GitHub-Hosted Runners
GitHub-hosted runners are virtual machines maintained by GitHub. Each time a workflow is triggered, you get a fresh environment with pre-installed tools, reducing setup time and maintenance overhead.Supported Environments
- Ubuntu (ubuntu-latest, ubuntu-22.04, ubuntu-20.04)
- Windows (windows-latest, windows-2019)
- macOS (macos-latest, macos-11)
Example: Matrix Build Workflow
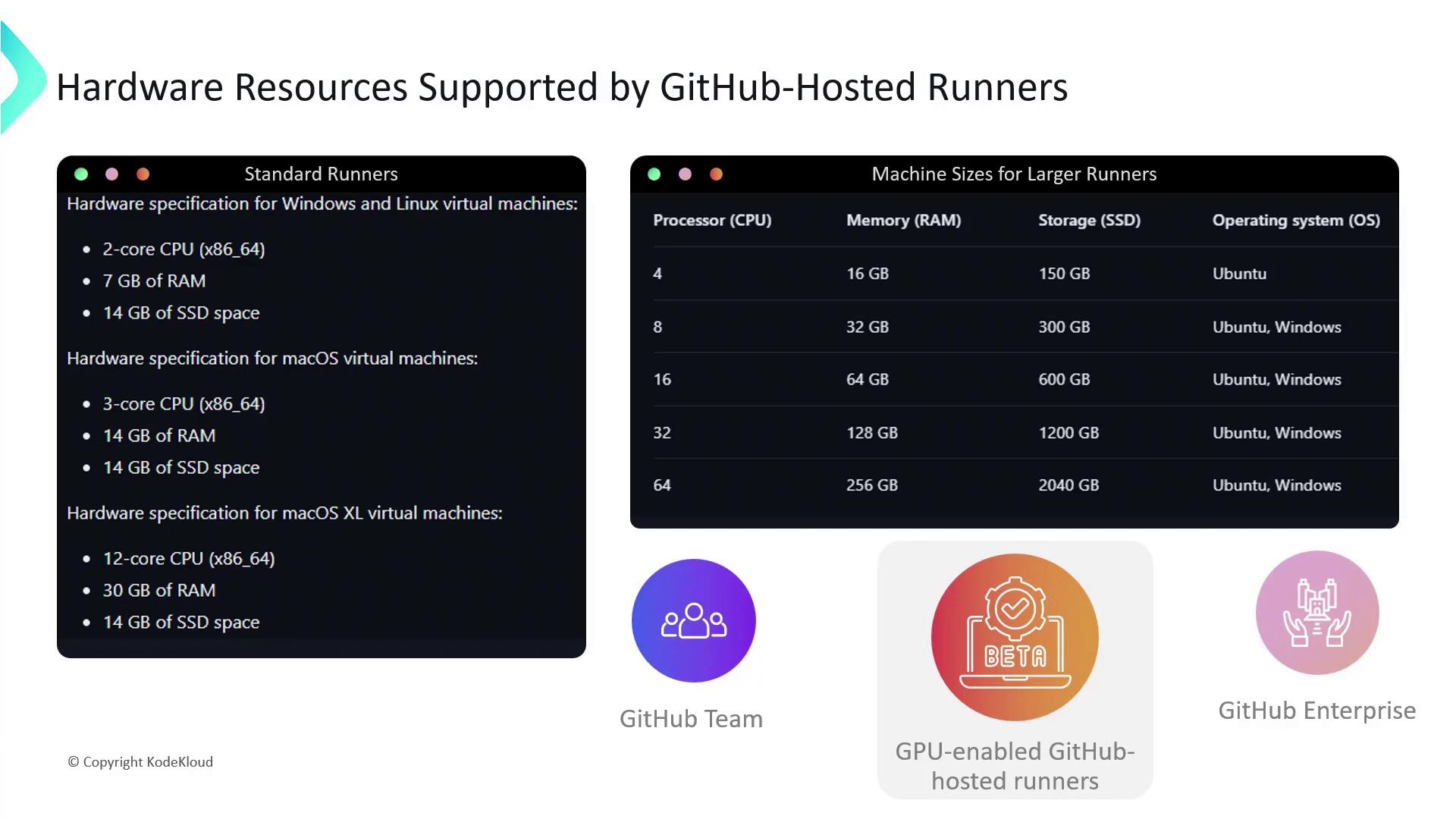
The following workflow runs unit tests across multiple OS environments using job matrices:- Standard runners: Suitable for most CI/CD tasks with moderate CPU, memory, and SSD.
- Larger runners: (GitHub Teams and Enterprise Cloud) Offer more CPU cores, RAM, and disk space.
GPU-enabled GitHub-hosted runners are currently in beta. Apply for the beta program if you require GPU resources.
Self-Hosted Runners
Self-hosted runners run on machines that you provision and manage. They provide full control over hardware, operating system, and installed software—ideal for custom requirements or compliance needs.Key Benefits
- Custom OS and software configurations
- Compliance with strict security policies
- Dedicated compute resources (no shared queue delays)
- Horizontal scaling and autoscaling
- Geographic placement for low-latency or data residency
- Navigate to Settings → Actions → Runners.
- Click Add runner, then select your operating system and architecture.
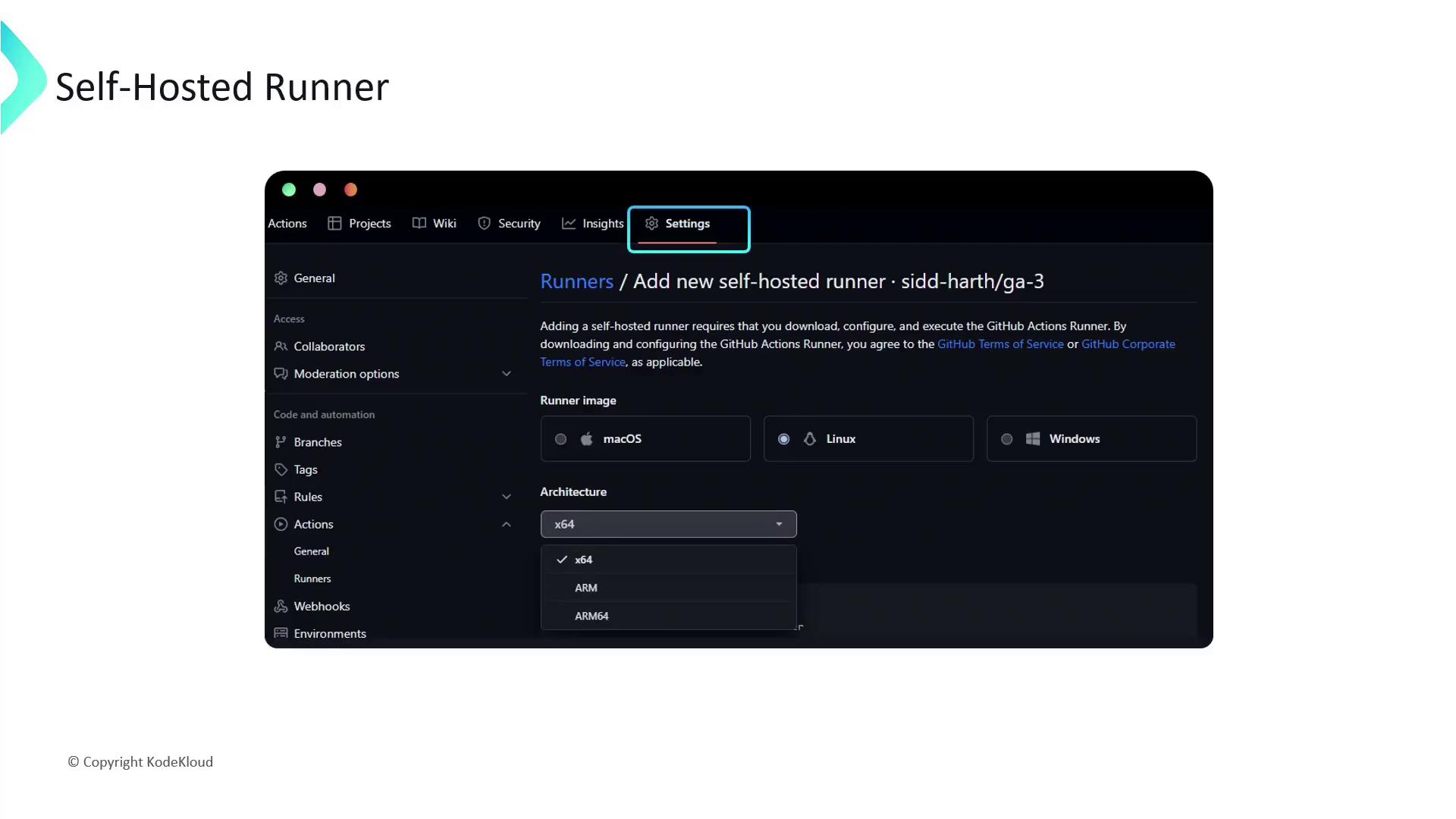
Installation and Configuration
Follow these steps to install and configure a self-hosted runner:runs-on field:
Maintaining self-hosted runners requires you to manage updates, security patches, and uptime. Ensure you have monitoring and backup strategies in place.
Comparison: GitHub-Hosted vs. Self-Hosted
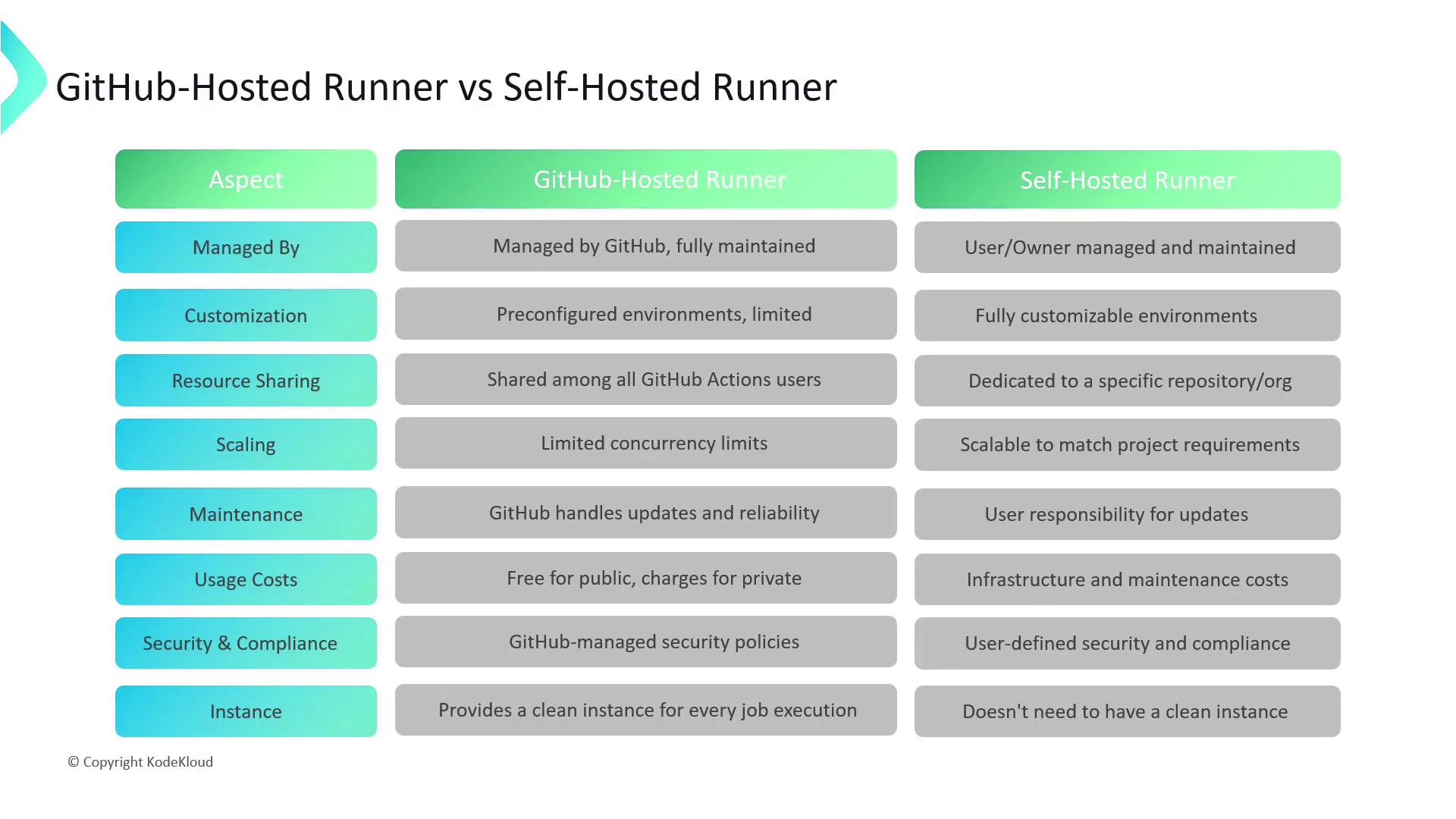
| Feature | GitHub-Hosted | Self-Hosted |
|---|---|---|
| Management | Maintained by GitHub | Managed by you or your organization |
| Customization | Predefined environments | Fully customizable |
| Resource Sharing | Shared pool with concurrency limits | Dedicated resources |
| Scaling | Fixed concurrency | Dynamic scaling |
| Maintenance | Automatic updates by GitHub | Manual updates and patching |
| Usage Costs | Free for public, paid quotas for private | Infrastructure & maintenance costs |
| Security & Compliance | GitHub’s security policies | Your own security measures |
| Instance Handling | Fresh VM per job | Persistent runner for multiple jobs |