GitHub Actions
Continuous Deployment with GitHub Actions
Workflow Deploy to Kubernetes Prod Environment
Deploying to a Kubernetes production cluster involves extending your existing CI/CD pipeline. In this guide, we’ll walk through updating a GitHub Actions workflow to add production deployment jobs, enforce environment protection rules, and validate your release.
1. Workflow Skeleton
Begin by defining the workflow trigger, environment variables, and placeholders for your jobs:
name: Solar System Workflow
on:
workflow_dispatch:
push:
branches:
- main
- 'feature/*'
env:
MONGO_URI: 'mongodb+srv://supercluster.d83jj.mongodb.net/superData'
MONGO_USERNAME: ${{ vars.MONGO_USERNAME }}
MONGO_PASSWORD: ${{ secrets.MONGO_PASSWORD }}
jobs:
unit-testing: {}
code-coverage: {}
docker: {}
dev-deploy: {}
dev-integration-testing: {}
2. Reference: Development Jobs
Use these dev-deploy and dev-integration-testing jobs as templates. They build, deploy to a development namespace, and verify the app is live.
dev-deploy:
name: Dev Deploy
needs: docker
environment:
name: development
url: ${{ steps.set-ingress-host.outputs.APP_INGRESS_HOST }}
outputs:
APP_INGRESS_HOST: ${{ steps.set-ingress-host.outputs.APP_INGRESS_HOST }}
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout Repository
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Install kubectl
uses: azure/setup-kubectl@v3
- name: Determine Ingress Host
id: set-ingress-host
run: |
HOST=$(kubectl -n ${{ vars.NAMESPACE }} \
get ingress -o jsonpath='{.items[0].spec.tls[0].hosts[0]}')
echo "APP_INGRESS_HOST=$HOST" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
dev-integration-testing:
name: Dev Integration Testing
needs: dev-deploy
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Validate Live Status
env:
URL: ${{ needs.dev-deploy.outputs.APP_INGRESS_HOST }}
run: |
echo "Testing https://$URL/live"
curl https://$URL/live -s -k | jq -r .status | grep -i live
For more on kubectl commands, see the kubectl Reference.
3. Adding Production Jobs
3.1 prod-deploy
Duplicate the dev-deploy job, adjust manifests, and target your production environment. This job also captures the load balancer IP for your Ingress controller.
prod-deploy:
name: Prod Deploy
needs: dev-integration-testing
environment:
name: production
url: https://${{ steps.set-ingress-host.outputs.APP_INGRESS_HOST }}
outputs:
APP_INGRESS_HOST: ${{ steps.set-ingress-host.outputs.APP_INGRESS_HOST }}
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout Repository
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Install kubectl
uses: azure/setup-kubectl@v3
- name: Capture Nginx Ingress IP
run: |
IP=$(kubectl -n ingress-nginx get svc ingress-nginx-controller \
-o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
echo "INGRESS_IP=$IP" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: Replace Tokens in Manifests
uses: cscheidlen/replace-tokens@v1
with:
tokenPrefix: '_'
tokenSuffix: '_'
files: ["kubernetes/production/*.yaml"]
env:
NAMESPACE: ${{ vars.NAMESPACE }}
REPLICAS: ${{ vars.REPLICAS }}
IMAGE: ${{ vars.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}/solar-system:${{ github.sha }}
INGRESS_IP: ${{ env.INGRESS_IP }}
- name: Preview Production Manifests
run: cat kubernetes/production/*.yaml
- name: Deploy to Production
run: kubectl apply -f kubernetes/production
- name: Determine Ingress Host
id: set-ingress-host
run: |
HOST=$(kubectl -n ${{ vars.NAMESPACE }} \
get ingress -o jsonpath='{.items[0].spec.tls[0].hosts[0]}')
echo "APP_INGRESS_HOST=$HOST" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
3.2 prod-integration-testing
Once the production deploy finishes, verify the live endpoint:
prod-integration-testing:
name: Prod Integration Testing
needs: prod-deploy
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Validate Production Live Status
env:
URL: ${{ needs.prod-deploy.outputs.APP_INGRESS_HOST }}
run: |
echo "Testing https://$URL/live"
curl https://$URL/live -s -k | jq -r .status | grep -i live
4. Consolidated Jobs Table
| Job Name | Description | Depends On |
|---|---|---|
| unit-testing | Run unit tests | – |
| code-coverage | Measure test coverage | unit-testing |
| docker | Build and push Docker image | code-coverage |
| dev-deploy | Deploy to development namespace | docker |
| dev-integration-testing | Smoke-test development deployment | dev-deploy |
| prod-deploy | Deploy to production namespace | dev-integration-testing |
| prod-integration-testing | Smoke-test production deployment | prod-deploy |
5. Running the Workflow
- Commit and push your changes to
mainor afeature/*branch. - Trigger the workflow manually or via a push event.
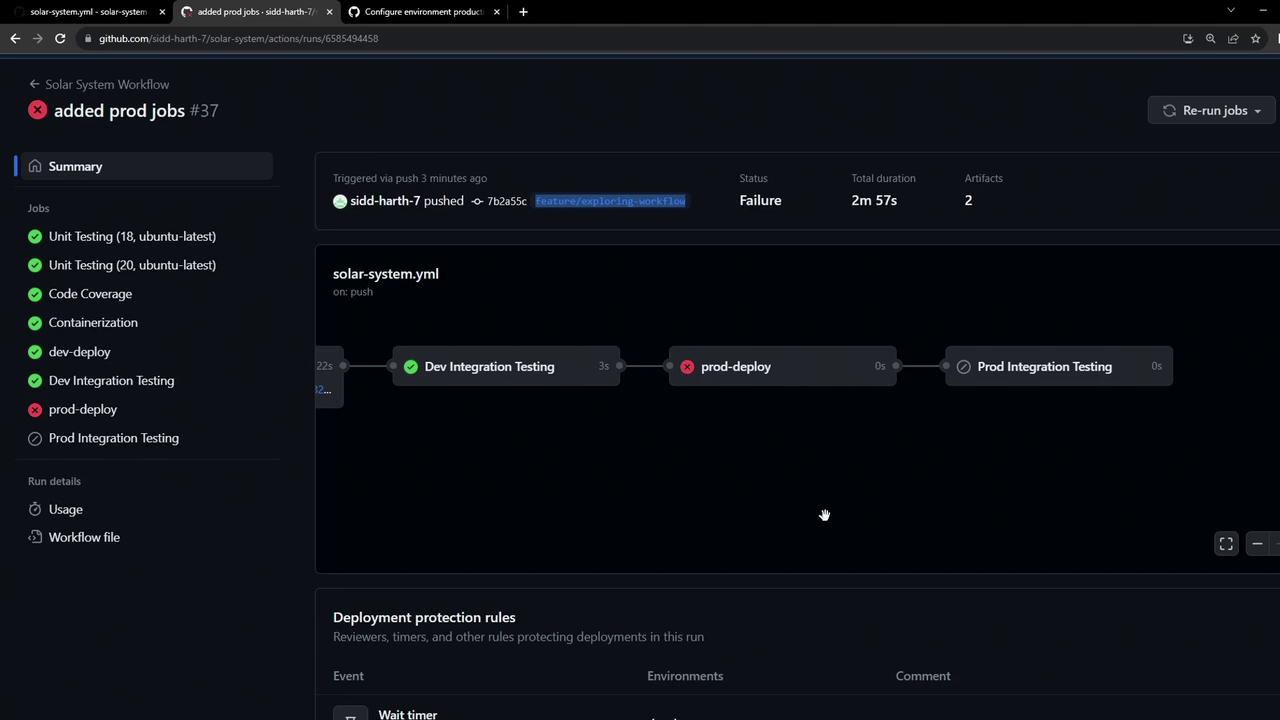
- Monitor the sequential execution: dev jobs ➔ prod-deploy ➔ prod-integration-testing.
Note
If prod-deploy is blocked by branch protection or environment rules, you’ll see an error and the integration test will be skipped.
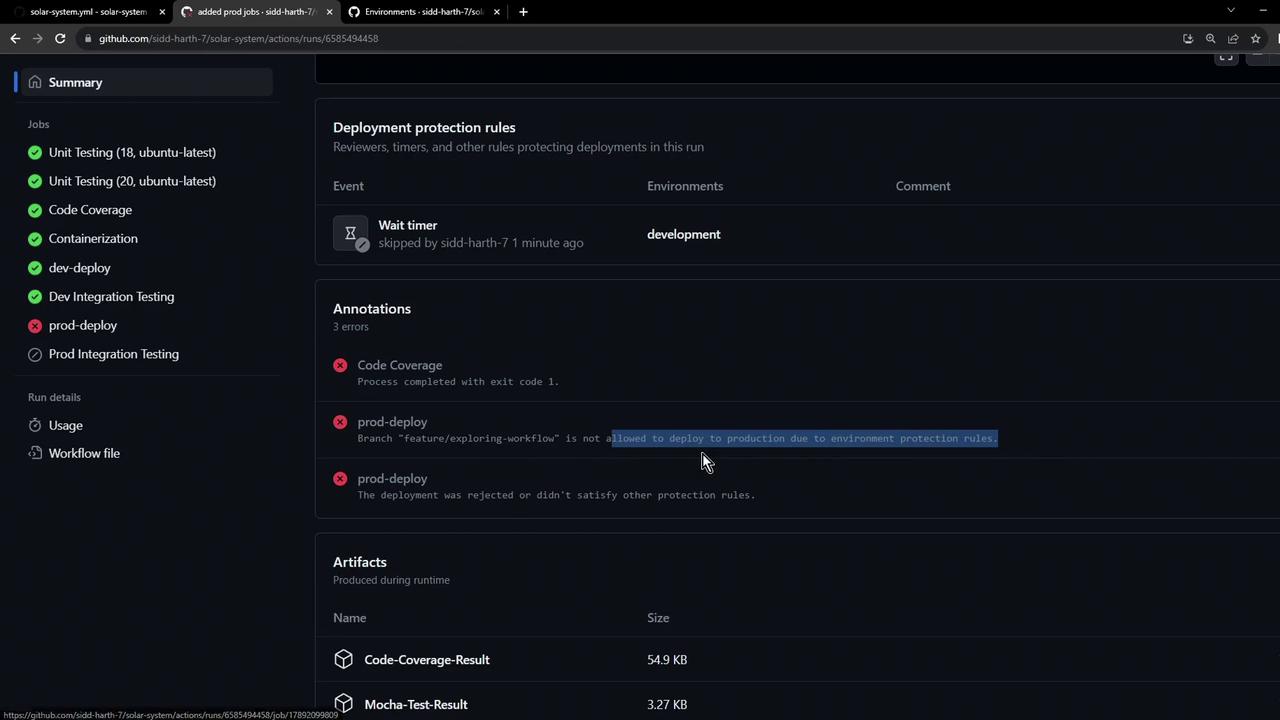
6. Environment Protection Rules
Configure deployment protection rules in your repository settings to enforce review policies, wait timers, or required approvals before production deployments.
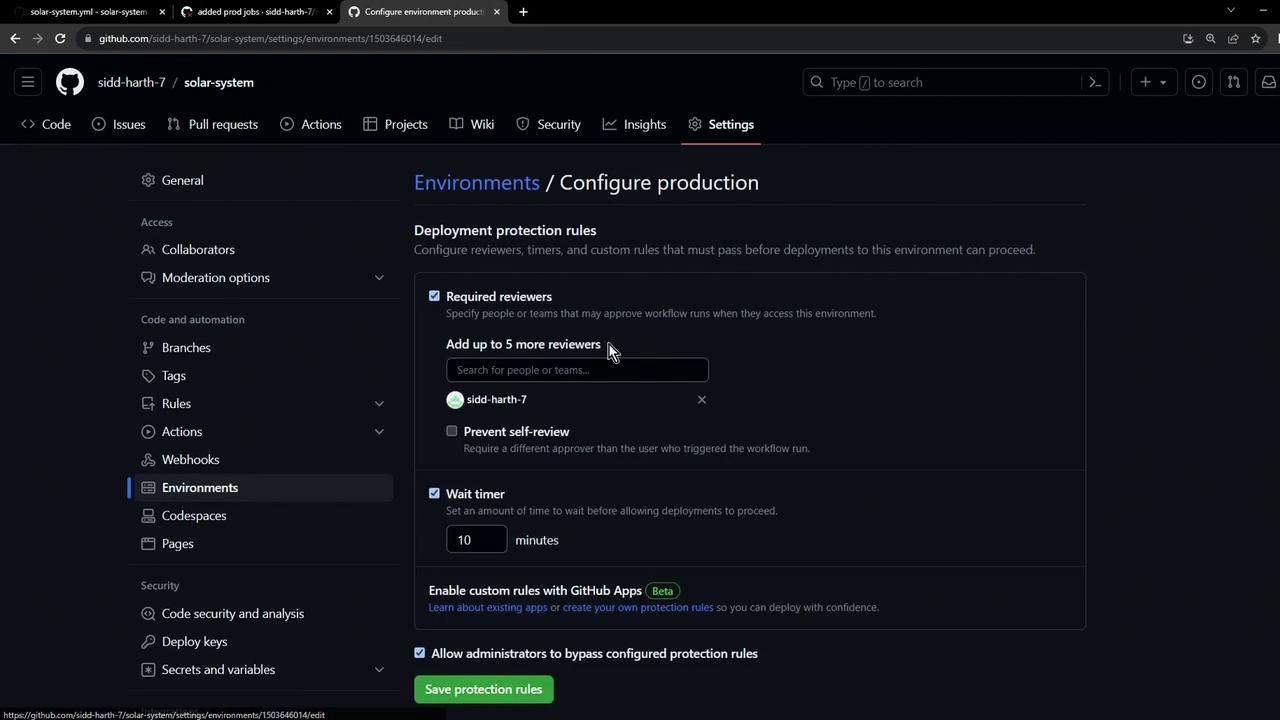
Warning
Triggering from an unauthorized branch (e.g., a feature branch without approval) will block prod-deploy. Subsequent jobs will be skipped.
Links and References
- GitHub Actions Documentation
- Kubernetes Basics
- azure/setup-kubectl
- cscheidlen/replace-tokens GitHub Action
Watch Video
Watch video content