GitLab CI/CD: Architecting, Deploying, and Optimizing Pipelines
Architecture Core Concepts
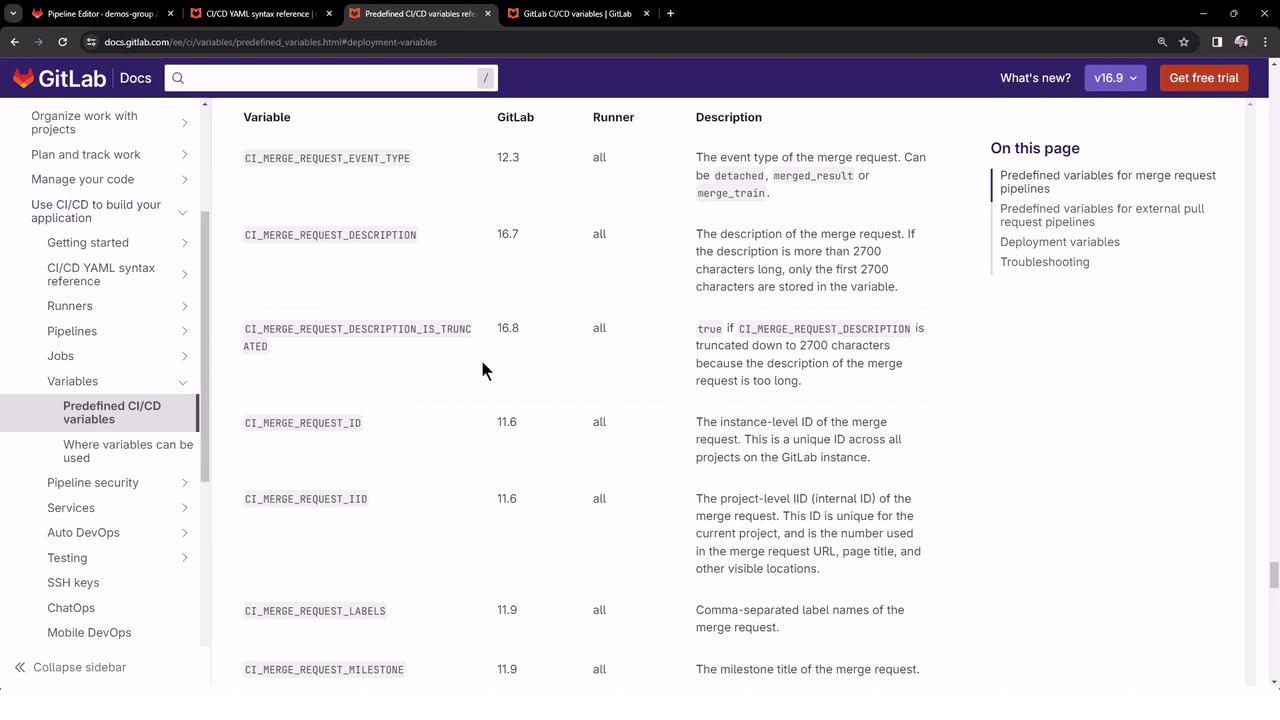
Exploring Predefined CICD Variables
In this lesson we explore GitLab’s predefined CI/CD variables—auto-generated environment variables that provide contextual information about jobs, pipelines, repositories, and more. Leveraging these variables makes your pipelines flexible and secure by avoiding hardcoded values.
For a complete list of all predefined variables, see the GitLab Documentation on Predefined CI/CD Variables.
Categories of Predefined Variables
| Category | Available In | Usage Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Pipeline-level Variables | Pipeline config & job scripts | Detect pipeline source, IDs, status |
| Runner-level Variables | Job execution | Access runner-specific details (e.g., shell, token) |
| Merge Request Variables | Merge request pipelines | Retrieve MR labels, branches, title |
Inspecting All Available Variables
To view every environment variable supplied to a CI job, add a job that runs the export command:
export CI_JOB_ID="50"
export CI_COMMIT_SHA="1ecfd27573eff1d6b4844ea3168962458c9f27a"
export CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA="1ecfd275"
export CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME="main"
export CI_REPOSITORY_URL="https://gitlab-ci-token:[masked]@example.com/gitlab-org/gitlab.git"
export CI_COMMIT_TAG="1.0.0"
export CI_JOB_NAME="spec:other"
export CI_JOB_STAGE="test"
export CI_JOB_MANUAL="true"
export CI_JOB_TRIGGERED="true"
export CI_PIPELINE_ID="1000"
export CI_PIPELINE_IID="10"
export CI_PAGES_DOMAIN="gitlab.io"
export CI_PAGES_URL="https://gitlab-org.gitlab.io/gitlab"
1. Creating a New GitLab Project
- Navigate to your GitLab instance and click New project.
- Select Create blank project, choose a group (e.g.,
demos-group), set visibility to Public, and initialize with a README. - Clone the repository locally or open it in the Web IDE.
Create a .gitlab-ci.yml file at the root of your project:
workflow:
name: Exploring Predefined Variable Pipeline
export_variable_job:
script:
- export
generic_predefined_variables:
script: |
echo "GITLAB_USER_LOGIN = $GITLAB_USER_LOGIN"
echo "GITLAB_USER_EMAIL = $GITLAB_USER_EMAIL"
echo "CI_COMMIT_AUTHOR = $CI_COMMIT_AUTHOR"
echo "CI_COMMIT_BRANCH = $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH"
echo "CI_PROJECT_NAME = $CI_PROJECT_NAME"
echo "CI_PROJECT_URL = $CI_PROJECT_URL"
echo "CI_JOB_STAGE = $CI_JOB_STAGE"
echo "CI_PIPELINE_NAME = $CI_PIPELINE_NAME"
echo "CI_PIPELINE_ID = $CI_PIPELINE_ID"
echo "CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE = $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE"
merge_request_predefined_variables:
script: |
echo "CI_MERGE_REQUEST_LABELS = $CI_MERGE_REQUEST_LABELS"
echo "CI_MERGE_REQUEST_TARGET_BRANCH_NAME = $CI_MERGE_REQUEST_TARGET_BRANCH_NAME"
echo "CI_MERGE_REQUEST_ASSIGNEES = $CI_MERGE_REQUEST_ASSIGNEES"
echo "CI_MERGE_REQUEST_SOURCE_BRANCH_NAME = $CI_MERGE_REQUEST_SOURCE_BRANCH_NAME"
echo "CI_MERGE_REQUEST_TITLE = $CI_MERGE_REQUEST_TITLE"
Commit and push your changes to trigger the pipeline:
git add .gitlab-ci.yml
git commit -m "Add predefined variable exploration pipeline"
git push origin main
2. Pipeline Overview
Once pushed, GitLab triggers a pipeline named Exploring Predefined Variable Pipeline. By default, all jobs run in the test stage and execute in parallel:
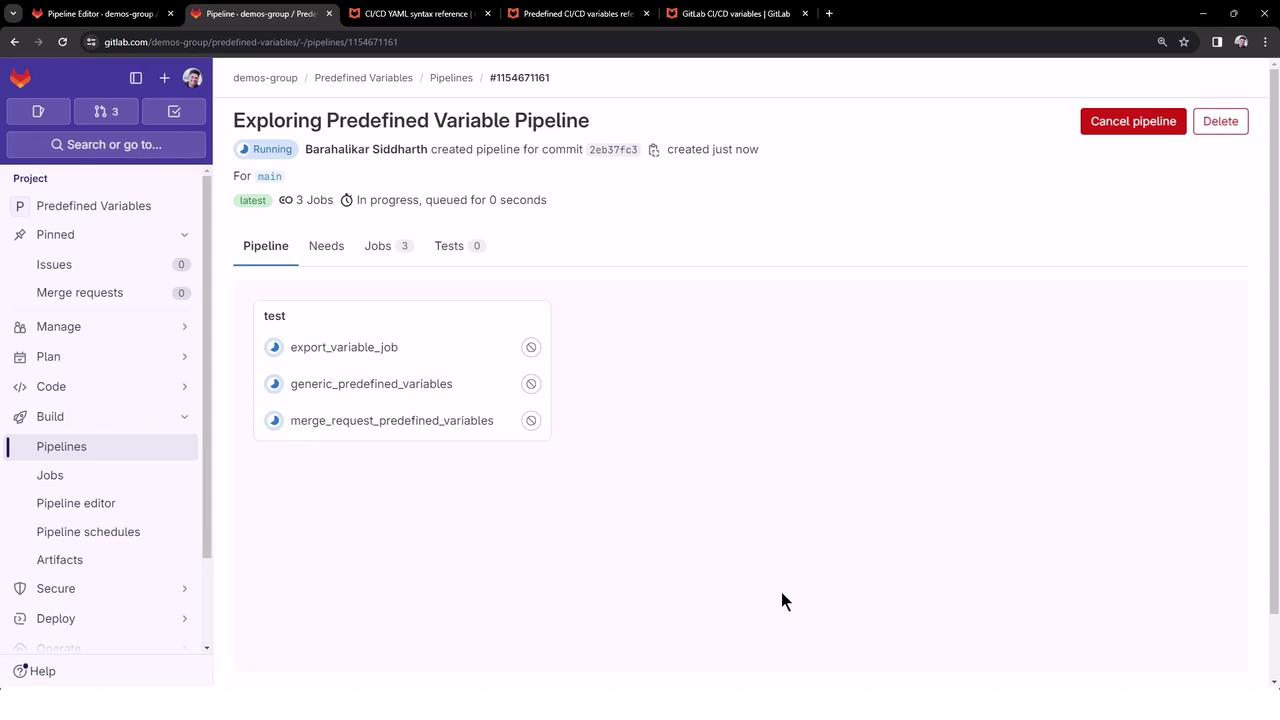
2.1 export_variable_job
This job dumps all environment variables. Here’s a truncated output:
$ export
declare -x CI="true"
declare -x CI_API_GRAPHQL_URL="https://gitlab.com/api/graphql"
declare -x CI_API_V4_URL="https://gitlab.com/api/v4"
declare -x CI_BUILD_ID="6035315241"
declare -x CI_COMMIT_SHA="2eb37fc3a7591ffecfbab205433395b34ef4a88c"
declare -x CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME="main"
declare -x CI_JOB_ID="6035315241"
declare -x CI_JOB_NAME="export_variable_job"
declare -x CI_JOB_STAGE="test"
declare -x CI_PIPELINE_ID="1154671161"
declare -x CI_PIPELINE_NAME="Exploring Predefined Variable Pipeline"
declare -x CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE="push"
# … plus over 100 more variables
Warning
Running export will print all environment variables, including sensitive tokens. Ensure your job logs are protected.
2.2 generic_predefined_variables
This job echoes commonly used variables to illustrate dynamic scripting:
$ echo "GITLAB_USER_LOGIN = $GITLAB_USER_LOGIN"
GITLAB_USER_LOGIN = sidd-harth
$ echo "GITLAB_USER_EMAIL = $GITLAB_USER_EMAIL"
GITLAB_USER_EMAIL = [email protected]
$ echo "CI_COMMIT_AUTHOR = $CI_COMMIT_AUTHOR"
CI_COMMIT_AUTHOR = Barahalikar Siddharth <[email protected]>
$ echo "CI_COMMIT_BRANCH = $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH"
CI_COMMIT_BRANCH = main
$ echo "CI_PROJECT_NAME = $CI_PROJECT_NAME"
CI_PROJECT_NAME = predefined-variables
$ echo "CI_PROJECT_URL = $CI_PROJECT_URL"
CI_PROJECT_URL = https://gitlab.com/demos-group/predefined-variables
$ echo "CI_JOB_STAGE = $CI_JOB_STAGE"
CI_JOB_STAGE = test
$ echo "CI_PIPELINE_ID = $CI_PIPELINE_ID"
CI_PIPELINE_ID = 1154671161
$ echo "CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE = $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE"
CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE = push
Use these variables to customize your jobs based on commit metadata and pipeline context.
2.3 merge_request_predefined_variables
This job attempts to print merge-request–specific variables:
$ echo "CI_MERGE_REQUEST_LABELS = $CI_MERGE_REQUEST_LABELS"
CI_MERGE_REQUEST_LABELS =
$ echo "CI_MERGE_REQUEST_TARGET_BRANCH_NAME = $CI_MERGE_REQUEST_TARGET_BRANCH_NAME"
CI_MERGE_REQUEST_TARGET_BRANCH_NAME =
$ echo "CI_MERGE_REQUEST_ASSIGNEES = $CI_MERGE_REQUEST_ASSIGNEES"
CI_MERGE_REQUEST_ASSIGNEES =
$ echo "CI_MERGE_REQUEST_SOURCE_BRANCH_NAME = $CI_MERGE_REQUEST_SOURCE_BRANCH_NAME"
CI_MERGE_REQUEST_SOURCE_BRANCH_NAME =
$ echo "CI_MERGE_REQUEST_TITLE = $CI_MERGE_REQUEST_TITLE"
CI_MERGE_REQUEST_TITLE =
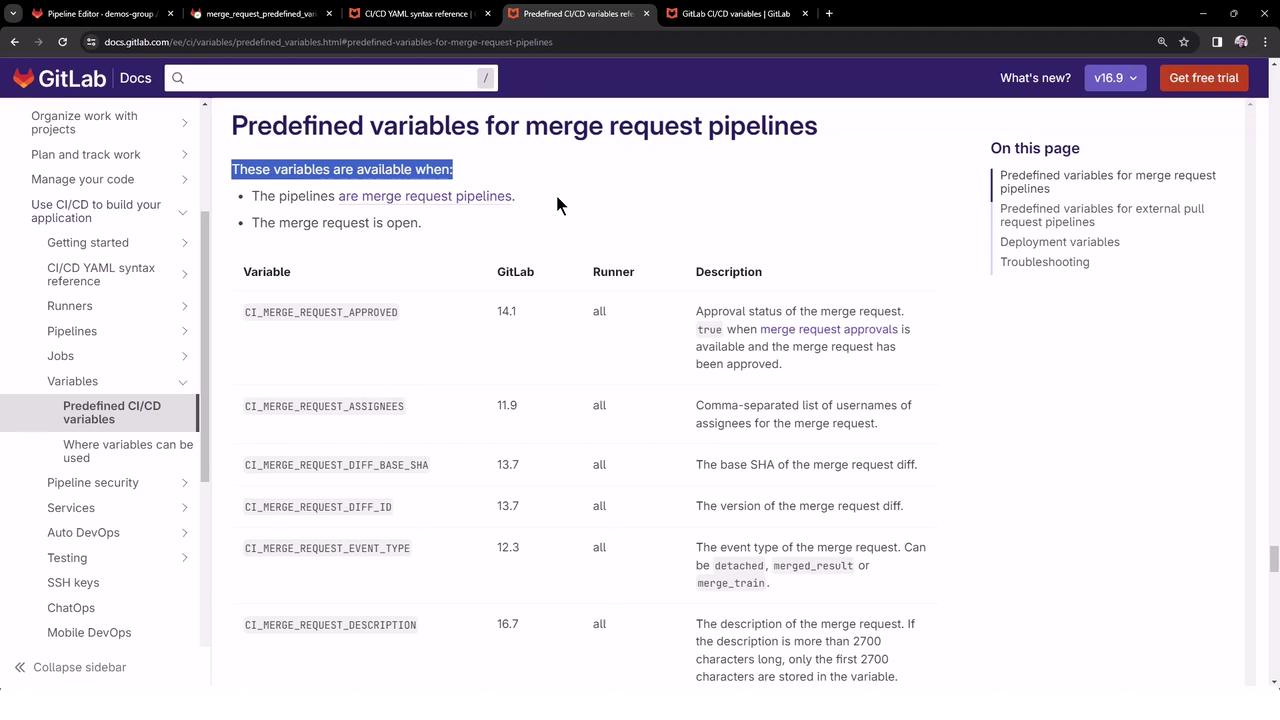
Note
Merge request variables are only populated in pipelines triggered by Merge Requests. In direct pushes, these remain empty.
For more on Merge Request CI/CD variables, see the GitLab Merge Request Variables documentation.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content