Timed Incremental Rollout Strategy
A timed incremental rollout gradually shifts traffic in phases:- Step 1: 10% traffic
- Step 2: 25% traffic
- Step 3: 50% traffic
- Step 4: 100% traffic
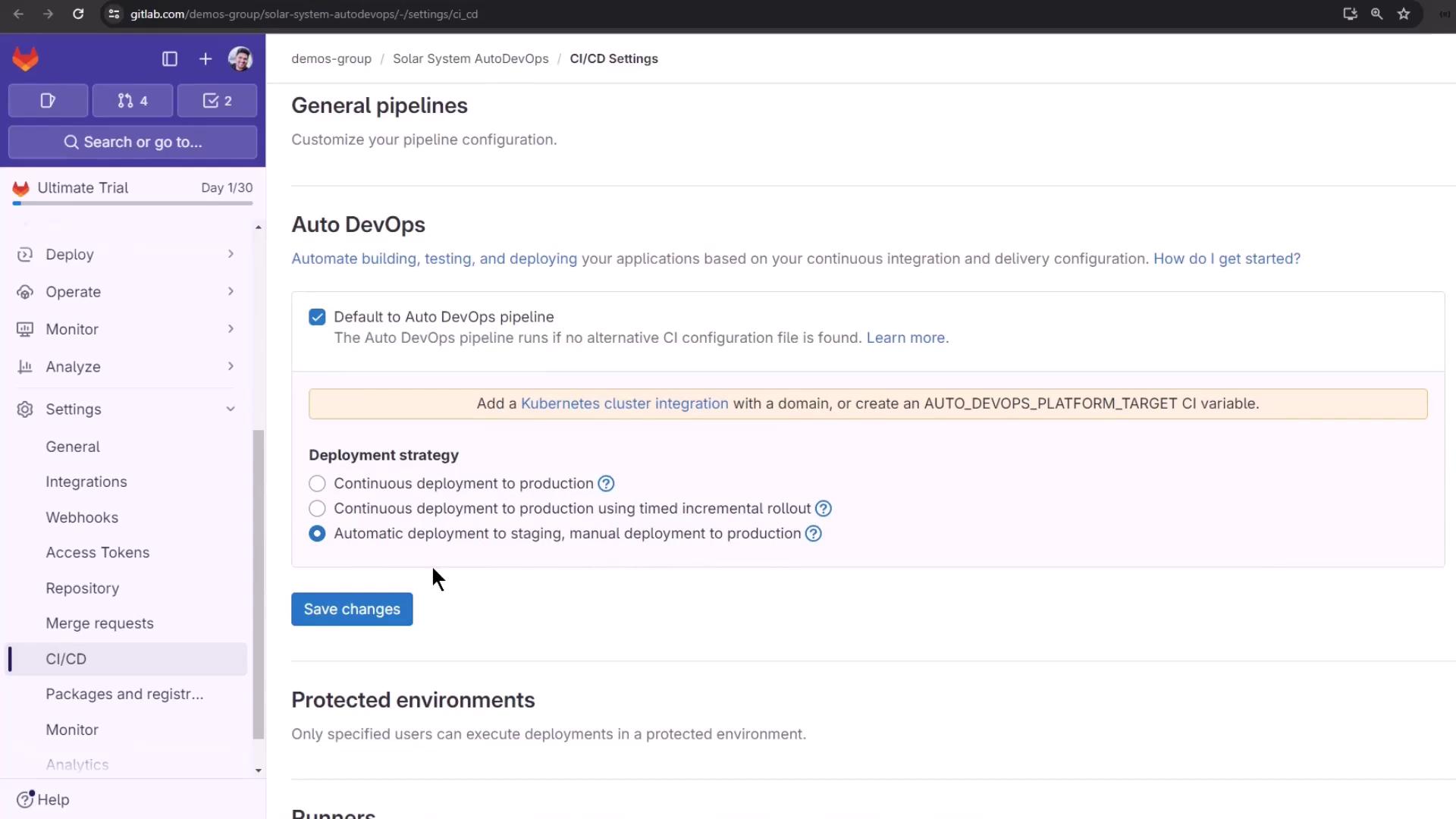
- Go to Settings > CI/CD > Auto DevOps
- Select Continuous deployment to production using timed incremental rollout
- Click Save changes
Adjust the interval between rollout steps by setting the
AUTO_DEPLOY_WAIT_TIME variable in your .gitlab-ci.yml or project settings.Reviewing Current Pipelines
Out of the box, Auto DevOps runs up to 17 jobs across multiple stages. You can disable unused jobs—like certain tests or scans—to speed up your pipeline while retaining essential checks like secret detection.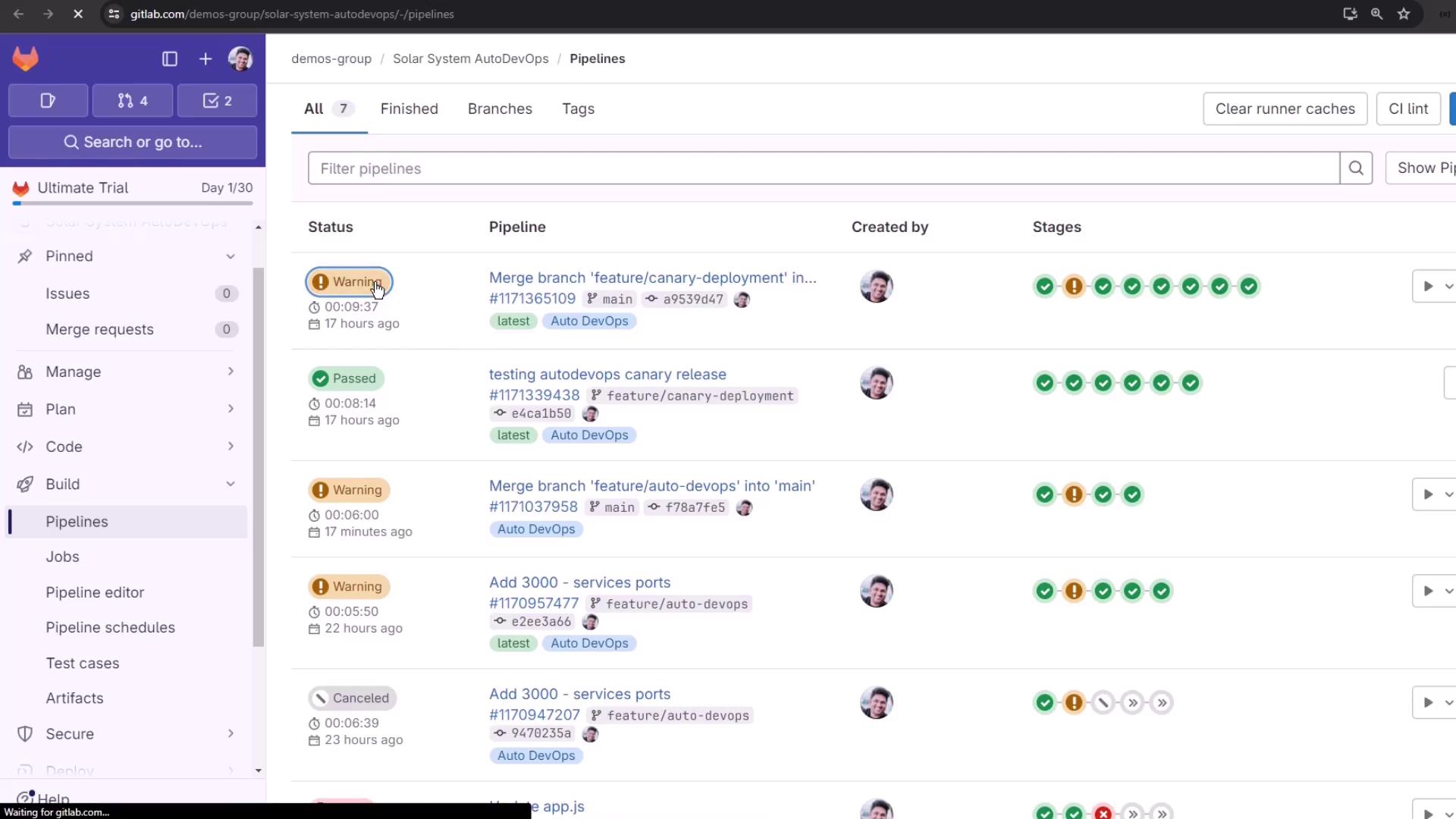
Adding Your Own .gitlab-ci.yml
Override or extend Auto DevOps by adding a custom CI configuration file at your repository root:
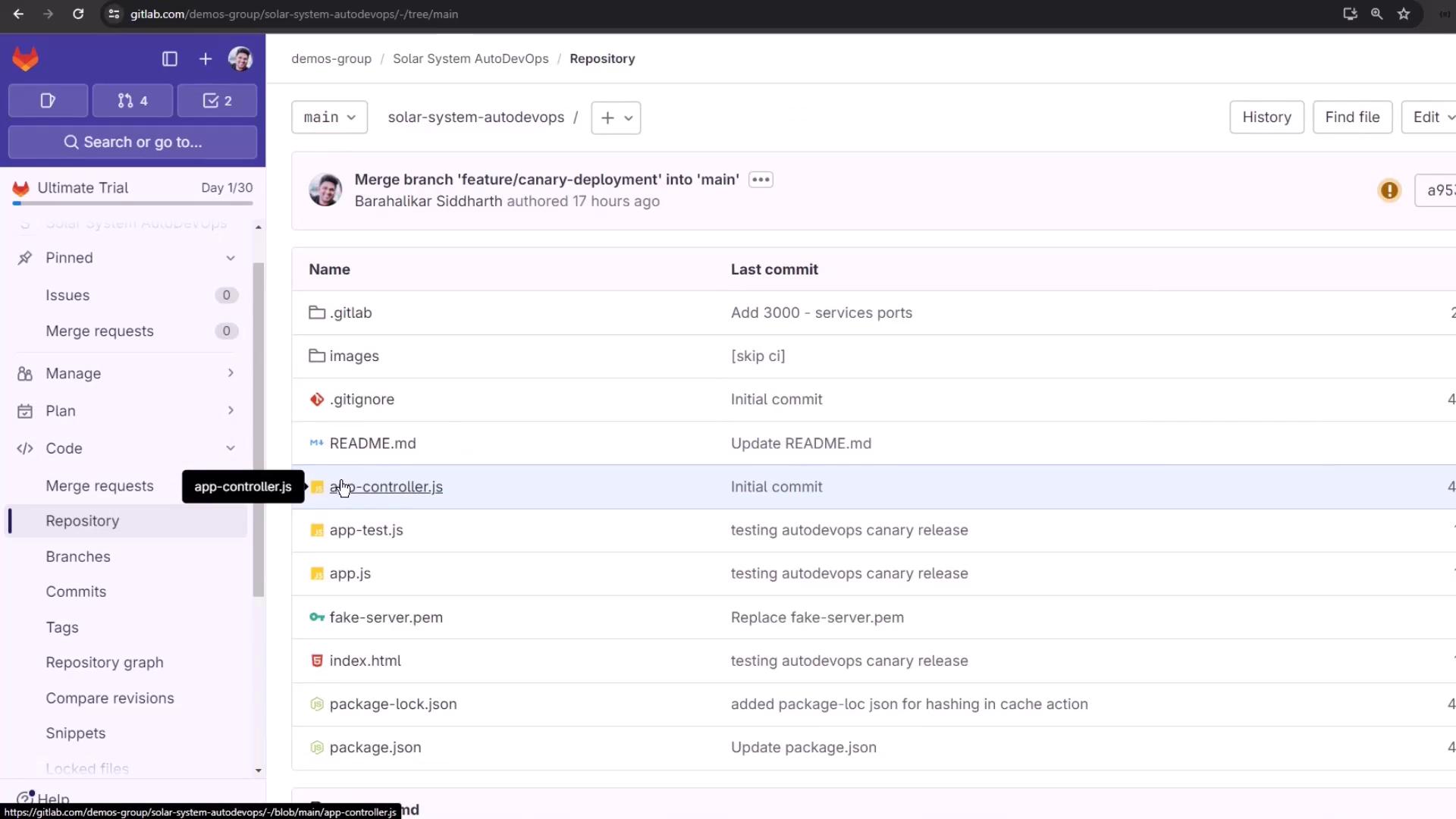
- In Files, click + and name the file
.gitlab-ci.yml. - Choose Apply a template or start from scratch.
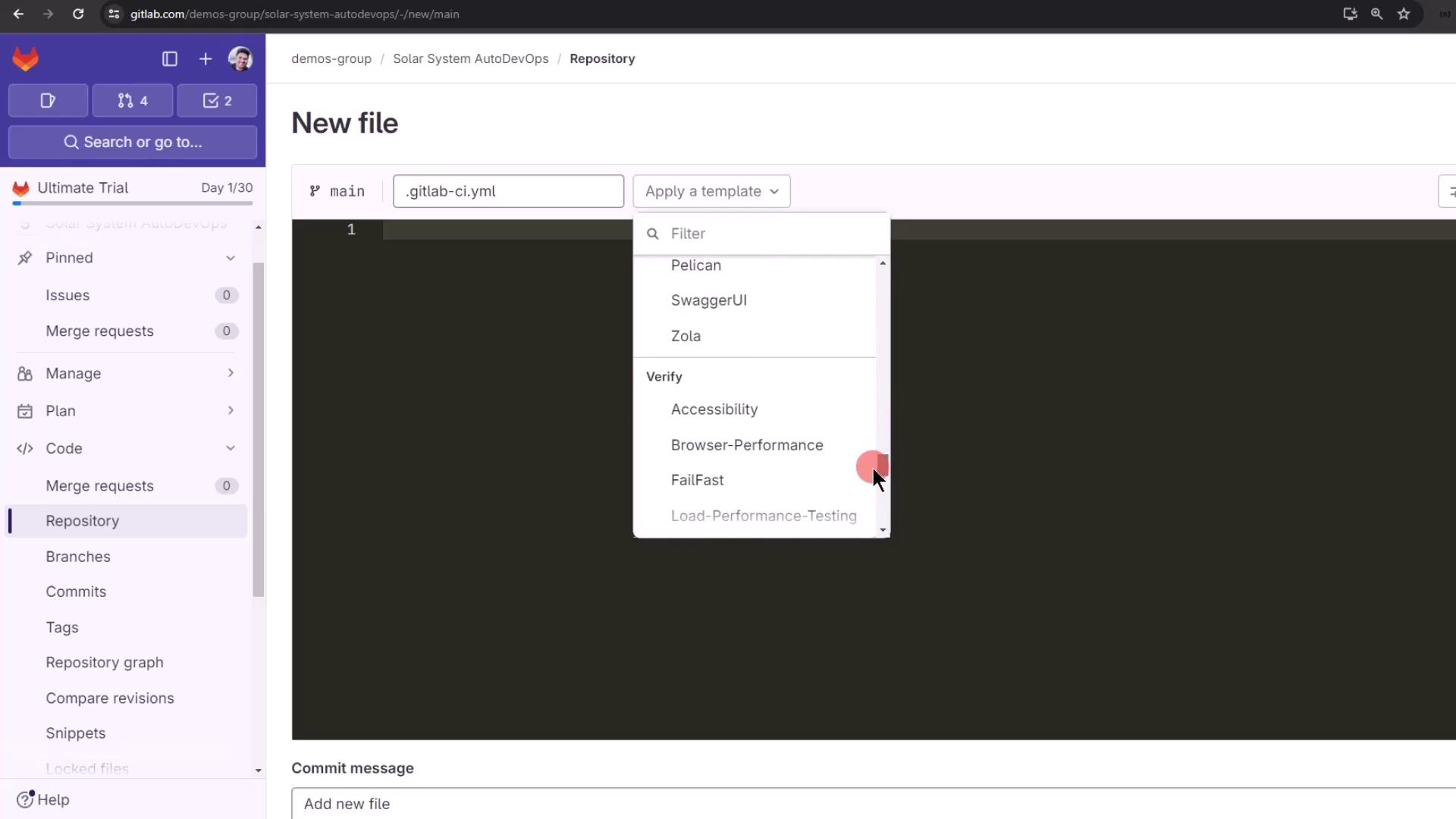
Including the Auto DevOps Template
Pull in the default Auto DevOps jobs without copying the full configuration: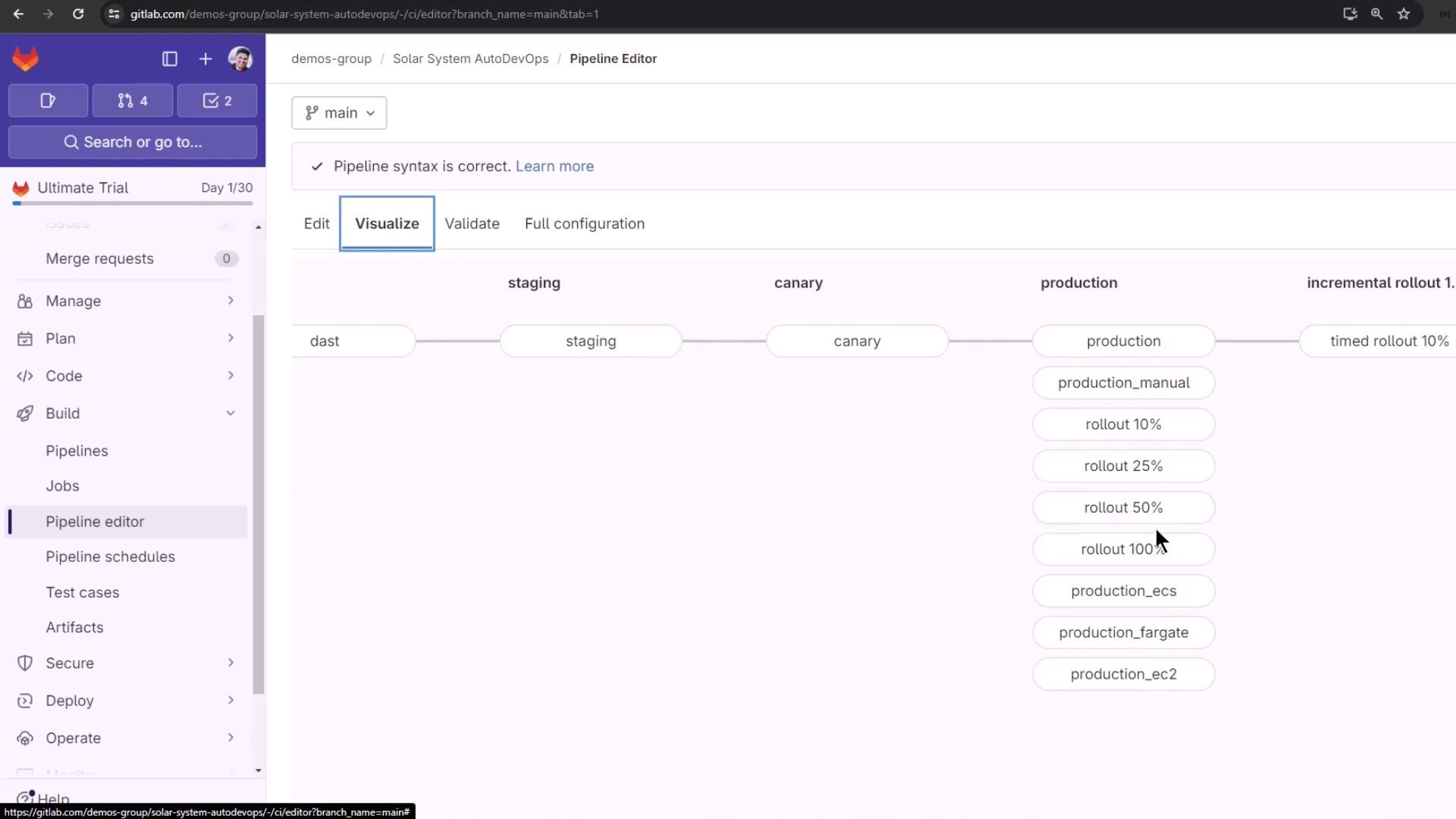
Auto DevOps Variables
The default template defines many variables you can override:| Variable | Purpose | Example Default |
|---|---|---|
AUTO_BUILD_IMAGE_VERSION | Build image version | v1.51.0 |
AUTO_DEPLOY_IMAGE_VERSION | Deploy image version | v2.80.1 |
DAST_VERSION | Version of DAST scans | 4 |
SECURE_ANALYZERS_PREFIX | Registry prefix for security analyzers | $CI_TEMPLATE_REGISTRY_HOST |
POSTGRES_USER | Username for review app database | user |
POSTGRES_PASSWORD | Password for review app database | testing-password |
.gitlab-ci.yml.
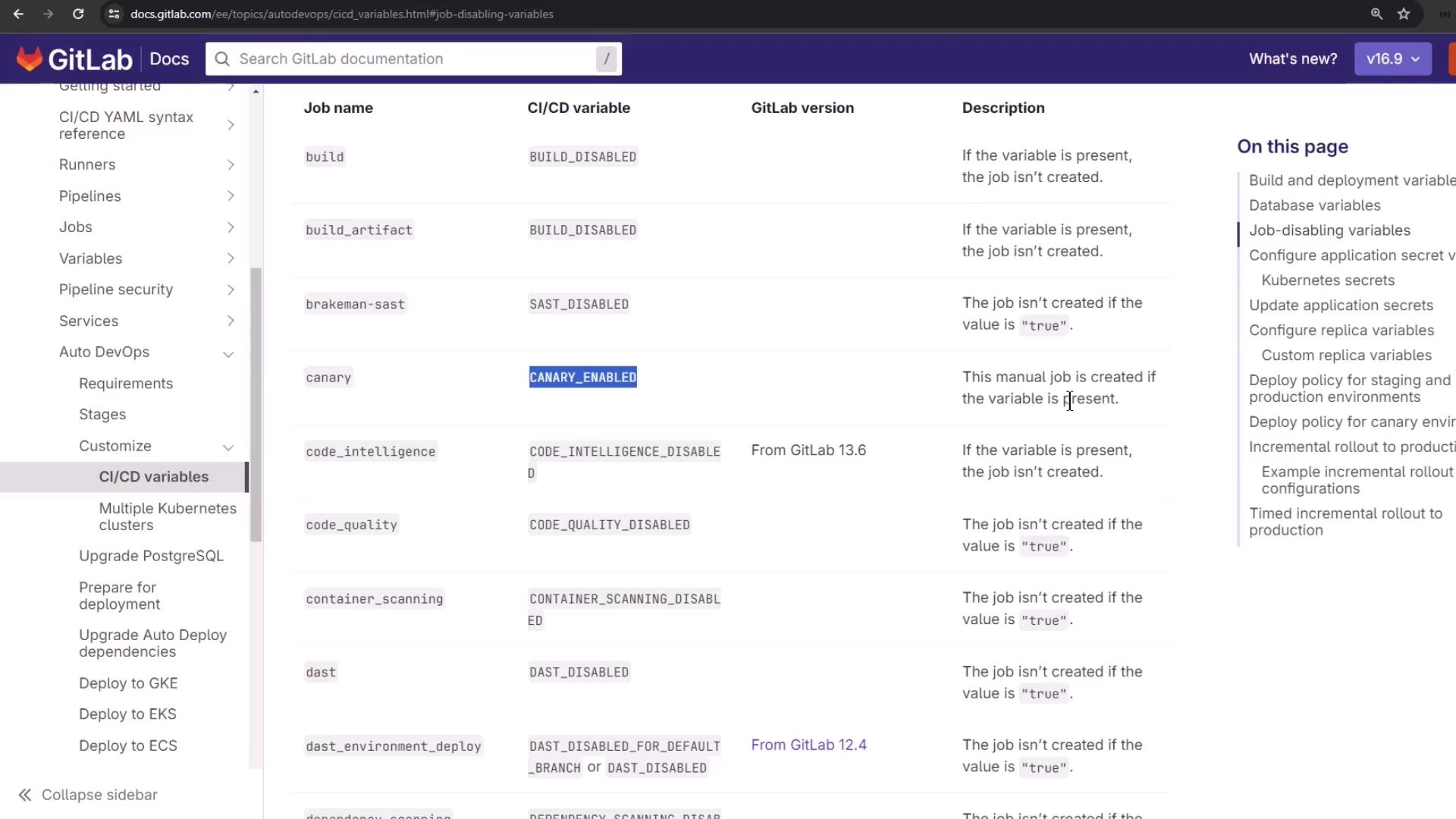
Disabling Unneeded Jobs
Disable specific Auto DevOps jobs by setting their variables to"true":
Full Example .gitlab-ci.yml
Combine the include and disabling variables to simplify your pipeline:
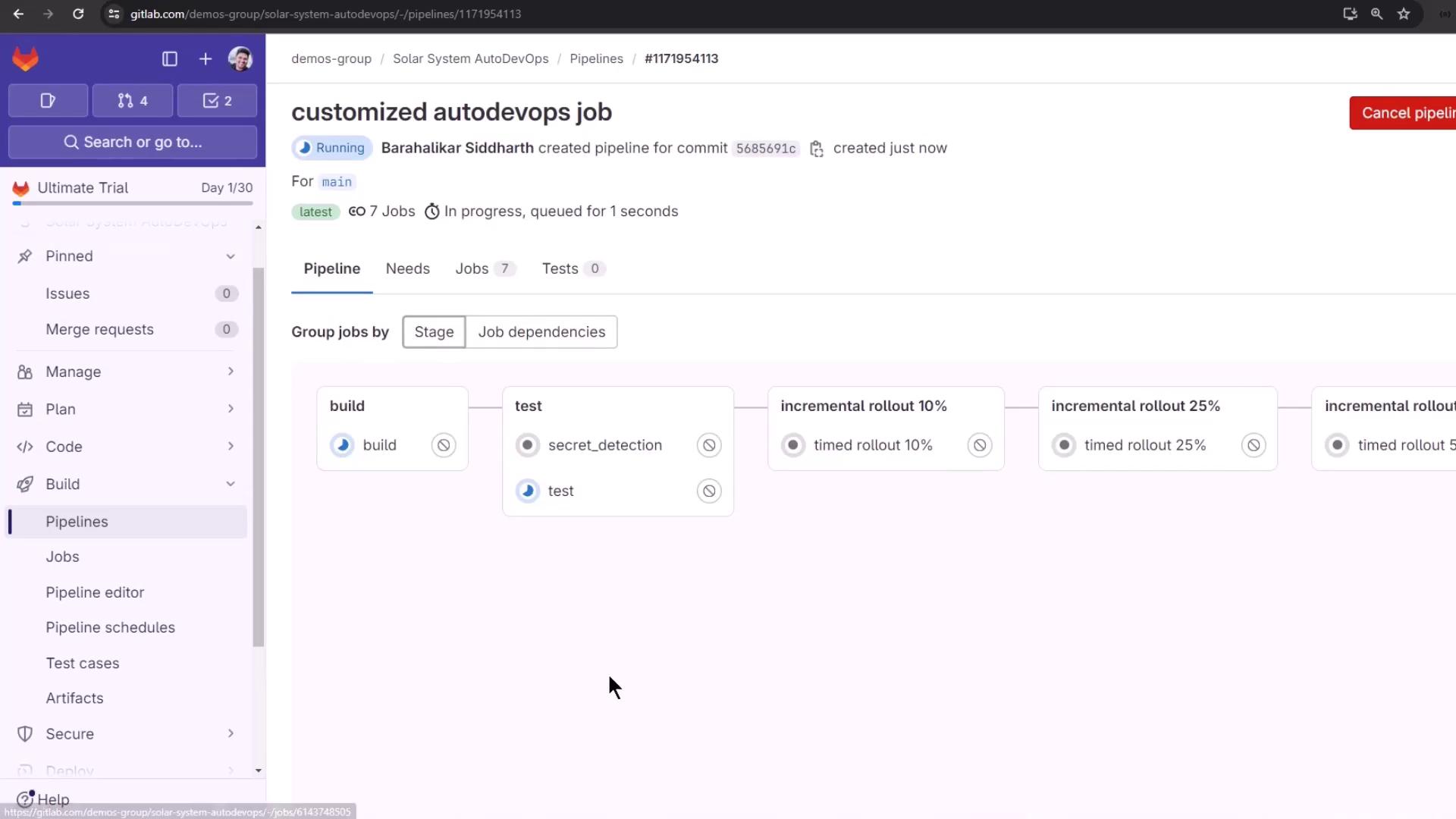
Running the Timed Rollout
After build and test, the pipeline moves through timed rollout steps (10%, 25%, 50%, 100%). Each step waits for the configured interval before proceeding.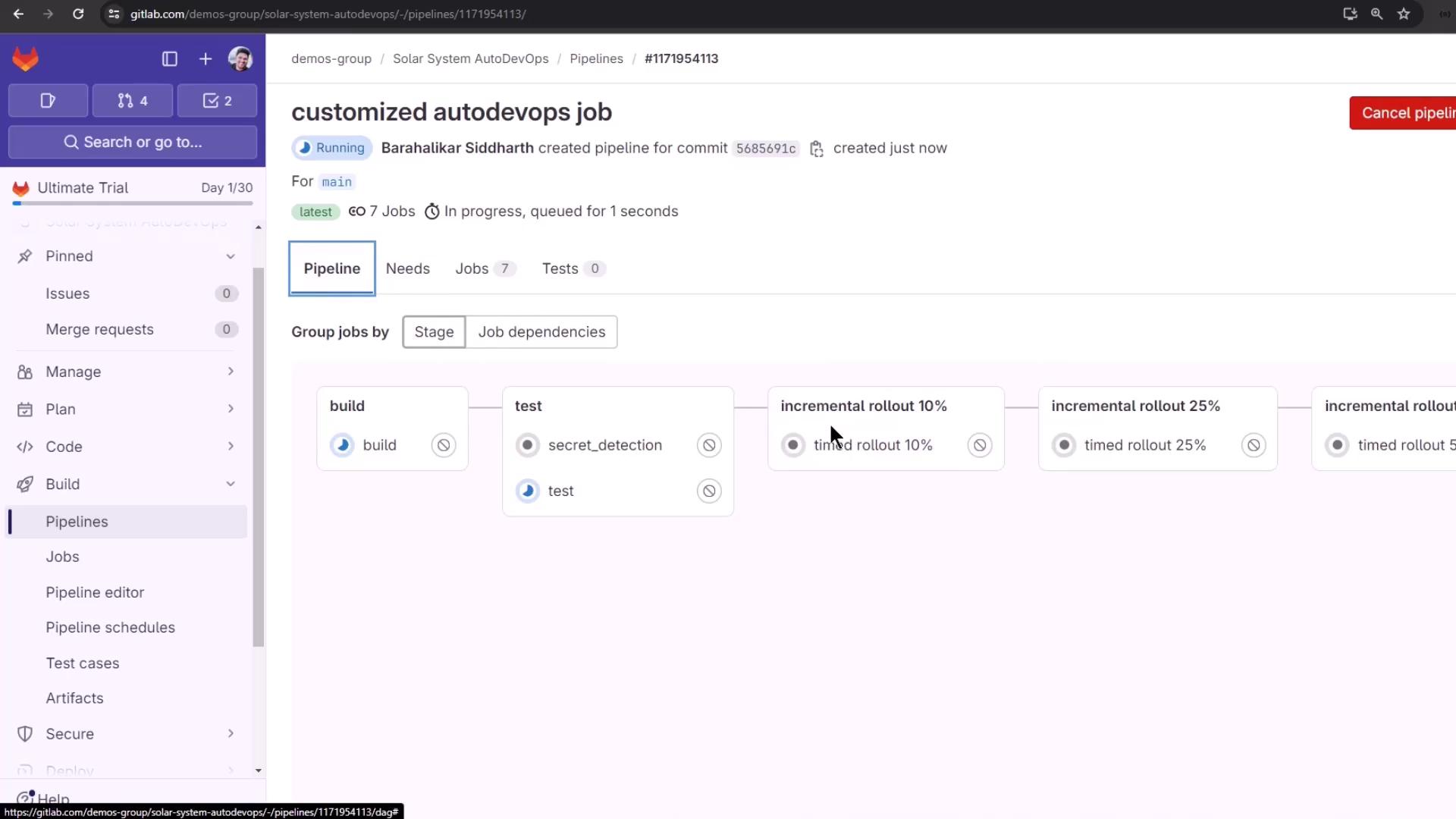

Inspecting the Deployment
Verify canary and stable pods using the Kubernetes CLI:
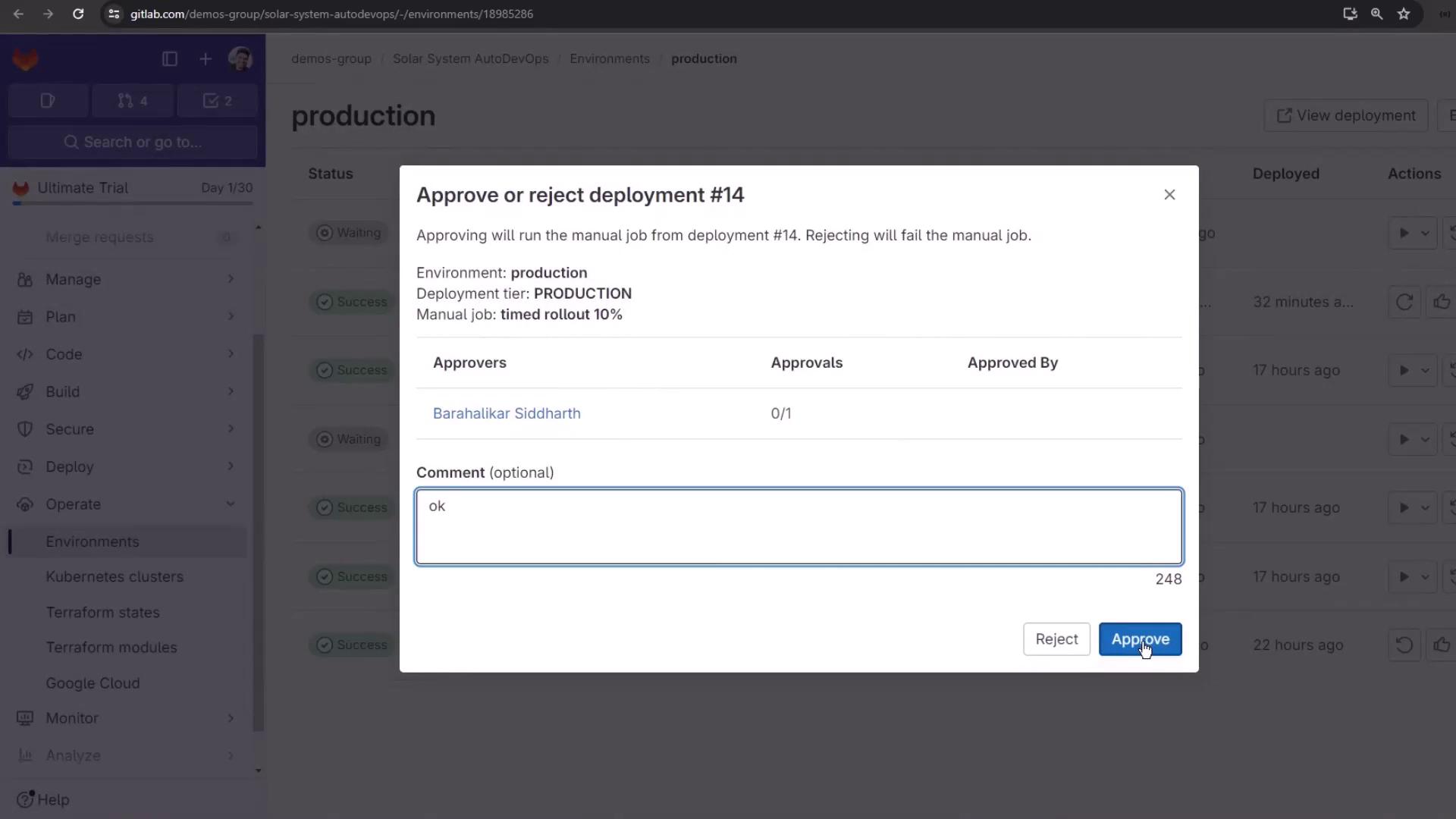
Approving Protected Deployments
Protected environments halt deployments until manual approval: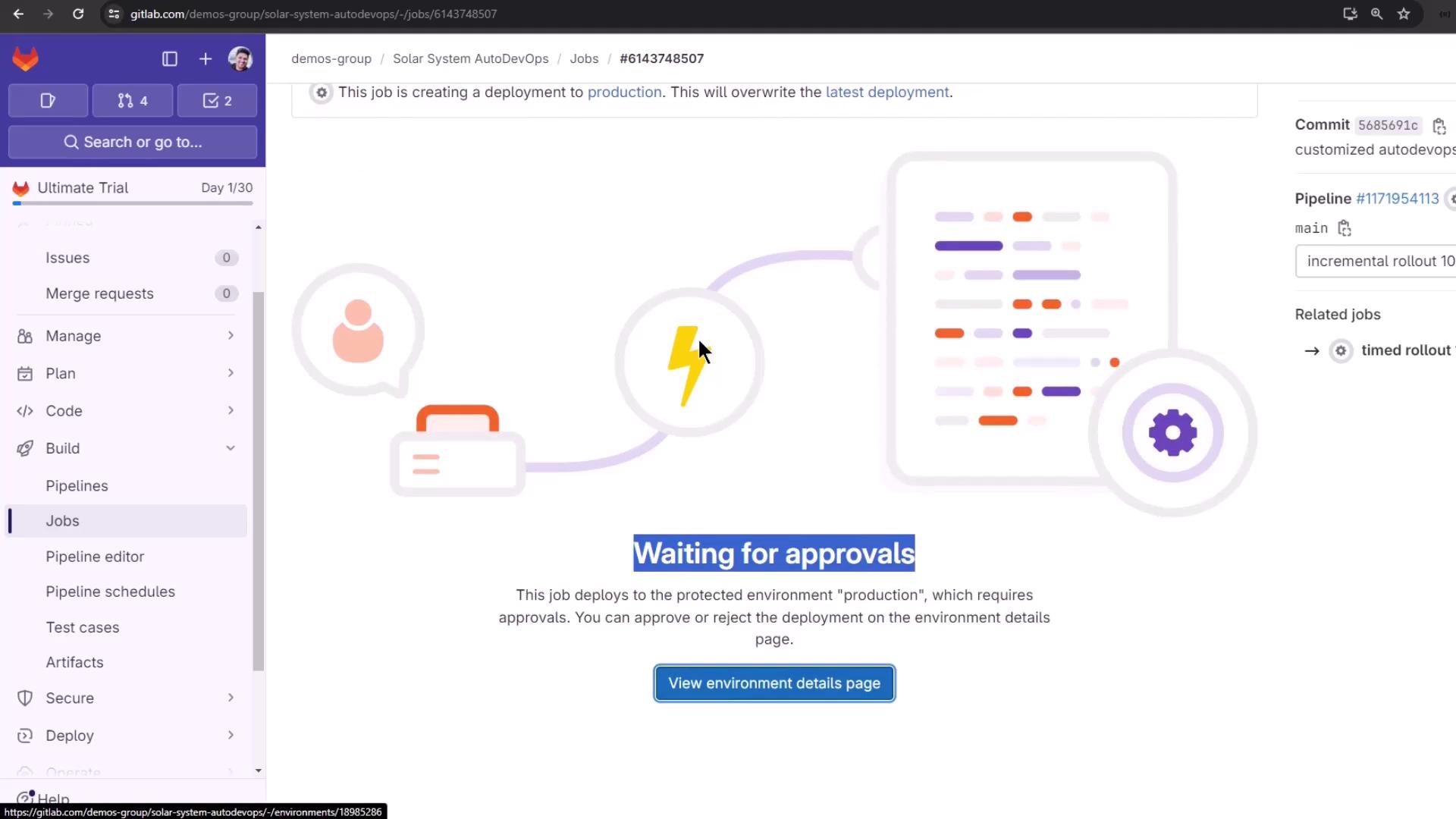

Monitoring Environments
View all deployments and their statuses under Operations > Environments: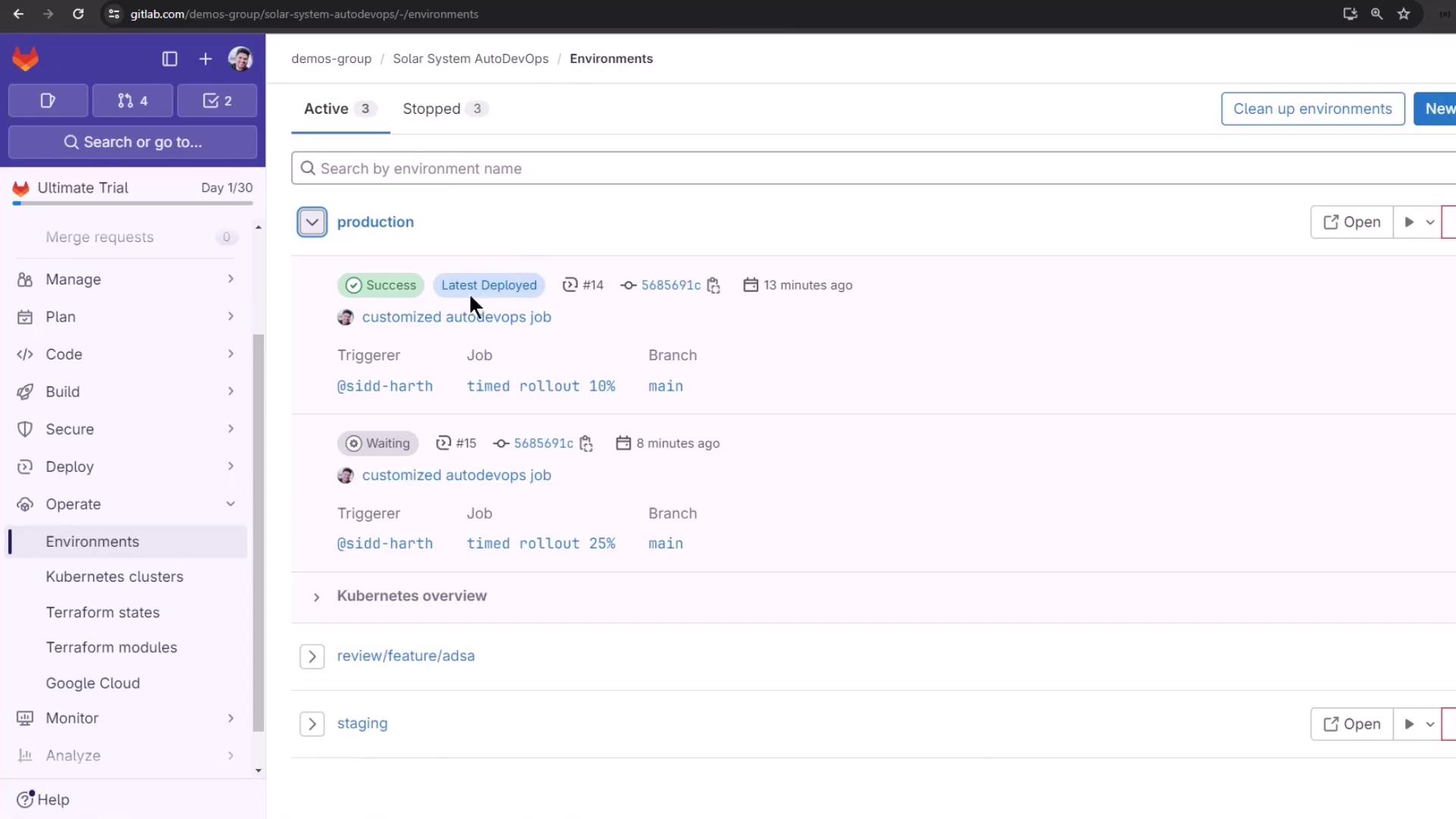
For more details, see the Auto DevOps documentation or explore these resources: