dev-deploy and dev-integration-testing jobs, renaming them for production, updating manifest paths, and configuring environment protection, you’ll achieve a safe, repeatable deployment process.
Workflow Configuration
Begin by updating the workflow metadata, trigger conditions, and shared environment variables:Production Deployment Jobs
Below is the new production deployment job, which depends ondev-integration-testing, runs against the production environment, and exports the ingress URL:
Note: Ensure thatvars.NAMESPACE,vars.REPLICAS, andsecrets.MONGO_PASSWORDare defined in your GitHub repository settings or organization variables.
Job Overview
Here’s a quick breakdown of the full CI/CD pipeline:| Job Name | Purpose | Depends On |
|---|---|---|
| unit-testing | Run unit tests | — |
| code-coverage | Measure code coverage | unit-testing |
| docker | Build and push Docker images | code-coverage |
| dev-deploy | Deploy to development namespace | docker |
| dev-integration-testing | Run integration tests against dev cluster | dev-deploy |
| prod-deploy | Apply production manifests to prod cluster | dev-integration-testing |
| prod-integration-testing | Validate production endpoint | prod-deploy |
Running the Workflow
After pushing these changes from a feature branch, GitHub Actions will schedule all jobs:unit-testingcode-coveragedockerdev-deploydev-integration-testingprod-deployprod-integration-testing
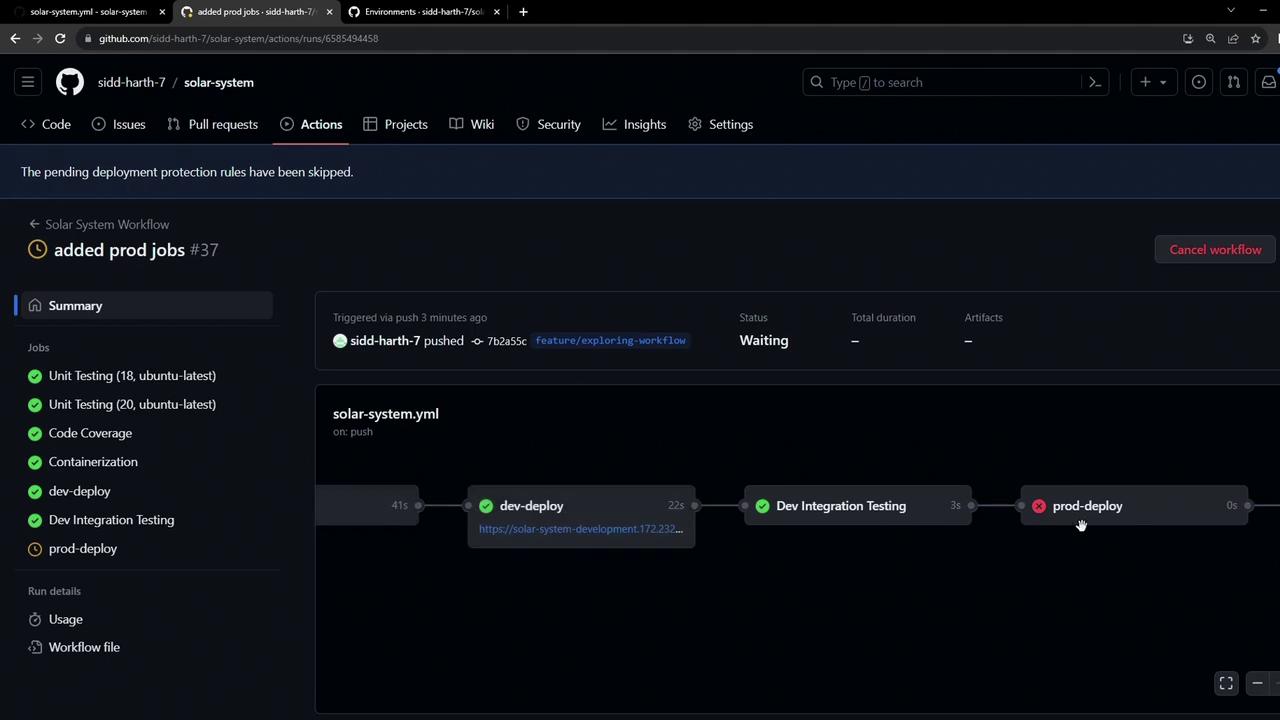
Warning: Because the production environment has branch protection rules (only main allowed), any attempt to deploy from a feature branch will be blocked. Subsequent jobs in the workflow are skipped when this rule is not met.
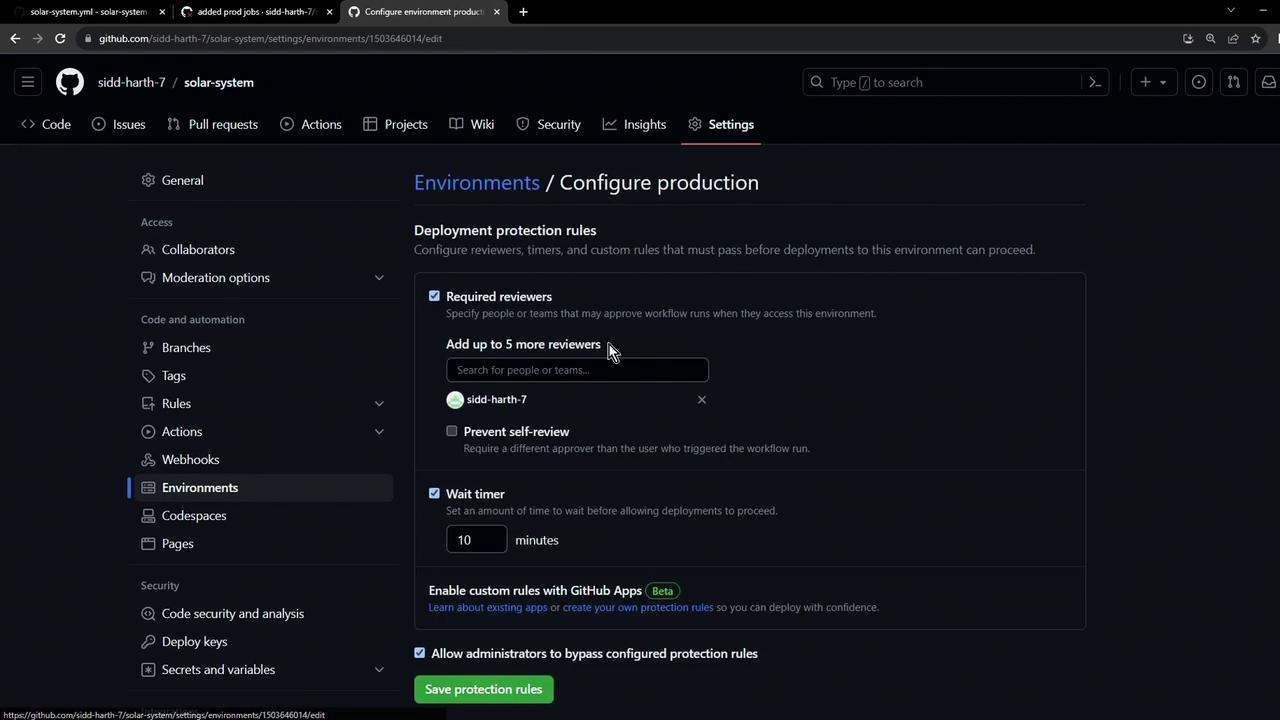
prod-deploy job and skips downstream steps. In the next lesson, we’ll cover how to configure approvals and satisfy these rules for safe, automated releases.