Step 1: Register a New Runner on GitHub
- Open your repository on GitHub.
- Navigate to Settings → Actions → Runners.
- Click New self-hosted runner.
- Select Linux and x64, then copy the setup commands provided.
Step 2: Download and Extract the Runner
SSH into your Ubuntu VM (or another Linux host), then run:Step 3: Configure the Runner
Run the interactive configuration script:Do not run this script as root unless you intentionally bypass the check.
Running GitHub Actions jobs as
Running GitHub Actions jobs as
root can introduce security and reliability risks.Bypass the Root Check (Optional)
If you need to run as root:- Choose a runner group (default: default for repo-level).
- Name your runner (e.g.,
prod-ubuntu-runner). - Assign labels (default:
self-hosted,Linux,X64; you can addprod,main). - Confirm or change the working directory (default:
_work).
Step 4: Verify Registration (Offline)
Once registration completes, your runner shows as Offline in the Runners list: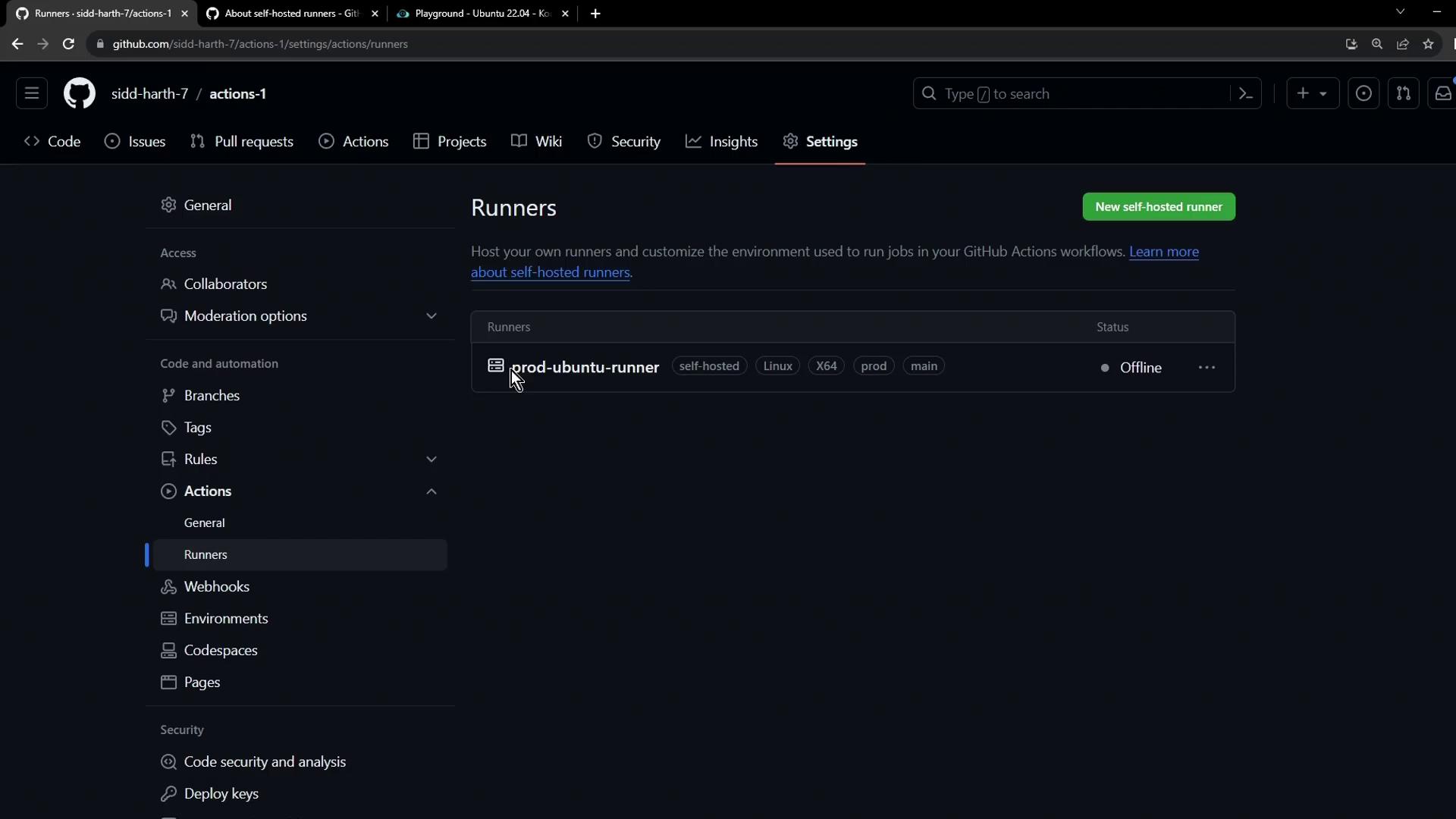
Step 5: Start the Runner
Back in your VM, launch the runner process so it connects to GitHub and listens for jobs:Step 6: Verify Runner Status (Online)
Refresh the Runners page. Your runner should now be Online and idle, ready to accept jobs: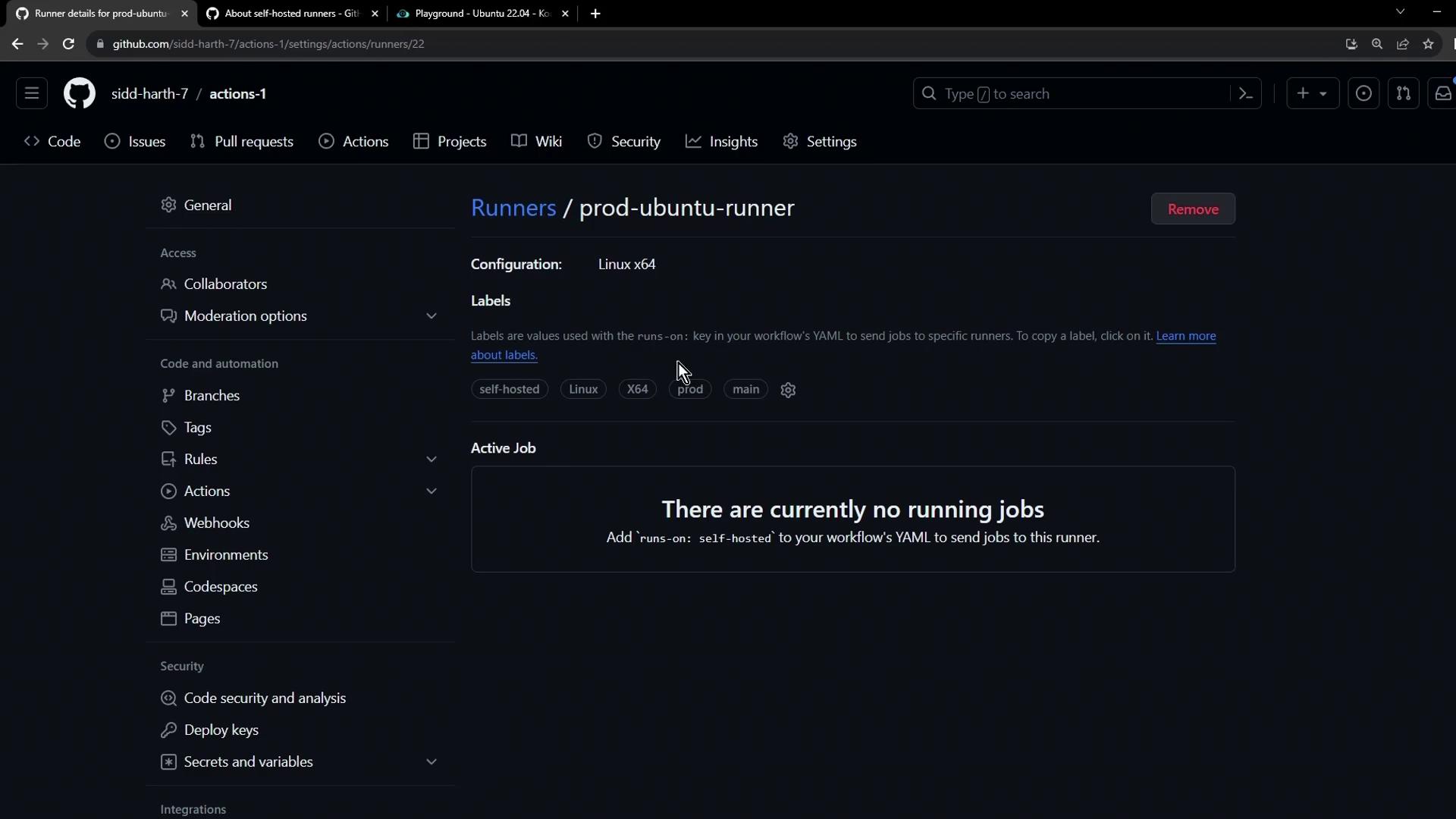
Step 7: Use Your Self-Hosted Runner in Workflows
Add this to any workflow file (.github/workflows/*.yml) to target your runner:
Ensure your self-hosted runner has all required tools and permissions for your workflows.