Deploying applications to Kubernetes is seamless with Helm charts and Lens. In this guide, you’ll learn how to add Helm repositories, browse and install charts, customize values, inspect deployed resources, and connect to your application—all within Lens.
Prerequisites
Lens installed and connected to your Kubernetes cluster
Helm CLI installed and configuredAccess to the internet (for public Helm repositories)
1. Add Helm Repositories in Lens
Open Lens and select Clusters → your-cluster .
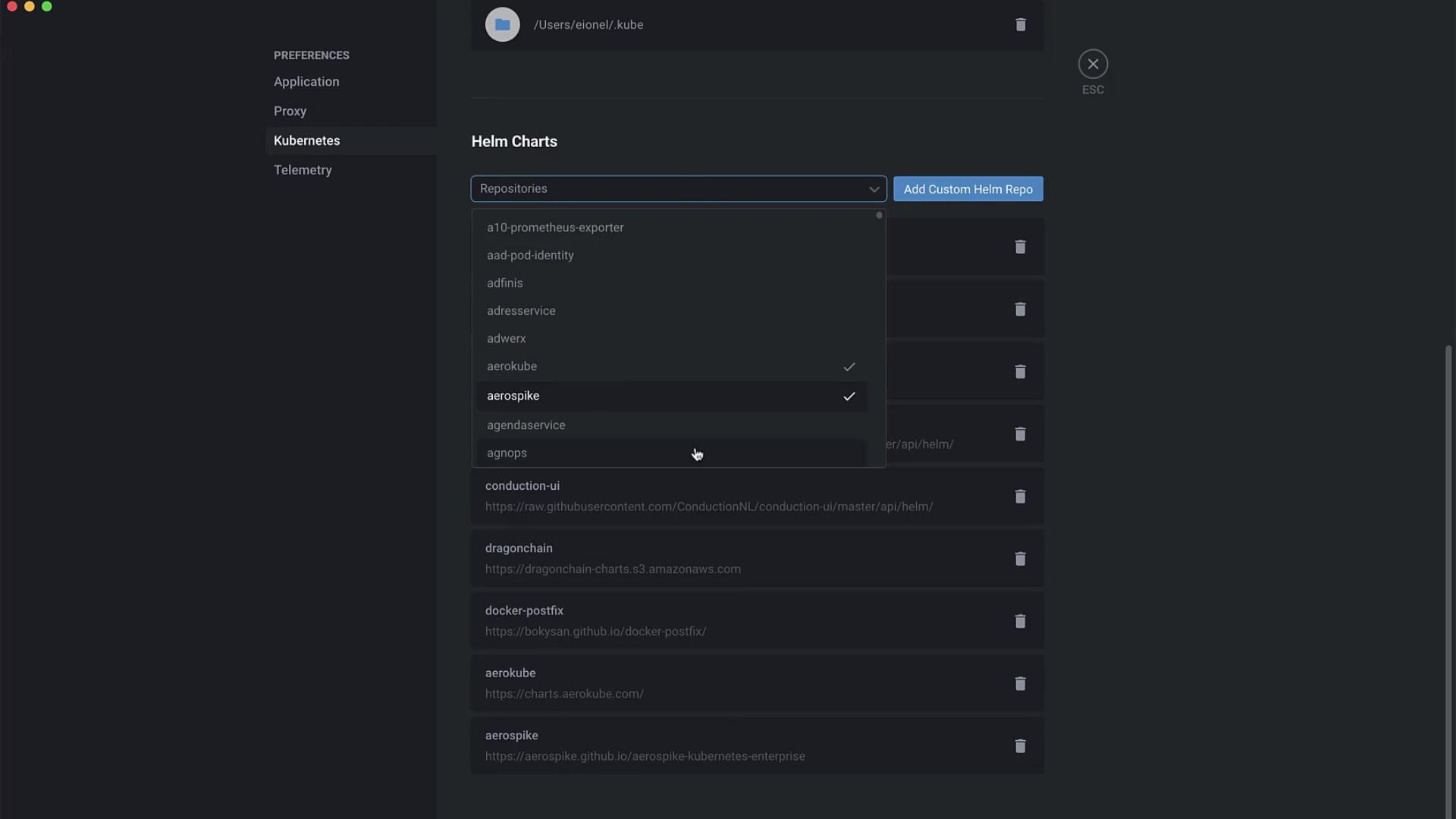
Go to Lens → Preferences → Kubernetes → Helm .
Click Add to include community and custom repositories (e.g., Aerokube, Armory, Bitnami).
2. Browse and Search Charts
Press Esc to close Preferences.
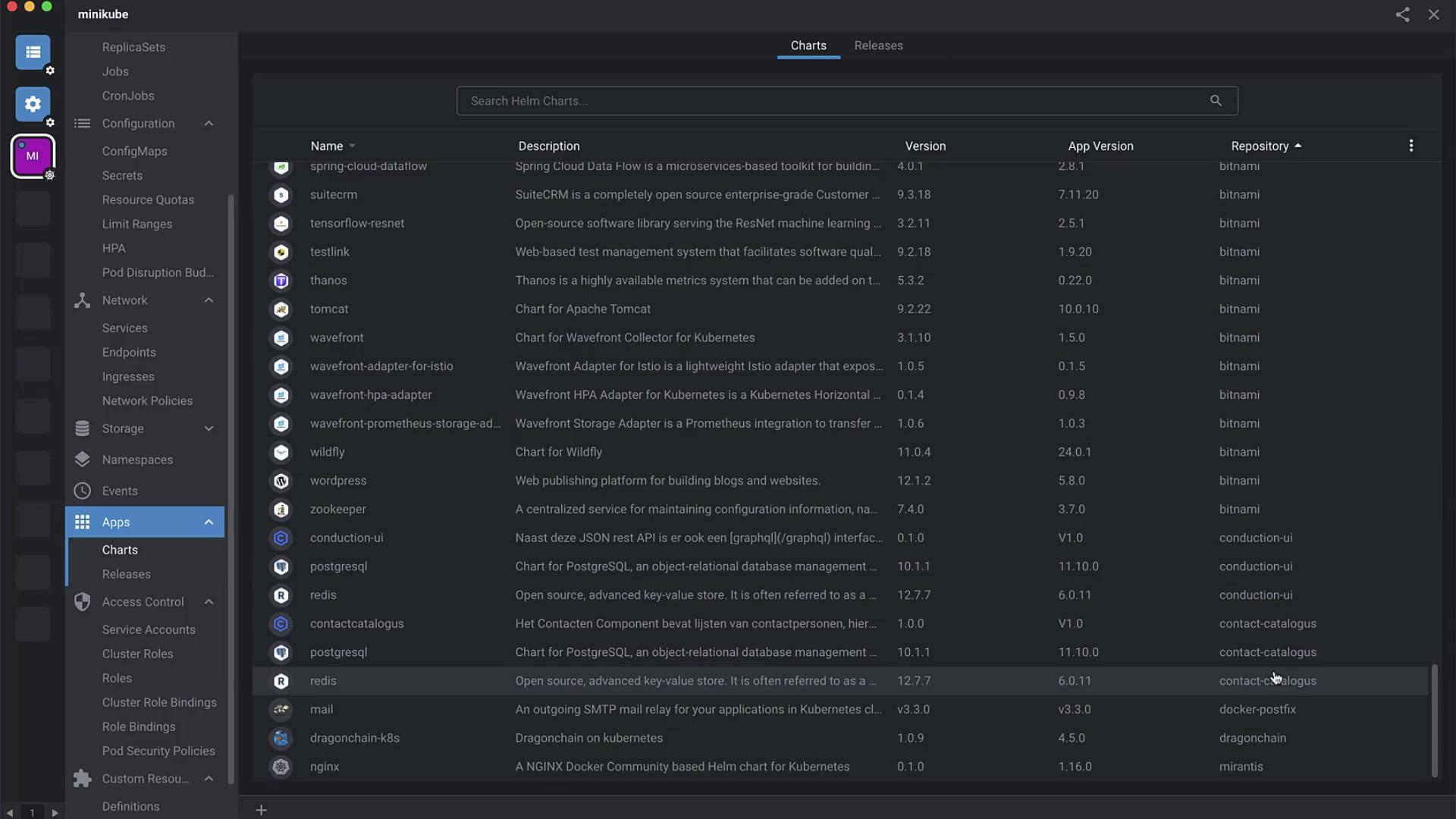
Navigate to Apps → Charts in the sidebar.
Filter by repository or search for cassandra .
Click Details on the Cassandra chart to view installation steps and default values.
3. Install the Cassandra Chart You can install directly in Lens or via the CLI:
# Add Bitnami repository (if not already added) helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami # Install Cassandra with default settings helm install my-release bitnami/cassandra # Install Cassandra with custom values helm install my-release -f values.yaml bitnami/cassandra
Back in Lens, click Install , review the form, then click Install again. Lens will deploy the chart to your cluster.
4. Review and Customize Default Values Before finalizing, Lens displays the values.yaml. Tweak global settings, storage, and more:
## Global Docker image parameters global : imageRegistry : "" imagePullSecrets : [] storageClass : "" ## Common parameters nameOverride : "" fullnameOverride : "" commonLabels : {} commonAnnotations : {} clusterDomain : cluster.local extraDeploy : [] ## Diagnostic mode diagnosticMode : enabled : false command : - sleep
Customize storageClass and imagePullSecrets to match your Kubernetes environment.
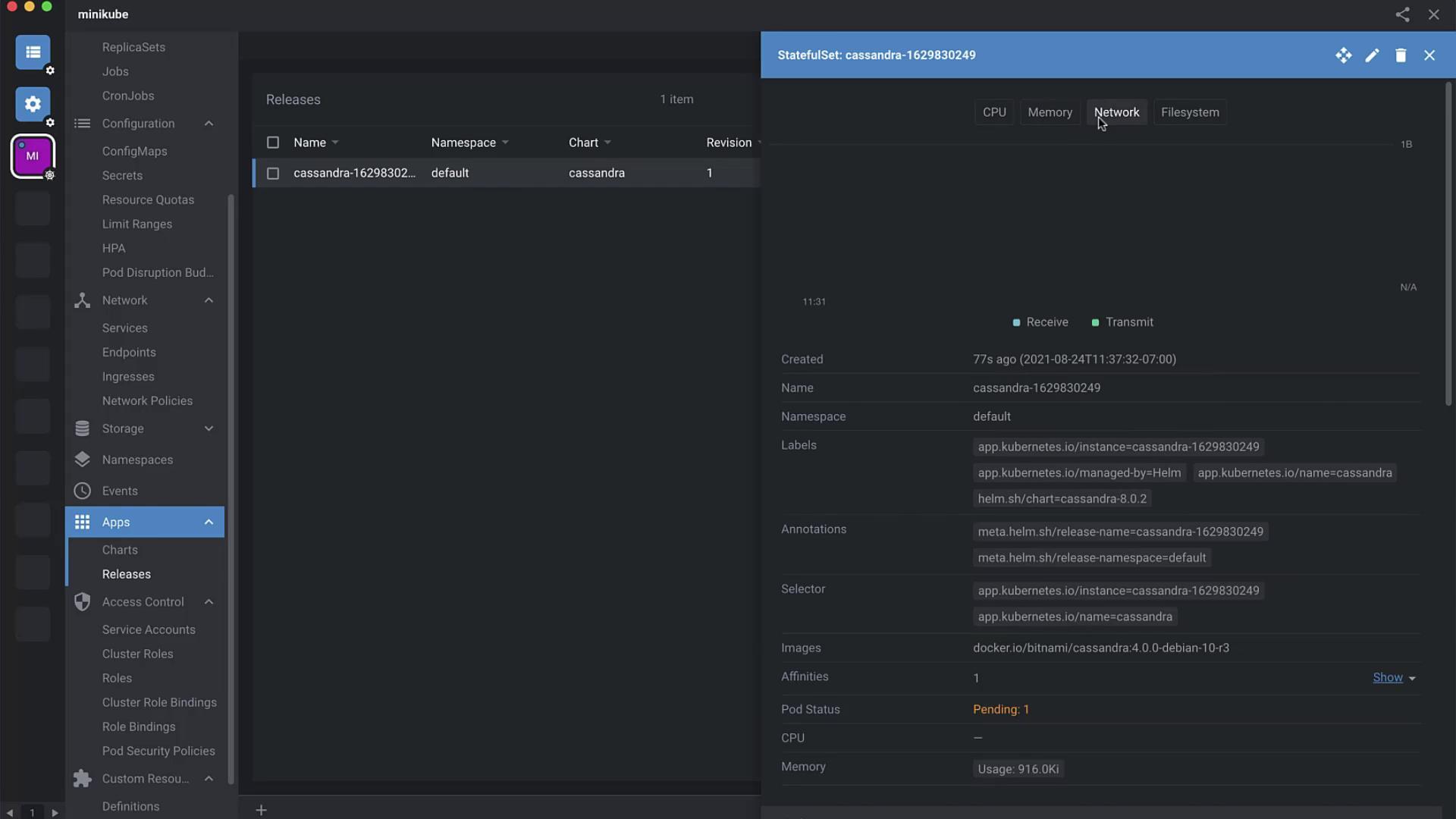
5. Inspect Deployed Resources After installation, click View Helm Release in Lens to explore all resources:
Resource Type Description ServiceAccount Identity for Cassandra pods Secret Stores credentials (cassandra user) Service Exposes port 9042 StatefulSet Manages Cassandra pods with storage ConfigMap Configuration for Cassandra
Lens lets you edit metadata (labels, annotations) on the fly and view logs, metrics, and YAML definitions.
6. Connect to Cassandra A. Using a Temporary Pod kubectl run cassandra-client --rm -i --tty --restart=Never \ --namespace default \ --env CASSANDRA_PASSWORD= $CASSANDRA_PASSWORD \ --image docker.io/bitnami/cassandra:4.0.0-debian-10-r3 -- bash
Inside the pod:
cqlsh -u cassandra -p $CASSANDRA_PASSWORD cassandra
B. Port-Forward from Local Host kubectl port-forward --namespace default svc/my-release-cassandra 9042:9042 & cqlsh -u cassandra -p $CASSANDRA_PASSWORD 127.0.0.1 9042
Links and References