Introduction to OpenAI
Text Generation
Overview of OpenAI Assistant
OpenAI Assistants are AI-driven conversational agents built on GPT models (like GPT-4) that automate tasks, enhance user interactions, and streamline workflows across industries—from customer support to finance and healthcare. In this guide, you’ll learn how they operate, explore core workflow states, discover key benefits, and see examples for customization.
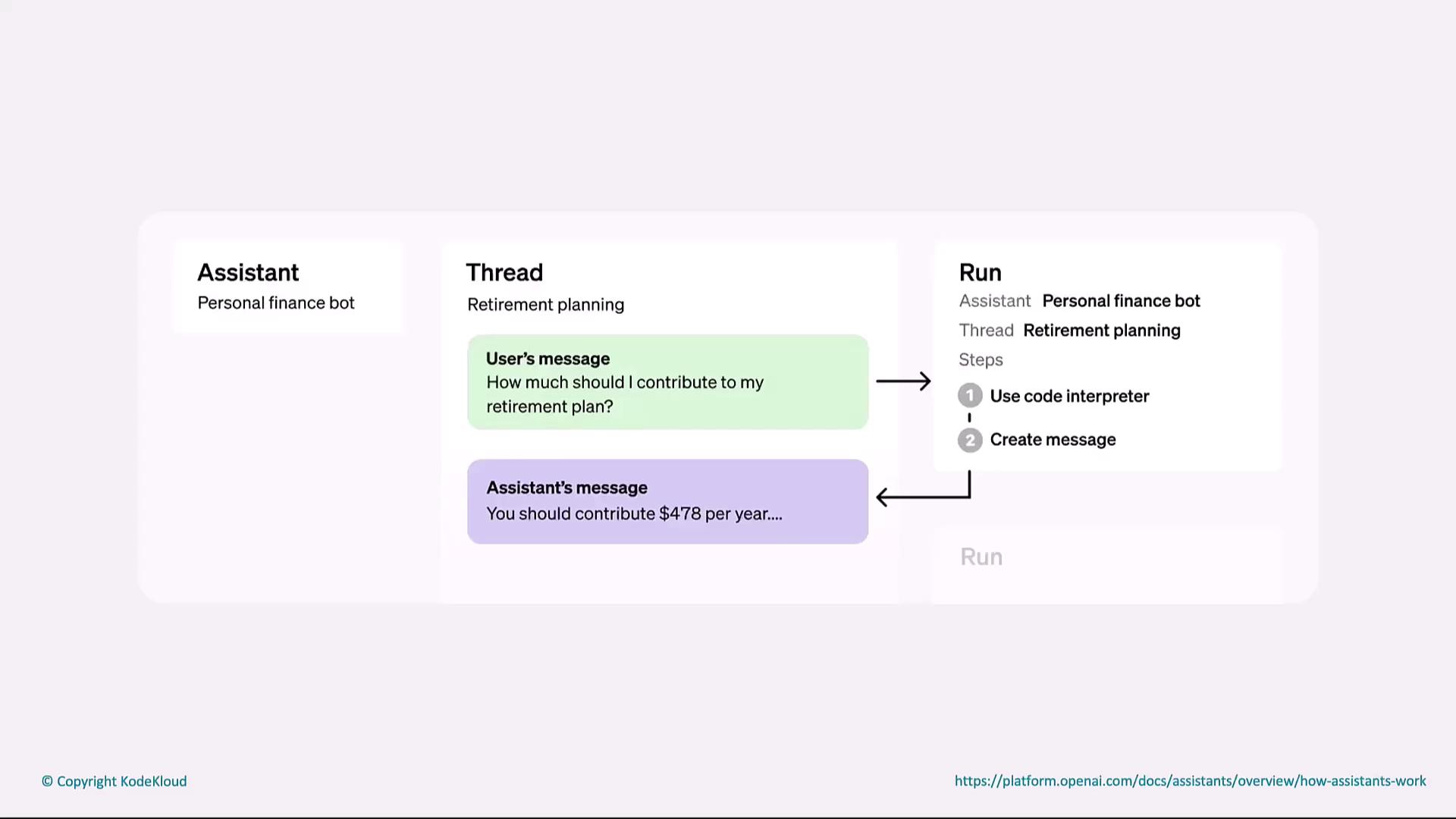
Personal Finance Assistant Example
This scenario showcases a personal finance bot helping with retirement planning. When a user asks, “How much should I contribute to my retirement plan?” the assistant:
- Receives the user message.
- Uses a code interpreter to calculate the optimal contribution.
- Sends back: “You should contribute $478 a year.”
On the right, the run panel highlights each step from computation to message creation.
What Are OpenAI Assistants?
OpenAI Assistants leverage large language models to:
- Perform specific tasks and automate repetitive workflows
- Engage in natural language conversations
- Integrate with external tools (APIs, databases, code interpreters)
These agents excel in contexts like customer support, education, financial advising, and medical triage by understanding intent, generating accurate responses, and maintaining conversational context.

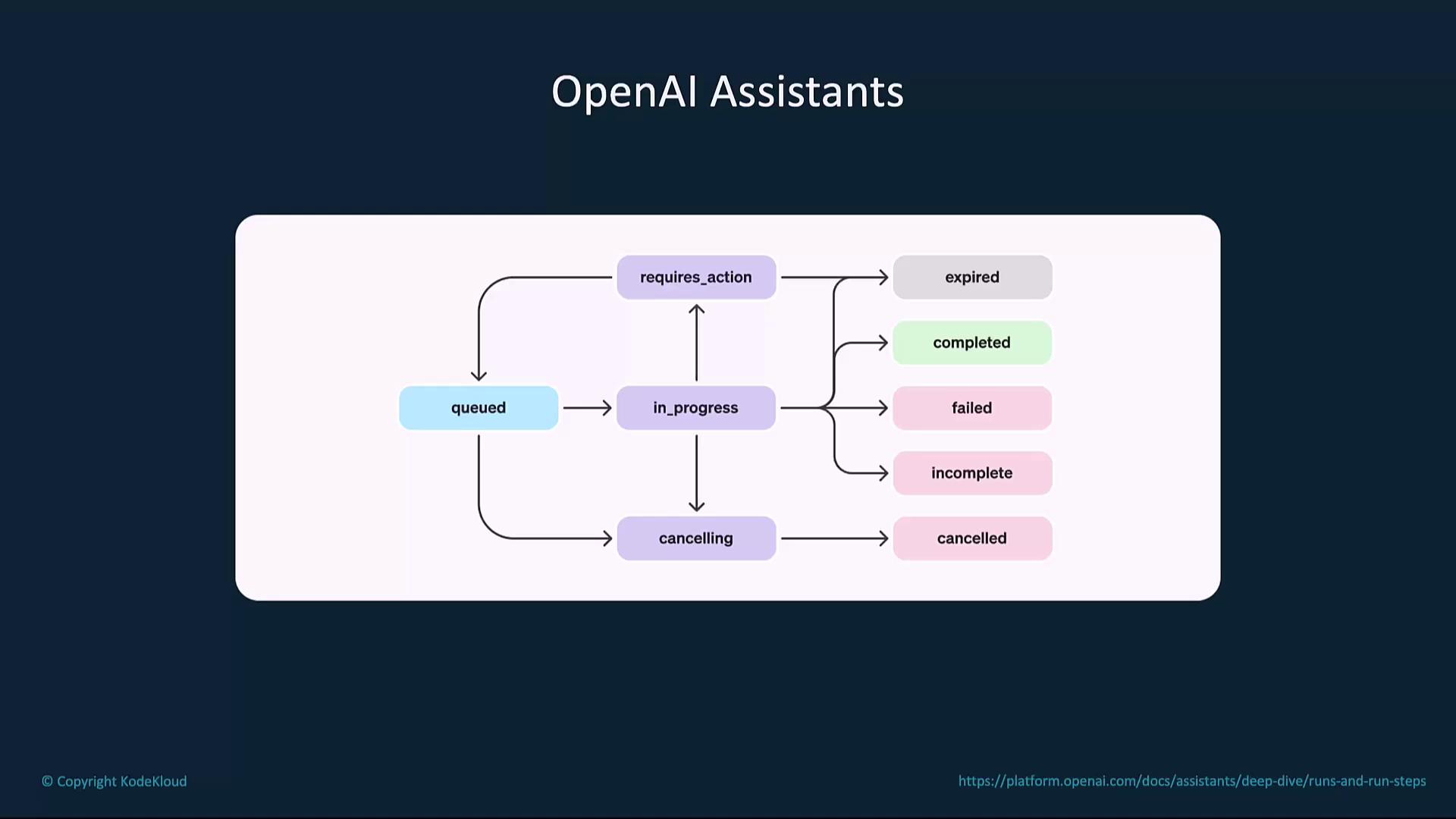
Core Workflow States
OpenAI Assistants track each task through a series of states:
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| queued | Task is waiting to start |
| in_progress | Task is actively running |
| requires_action | Task needs user input or intervention |
| cancelling | Task is being stopped |
Final outcomes:
| Final State | Meaning |
|---|---|
| completed | Task finished successfully |
| failed | Task encountered an error |
| cancelled | Task was intentionally stopped |
| expired | Task timed out without completion |
| incomplete | Task was partially done |
Key Benefits

Automation & Efficiency
Free up teams by automating FAQs, ticket routing, and data processing.Scalability
Seamlessly handle spikes in demand without hiring additional staff.24×7 Availability
Provide nonstop support—ideal for global audiences or critical services.Personalization
Adapt responses based on user history and preferences.Data Insights & Analytics
Monitor conversations to extract sentiment, trends, and improvement areas.Continuous Learning
Fine-tune on domain-specific datasets (e.g., legal, medical) to boost accuracy.
Assistant Example: Customer Support
Here’s a Python snippet demonstrating a simple customer support assistant with GPT-4:
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI()
def support_response(user_query: str) -> str:
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a customer support assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": user_query}
],
max_tokens=150,
temperature=0,
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
if __name__ == "__main__":
query = "Help me answer this technical question about my new snowblower."
print(support_response(query))
Note
Adjust temperature, max_tokens, and top_p to control response creativity, length, and diversity.
Building Custom OpenAI Assistants
You can tailor assistants to your business needs by focusing on:
Training Data
Fine-tune on domain-specific records or custom corpora to enhance subject-matter accuracy.Context Handling
Implement memory by storing conversation history, user preferences, or session variables.Model Parameters
Configuretemperature,max_tokens, andtop_pfor your desired output style.

Warning
When fine-tuning with sensitive or personal data, ensure you comply with privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). Always anonymize PII and validate data sources.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content