GitHub Actions
Continuous Deployment with GitHub Actions
Workflow Setup Kubectl
In this guide, we’ll enhance our Solar System GitHub Actions workflow by installing the kubectl CLI on the runner. We’ll introduce a new job—dev-deploy—which deploys our application to the development Kubernetes namespace. This job will:
- Check out the code
- Install
kubectl - Validate cluster connectivity by fetching version and node details
Existing Workflow Overview
Below is the current workflow up to the docker job. It runs on pushes to the main branch or any feature/* branch, and it uses MongoDB credentials stored in GitHub Secrets and Variables.
name: Solar System Workflow
on:
workflow_dispatch:
push:
branches:
- main
- 'feature/*'
env:
MONGO_URI: mongodb+srv://supercluster.d3jj.mongodb.net/superData
MONGO_USERNAME: ${{ vars.MONGO_USERNAME }}
MONGO_PASSWORD: ${{ secrets.MONGO_PASSWORD }}
jobs:
unit-testing:
# …
code-coverage:
# …
docker:
name: Containerization
needs: [unit-testing, code-coverage]
permissions:
packages: write
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout Repo
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Docker Hub Login
uses: docker/[email protected]
with:
username: ${{ vars.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
- name: GHCR Login
uses: docker/[email protected]
with:
registry: ghcr.io
username: ${{ github.repository_owner }}
password: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
- name: Docker Build & Push
uses: docker/build-push-action@v4
with:
context: .
push: true
tags: |
${{ vars.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}/solar-system:${{ github.sha }}
ghcr.io/${{ github.repository_owner }}/solar-system:${{ github.sha }}
Job Summary
| Job Name | Purpose | Depends On |
|---|---|---|
| unit-testing | Run unit tests | – |
| code-coverage | Generate code coverage reports | unit-testing |
| docker | Build & push Docker images | unit-testing, code-coverage |
| dev-deploy | Install kubectl & verify cluster | docker |
Adding the dev-deploy Job
Append the following job after docker to install kubectl and fetch cluster details:
dev-deploy:
name: Deploy to Development Cluster
needs: docker
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout Repo
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Install kubectl CLI
uses: azure/setup-kubectl@v3
with:
version: 'v1.26.0'
- name: Fetch Kubernetes Cluster Details
run: |
kubectl version --short
echo "------------------------------"
kubectl get nodes
You can find the azure/setup-kubectl action in the GitHub Marketplace:
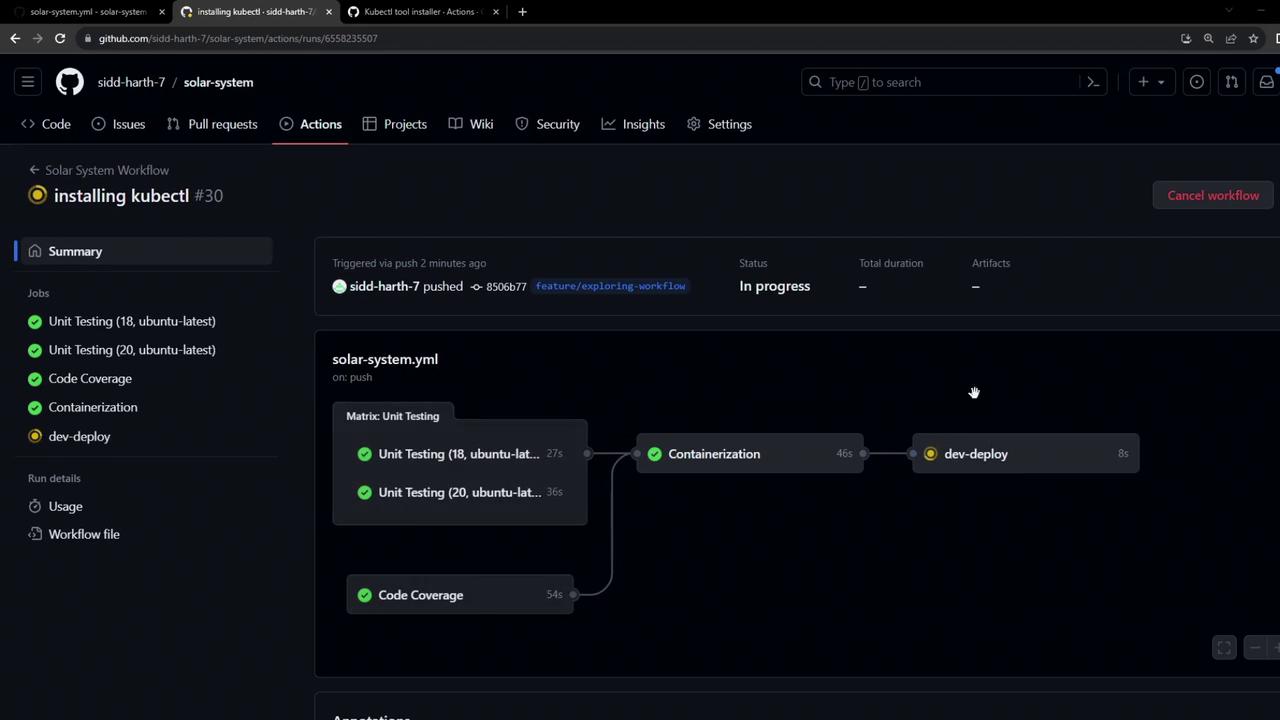
After committing with the message “Installing kubectl,” your workflow will trigger a new run:

You can then view the real-time progress of each step:
Troubleshooting: Kubeconfig Required
If you see an error like this, it means kubectl has no cluster context:
kubectl version --short
Client Version: v1.26.0
Error from server (Unauthorized): the server is currently unable to handle the request
Warning
You must provide a valid Kubeconfig so kubectl can authenticate with your Kubernetes API. Never commit this file to version control—store it as a GitHub Secret.
A typical kubeconfig looks like this:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Config
preferences: {}
clusters:
- cluster:
certificate-authority-data: <base64-encoded-ca>
server: https://example.k8s.cluster:6443
name: my-cluster
contexts:
- context:
cluster: my-cluster
namespace: default
user: my-cluster-admin
name: my-cluster-context
current-context: my-cluster-context
users:
- name: my-cluster-admin
user:
client-certificate-data: <base64-encoded-cert>
client-key-data: <base64-encoded-key>
Using the Kubeconfig in Your Workflow
- Add the Kubeconfig as a secret, e.g.,
KUBECONFIG_DATA. - Inject it into the runner and write it to
~/.kube/config:
- name: Configure Kubeconfig
run: |
mkdir -p ~/.kube
echo "${{ secrets.KUBECONFIG_DATA }}" | base64 --decode > ~/.kube/config
With this step in place, your dev-deploy job will authenticate successfully and you’ll see both version and node information printed.
Links and References
- GitHub Actions: Workflow Syntax
- azure/setup-kubectl Action
- Kubernetes Configuration Docs
- GitHub Secrets
Watch Video
Watch video content