Certified Jenkins Engineer
Setting up CI Pipeline
Demo Using Options Directive
In this lesson, you’ll learn how to leverage the options directive to fine-tune your Jenkins Declarative Pipeline. You can apply options globally (pipeline level) or locally (per stage), enabling features like timestamps, retries, and build concurrency control.
Inspecting Available Options
Before configuring your pipeline, explore all supported options in the official Jenkins Pipeline Syntax documentation.
Note
Refer to the Pipeline Syntax documentation for an up-to-date list of directives you can use.
Adding Timestamps to a Stage
Including timestamps in your console log helps you measure step durations and troubleshoot performance issues. To enable timestamps for a specific stage:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Install Dependencies') {
options {
timestamps()
}
steps {
sh 'npm install --no-audit'
}
}
}
}
Retrying a Stage on Failure
When interacting with external systems (e.g., databases or APIs), transient failures can occur. Use retry(count) to automatically rerun the stage upon failure:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Unit Testing') {
options {
retry(2)
}
steps {
withCredentials([usernamePassword(
credentialsId: 'mongo-db-credentials',
passwordVariable: 'MONGO'
)]) {
sh 'npm test'
}
}
post {
always {
junit allowEmptyResults: true,
testResults: 'test-results.xml'
}
}
}
}
}
If your MONGO_URI is missing, Jenkins reports:
MongooseError: The `uri` parameter to `openUri()` must be a string, got `undefined`.
With retry(2), Jenkins will attempt the stage up to two additional times before failing.
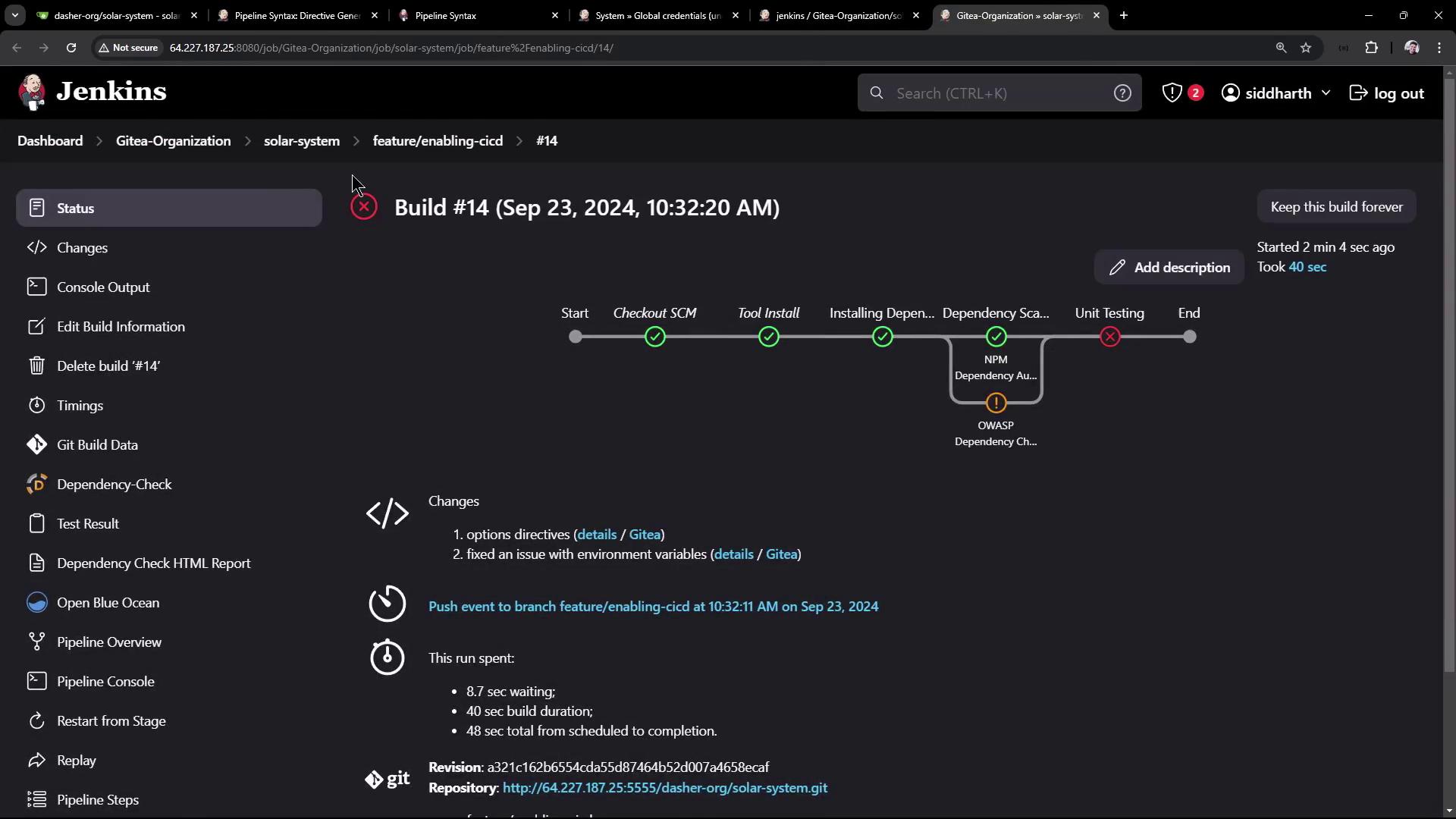
You can track retry attempts in the console output.
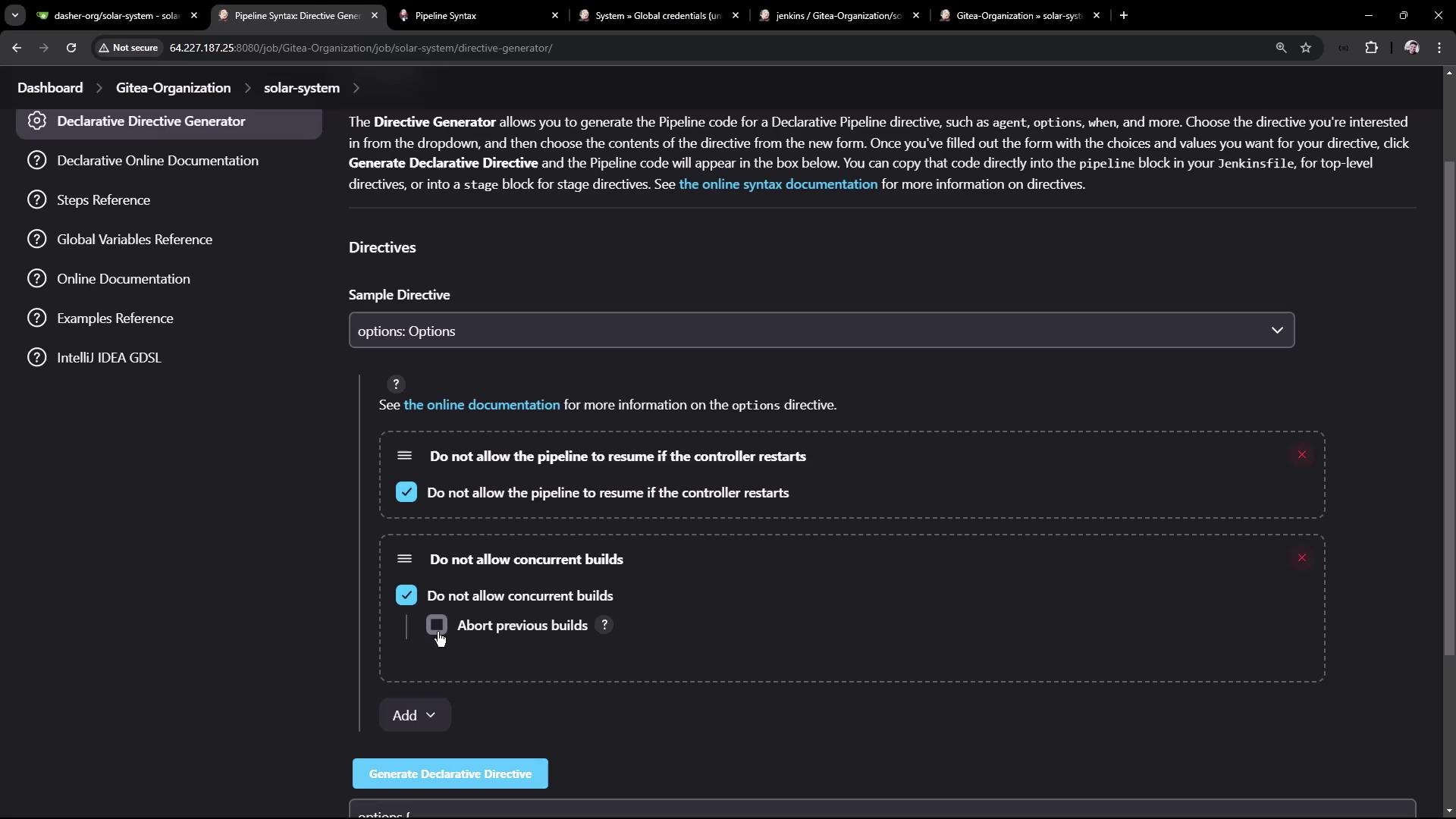
Disabling Resume and Concurrent Builds
At the pipeline level, you can:
- Prevent resume after a restart using
disableResume(). - Abort previous builds when a new one starts using
disableConcurrentBuilds(abortPrevious: true).
pipeline {
agent any
environment {
MONGO_URI = "mongodb+srv://supercluster.d83jj.mongodb.net/superData"
}
options {
disableResume()
disableConcurrentBuilds(abortPrevious: true)
}
stages {
stage('Install Dependencies') {
options { timestamps() }
steps {
sh 'sleep 100s'
sh 'npm install --no-audit'
}
}
stage('Dependency Scanning') {
steps {
// Security and license checks go here
}
}
stage('Unit Testing') {
options { retry(2) }
steps {
withCredentials([usernamePassword(
credentialsId: 'mongo-db-credentials',
usernameVariable: 'MONGO_USERNAME',
passwordVariable: 'MONGO_PASSWORD'
)]) {
sh 'npm test'
}
}
post {
always {
junit allowEmptyResults: true,
testResults: 'test-results.xml'
}
}
}
}
}
When a new build is triggered during the sleep 100s step, the previous build is aborted:
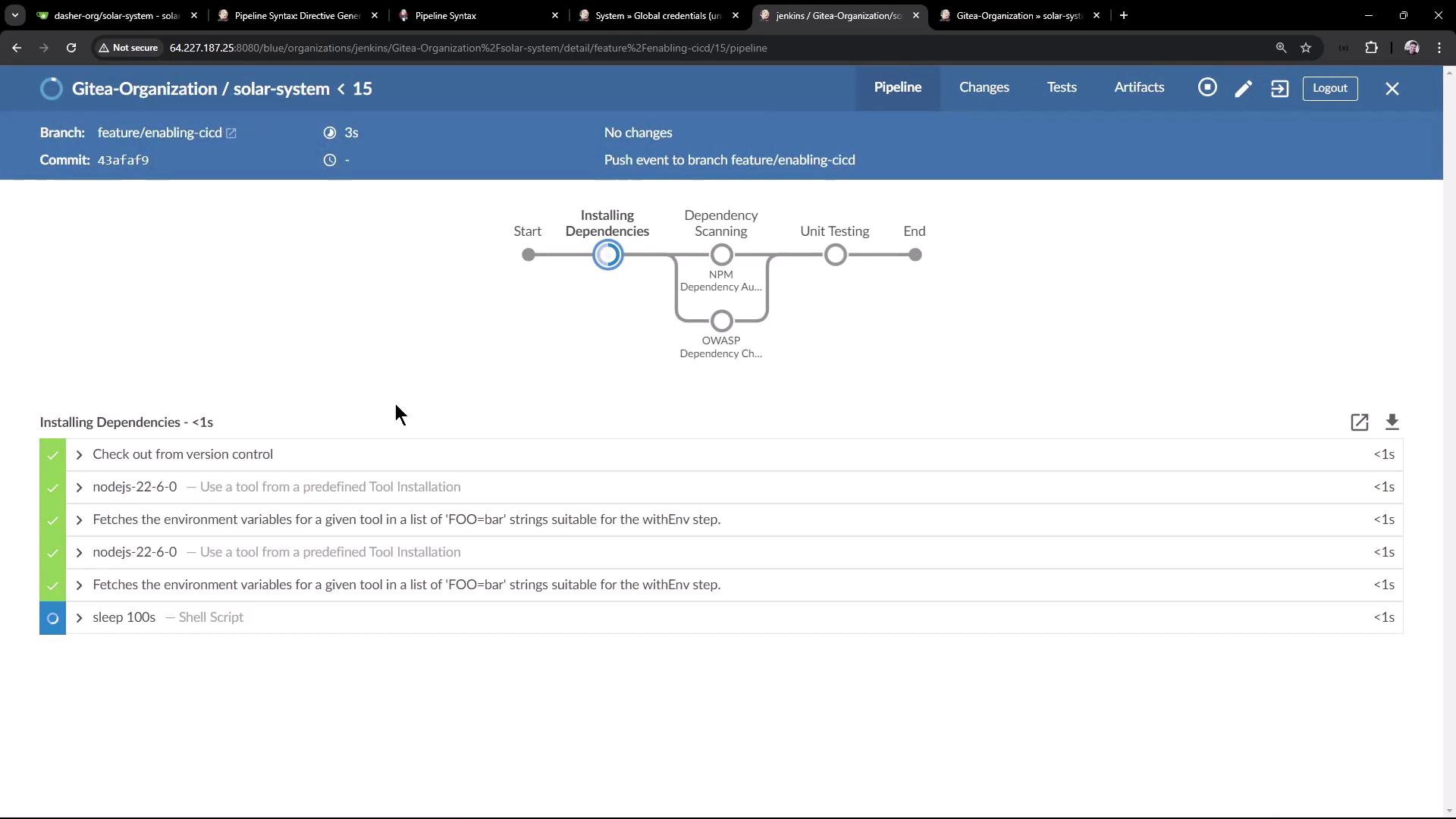
16:06:57 + sleep 100s
16:07:25 Sending interrupt signal to process
Superseded by #16
16:07:29 Terminated: script returned exit code 143
Warning
Using disableResume() will remove the ability to resume pipeline execution after a Jenkins restart. Use it only if you have idempotent stages or external state management.
Summary of Pipeline Options
| Option | Scope | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
timestamps() | Stage | Prefixes each log line with a timestamp. | options { timestamps() } |
retry(count) | Stage | Retries a failing stage up to count times. | options { retry(2) } |
disableResume() | Pipeline | Disables pipeline continuation after a Jenkins restart. | options { disableResume() } |
disableConcurrentBuilds(...) | Pipeline | Prevents concurrent runs; can abort previous builds when triggered. | options { disableConcurrentBuilds(abortPrevious: true) } |
Links and References
Explore these resources to discover more ways to customize your Jenkins pipelines and streamline your CI/CD workflows.
Watch Video
Watch video content