mvn clean package -DskipTests=trueUnit Test Execute unit tests mvn test (with optional sleep loop)
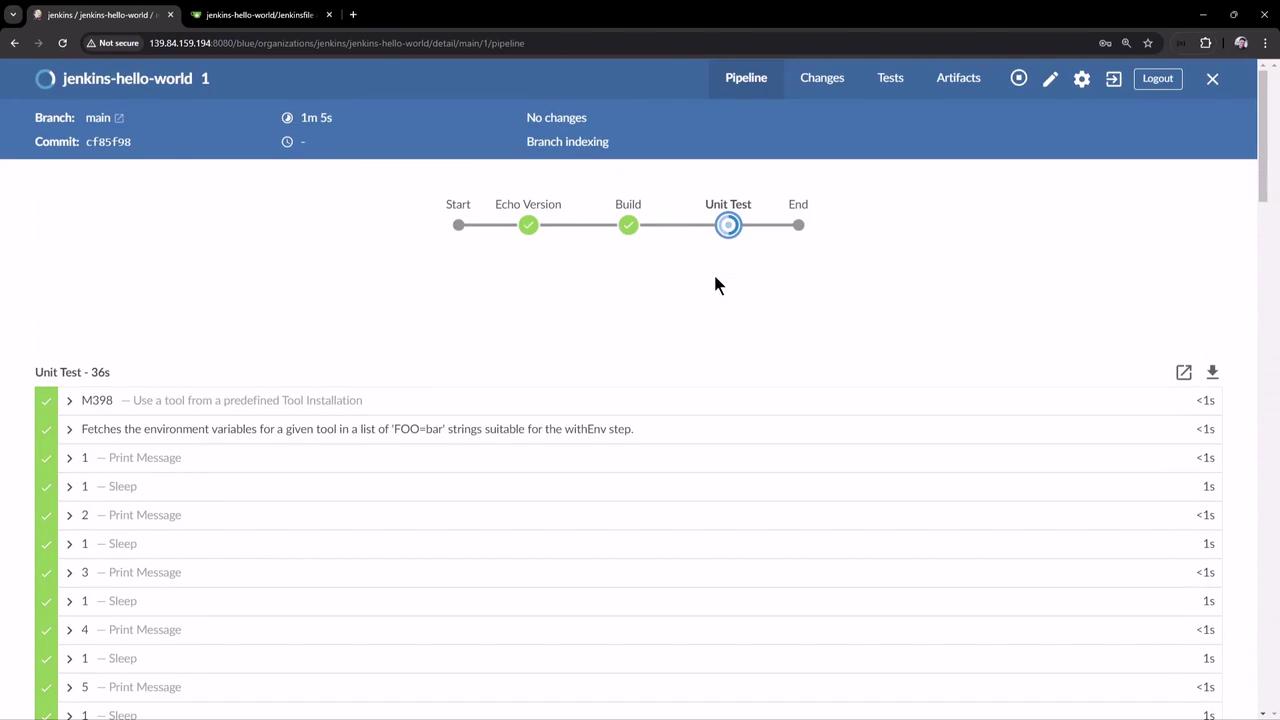
After triggering the pipeline, you can monitor each stage in real time:
Viewing Console Logs Echo Version stage output:mvn -version Apache Maven 3.9.8 (3645f66c…) Maven home: /var/lib/jenkins/tools/hudson.tasks.Maven.MavenInstallation/M398 Java version: 17.0.7, vendor: Ubuntu OS name: "linux", version: "6.8.0-39-generic"
Build stage output:mvn clean package -DskipTests=true [INFO] Scanning for projects… [INFO] Building hello-demo 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT [INFO] --- maven-clean-plugin:3.3.2:clean ( default-clean ) @ hello-demo --- …
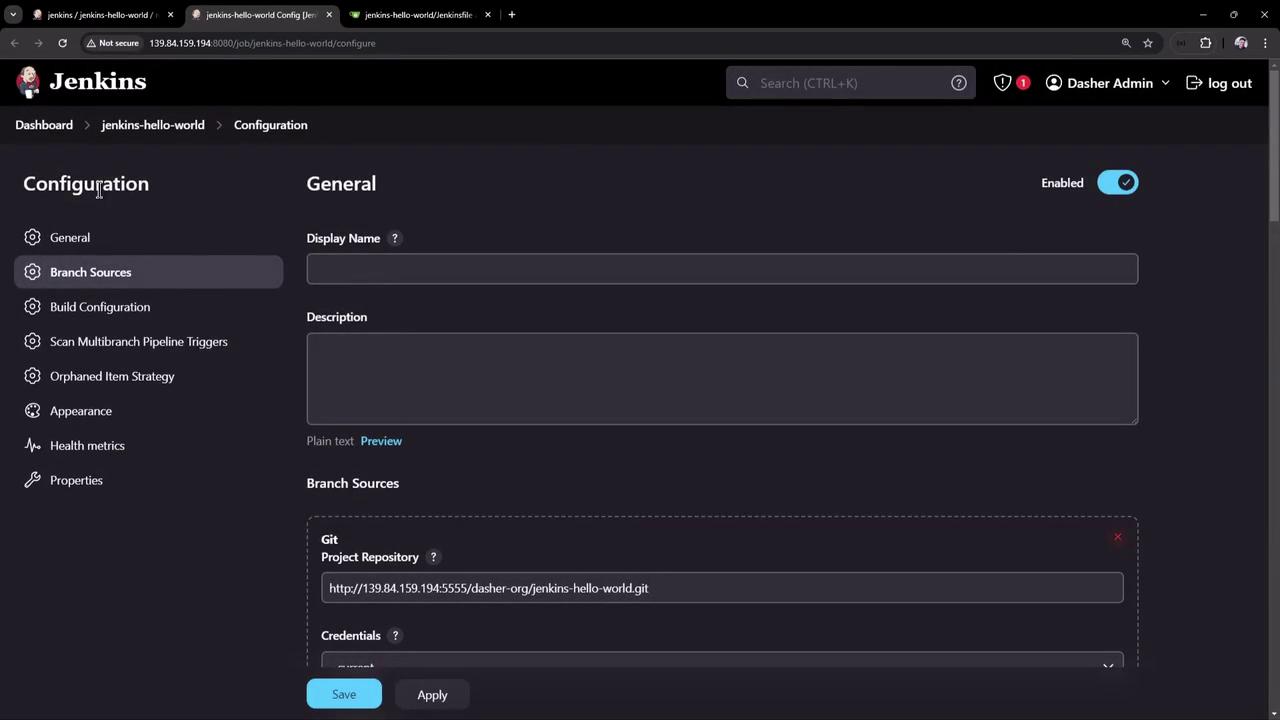
4. Inspect the Multibranch Pipeline Configuration Blue Ocean automatically creates a Multibranch Pipeline job in the classic UI:
When Jenkins scans your repository, it runs:
> git ls-remote -h -- http://…/jenkins-hello-world.git Checking branch main 'Jenkinsfile' found Met criteria Scheduled build for branch: main Processed 1 branches Finished: SUCCESS
5. Edit the Pipeline in Blue Ocean Back in Blue Ocean:
Select your branch and click the pencil icon to open the visual editor.
Remove the sleep loop in Unit Test to simplify:
stage( 'Unit Test' ) { steps { sh 'mvn test' } }
Press Ctrl+S (or Command+S on Mac) to save and commit the changes to your Jenkinsfile.
6. Archive Build Artifacts
In the Build stage, click + Add Step → Archive Artifacts .
Enter the file pattern: target/hello-demo-*.jar.
Verify on the Jenkins controller:
cd /var/lib/jenkins/workspace/jenkins-hello-world_main/target ls hello-demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
Your updated Build stage:
stage( 'Build' ) { steps { sh 'mvn clean package -DskipTests=true' archiveArtifacts 'target/hello-demo-*.jar' } }
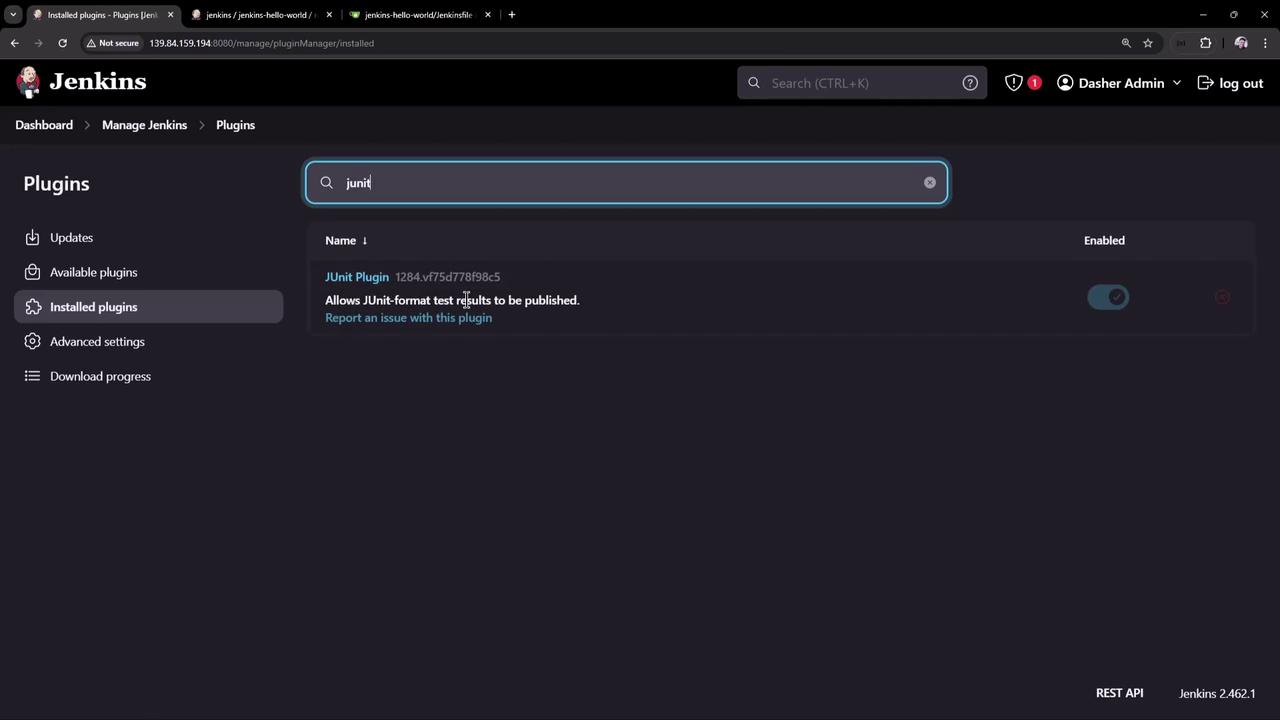
7. Publish JUnit Test Results The JUnit plugin is pre-installed, as shown here:
To add JUnit reporting:
Edit the Unit Test stage → + Add Step → Archive JUnit-formatted test results .
Enter target/surefire-reports/TEST-*.xml and select Keep properties and Keep test names .
Final Unit Test stage snippet:
stage( 'Unit Test' ) { steps { sh 'mvn test' junit testResults : 'target/surefire-reports/TEST-*.xml' , keepProperties : true , keepTestNames : true } }
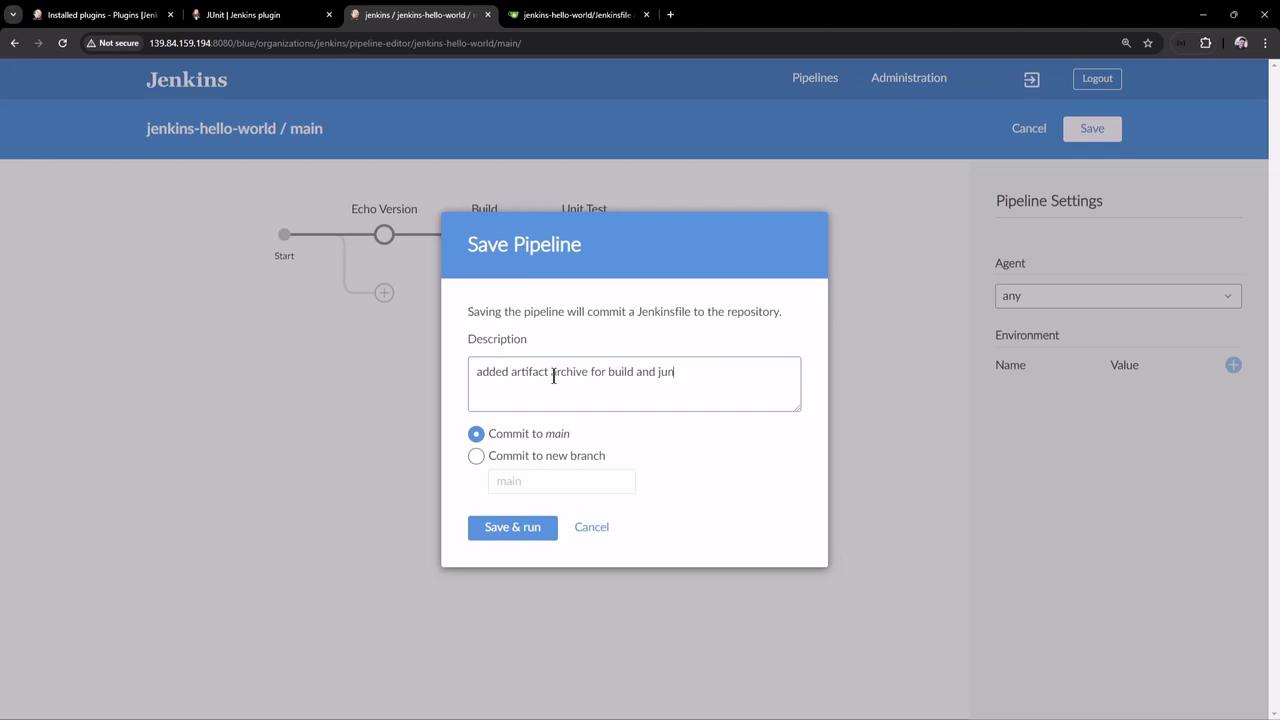
8. Commit and Validate Changes Click Save , add a commit message (e.g., “Archive artifacts and publish JUnit reports”), and push to the main branch:
If you mistype the artifact pattern (for example, hello-world-*.jar), the build will fail: > archiveArtifacts 'target/hello-world-*.jar' No artifacts found that match the file pattern 'target/hello-world-*.jar'
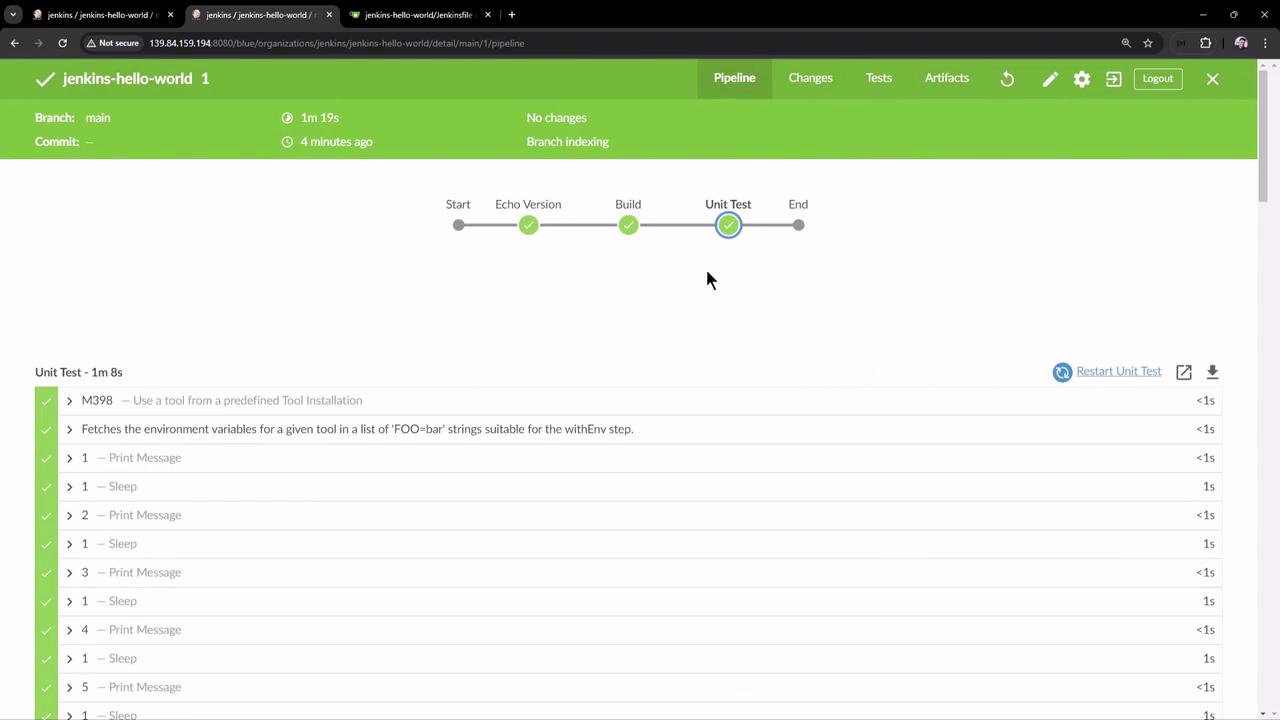
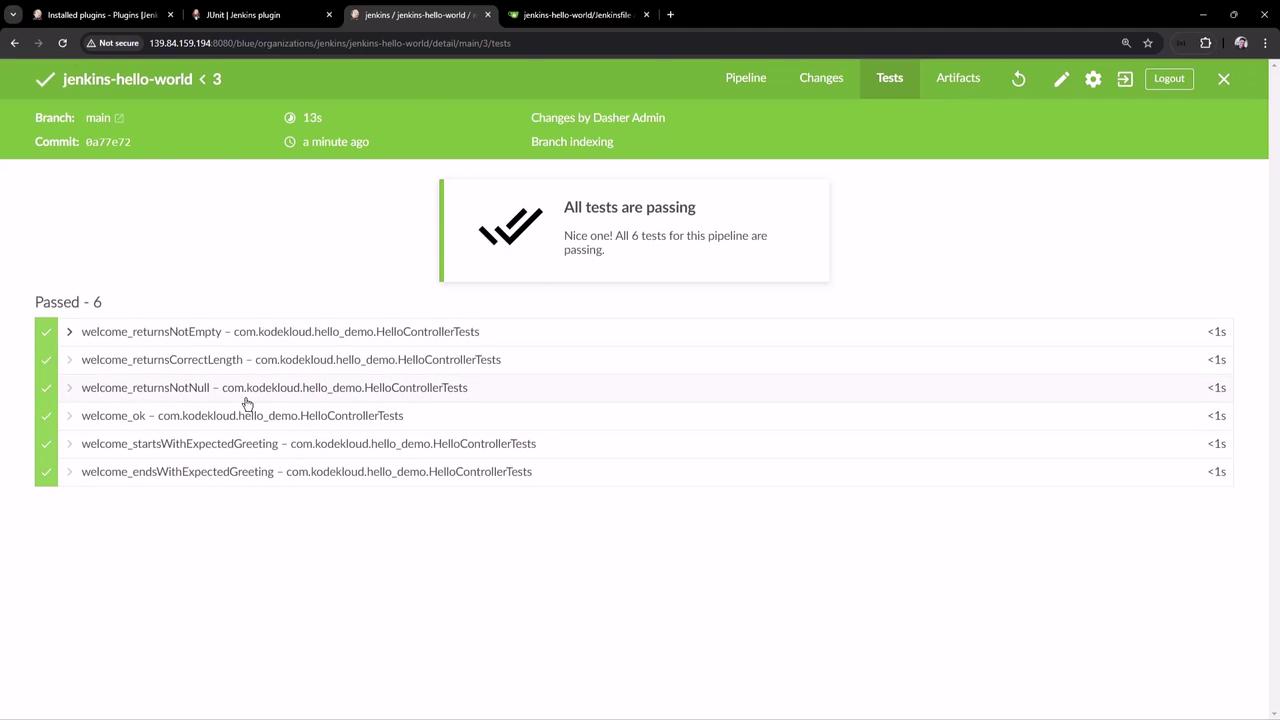
Double-check your paths before committing. 9. View Pipeline Results Once the pipeline completes successfully, Blue Ocean displays:
Build stage with archived artifactsUnit Test stage with pass/fail detailsA summary showing all tests passed
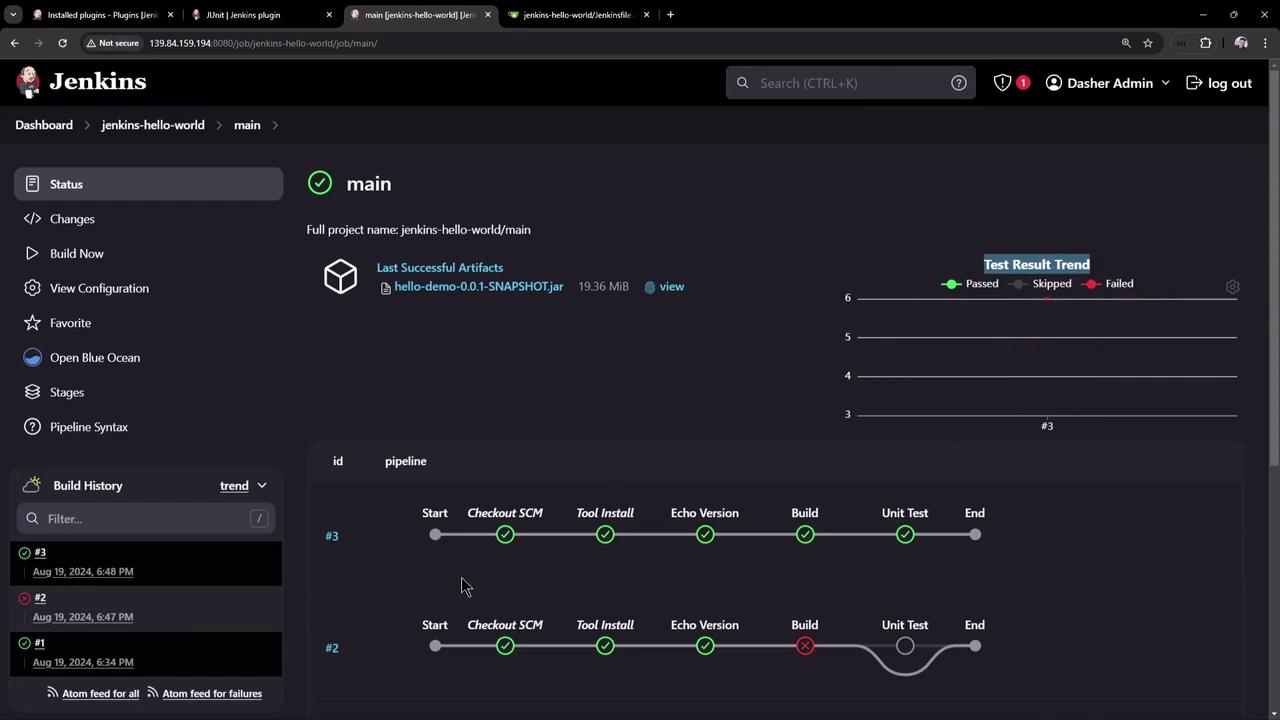
In the classic UI, you can also review build history, visualize test trends, and download artifacts:
Additional Resources