Certified Jenkins Engineer
Setting up CI Pipeline
Demo Unit Testing and Analyze JUnit Reports
Optimize your Jenkins CI/CD pipeline by adding a dedicated Unit Testing stage, securely managing database credentials, and publishing JUnit reports for clear visibility into your test results.
Table of Contents
- Pipeline Stages Overview
- Adding the Unit Testing Stage
- Debugging a Failed Test Stage
- Configuring Environment Variables
- Managing Jenkins Credentials
- Wrapping Tests with Credentials
- Publishing and Viewing Test Results
- Final Pipeline Snippet
- References
Pipeline Stages Overview
| Stage Name | Purpose | Example Command |
|---|---|---|
| Installing Dependencies | Install project dependencies with npm | sh 'npm install' |
| Dependency Scanning | Audit packages for vulnerabilities | npm audit / OWASP tools |
| Unit Testing | Run Mocha tests and generate JUnit XML report | sh 'npm test' |
Adding the Unit Testing Stage
Open your Jenkinsfile and insert a Unit Testing stage right after Dependency Scanning:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Installing Dependencies') {
steps {
sh 'npm install'
}
}
stage('Dependency Scanning') {
// existing scanning steps
}
stage('Unit Testing') {
steps {
sh 'npm test'
}
}
}
}
Commit and push the changes to trigger a new build:
git add Jenkinsfile
git commit -m "Add Unit Testing stage"
git push origin feature/enabling-cicd
Navigate to the Jenkins pipeline UI; the build will start automatically.
Debugging a Failed Test Stage
In our example, the Unit Testing stage fails because MongoDB credentials are missing:
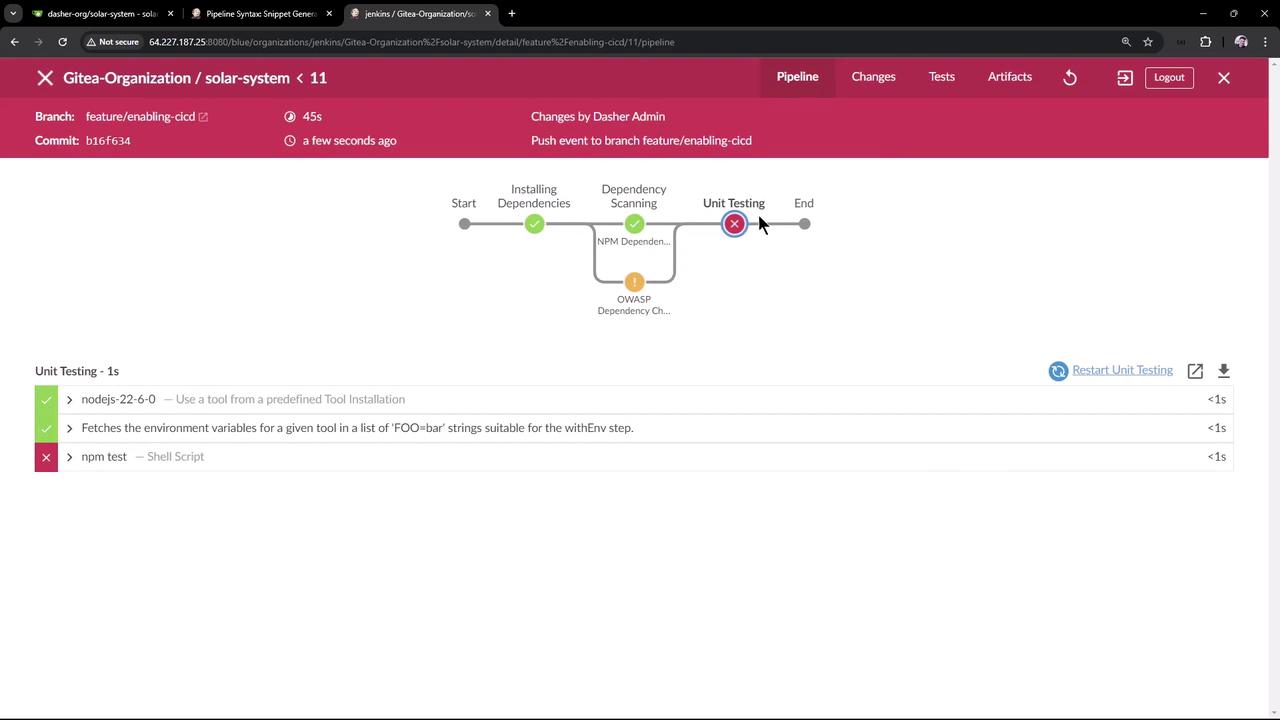
Error Output
> npm test
> Solar [email protected] test
> mocha app-test.js --timeout 10000 --reporter mocha-junit-reporter --exit
MongooseError: The `uri` parameter to `openUri()` must be a string, got `undefined`. Make sure the first parameter to `mongoose.connect()` or `mongoose.createConnection()` is a string.
Your app.js expects these environment variables:
mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGO_URI, {
user: process.env.MONGO_USERNAME,
pass: process.env.MONGO_PASSWORD,
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true
}, err => {
if (err) console.log("error!! " + err);
});
Without MONGO_URI, MONGO_USERNAME, or MONGO_PASSWORD, the connection fails.
Configuring Environment Variables
You can define MONGO_URI in your Jenkinsfile, but be aware of plaintext exposure.
pipeline {
agent any
environment {
MONGO_URI = "mongodb+srv://supercluster.d83jj.mongodb.net/superData"
}
stages { ... }
}
Warning
Storing sensitive connection strings directly in the Jenkinsfile exposes them in plaintext. Use Jenkins Credentials for usernames and passwords.
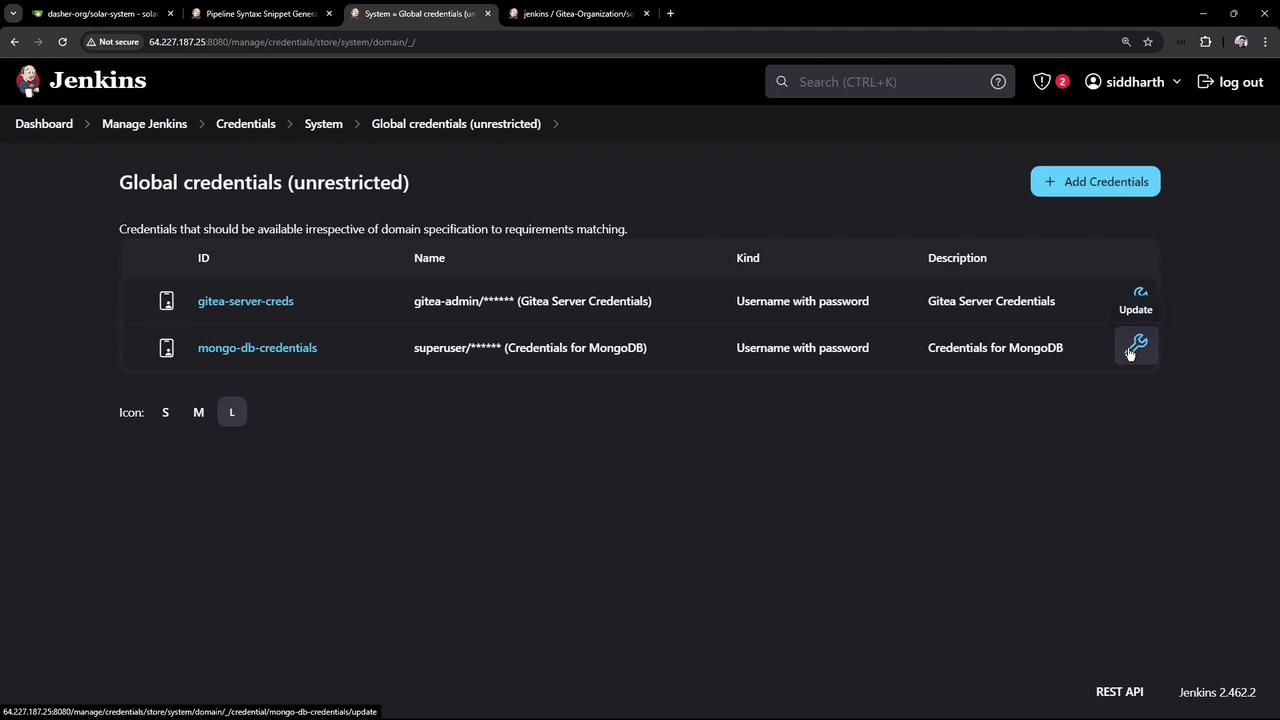
Managing Jenkins Credentials
- Go to Manage Jenkins > Credentials > System > Global credentials (unrestricted).
- Click Add Credentials and choose Username with password.
- ID:
mongo-db-credentials - Username:
superuser - Password:
superpassword
- ID:
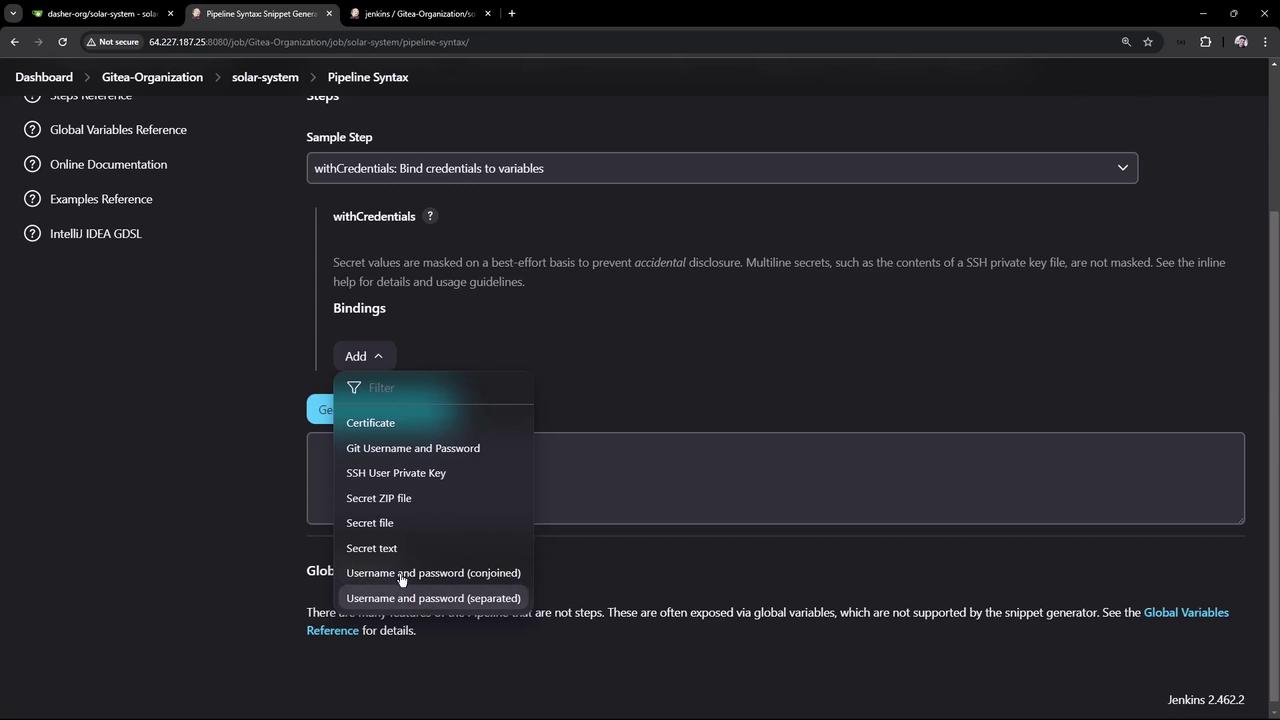
Use the Pipeline Syntax Snippet Generator to see how withCredentials bindings look:
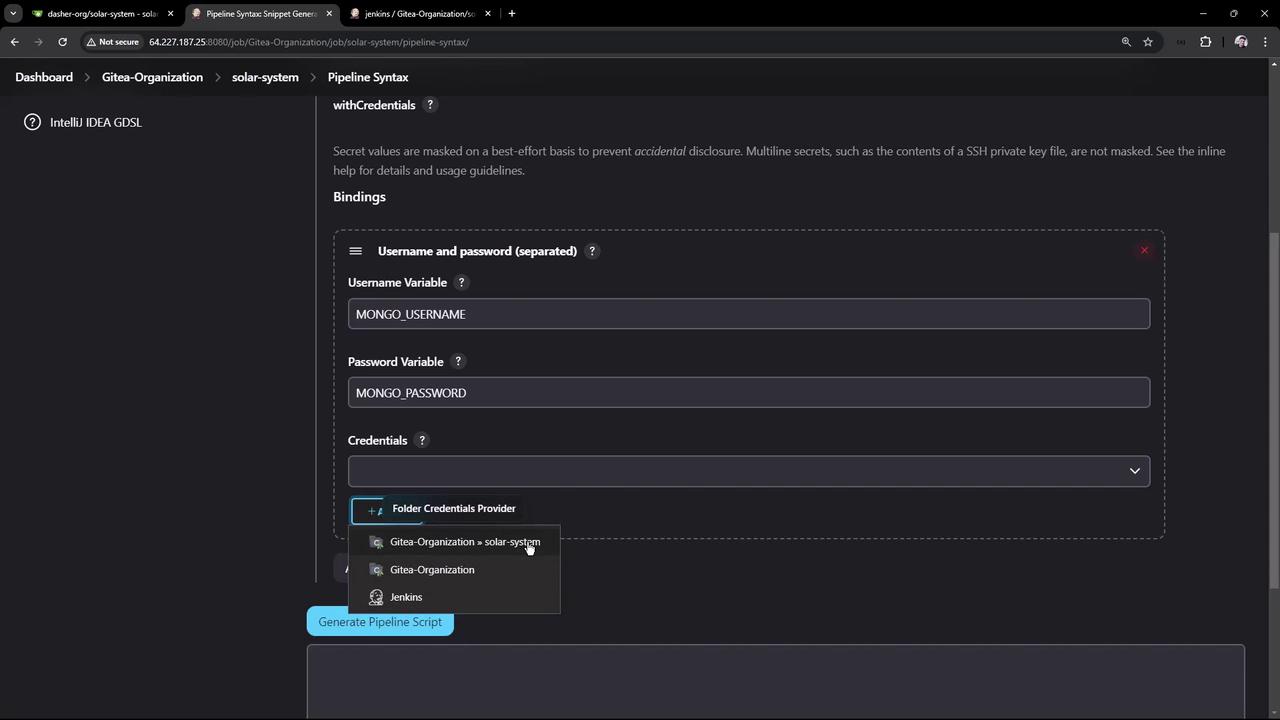
Wrapping Tests with Credentials
Update the Unit Testing stage to inject credentials at runtime and archive JUnit reports:
stage('Unit Testing') {
steps {
withCredentials([
usernamePassword(
credentialsId: 'mongo-db-credentials',
usernameVariable: 'MONGO_USERNAME',
passwordVariable: 'MONGO_PASSWORD'
)
]) {
sh 'npm test'
}
// Archive JUnit XML results
junit allowEmptyResults: true, testResults: '**/test-results.xml'
}
}
Note
The junit step will fail the build if no XML files are found unless you set allowEmptyResults: true.
See Pipeline Syntax: junit for details.
Commit and push—your next build will connect to MongoDB, run tests, and generate a JUnit report.
Publishing and Viewing Test Results
After a successful build:
- Open the Workspace to verify
test-results.xmlexists. - Click Test Result in the sidebar for a summary of test cases.
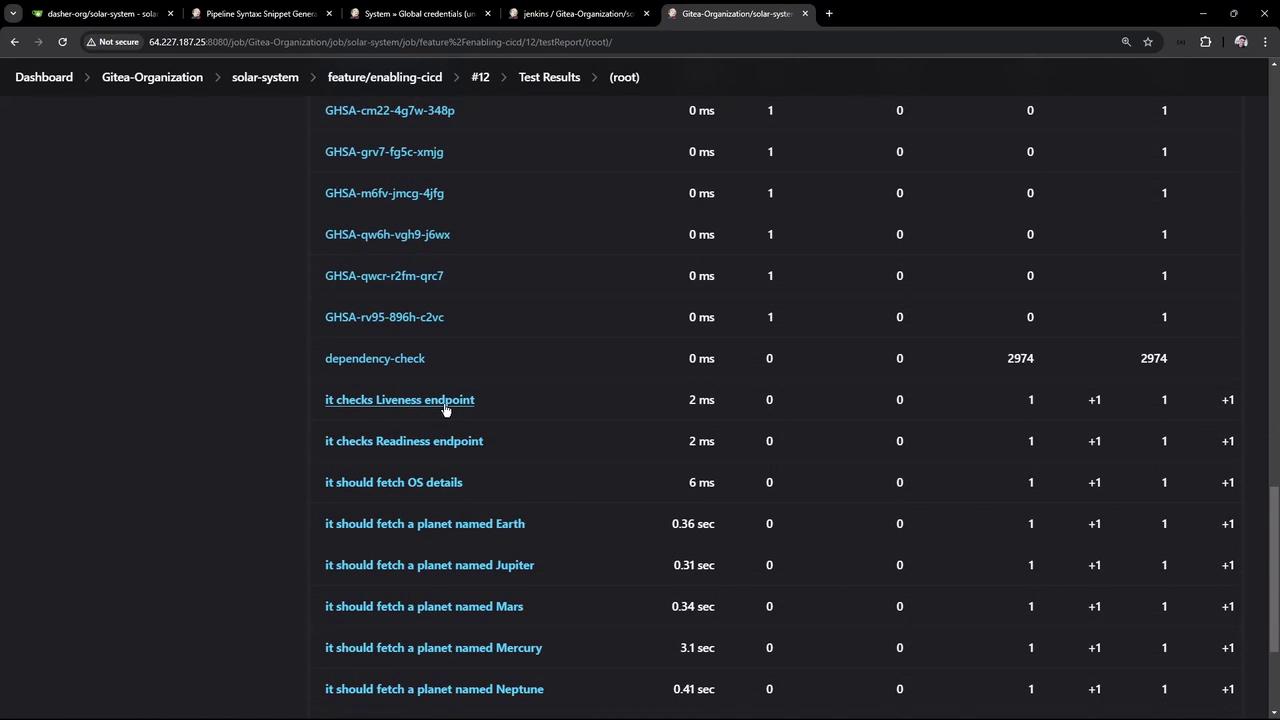
You’ll see each test—liveness, readiness, and planet-fetching endpoints—with pass/fail status.
Final Pipeline Snippet
pipeline {
agent any
tools {
// e.g., nodejs 'nodejs-22-6-0'
}
environment {
MONGO_URI = "mongodb+srv://supercluster.d83jj.mongodb.net/superData"
}
stages {
stage('Installing Dependencies') {
steps {
sh 'npm install'
}
}
stage('Dependency Scanning') {
parallel {
stage('NPM Dependency Audit') {
steps {
sh 'npm audit --audit-level=high'
}
}
stage('OWASP Dependency Check') {
steps {
// OWASP scanning commands
}
}
}
}
stage('Unit Testing') {
steps {
withCredentials([
usernamePassword(
credentialsId: 'mongo-db-credentials',
usernameVariable: 'MONGO_USERNAME',
passwordVariable: 'MONGO_PASSWORD'
)
]) {
sh 'npm test'
}
junit '**/test-results.xml'
}
}
}
}
With this setup, your Jenkins pipeline runs secure unit tests against MongoDB and provides detailed JUnit reports right in the UI.
References
Watch Video
Watch video content