GitHub Actions
Security Guide
Security hardening for GitHub Actions
In this guide, we’ll cover essential best practices to secure your GitHub Actions workflows. By implementing these measures—encrypting secrets, leveraging OIDC, sanitizing inputs, and vetting third-party actions—you’ll greatly reduce your CI/CD attack surface.
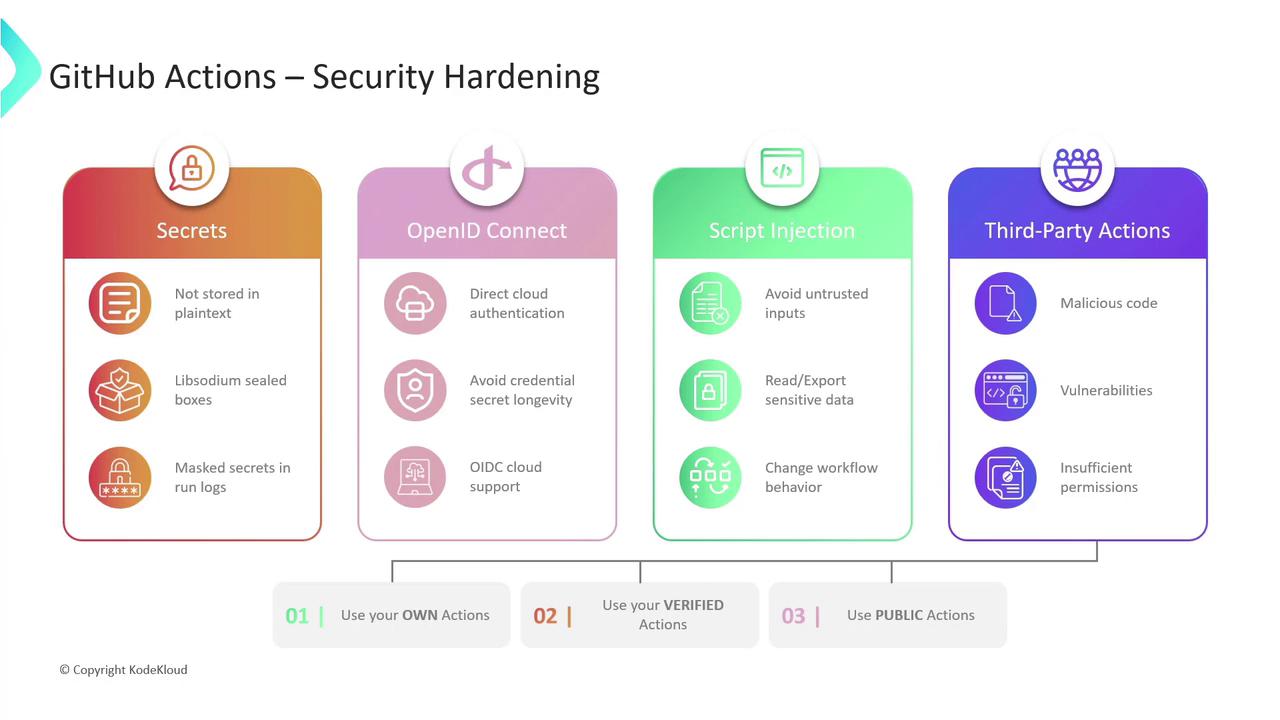
1. Secure Storage of Sensitive Information
Never commit credentials or tokens in plaintext. Instead, store them in GitHub Secrets, which are encrypted at rest and in transit using Libsodium sealed boxes. Secrets can be defined at the organization, repository, or environment level. GitHub also masks secret values in workflow logs to prevent accidental exposure.
Warning
Avoid embedding any sensitive data directly in your YAML. Always reference secrets using ${{ secrets.YOUR_SECRET_NAME }}.
2. OpenID Connect (OIDC)
Rather than managing long-lived cloud credentials, configure your workflows to request short-lived tokens via OpenID Connect (OIDC). When you trust GitHub’s OIDC issuer in AWS, Azure, or GCP, your jobs can assume roles or service accounts on the fly—without secrets.
Note
Before enabling OIDC, update your cloud trust policies to accept tokens from token.actions.githubusercontent.com.
3. Mitigating Script Injection Attacks
Workflows often process inputs from environment variables, third-party services, or user parameters. Malicious actors can exploit improper handling to inject commands or scripts.
- Sanitize and validate all external inputs.
- Avoid building shell commands via string concatenation.
- Use strongly typed inputs in custom actions (e.g.,
boolean,integer). - Run untrusted code inside containerized steps to provide isolation.
Warning
Never pass unescaped variables directly into run: blocks. Use parameterized inputs instead.
4. Evaluating Third-Party Actions
While reusable actions streamline your workflows, they can introduce risks:
- Malicious logic: Hidden backdoors or exfiltration code
- Undisclosed vulnerabilities: Bugs exploitable after installation
- Excessive permissions: Actions requesting more scopes than necessary
| Action Source | Risk | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Community (unverified) | Malicious code, unknown vulnerabilities | Review source, pin to commit SHA, grant minimal scopes |
| GitHub-verified Marketplace | Lower review risk | Confirm blue check, pin versions, audit permissions |
| Custom internal actions | Full control | Maintain code, update dependencies, enforce least privilege |
Best Practices
- Author and maintain your own actions when possible.
- Combine internal actions with verified Marketplace actions.
- Pin action versions to a specific tag or commit SHA to prevent unexpected changes.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content