GitHub Actions Certification
GitHub Actions in the Enterprise Cloud
Configure self hosted runners with proxies
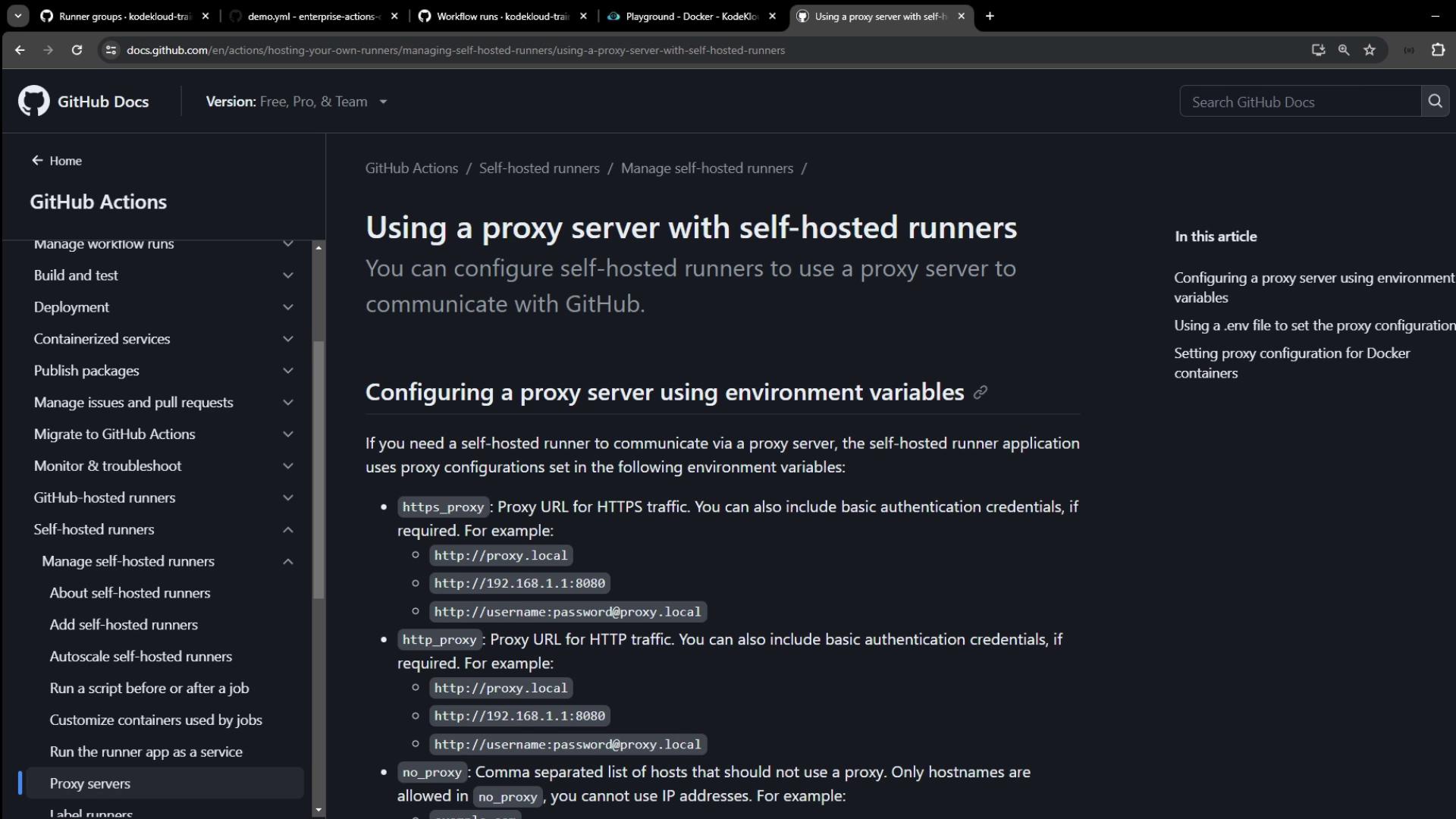
In this guide, you’ll learn how to route your self-hosted GitHub Actions runner traffic through an HTTP/HTTPS proxy. A proxy server acts as an intermediary, forwarding requests between your runner and the Internet for improved security, privacy, or access to geo-restricted endpoints.
Proxy Configuration Options
You can configure proxy settings for your self-hosted runner in two primary ways:
| Method | Description | Configuration Location |
|---|---|---|
| Environment Variables | Set HTTPS_PROXY, HTTP_PROXY, and NO_PROXY on the host. | Shell profile or CI service |
.env File | Place a .env file in the runner directory with the same vars. | Runner install folder |
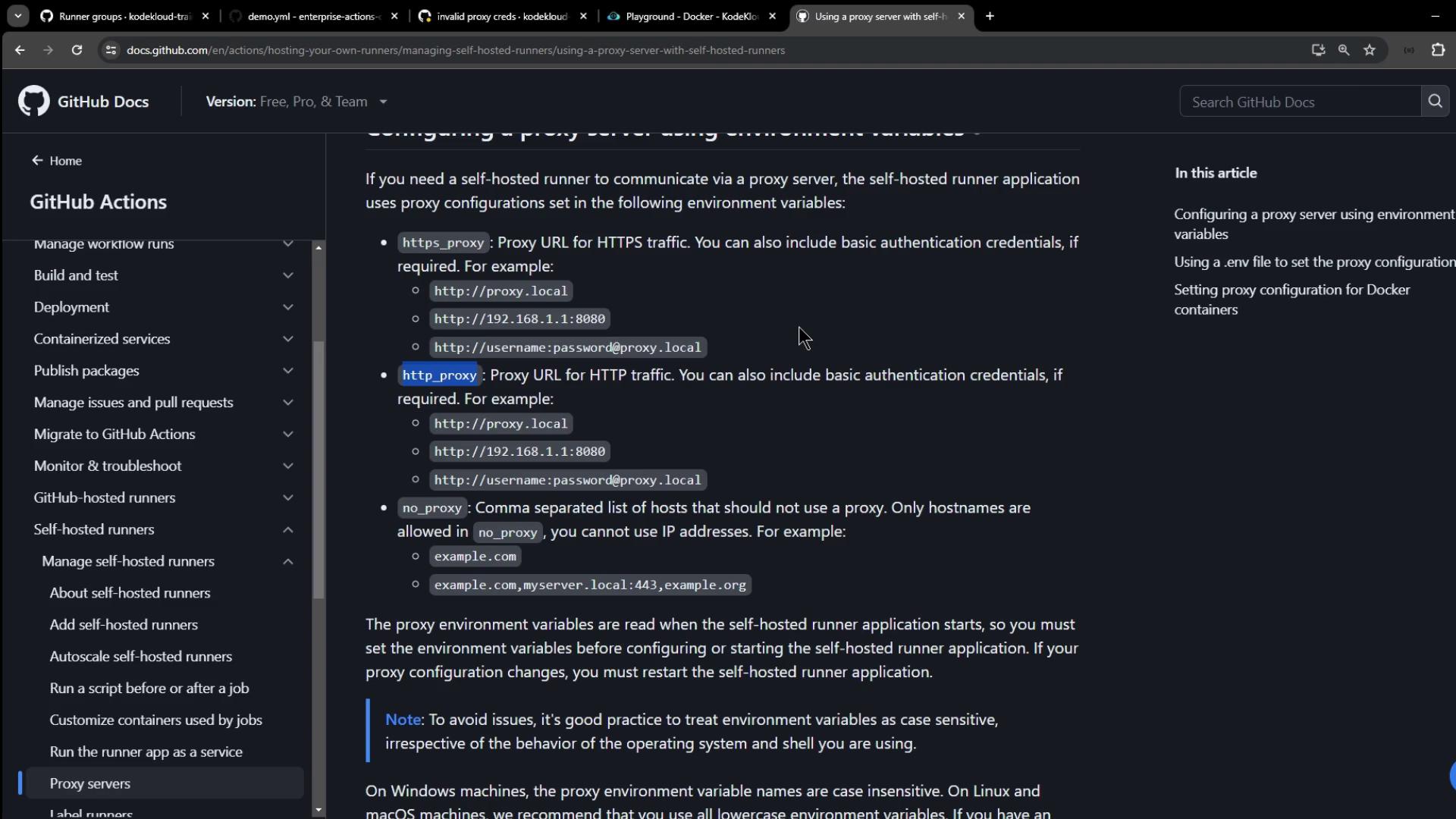
1. Environment Variables
On the machine hosting your runner, export:
| Variable | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| HTTPS_PROXY | Proxy for HTTPS requests | http://proxy.local:8080 |
| HTTP_PROXY | Proxy for HTTP requests | http://username:[email protected] |
| NO_PROXY | Hosts or domains to bypass the proxy | example.com,myserver.local:443 |
export HTTPS_PROXY="http://proxy.local:8080"
export HTTP_PROXY="http://proxy.local:8080"
export NO_PROXY="example.com,myserver.local:443"
Note
NO_PROXY accepts comma-separated hostnames, IP addresses, or domains (optionally with ports).
2. .env File
If modifying system environment variables is impractical, create a .env file in the directory where you extracted the runner:
https_proxy=http://proxy.local:8080
http_proxy=http://proxy.local:8080
no_proxy=example.com,myserver.local:443
Docker Containers
For workflows that launch Docker containers, configure Docker’s proxy settings separately.
For example, create or edit /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/http-proxy.conf:
[Service]
Environment="HTTP_PROXY=http://proxy.local:8080" "HTTPS_PROXY=http://proxy.local:8080"
Then reload and restart Docker:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart docker
Demo: Proxy in a Workflow
The following sample workflow sends external HTTP requests with and without proxy authentication.
name: Demo Proxy Configuration
on: workflow_dispatch
jobs:
demo_job:
runs-on: self-hosted
steps:
- name: Hello
run: echo "Hello from self-hosted runner!"
- name: External Call (No Proxy)
run: curl -v http://httpbin.org/ip
- name: External Call (Invalid Proxy Credentials)
run: |
curl -v \
-x http://wrong-user:wrong-pass@localhost:3128 \
http://httpbin.org/ip
Logs: No Proxy
$ curl -v http://httpbin.org/ip
* Connected to httpbin.org (3.214.174.72) port 80 (#0)
> GET /ip HTTP/1.1
> Host: httpbin.org
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
{"origin": "35.188.139.128"}
This request bypasses any proxy and connects directly.
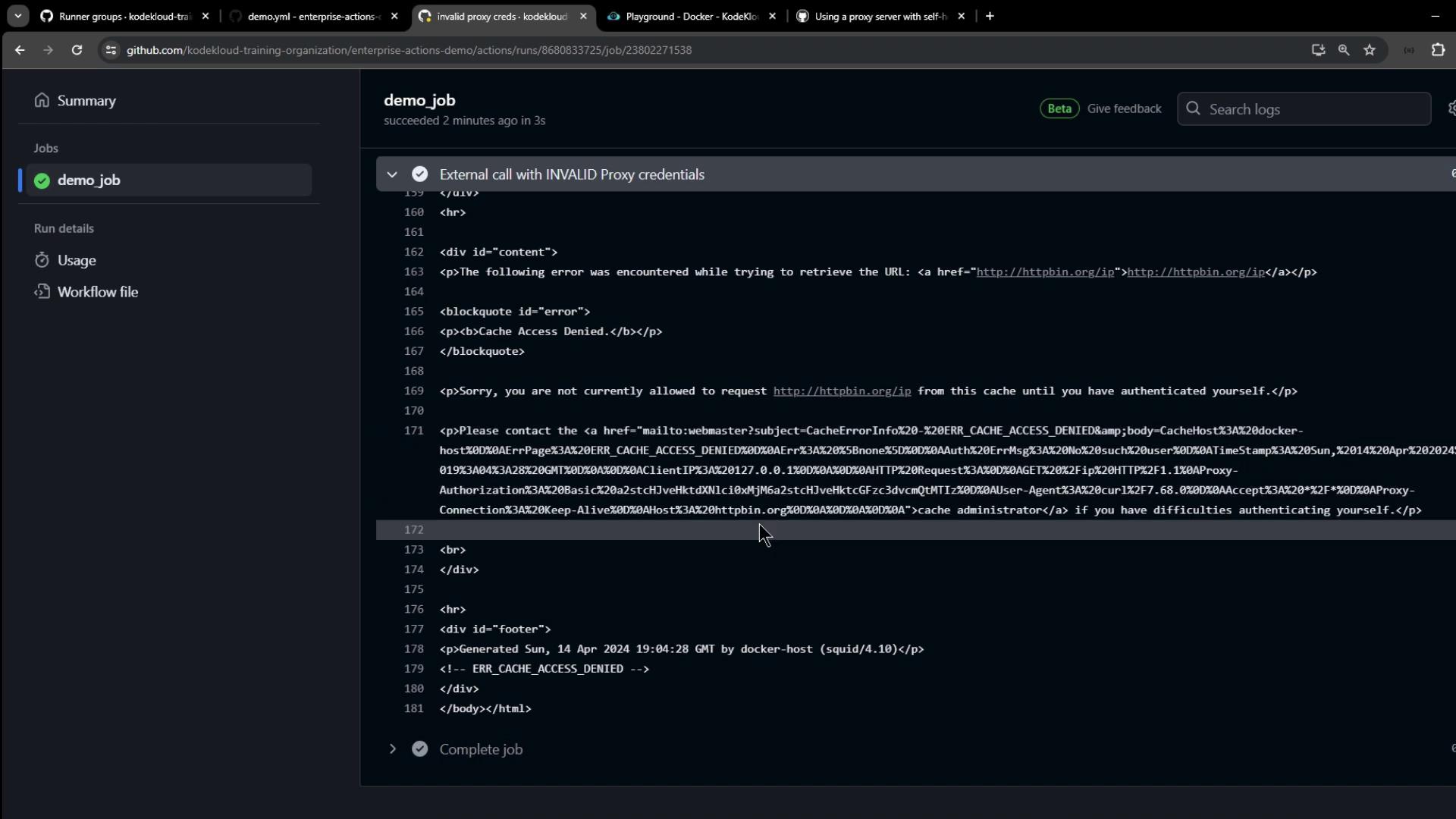
Logs: Invalid Proxy Credentials
$ curl -v -x http://wrong-user:wrong-pass@localhost:3128 http://httpbin.org/ip
* Connected to localhost (127.0.0.1) port 3128 (#0)
> GET http://httpbin.org/ip HTTP/1.1
> Proxy-Authorization: Basic e3dyb25nLXVzZXI6d3Jvbmc=
< HTTP/1.1 407 Proxy Authentication Required
<title>ERROR: Cache Access Denied</title>
Warning
Avoid hard-coding credentials in workflows. Instead, store proxy credentials securely on the runner host or via GitHub Secrets.
Setting Proxy Variables on the Runner Host
On your VM or bare-metal host, export the proxy variables before launching the runner service:
export HTTPS_PROXY="http://user:password@localhost:3128"
export HTTP_PROXY="http://user:password@localhost:3128"
export NO_PROXY="example.com,myserver.local:443"
systemctl status squid # Verify your Squid or other proxy service
Restart the runner service so it picks up the new environment:
# Example if using a systemd service
systemctl restart actions.runner.your-repo.service
Verifying Proxy Usage in Your Workflow
Update your workflow to print proxy variables and make an HTTPS request:
name: Verify Proxy Usage
on: workflow_dispatch
jobs:
verify_proxy:
runs-on: self-hosted
steps:
- name: Show Proxy Environment
run: |
echo "HTTPS_PROXY: $HTTPS_PROXY"
echo "HTTP_PROXY: $HTTP_PROXY"
echo "NO_PROXY: $NO_PROXY"
- name: External Call via Proxy
run: curl -v https://httpbin.org/ip
Once the run completes:
Logs: Proxy in Action
* Uses proxy env variable HTTP_PROXY = 'localhost:3128'
* Connected to localhost (127.0.0.1) port 3128 (#0)
> GET https://httpbin.org/ip HTTP/1.1
> Proxy-Authorization: Basic e2VjaGF0ZXpzOnBhc3N3b3JkMQ==
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
{"origin": "127.0.0.1, 35.188.139.128"}
The runner picks up the proxy variables automatically, authenticates with your proxy (e.g., Squid), and successfully forwards requests.
Thank you for following this tutorial on setting up proxies for your self-hosted GitHub Actions runners! For more details, see the GitHub Actions documentation.
Watch Video
Watch video content