DevSecOps - Kubernetes DevOps & Security
DevOps Pipeline
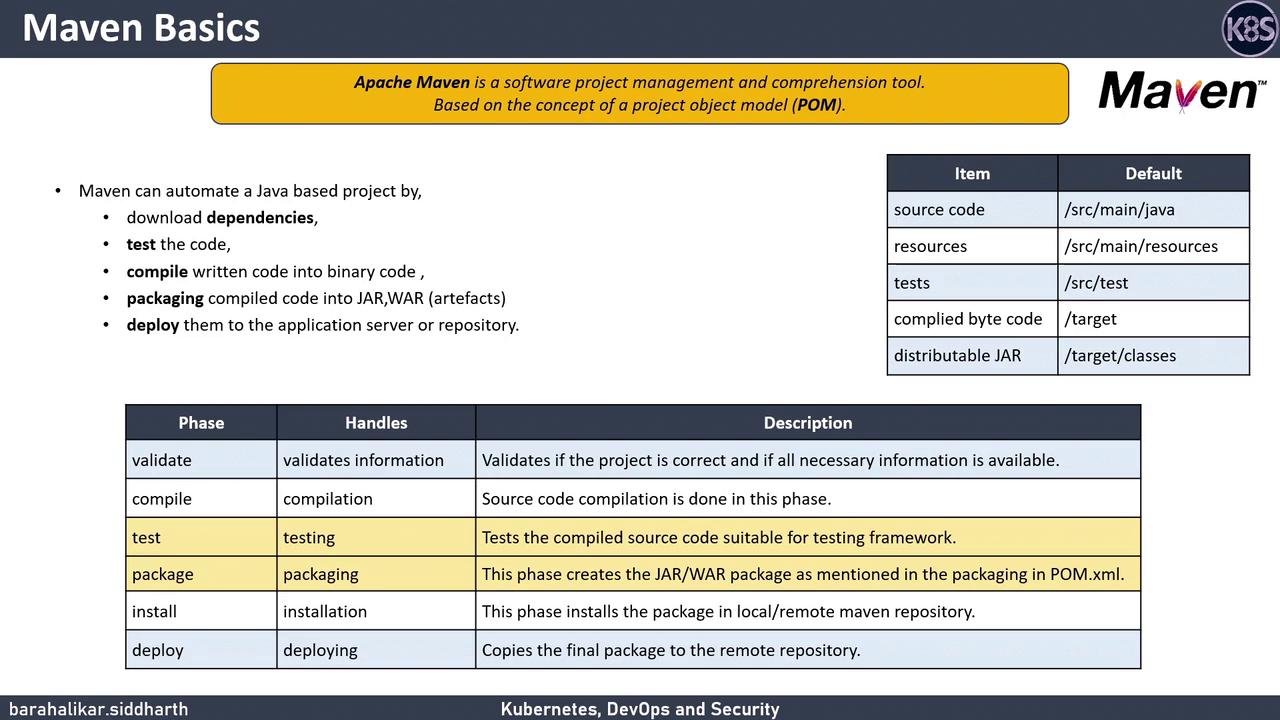
Maven Basics
In this guide, you’ll learn what Apache Maven is, why it’s essential for Java project automation, and how to leverage its lifecycle and directory conventions to streamline your build, test, and deployment processes.
What Is Maven?
Apache Maven is a powerful build automation and project management tool based on the Project Object Model (POM). By defining dependencies and build settings in a pom.xml file, Maven handles:
- Downloading and managing third-party libraries
- Compiling Java source code
- Running unit tests
- Packaging artifacts (JAR, WAR)
- Deploying to local or remote repositories
Note
Your pom.xml sits at the root of your project. It controls everything from dependency versions to plugin executions.
Standard Project Structure
Maven enforces a conventional directory layout to keep builds predictable:
my-app
├── src
│ ├── main
│ │ ├── java # Application source code
│ │ └── resources # Configuration files & properties
│ └── test
│ ├── java # Unit test source code
│ └── resources # Test-specific resources
└── target # Compiled classes & packaged artifacts
Core Lifecycle Phases
Maven executes build steps in a predefined sequence of lifecycle phases. Common phases you’ll use daily:
| Phase | Description | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| validate | Ensure project is correct and all info is available | Checks pom.xml validity |
| compile | Compile application source code | Generates .class files in target/classes |
| test | Run unit tests | Executes tests in src/test/java |
| package | Bundle compiled code into a JAR/WAR | Produces artifact in target/ |
| install | Install package to local repository | Installs to ~/.m2/repository |
| deploy | Copy final artifacts to remote repositories | Publishes for sharing across teams |
Running Tests
To compile your code and run all unit tests:
mvn test
This executes the test phase, compiling classes and running tests under src/test/java.
Packaging Artifacts
When you’re ready to create your deployable artifact:
mvn package
Maven runs up to the package phase, producing a JAR or WAR (depending on your packaging setting) in the target directory.
Warning
Ensure your pom.xml <packaging> element matches your intended artifact type (jar, war, etc.) to avoid build failures.
Integrating Maven with Jenkins
Automate your CI/CD pipeline by invoking Maven goals in a Jenkinsfile:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
sh 'mvn clean compile'
}
}
stage('Test') {
steps {
sh 'mvn test'
}
}
stage('Package') {
steps {
sh 'mvn package'
}
}
}
post {
always {
junit 'target/surefire-reports/*.xml'
}
}
}
This pipeline runs through the compile, test, and package phases and archives test results automatically.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content