GitLab CI/CD: Architecting, Deploying, and Optimizing Pipelines
Optimization Security and Monitoring
Template SAST
Overview
Static Application Security Testing (SAST) integrates directly into your GitLab CI/CD pipelines to catch code and manifest vulnerabilities early. It supports scanning source code, Kubernetes YAML, and Helm charts before deployment. While all GitLab plans can run SAST analyzers, Ultimate subscribers enjoy rich dashboards; free tiers can parse JSON reports.
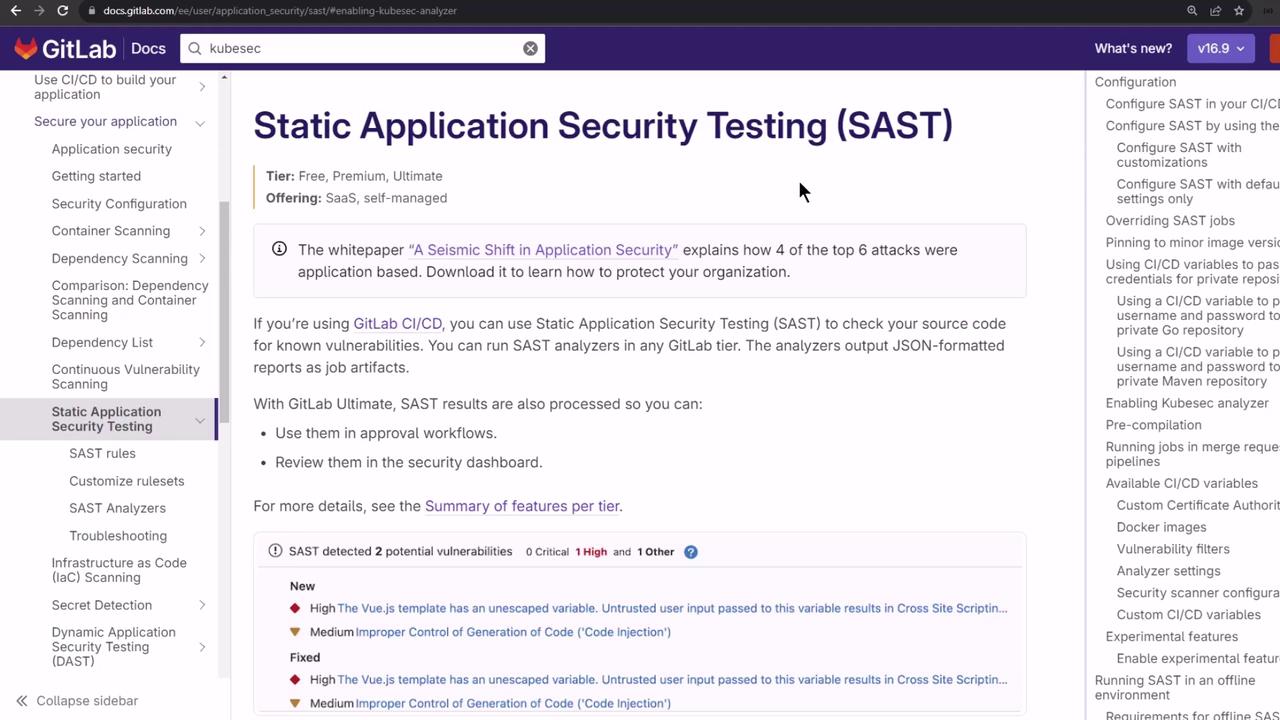
Supported Languages and Manifests
GitLab’s SAST documentation lists supported languages, frameworks, and manifest types. In JavaScript/Node.js projects, analyzers include Semgrep and NodeJsScan. Kubernetes YAML can be scanned with KubeSec.
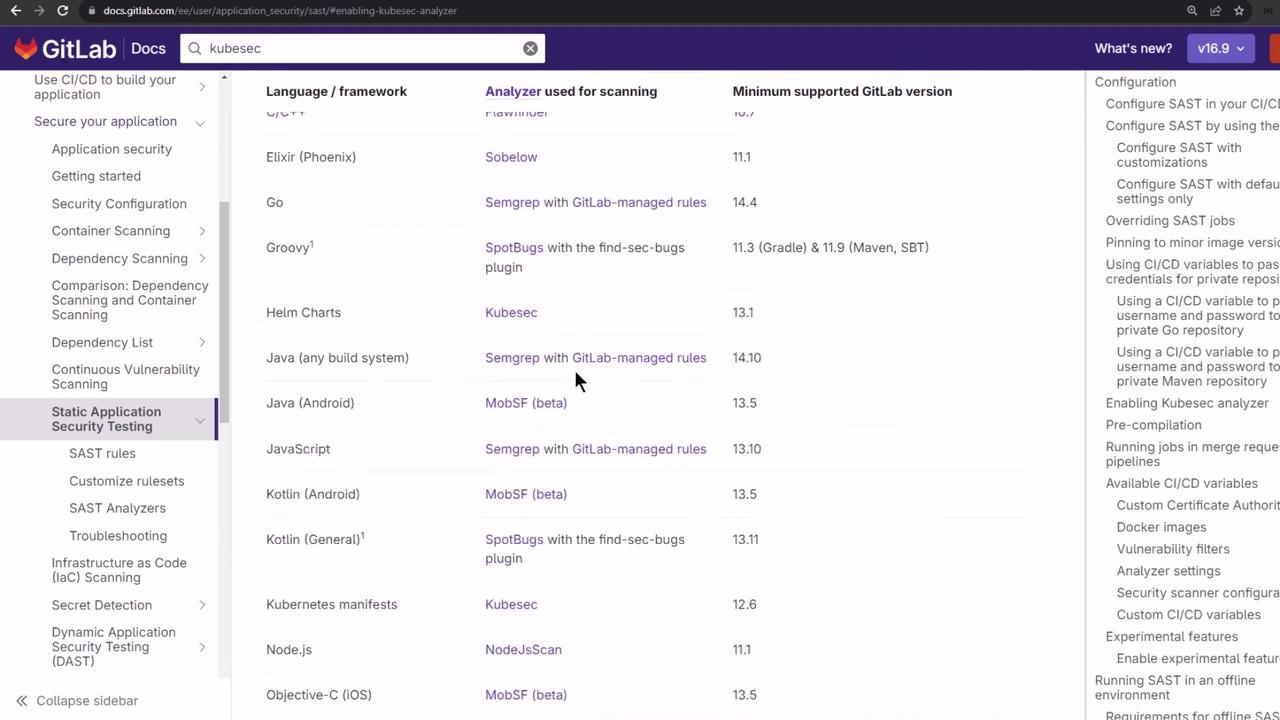
Available Analyzers
The following table summarizes core SAST analyzers:
| Analyzer | Purpose | Installation / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| NodeJsScan | Finds Node.js vulnerabilities | pip install njsscan==<version> |
| Semgrep | Pattern-based static checks | Bundled in CI template |
| KubeSec | Analyzes Kubernetes manifest YAMLs | Bundled in CI template |
Each analyzer repository includes detailed scanning logic and JSON report schemas.
Enabling SAST via CI/CD Template
GitLab’s built-in template Jobs/SAST.gitlab-ci.yml auto-detects languages and injects relevant jobs. To activate it:
include:
- template: Jobs/SAST.gitlab-ci.yml
External YAML files or local snippets can be added with the include keyword, streamlining long configurations and avoiding duplication.

GitLab also offers a Browse templates UI to select from all out-of-the-box CI/CD snippets.
Default SAST Jobs
The Jobs/SAST.gitlab-ci.yml template defines jobs like:
sast-analyzer:
extends: sast
allow_failure: true
script:
- echo "$CI_JOB_NAME is for pipeline configuration only"
- exit 1
semgrep-sast:
extends: sast-analyzer
image: "$SAST_ANALYZER_IMAGE"
variables:
SAST_ANALYZER_IMAGE_TAG: "$SAST_ANALYZER_IMAGE_TAG"
rules:
- if: $SAST_DISABLED == 'true' || $SAST_DISABLED == '1'
when: never
- if: $SAST_EXCLUDED_ANALYZERS =~ /semgrep-sast/
when: never
- exists:
- "**/*.js"
By default, SAST jobs run in the test stage and publish a JSON report at gl-sast-report.json:
sast:
stage: test
artifacts:
reports:
sast: gl-sast-report.json
rules:
- when: always
allow_failure: true
- changes:
- "**/*.js"
- "**/*.rb"
Note
All SAST jobs default to allow_failure: true, so pipelines won’t be blocked by detected issues.
Customizing SAST Configuration
You can tweak the SAST template by setting CI variables:
variables:
SCAN_KUBERNETES_MANIFESTS: "true"
This variable injects the kubesec-sast job. Additional options:
variables:
SECURE_ANALYZERS_PREFIX: "$CI_TEMPLATE_REGISTRY_HOST/security-products"
SAST_EXCLUDED_ANALYZERS: "nodejs-scan"
SAST_EXCLUDED_PATHS: "spec,test,tmp"
Adjusting the SAST Stage
To run SAST in a custom stage (for example, .pre):
stages:
- .pre
- test
- deploy
include:
- template: Jobs/SAST.gitlab-ci.yml
variables:
SCAN_KUBERNETES_MANIFESTS: "true"
sast:
stage: .pre
You can comment out unused templates:
# include:
# - template: Security/Code-Quality.gitlab-ci.yml
Example .gitlab-ci.yml
A minimal pipeline running SAST and Node.js unit tests:
stages:
- .pre
- test
include:
- template: Jobs/SAST.gitlab-ci.yml
variables:
SCAN_KUBERNETES_MANIFESTS: "true"
.prepare_nodejs_environment:
image: node:16
before_script:
- npm ci
sast:
stage: .pre
unit_testing:
stage: test
extends: .prepare_nodejs_environment
script:
- npm test
artifacts:
when: always
expire_in: 3 days
paths:
- test-results.xml
reports:
junit: test-results.xml
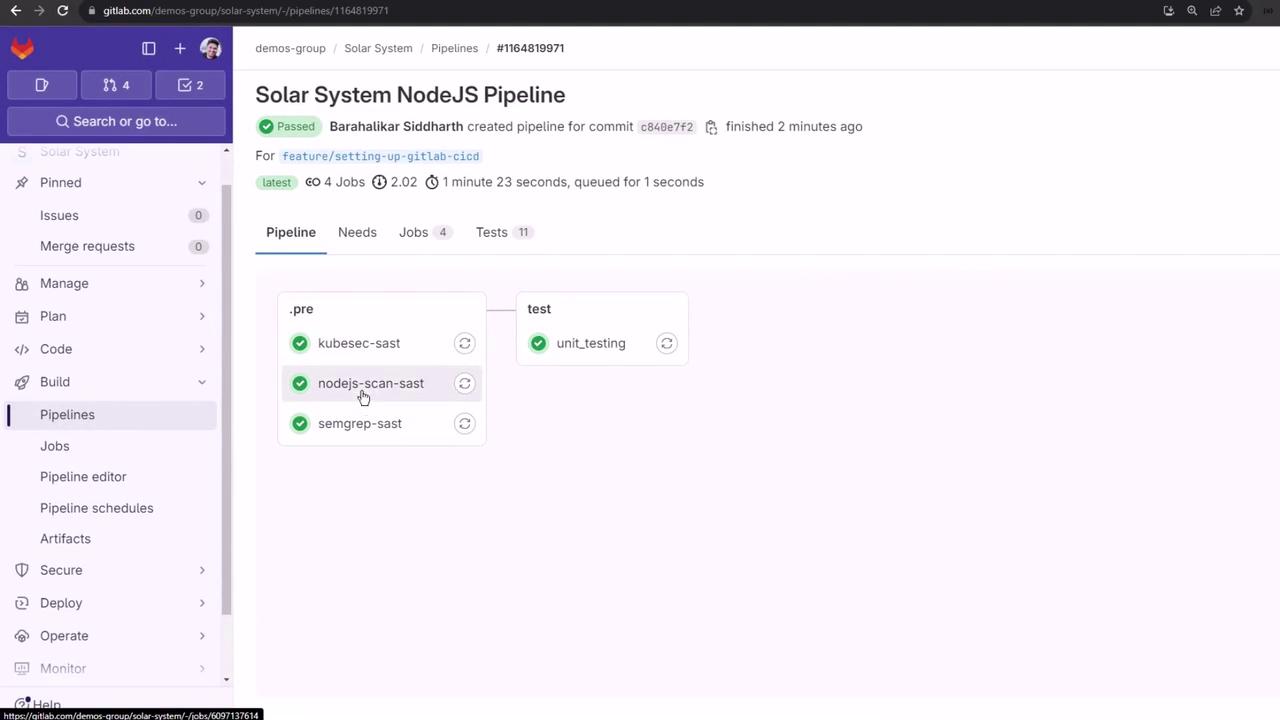
After pushing, you’ll see SAST in .pre followed by unit_testing in test.
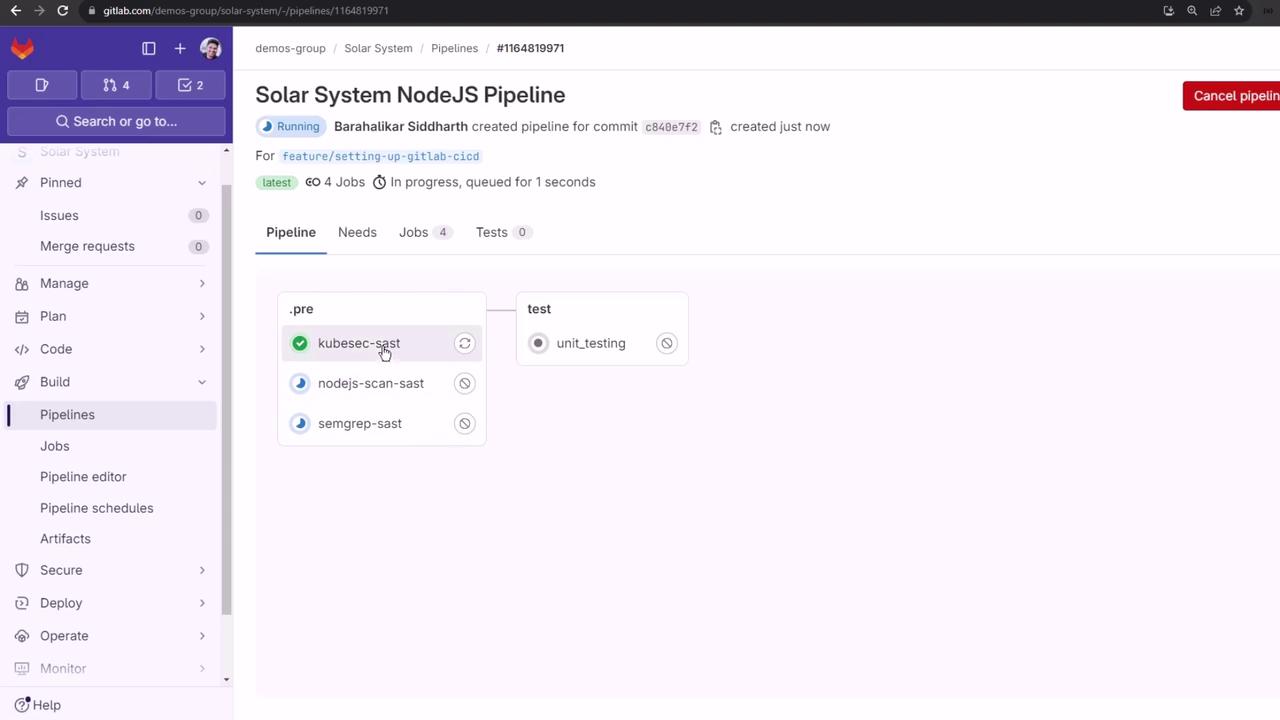
Viewing SAST Reports
Each SAST job outputs a gl-sast-report.json. Download and inspect it with any JSON viewer.
Example KubeSec Report
{
"version": "15.0.7",
"vulnerabilities": [],
"scan": {
"analyzer": {
"id": "kubesc",
"name": "Kubesc",
"version": "4.0.10"
},
"scanner": {
"id": "kubesc",
"name": "Kubesc",
"version": "2.14.0"
}
},
"type": "sast"
}
Example NodeJsScan Report
{
"version": "15.0.7",
"vulnerabilities": [
{
"id": "2d92ba5c9c2e73c14c5a0da201ba74110e14c4ec9640dbf1becfcb05c5295b",
"name": "node_nosqli_injection",
"description": "Untrusted user input in findOne() can result in NoSQL Injection.",
"severity": "High",
"location": {
"file": "app.js",
"start_line": 44,
"end_line": 53
},
"identifiers": [
{
"type": "njsscan_rule_type",
"value": "CWE-943"
}
],
"scanner": {
"id": "nodejs-scan",
"name": "NodeJsScan"
}
}
]
}
Even when vulnerabilities are flagged, subsequent jobs run by default. In higher tiers, issues appear in the Security Dashboard and MR views.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content