AWS Solutions Architect Associate Certification
Designing for Reliability
Turning up Reliability on Storage Services
Future Solutions Architects,
In this lesson, we explore how to enhance reliability in AWS storage services. Although AWS inherently provides a high level of reliability, implementing best practices and configurations can further improve availability and resiliency. These enhancements are particularly important for the Associate-level exam and for designing robust architectures.
Below is an organized overview of storage services—covering block storage, file storage, and object storage—as well as backup and disaster recovery strategies.
Block Storage
AWS block storage includes services such as EBS volumes, EFS file systems, snapshots, S3 backups, FSx for Lustre, FSx for NetApp, and more. These services typically create at least three redundant copies of your data. For instance, AWS automatically makes three copies when taking an EBS snapshot or using an EFS file system.
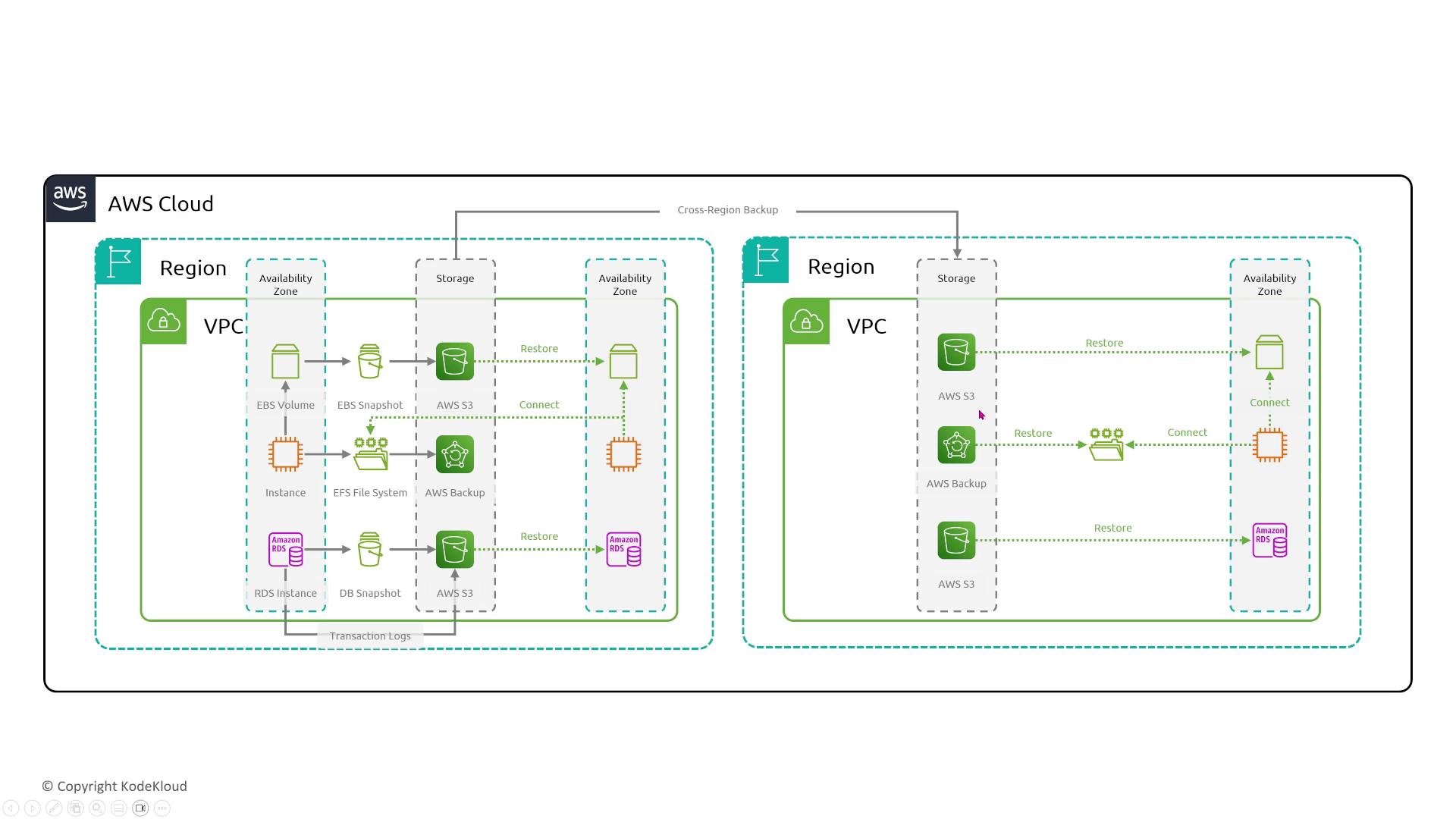
EBS Volumes
EBS volumes serve as durable, reliable hard drives attached to EC2 instances. To enhance data protection, regularly schedule snapshots. It is important to note that adjusting performance parameters such as switching to GP3 or increasing IOPS does not change the underlying redundancy, which is already maximized by AWS. Snapshots ensure fast recovery in the event of data corruption or accidental deletion, but they do not increase the intrinsic fault tolerance of the volume.
Instance Store
In contrast, instance store volumes, which are local storage on the EC2 instance's host, deliver excellent performance (up to 150,000–185,000 IOPS) via NVMe storage. However, they are ephemeral and do not persist when the instance fails or is relocated. Therefore, for scenarios where data durability is essential, always choose EBS over instance store.

File and Network Storage
Amazon EFS
Amazon EFS (Elastic File System) is designed for inherent redundancy. It spans multiple Availability Zones (AZs) within a region, ensuring data is automatically backed up with at least three copies. EFS can also be replicated across regions if required.
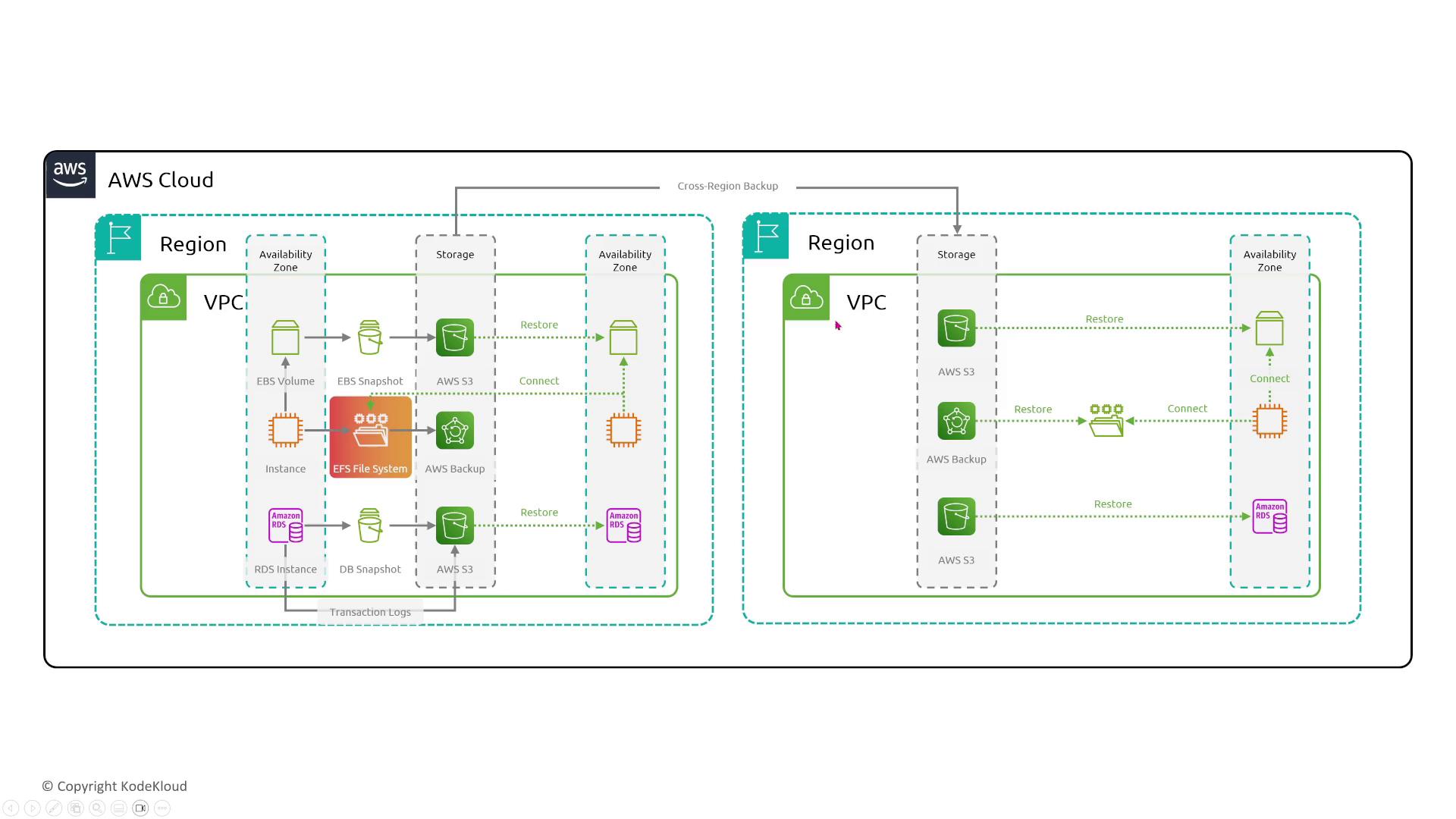
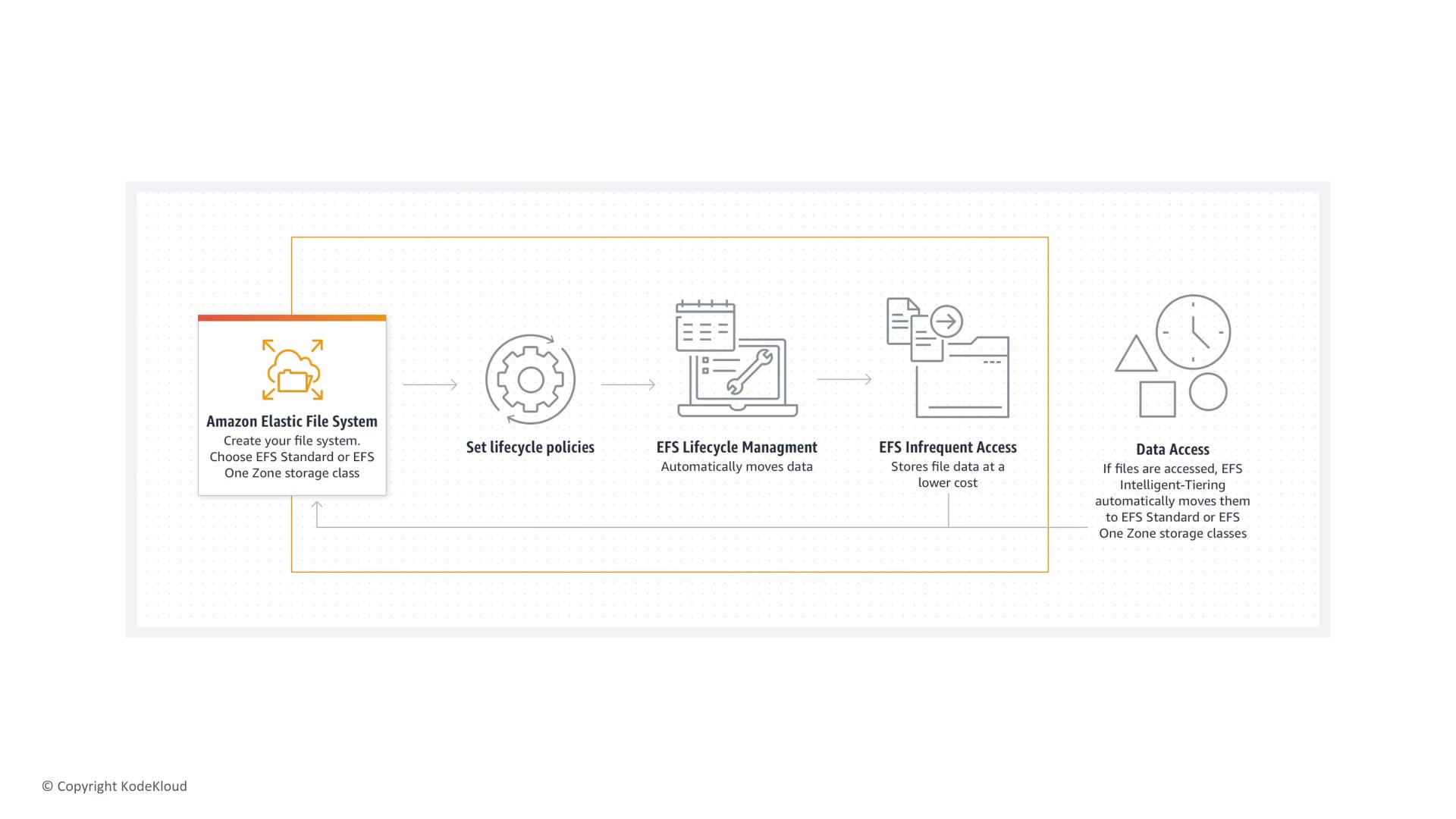
EFS offers configurable performance options and lifecycle management, such as intelligent tiering that moves infrequently accessed files to a different storage class similar to that available in Amazon S3. However, while these features enhance performance and cost-efficiency, they do not modify the inherent fault tolerance. Choosing the EFS One Zone option will reduce resiliency compared to the default multi-AZ setup.
EFS lifecycle management can automate data movement based on usage patterns:
FSx Services
FSx for Windows File Server
This service integrates with Active Directory and provides full redundancy through AWS-managed replication. There are no additional configurations to enhance reliability beyond enforcing strong security practices.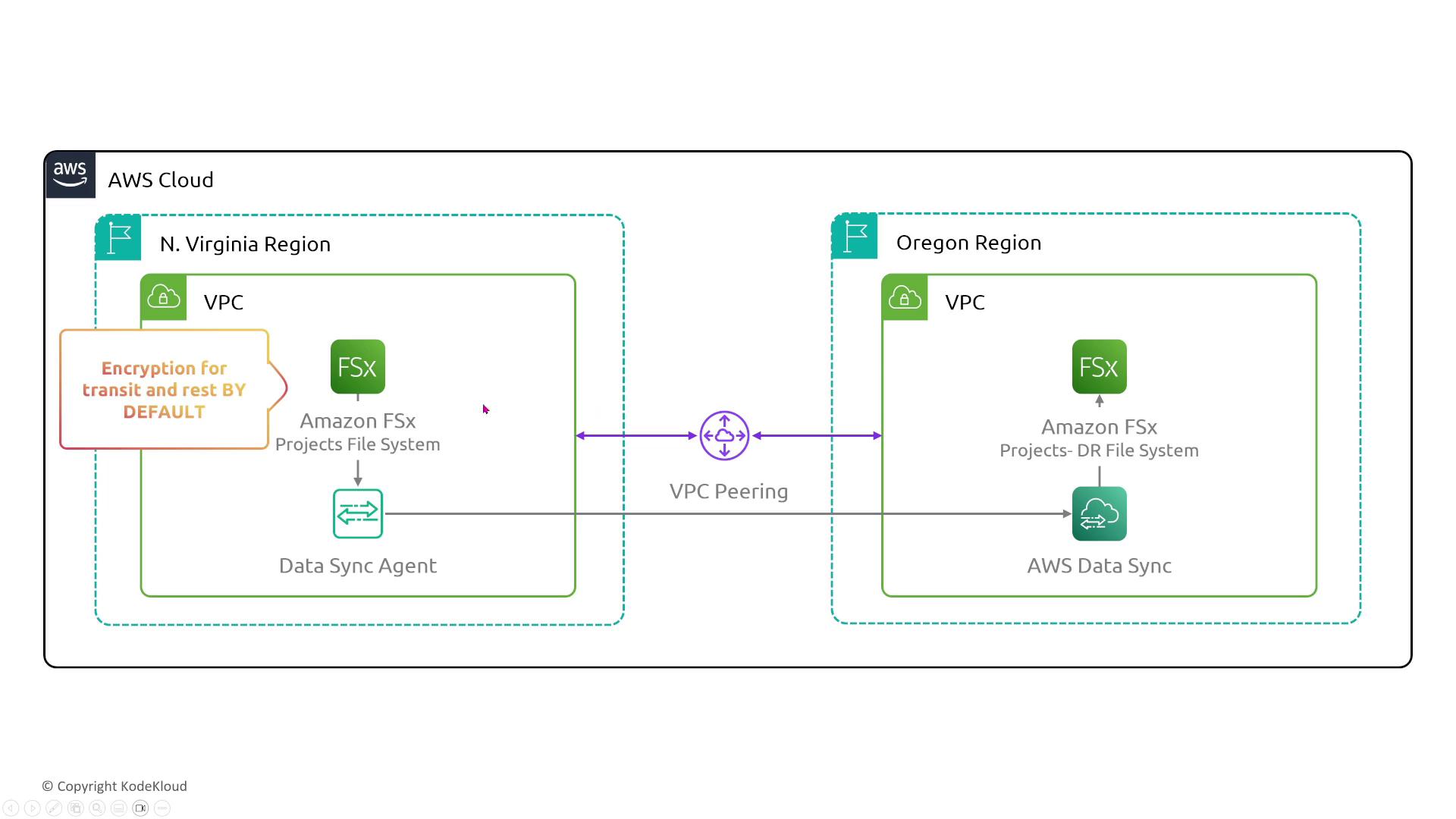
FSx for Lustre
FSx for Lustre is commonly employed in high-performance computing (HPC) simulations where both performance and reliability are critical. For enhanced backup and redundancy, it is frequently linked to Amazon S3. Additional redundancy settings are not available because the service is designed with inherent reliability.
OpenZFS and ONTAP in FSx for OpenZFS
These services offer advanced features such as snapshot volumes and clone volumes. While they do not add extra built-in reliability controls, proper configuration can significantly improve backup speed and data availability. Reliability is largely determined by how the features are utilized rather than by enabling an extra reliability option.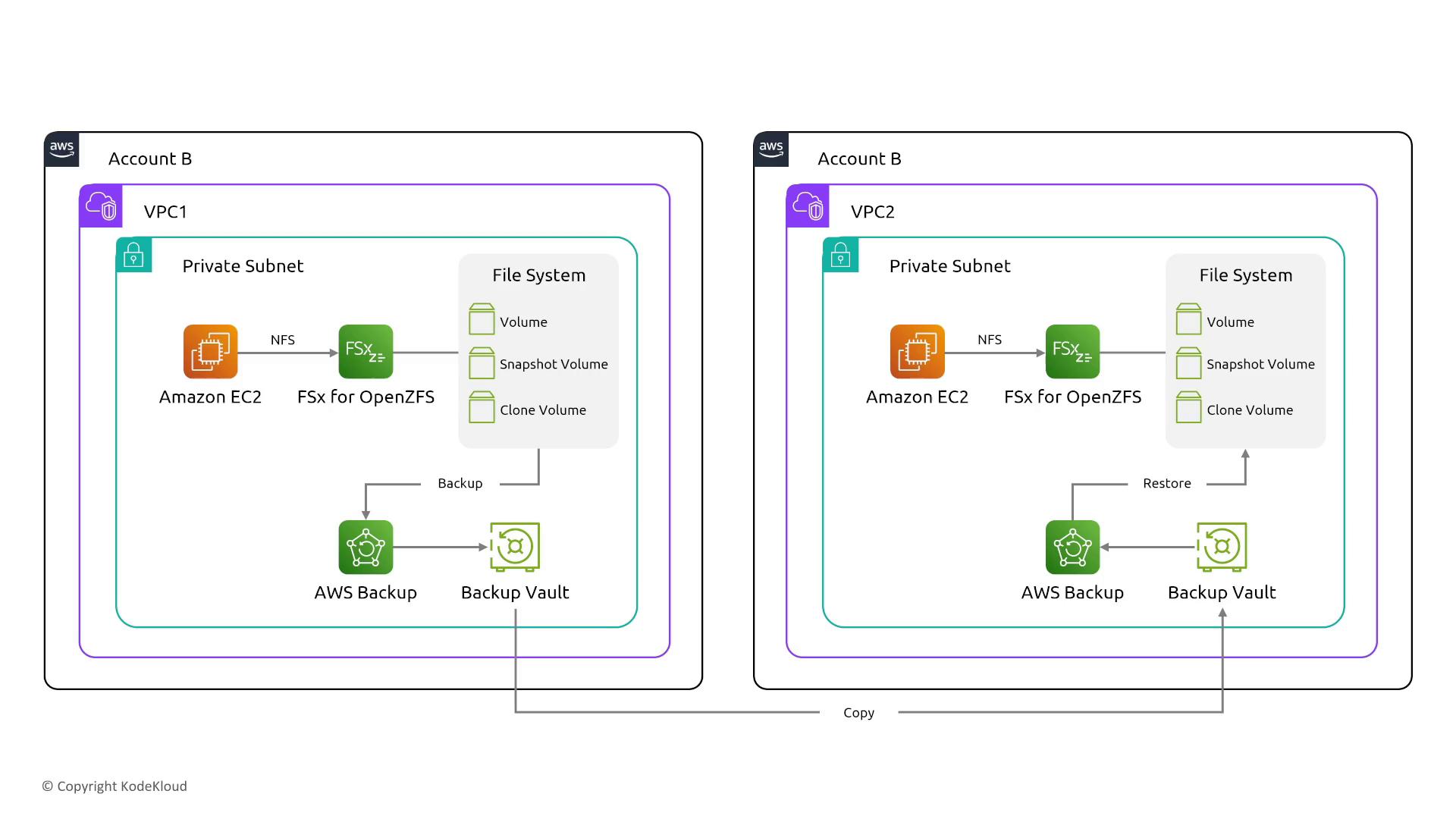
Amazon ONTAP
Similar to OpenZFS, Amazon ONTAP is built with resiliency in mind. Although features like deduplication, compression, and encryption improve efficiency and indirectly support reliability, the core reliability mechanisms rely on AWS’s default three-copy storage design.
Object Storage: Amazon S3
Amazon S3 delivers simple and reliable storage with a built-in design that maintains at least three copies of your data (excluding the S3 One Zone option, which stores data in a single AZ). Standard security measures include private buckets, server-side encryption, IAM controls, bucket policies, and NACLs for access management.

Understanding how S3 evaluates permissions is crucial. Even though measures like public access blocks and logging are essential for security, they do not increase the service’s inherent reliability. Amazon S3 automatically provides high availability through its redundant storage design.
When replicating data between buckets—such as configuring a source bucket with disabled replication and a secondary bucket for compliance or disaster recovery—remember that S3’s automatic redundancy typically negates the need for additional reliability adjustments.
Backup, Disaster Recovery, and Redundancy
Ensuring data reliability extends beyond primary storage configurations. Robust backup and disaster recovery strategies are essential for restoring services in case of data corruption or accidental deletion. Using EBS snapshots, EFS snapshots, or FSx snapshots, you can safeguard your data by storing backups in encrypted vaults. Often, these backups are replicated to further mitigate data loss.
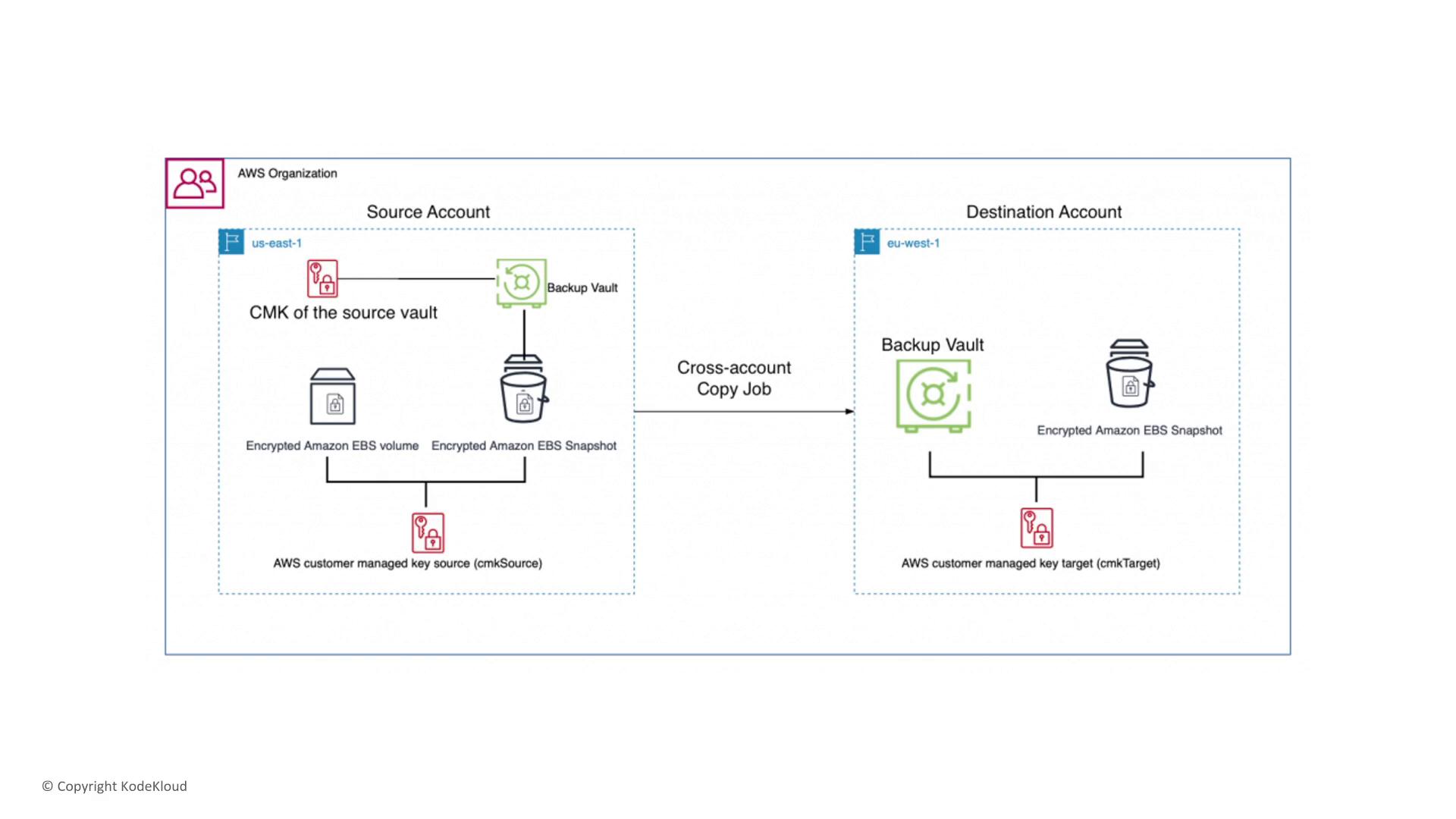
A typical backup scenario might involve:
- Storing critical backups with encryption via a customer-managed key (CMK).
- Implementing lifecycle policies that prevent inadvertent deletion or alteration.
- Using a VPC interface endpoint for secure private data transfers during backup replication and recovery.


For secure, private data transfers with added redundancy, consider using a VPC interface endpoint when communicating with AWS Backup services.
Elastic Disaster Recovery (EDR)
Elastic Disaster Recovery (EDR) is vital in ensuring rapid application recovery during outages. By replicating on-premises data to a staging area in AWS, EDR enables you to launch EC2 instances quickly in the event of an emergency. The EDR console offers insights into job execution and instance details, reinforcing your application's resiliency.

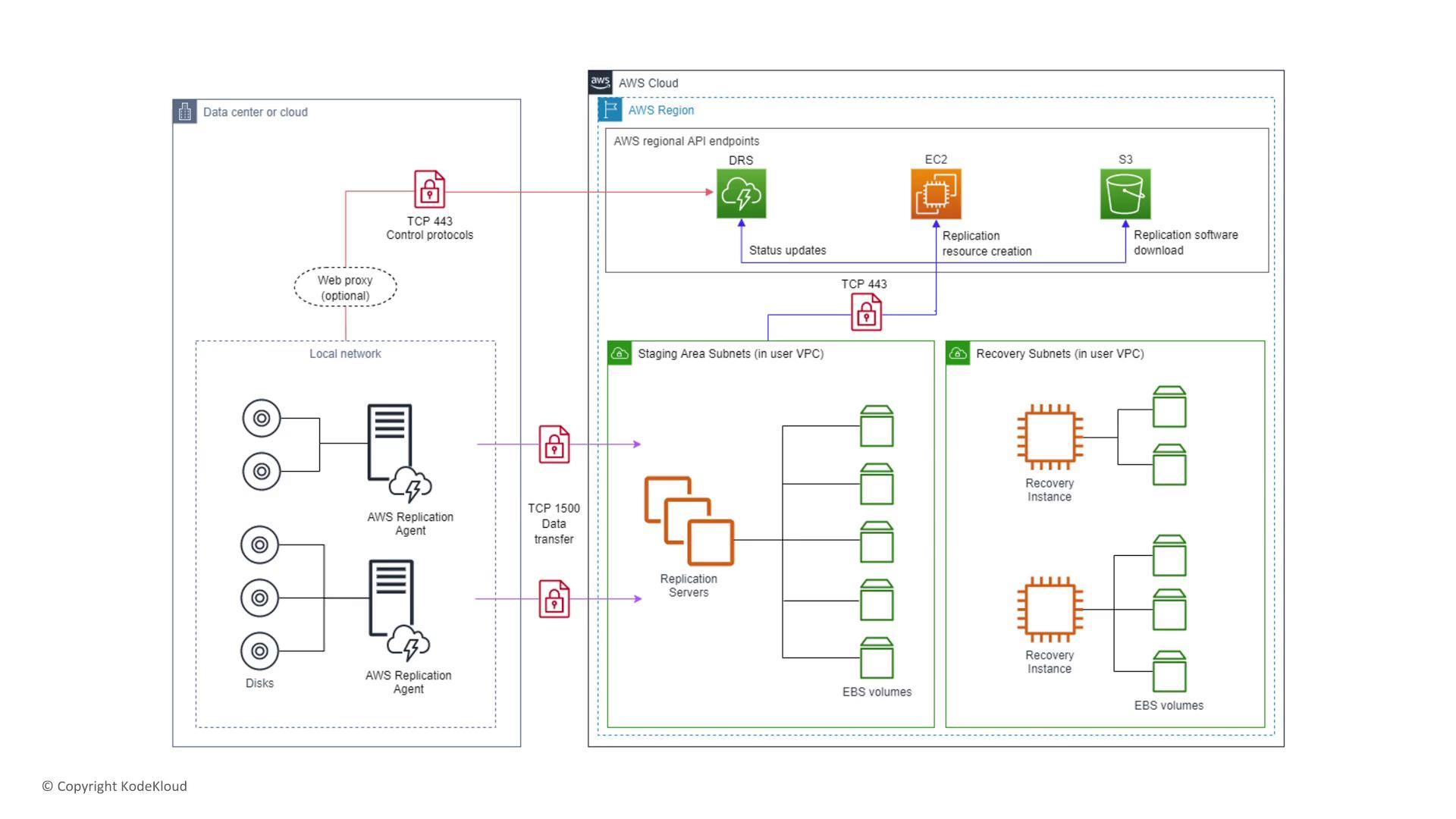
Remember, in failover and failback procedures, “fail back” refers to reverting to the primary environment after a recovery event or test. EDR’s capabilities ensure that even during outages, your applications remain available.
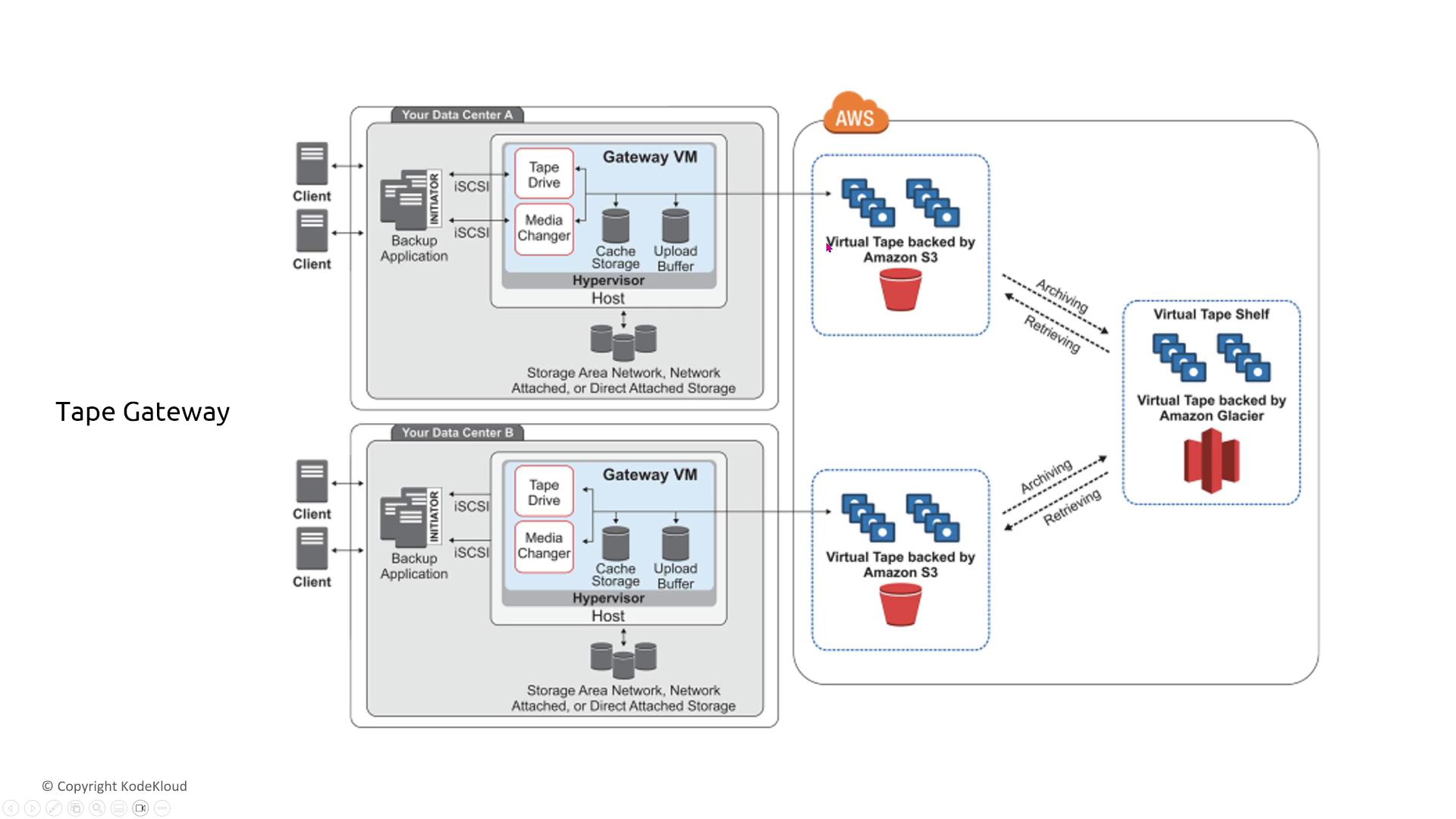
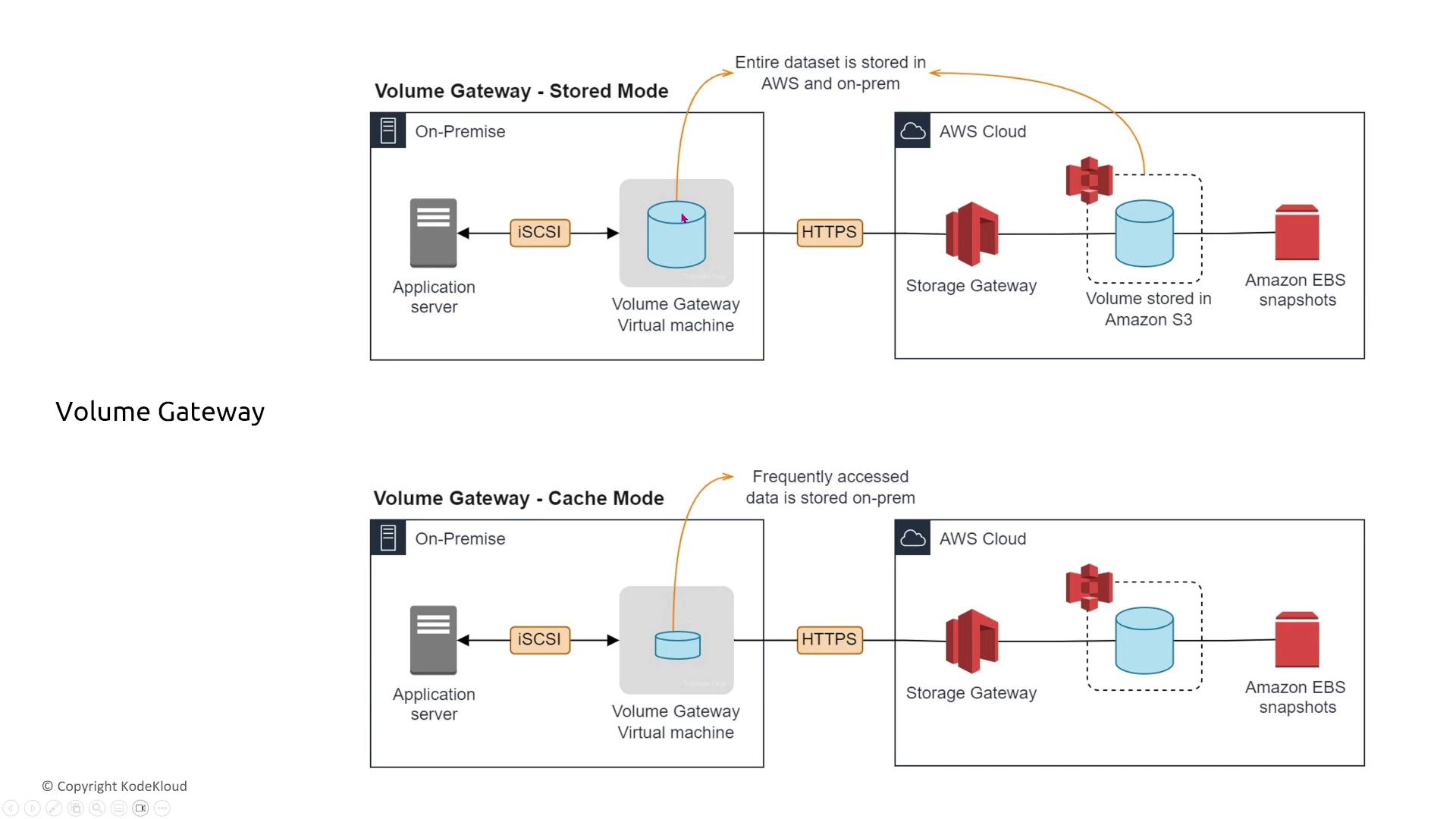
Storage Gateway
Storage Gateway bridges on-premises data centers with AWS storage solutions. It is available as a volume gateway, tape gateway, or file gateway, each with its own considerations:
- A storage gateway appliance is deployed in your corporate data center and connects with AWS over the internet or via a private link.
- The appliance itself represents a single point of failure. Although you can restart the virtual machine, the attached disks must be properly managed to avoid data loss.
- For file and tape gateways, the underlying AWS storage (typically S3 or Glacier) ensures redundancy, even if the local gateway experiences issues.
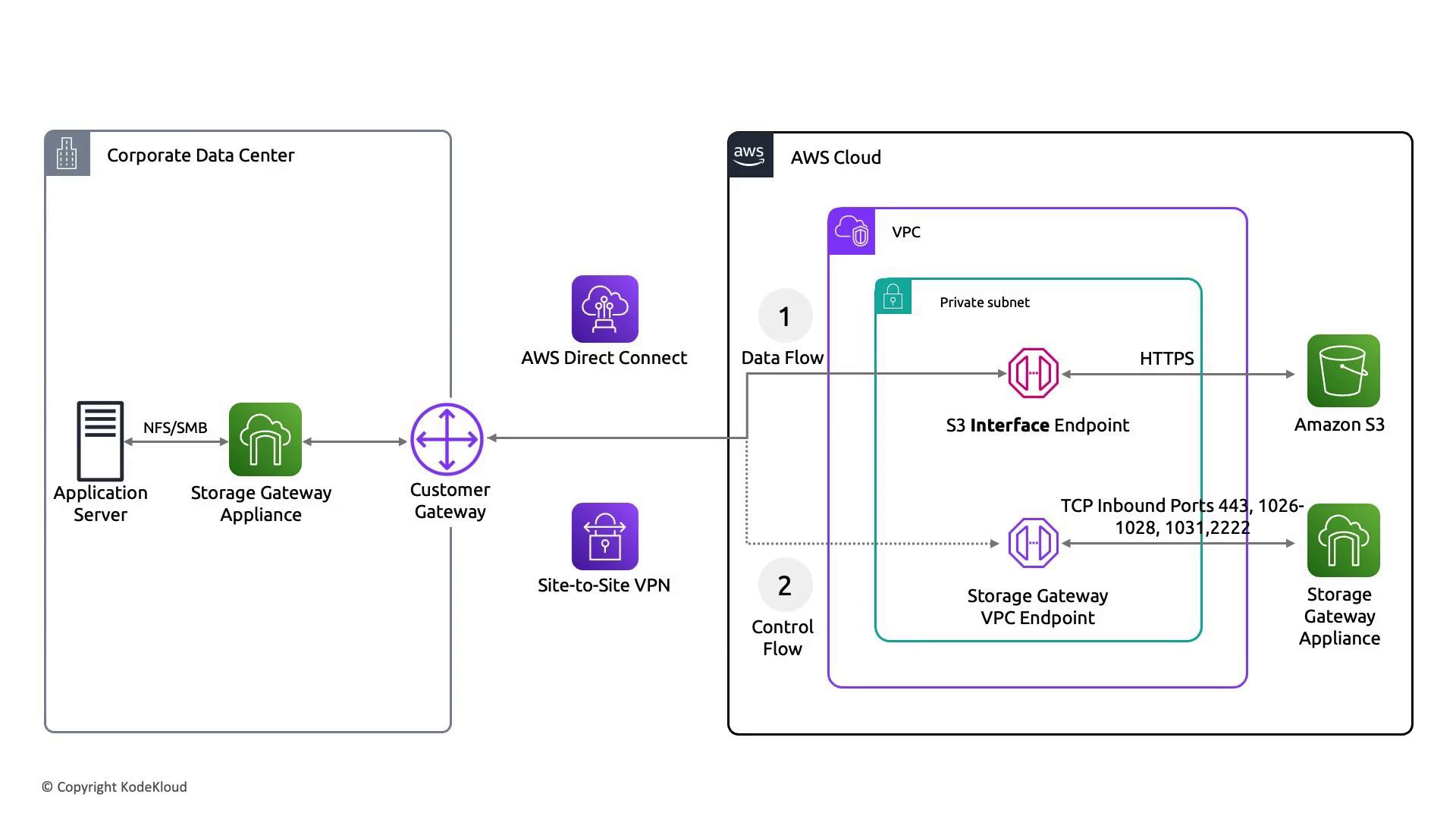
For FSx File Gateway and Tape Gateway deployments, ensure that you have a well-established recovery procedure. Running multiple instances of the gateway does not automatically provide active-active redundancy because these gateways typically attach to a single disk or storage volume at any given time.
Final Thoughts
In summary, AWS storage services are engineered to be highly redundant and reliable by default—with at least three copies of your data in most cases. However, understanding the differences between services such as EBS versus instance store and the significance of automated backups and disaster recovery is crucial for building resilient architectures. Backup strategies and Elastic Disaster Recovery (EDR) are essential for ensuring data restoration and maintaining service availability in the event of failures.
As you design your systems, keep in mind:
- AWS employs multiple copies of your data to ensure durability, similar to how scaling your application across multiple EC2 instances maintains performance and availability.
- Proper backup and data recovery plans are vital parts of your strategy.
I'm Michael Forrester. Thank you for reviewing this lesson. In upcoming lessons, we will delve into compute services and related concepts.
Note
For more detailed information on AWS storage solutions, consider visiting the AWS Documentation.
Watch Video
Watch video content
Practice Lab
Practice lab