In this guide, we’ll extend our GitLab CI pipeline by adding an integration testing job. After deploying to Kubernetes, we’ll extract the Ingress host URL, save it as a dotenv report, and consume it in downstream tests to verify our service endpoints.
1. Define the Integration Testing Job Begin by declaring a k8s_dev_integration_testing job in the dev-deploy stage. This job installs curl and jq, then probes the /live and /ready endpoints to confirm service health:
k8s_dev_integration_testing : stage : dev-deploy image : alpine:3.7 before_script : - apk --no-cache add curl jq script : - curl -s -k https://$INGRESS_URL/live | jq -r .status | grep -i live - curl -s -k https://$INGRESS_URL/ready | jq -r .status | grep -i ready
2. Capture the Ingress Host URL in CI After your application manifests are applied, list the Ingress resource to confirm its host:
kubectl -n development get ing
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE solar-system <none> solar-system-development.139.84.208.48.nip.io 139.84.208.48 80,443 39m
Extract the hostname via JSONPath:
kubectl -n development get ing -o jsonpath="{.items[0].spec.tls[0].hosts[0]}"
Automate this in your deploy job and append the result to a dotenv file:
k8s_dev_deploy : stage : dev-deploy image : alpine:3.7 script : - export KUBECONFIG=$DEV_KUBE_CONFIG - kubectl version -o yaml - kubectl config get-contexts - kubectl get nodes - export INGRESS_IP=$(kubectl -n ingress-nginx get svc ingress-nginx-controller \ -o jsonpath="{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}") - echo "🔍 Ingress IP : $INGRESS_IP" - kubectl -n $NAMESPACE create secret generic mongo-db-creds \ --from-literal=MONGO_URI=$MONGO_URI \ --from-literal=MONGO_USERNAME=$MONGO_USERNAME \ --from-literal=MONGO_PASSWORD=$MONGO_PASSWORD \ --save-config --dry-run=client -o yaml | kubectl apply -f - - for manifest in kubernetes/manifest/*.yaml; do envsubst < "$manifest" | kubectl apply -f - done - echo "INGRESS_URL=$(kubectl -n $NAMESPACE get ing \ -o jsonpath='{.items[0].spec.tls[0].hosts[0]}')" >> app_ingress_url.env artifacts : reports : dotenv : app_ingress_url.env
By registering app_ingress_url.env as a dotenv report, GitLab exposes INGRESS_URL as a CI variable for subsequent jobs.
3. Consume the Ingress URL in Integration Tests Now update the integration testing job to depend on the deploy job. This ensures that INGRESS_URL is available:
k8s_dev_integration_testing : stage : dev-deploy needs : - k8s_dev_deploy image : alpine:3.7 before_script : - apk --no-cache add curl jq script : - echo "Using Ingress URL : $INGRESS_URL" - curl -s -k https://$INGRESS_URL/live | jq -r .status | grep -i live - curl -s -k https://$INGRESS_URL/ready | jq -r .status | grep -i ready
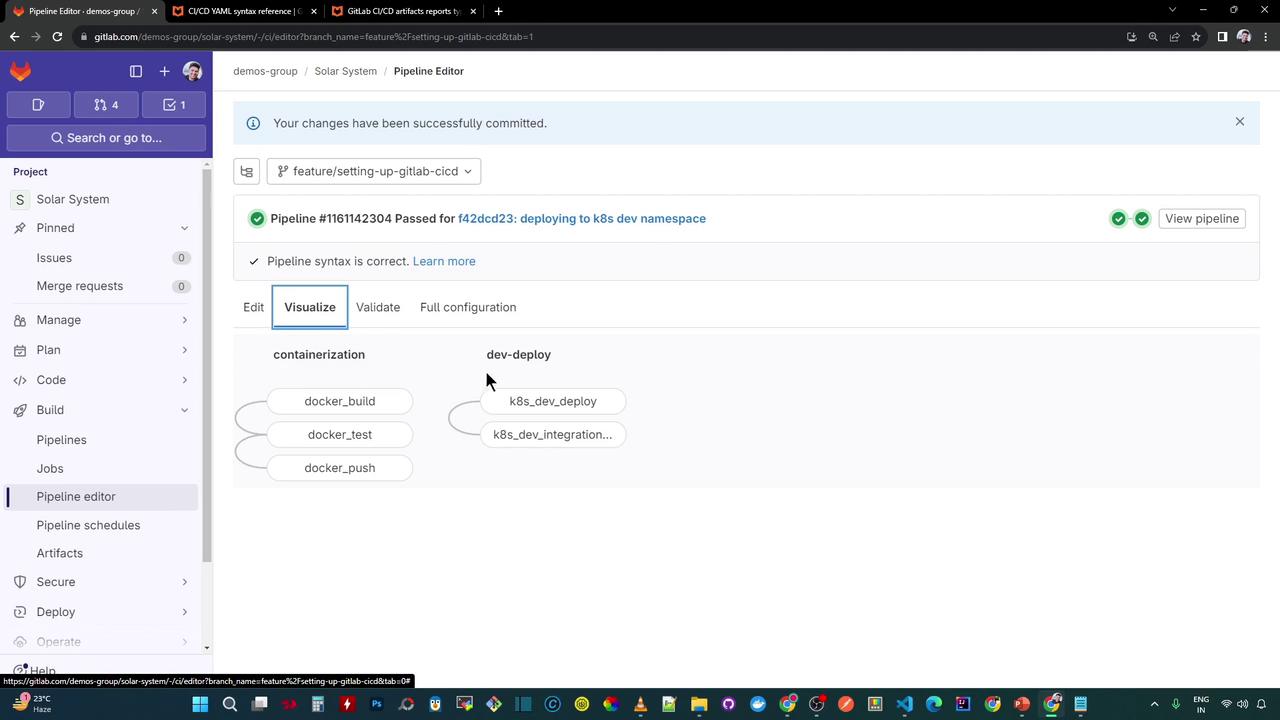
4. Visualize the Pipeline After committing your .gitlab-ci.yml, your pipeline in the dev-deploy stage will include two sequential jobs:
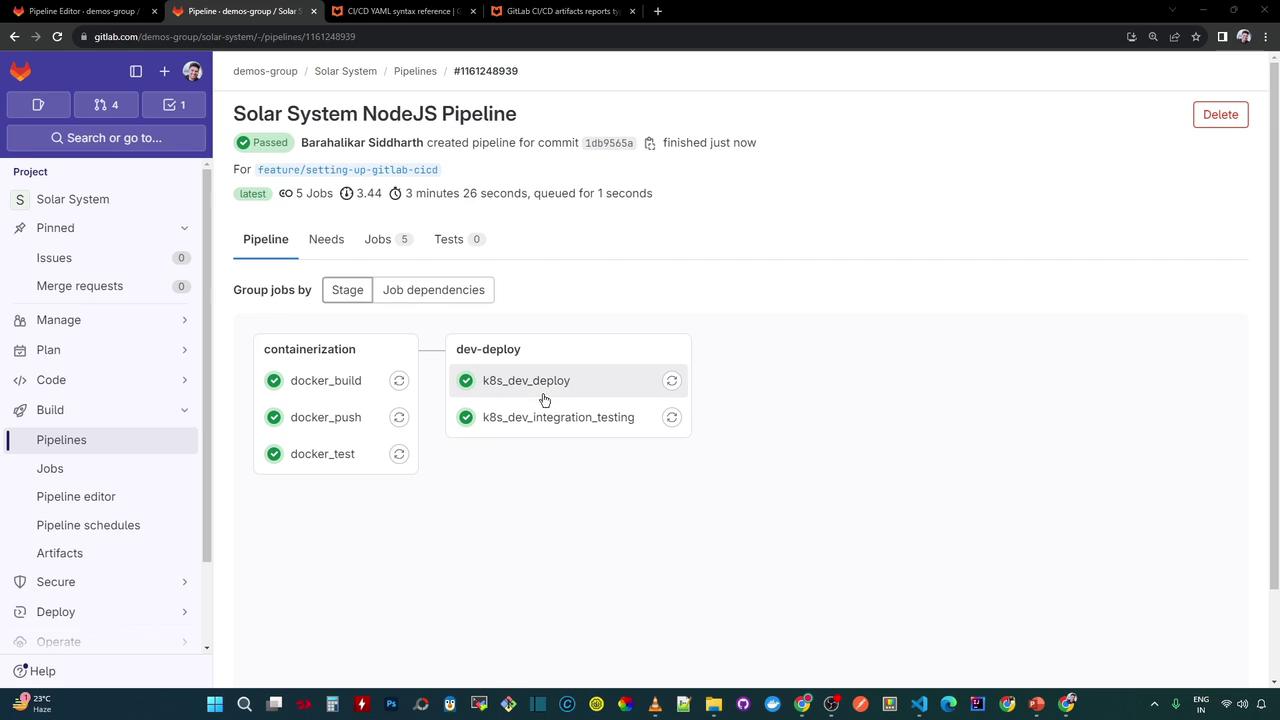
Upon completion, both jobs report success:
References