- Distributing requests for high availability
- Offloading SSL/TLS and request routing
- Caching responses to cut backend load
- Controlling outbound traffic and anonymizing clients
Load Balancing
By distributing incoming requests across multiple servers, Nginx prevents any single backend from becoming a bottleneck. You declare anupstream block listing your servers, then proxy traffic to it.
Nginx supports multiple algorithms including
round_robin (default), least_conn, and ip_hash. Choose one based on your workload characteristics.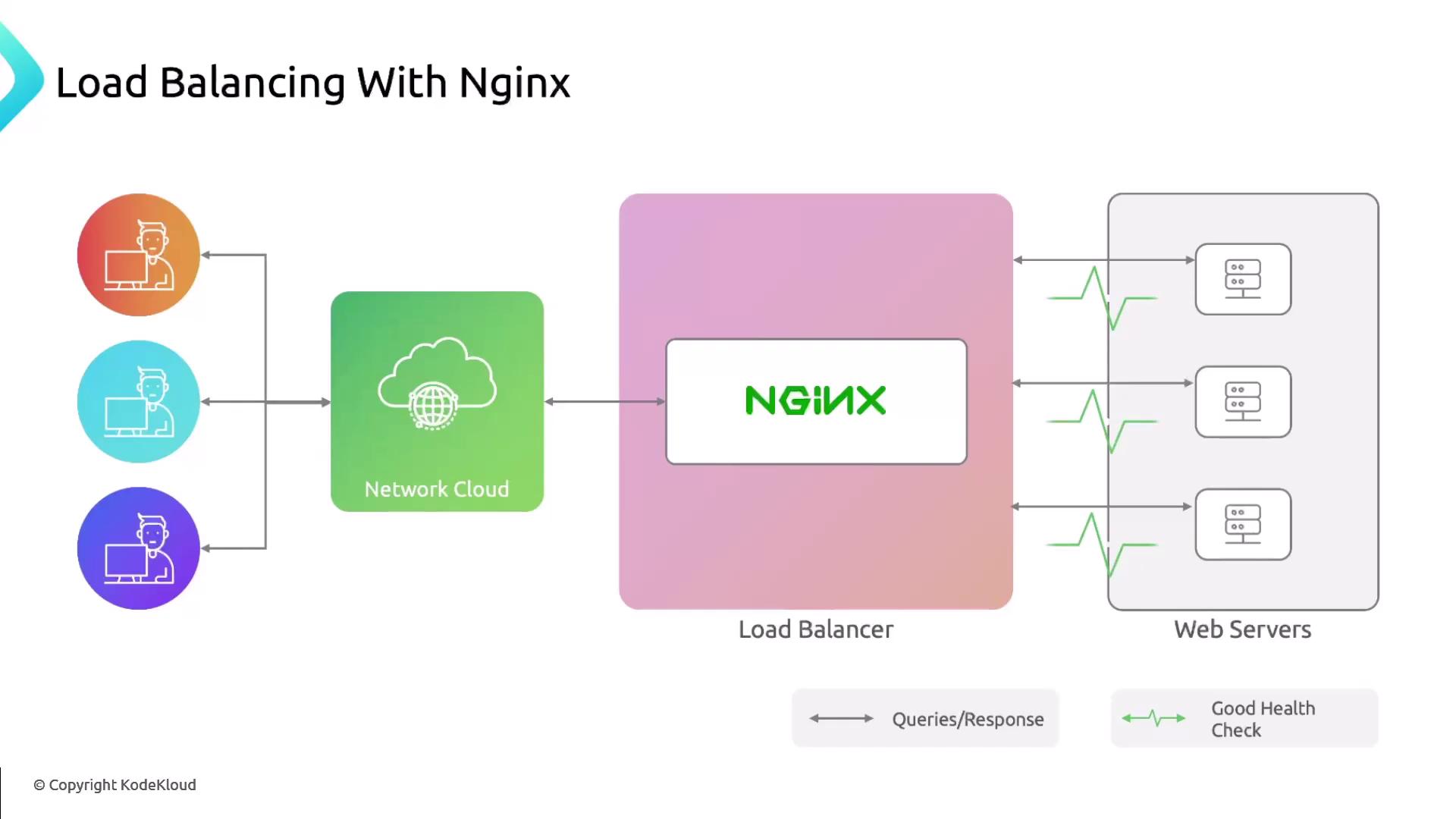
Reverse Proxy
A reverse proxy accepts client requests, applies routing or SSL offloading, then forwards them to one or more backend servers. This hides your infrastructure behind a single public endpoint.
Load Balancer vs. Reverse Proxy
| Feature | Load Balancer | Reverse Proxy |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Distribute traffic across servers | Intercept and forward requests |
| Backend Servers | Requires two or more | Can work with a single server |
| Common Use Cases | Scaling, failover, health checks | SSL/TLS termination, path-based routing |
Forward Proxy
A forward proxy sits between clients and the internet, filtering or anonymizing outbound requests. Configure Nginx to restrict sites or mask client IPs for privacy.Opening a forward proxy to the public can lead to abuse. Always secure it with
allow/deny or authentication mechanisms.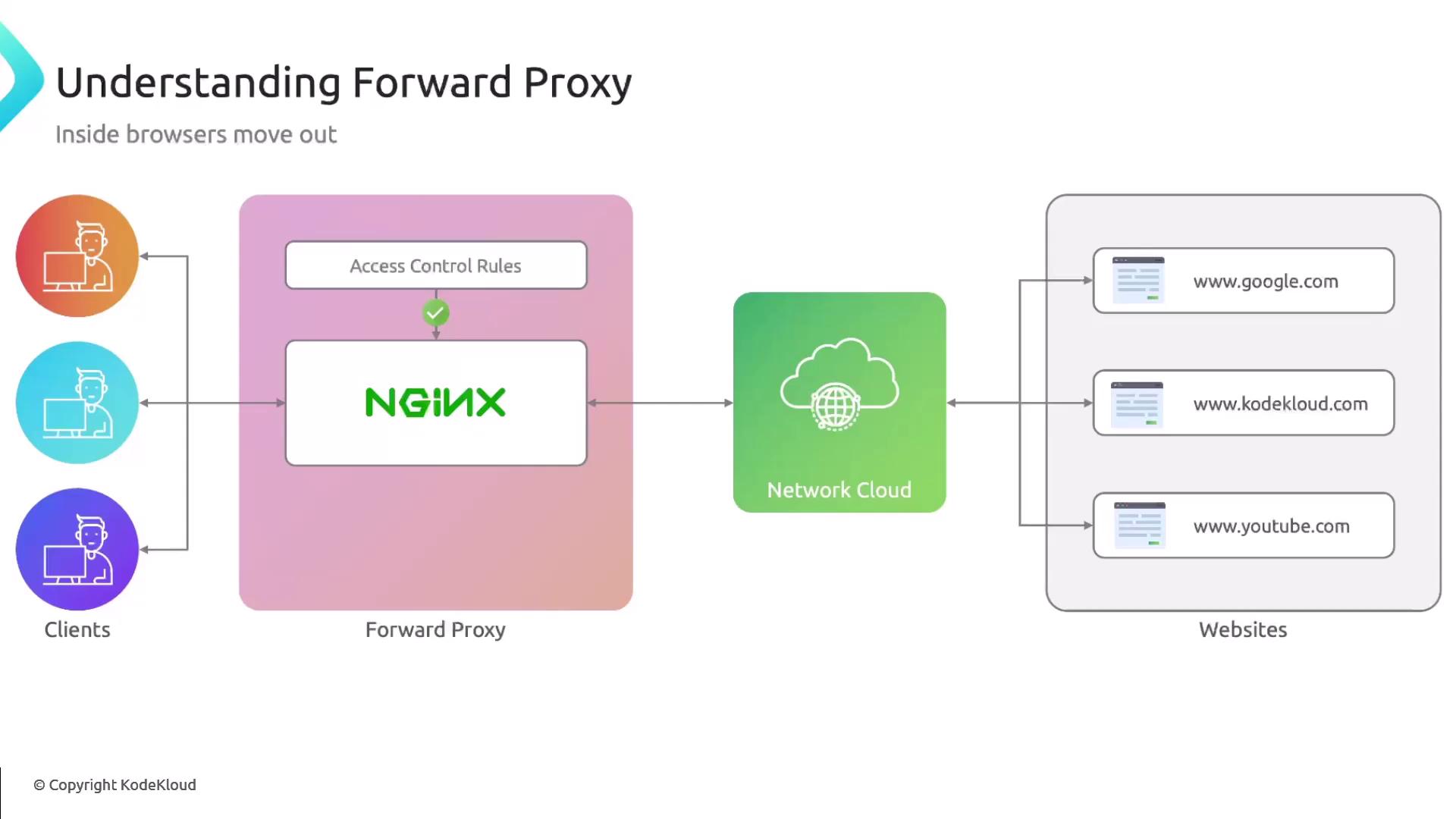
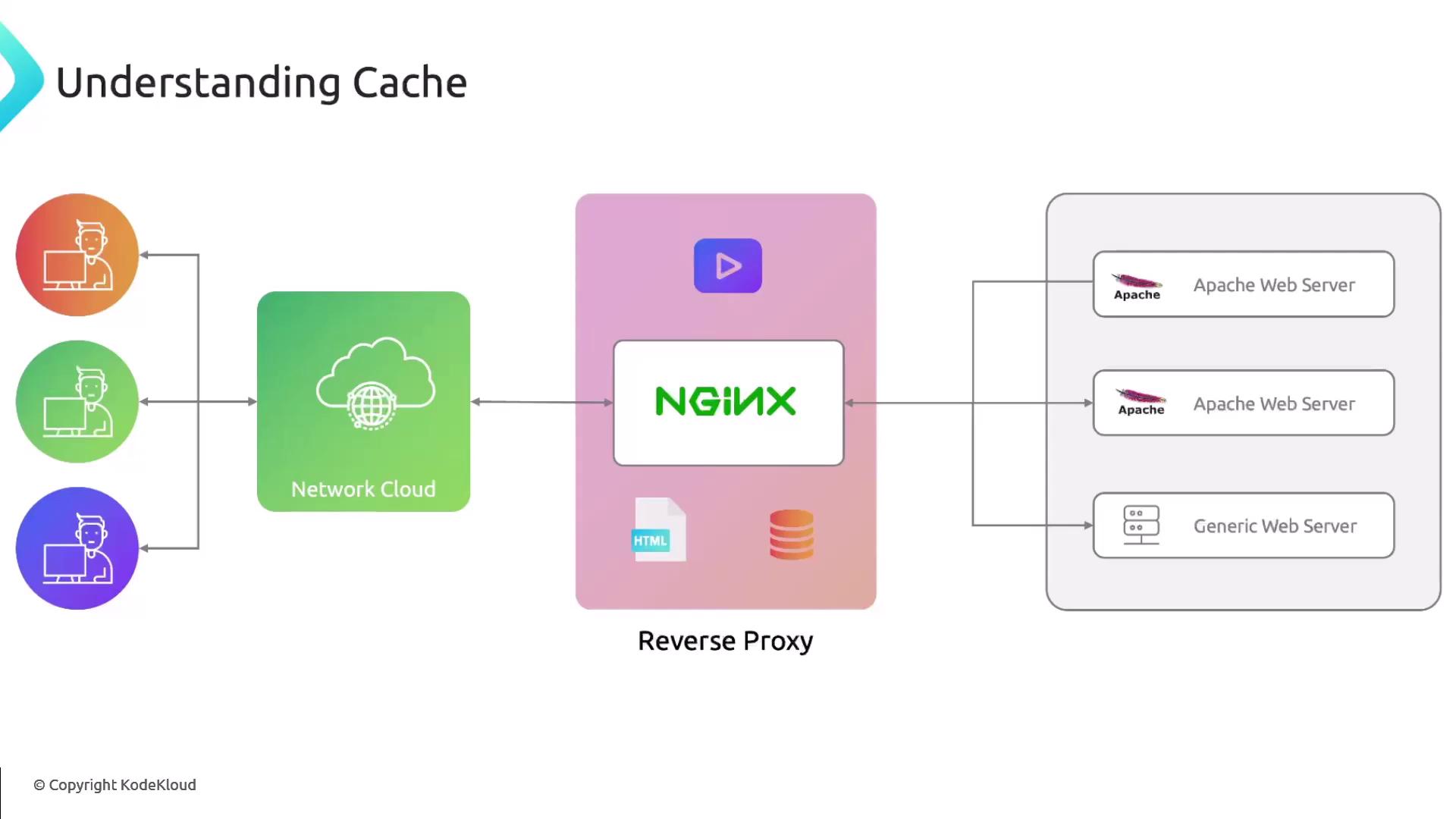
Caching
Caching with Nginx reduces response times and eases load on backend services. Define a cache zone, set key parameters, and control how responses are stored.Monitor cache usage and tune
inactive and max_size to avoid running out of disk space. Use proxy_cache_bypass for selective caching.