In this lesson, we’ll set up a DevSecOps environment on an Azure Virtual Machine. We’ll install Docker, Kubernetes (kubeadm & kubectl), Jenkins, and Maven, then deploy a simple Nginx application. This end-to-end tutorial is ideal for anyone looking to automate CI/CD in the cloud.
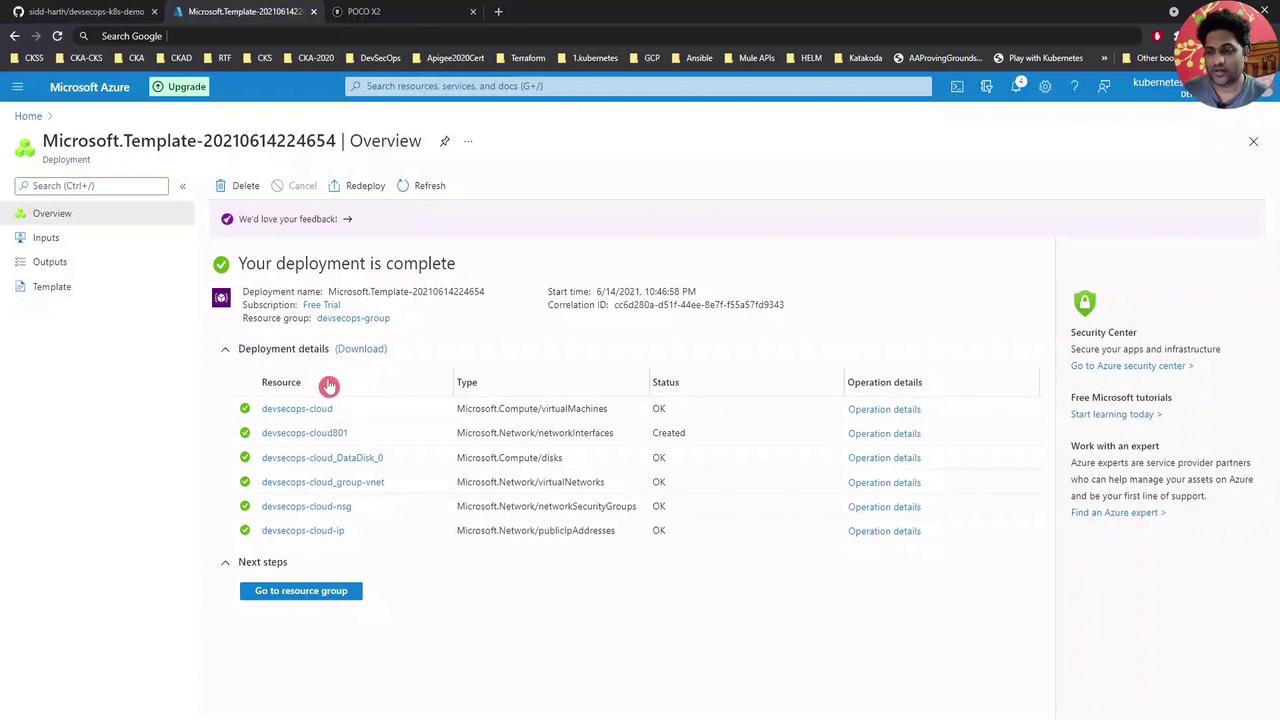
Verifying Deployment in Azure After your deployment finishes, confirm that all resources (VM, network interfaces, disks, VNet, NSGs, public IP) show a Succeeded status:
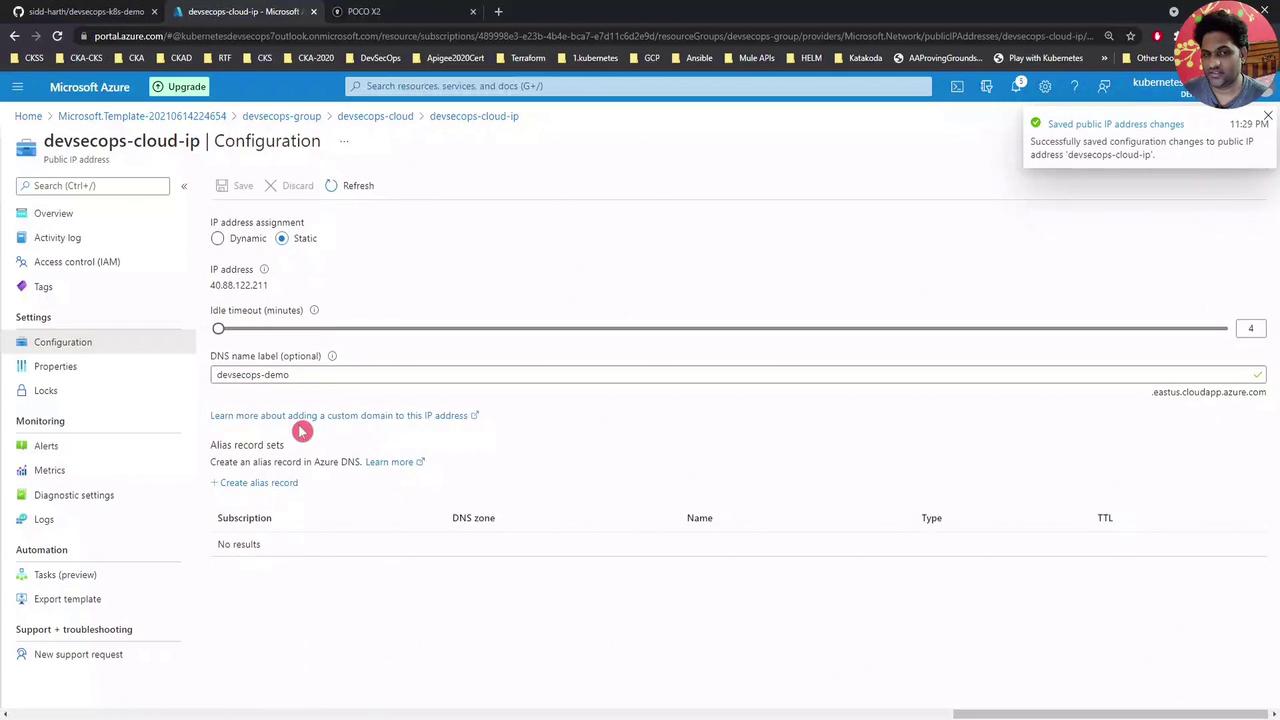
Tip: Use the Azure portal’s search and filter features to quickly locate resources in large subscriptions.Configuring a DNS Name Assigning a DNS label to your VM’s public IP makes SSH and service URLs easier to remember:
In the Azure portal, go to your Resource Group .
Select the Public IP resource (e.g., devsecops-cloud-ip).
Under Configuration , enter a DNS name label (e.g., DevSecOpsDemo).
Click Save .
After saving, refresh the VM overview to see the FQDN:DevSecOpsDemo.eastus.cloudapp.azure.com
DNS changes can take a few minutes to propagate. Use nslookup DevSecOpsDemo.eastus.cloudapp.azure.com to verify resolution.
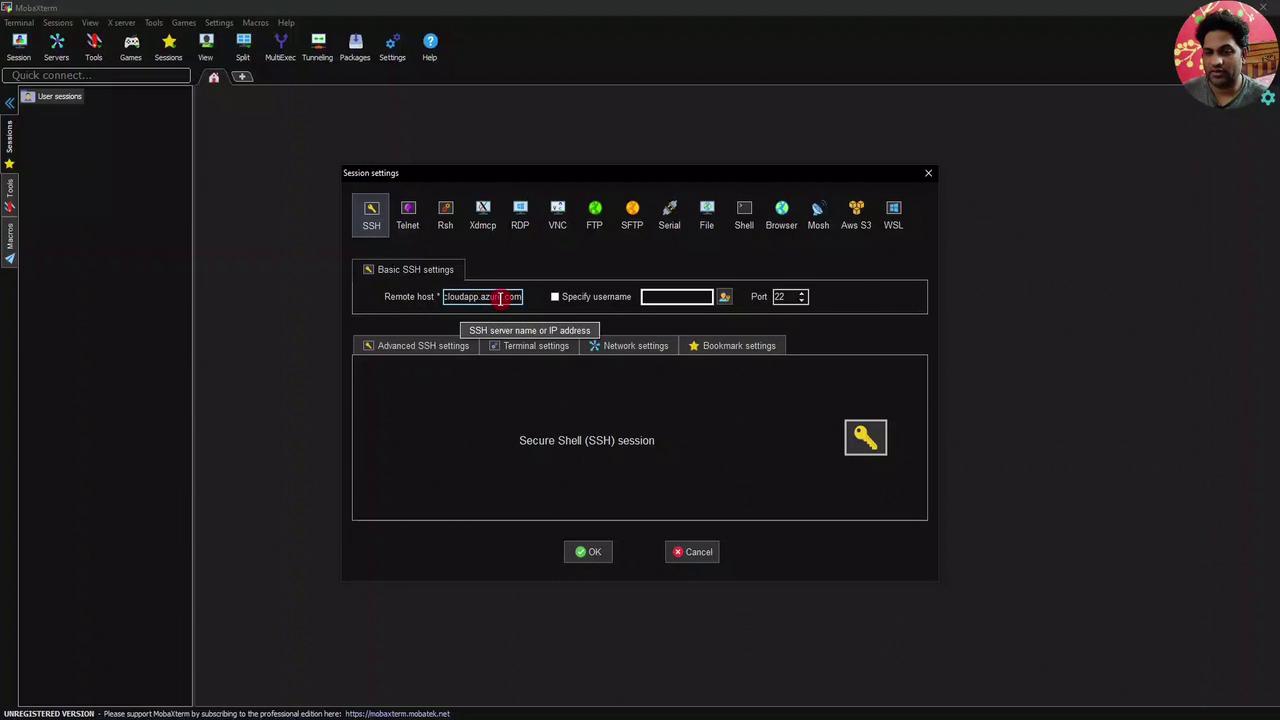
Connecting via SSH Use any SSH client. Here’s an example with MobaXterm:
Remote host: DevSecOpsDemo.eastus.cloudapp.azure.com
Username: your VM admin (e.g., devsecops)
Enter your password or SSH key to log in.
Preparing the VM Switch to the root user to avoid typing sudo repeatedly:
devsecops@devsecops-cloud:~$ sudo -i root@devsecops-cloud:~#
Cloning the Demo Repository Download the demo scripts and navigate to the install script directory:
root@devsecops-cloud:~# git clone https://github.com/sidd-harth/devsecops-k8s-demo.git root@devsecops-cloud:~# cd devsecops-k8s-demo/setup/vm-install-script/ root@devsecops-cloud:~/devsecops-k8s-demo/setup/vm-install-script# ls -l -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3024 Jun 14 18:02 install-script.sh
Running the Install Script The install-script.sh automates installation of:
Component Installation Method Version Docker apt Latest Kubernetes kubeadm, kubectl v1.20.0 Jenkins apt 2.289.1 Maven apt 3.x
Always review scripts from external sources before executing them on production systems.
Execute the installer (this may take several minutes):
root@devsecops-cloud:~/devsecops-k8s-demo/setup/vm-install-script# bash install-script.sh ... Setting up jenkins (2.289.1) ... ...
When finished, confirm your Kubernetes node is ready:
root@devsecops-cloud:~# kubectl get node -o wide NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION devsecops-cloud Ready control-plane,master 4m v1.20.0 10.0.0.4 Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 5.4.0-1
Deploying a Sample Nginx Application
Create the Nginx pod:
root@devsecops-cloud:~# kubectl run nginx-pod --image=nginx pod/nginx-pod created
Check pod status:
root@devsecops-cloud:~# kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE nginx-pod 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 15s
Watch until it’s running:
root@devsecops-cloud:~# kubectl get pods -w NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE nginx-pod 1/1 Running 0 25s
Expose it via a NodePort service:
root@devsecops-cloud:~# kubectl expose pod nginx-pod --type=NodePort --port=80 service/nginx-pod exposed root@devsecops-cloud:~# kubectl get svc nginx-pod NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT ( S ) AGE nginx-pod NodePort 10.96.xxx.xxx < non e > 80:32325/TCP 1m
In your browser, go to:
http://DevSecOpsDemo.eastus.cloudapp.azure.com:32325
You should see the default Nginx welcome page.
Next, we’ll configure a Jenkins pipeline to automate builds and deployments in Kubernetes.
Links and References