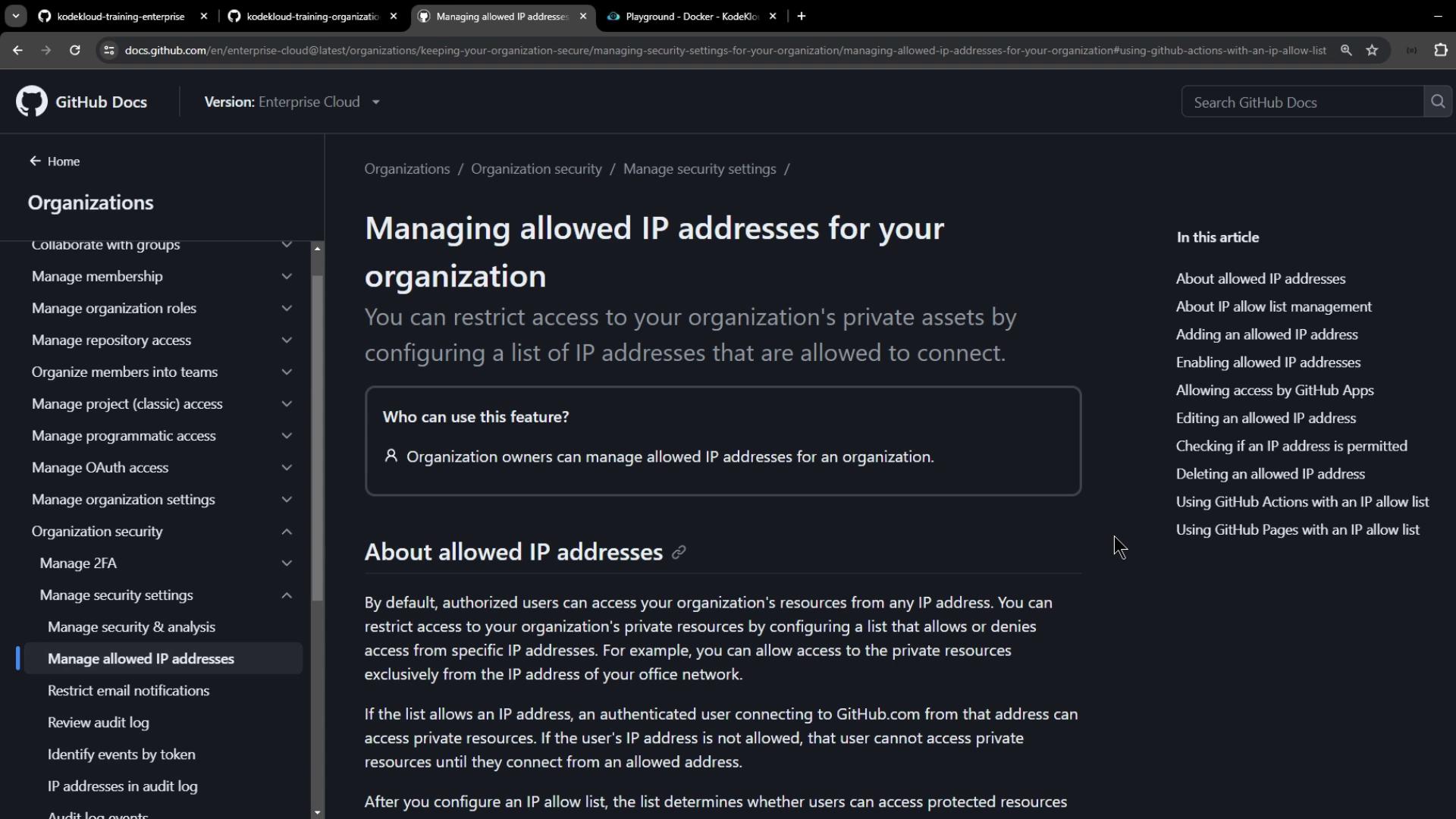
- Adding and managing allowed IP addresses or CIDR ranges
- Enabling allow lists for GitHub Apps, GitHub Actions, and GitHub Pages
- Verifying whether an IP is permitted before enforcement
Using IP allow lists with GitHub Actions
To ensure your workflows run only on known IPs, choose runners with static addresses. You have two options:| Runner Type | IP Stability | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Self-hosted runners | Static or dynamic | You manage the environment and networking |
| GitHub-hosted “large” | Static IP available | Enhanced VMs with more RAM, CPU, disk, auto-scaling, and defined IPs |
Workflows on static-IP runners won’t fail due to IP restrictions.
Consider self-hosted runners or GitHub-hosted “large” runners if you need fixed IPs.
Consider self-hosted runners or GitHub-hosted “large” runners if you need fixed IPs.
Configuring IP allow lists at the enterprise level
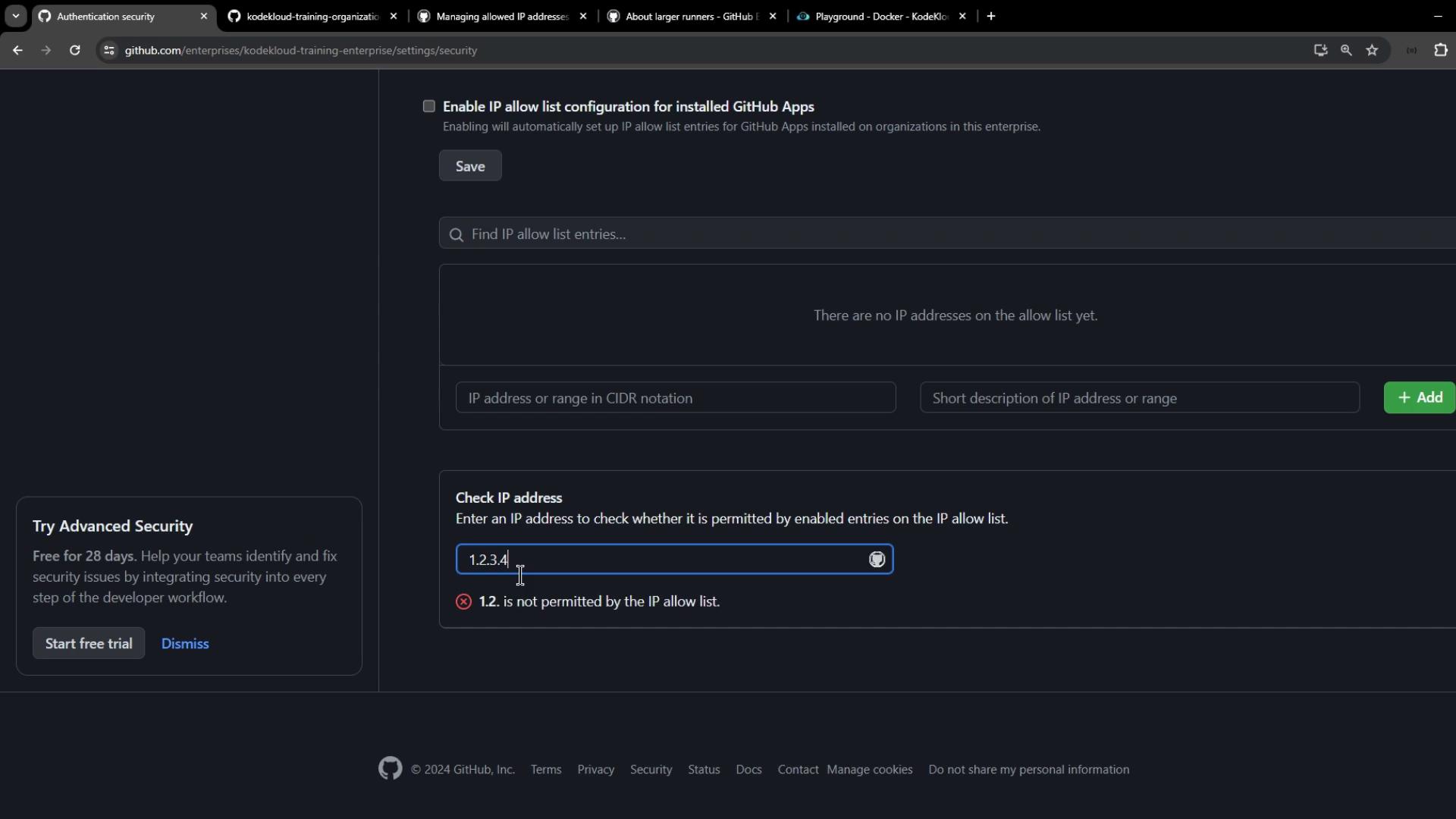
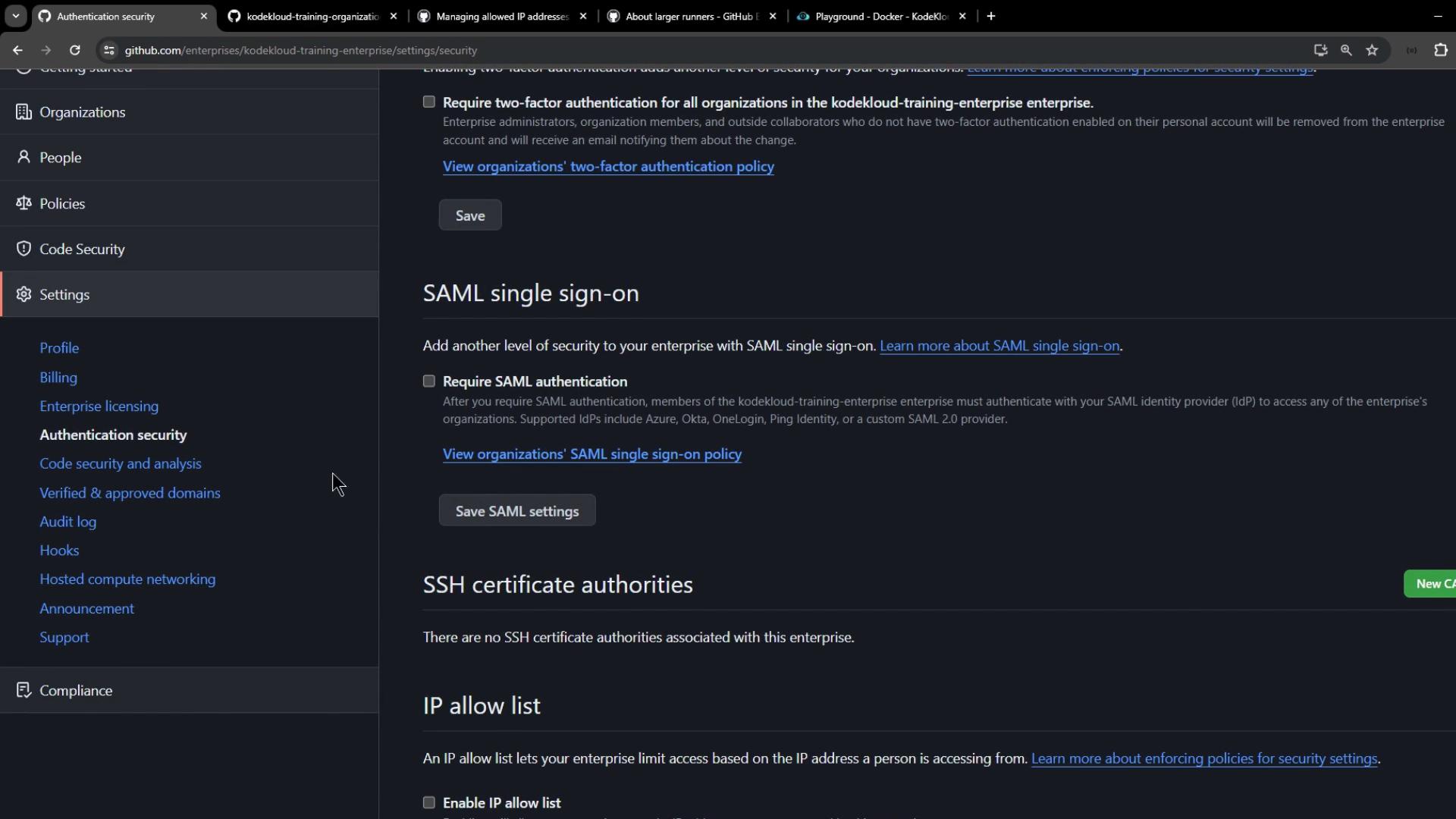
When you enable an IP allow list at the Enterprise level, it applies to all member organizations. The steps mirror the organization-level process:- Navigate to Enterprise Settings
- Select Authentication security
- Under IP allow list, click Add IP or Add CIDR range
- Use the built-in checker to validate an IP before enforcement
- Toggle IP allow list to Enabled and select services (Apps, Actions, Pages)
Handling dynamic IP addresses
If your self-hosted runners use dynamic IPs, automate updates to the allow list via a scheduled script or CI job that calls the GitHub REST API. This prevents runner lockouts when IPs change.Failing to refresh dynamic IP addresses can block your self-hosted runners and halt CI/CD pipelines.
Configuring IP allow lists at the organization level
The organization-level workflow is identical to the enterprise process:- Navigate to Organization Settings
- Select Authentication security
- Add and verify IP addresses or CIDR ranges
- Enable the IP allow list and choose applicable services (Apps, Actions, Pages)