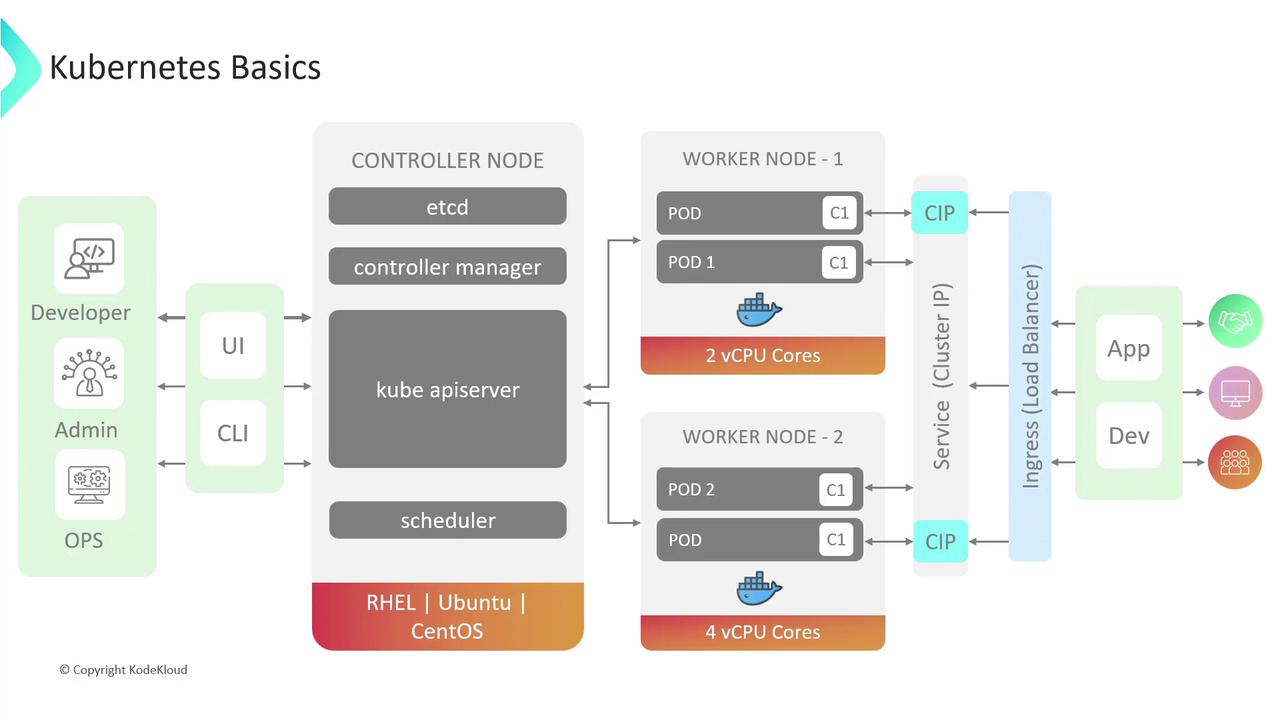
Kubernetes Architecture and Cluster Components
A Kubernetes cluster consists of control plane nodes and worker nodes. Control plane components manage and maintain cluster state, while worker nodes run application containers.| Component | Role | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| kube-apiserver | Central API endpoint | Validates and configures data for API objects. |
| etcd | Distributed key–value store | Stores all cluster data and configuration. |
| kube-controller-manager | Control loops to enforce desired state | Manages node health, replication, and endpoint tracking. |
| kube-scheduler | Pod placement based on resource availability | Assigns pods to suitable nodes. |
| kubelet (worker) | Node agent ensuring containers run as expected | Registers node with control plane and reports status. |
| kube-proxy (worker) | Networking and load balancing for pods | Maintains network rules on nodes. |
| Container runtime (worker) | Executes container images (e.g., Docker, CRI-O) | Interfaces with kubelet to pull and run containers. |
Pods and Workloads
A Pod is the smallest deployable unit in Kubernetes, encapsulating one or more containers that share:- A network namespace (IP address and ports)
- Shared storage volumes
- Container execution configuration
To achieve high availability and self-healing, wrap pods in higher-level controllers such as ReplicaSets and Deployments.
ReplicaSets and Deployments
- ReplicaSet: Ensures a specified number of pod replicas are running at any time.
- Deployment: Declaratively manages ReplicaSets to facilitate rolling updates and rollbacks.
Service Discovery and Networking
Kubernetes Services provide stable endpoints to access pods. Common types include:| Service Type | Scope | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| ClusterIP | Internal cluster only | Microservices communicating within the cluster. |
| NodePort | Static port on every node | Development or simple external access. |
| LoadBalancer | External cloud load balancer | Production traffic with a single public IP. |
Provisioning a
LoadBalancer service may incur additional cloud provider costs. Review your cloud network pricing before use.Ingress
Ingress resources enable advanced HTTP(S) routing:- Path-based routing: Route requests by URL path (e.g.,
/app1,/app2). - Host-based routing: Direct traffic based on hostname (e.g.,
app.example.com). - TLS termination: Consolidate HTTPS certificates at the edge.