
Messaging and Events
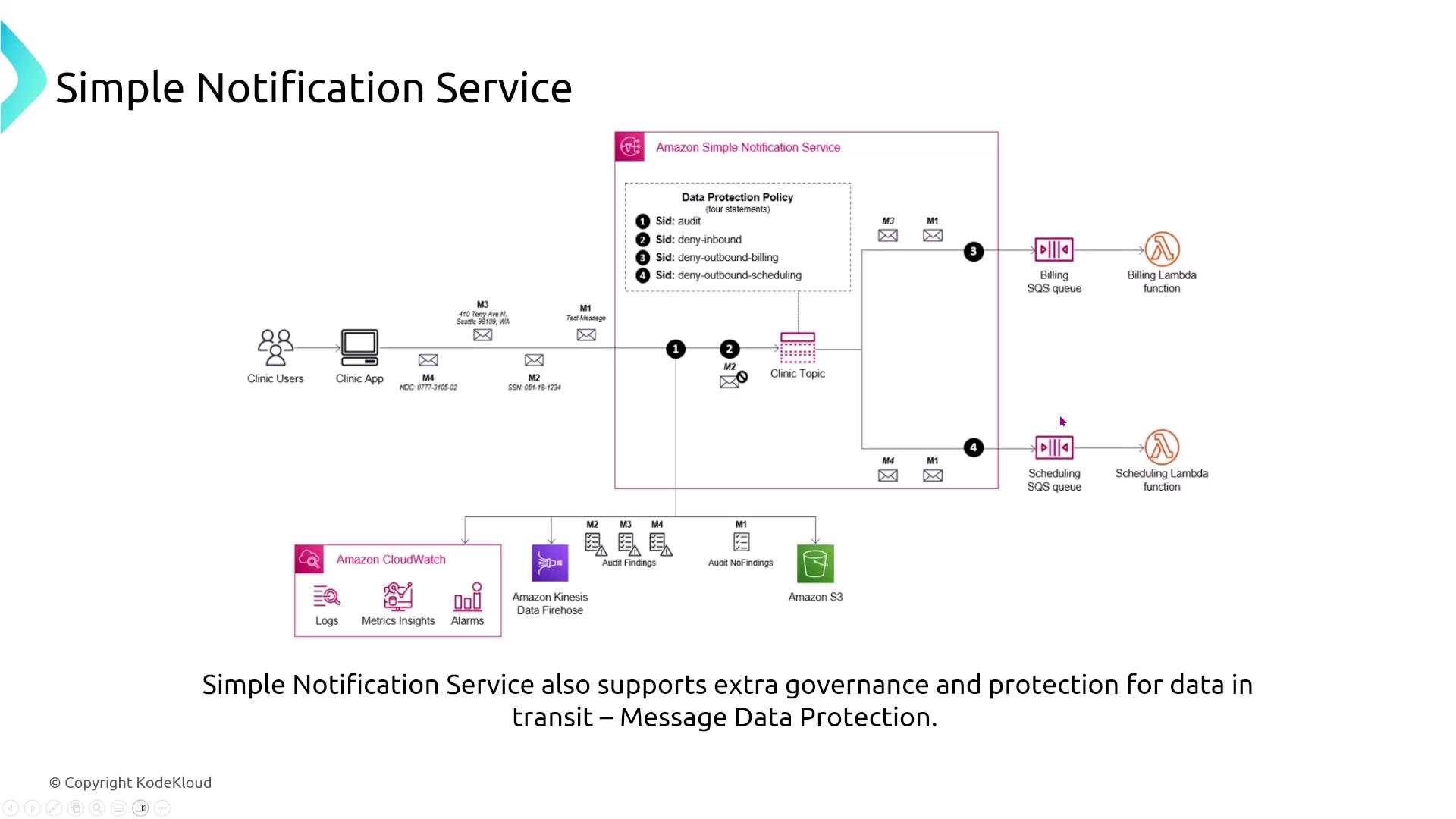
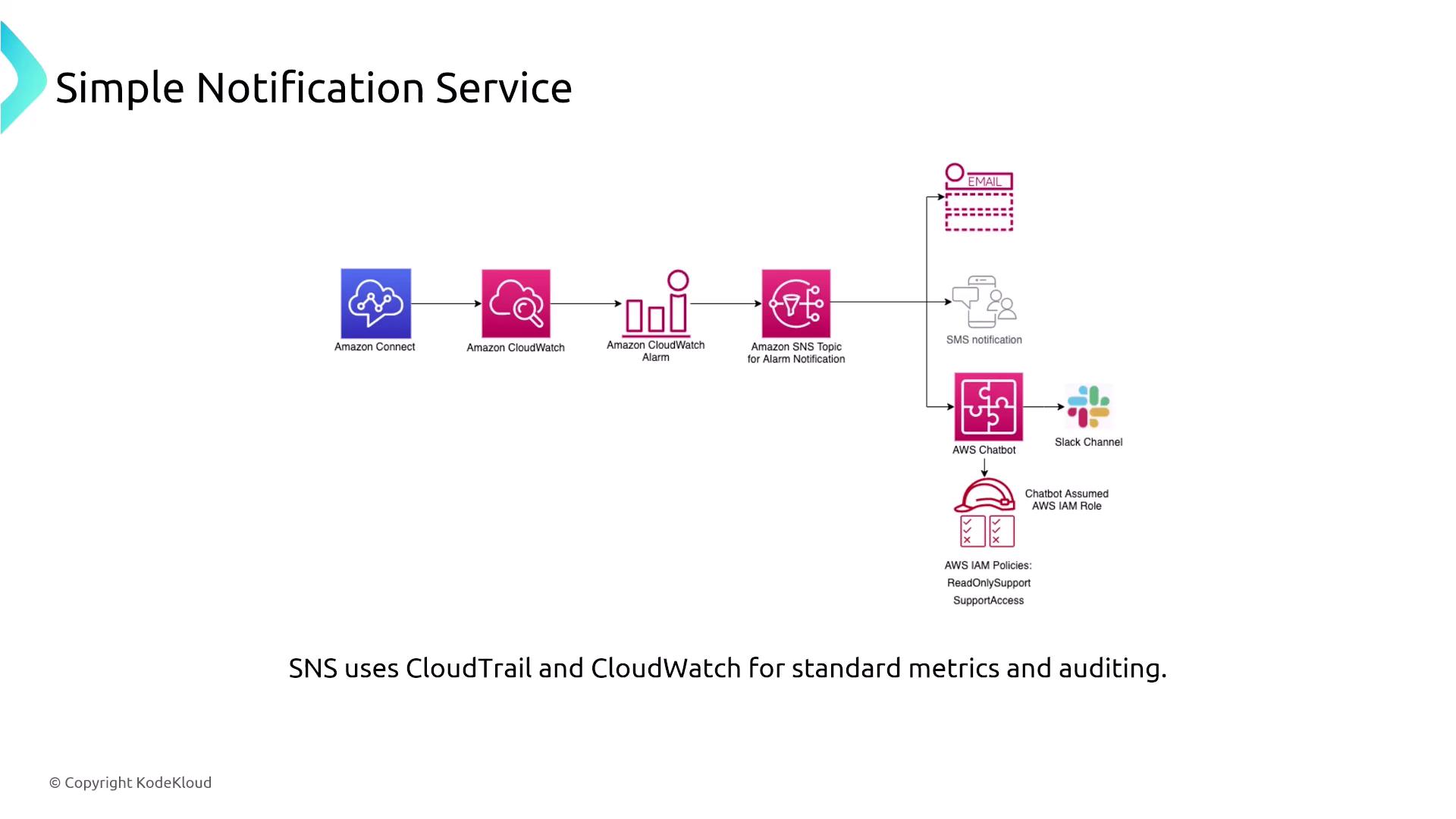
Next, we delve into messaging and event services, starting with the Simple Notification Service (SNS). SNS is a robust notification system that dispatches messages to a topic. Depending on the subscription configuration, these messages can be delivered to one or more endpoints such as SQS queues, email addresses, or SMS numbers. For example, a message might be replicated across three SQS queues as dictated by an application workflow. SNS secures data by encrypting both topics and queues using server-side encryption (SSE) via AWS Key Management Service (KMS).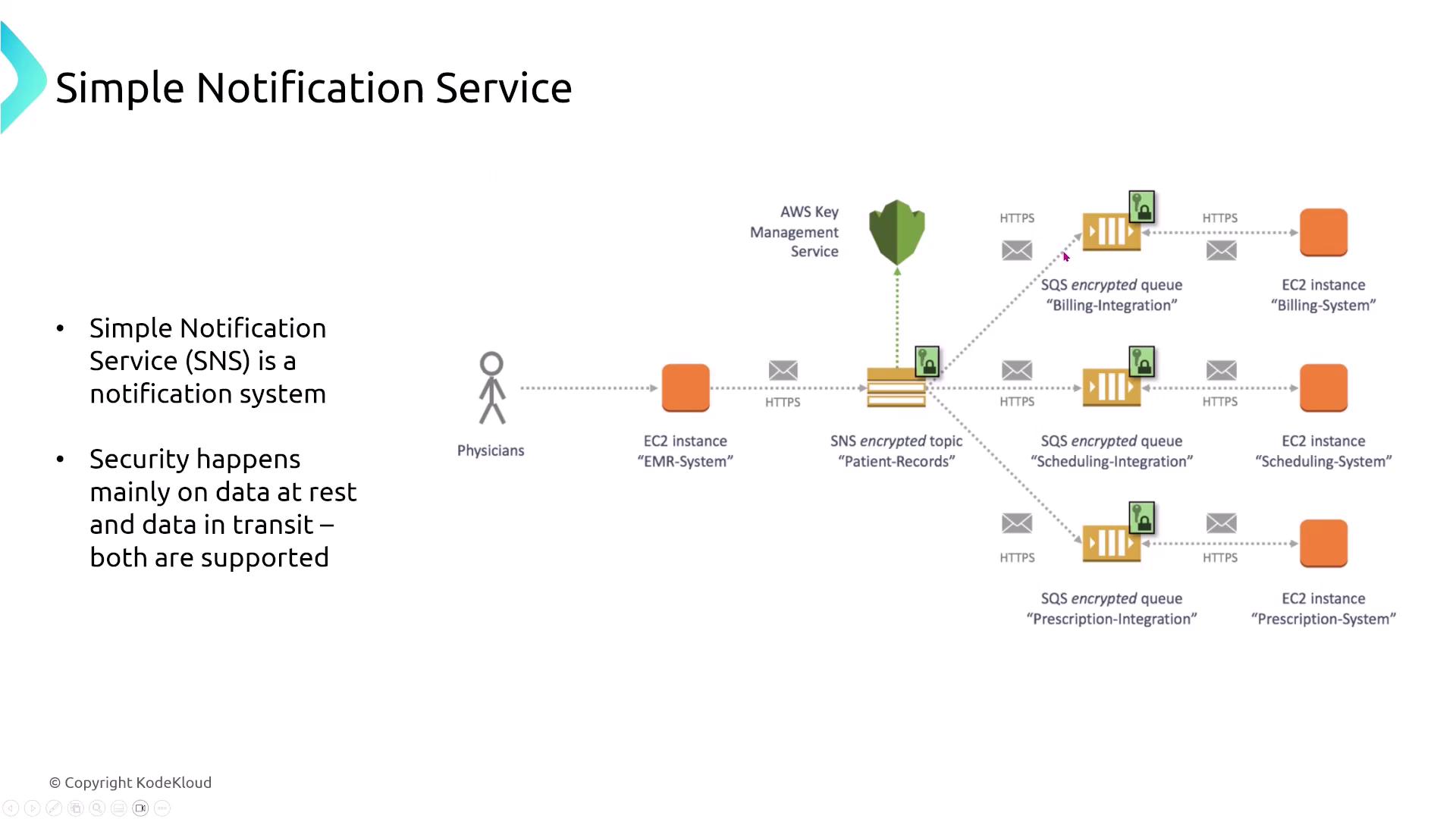


Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS)
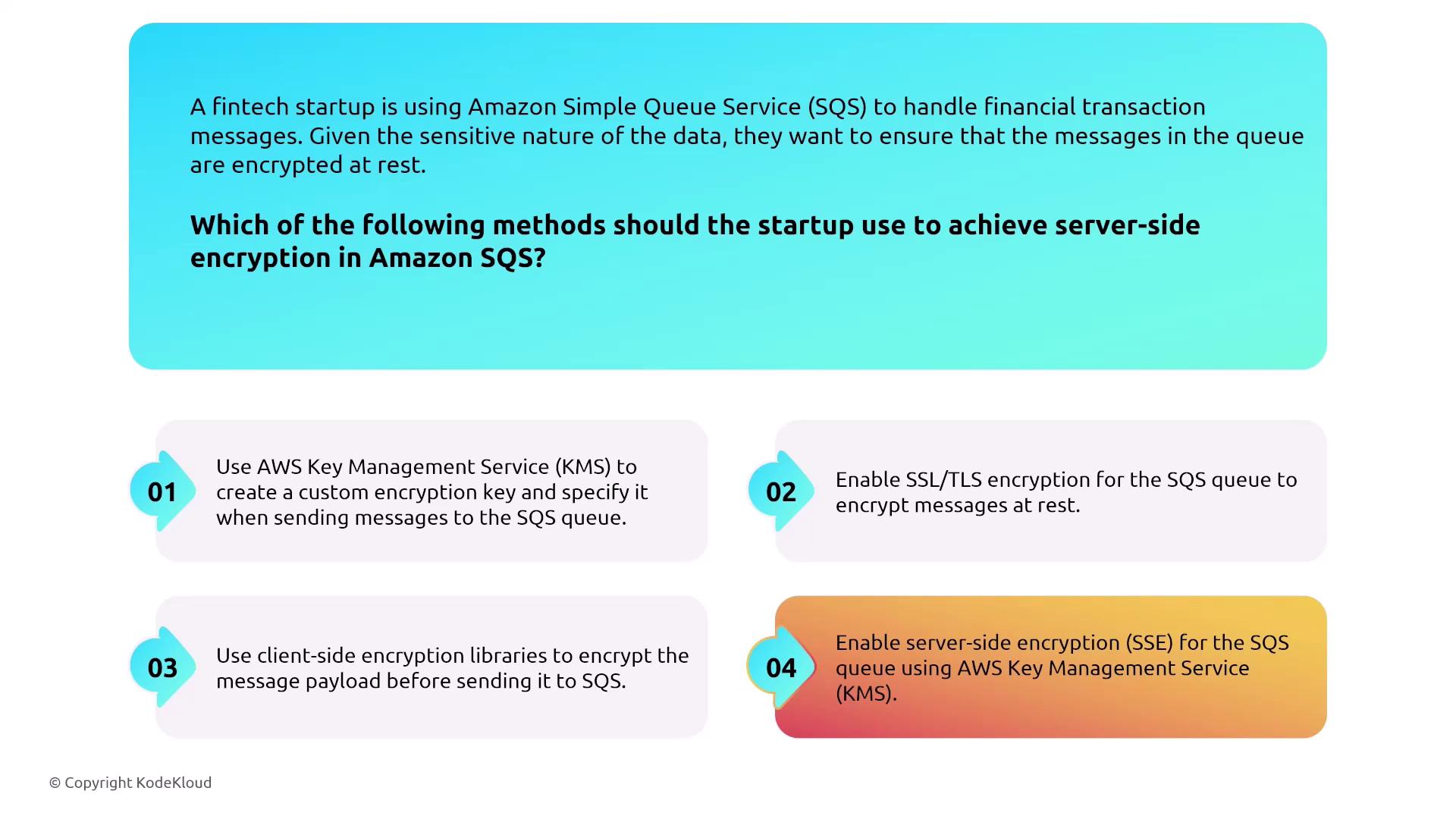
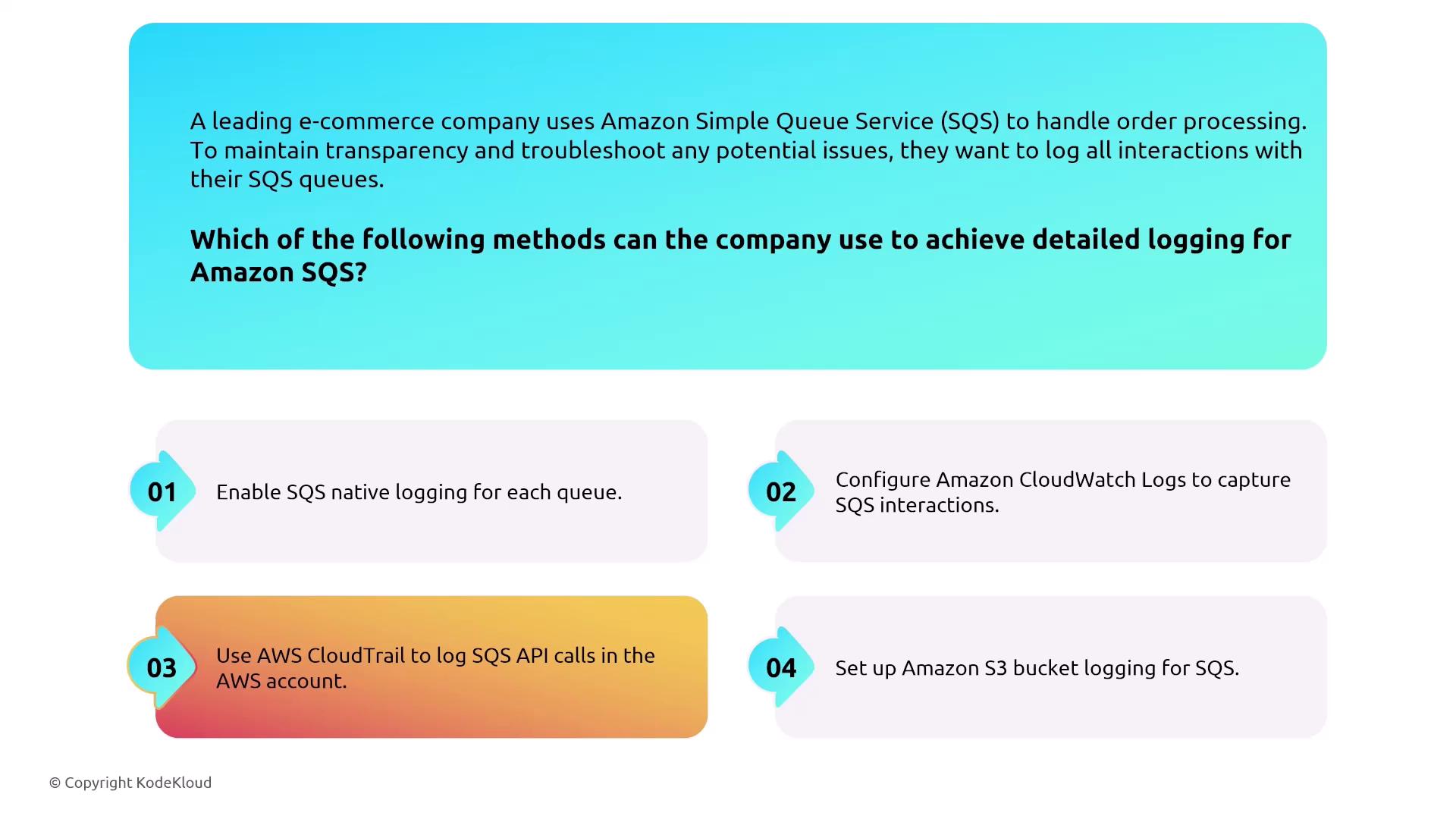
Now let’s discuss Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS). Launched shortly after S3, SQS is a highly managed queuing service available in both standard and FIFO versions. It provides built-in encryption at rest via KMS and supports private traffic through VPC interface endpoints powered by AWS PrivateLink. Although SQS offers CloudWatch metrics and API activity tracking through CloudTrail, note that it does not log individual queue messages natively without CloudTrail integration.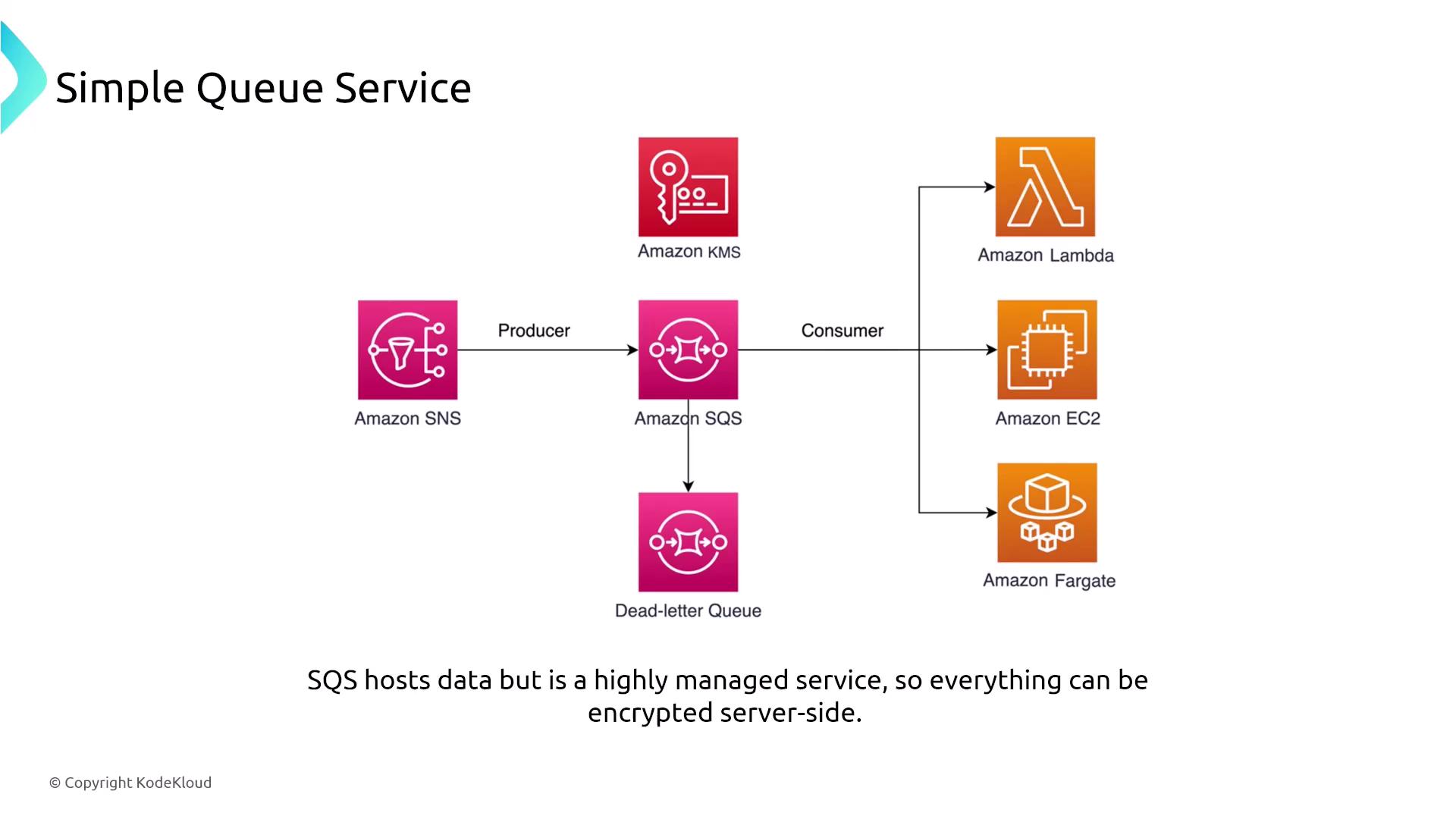
Amazon MQ
Moving on to Amazon MQ—a managed message broker service based on ActiveMQ (with support for RabbitMQ). Unlike SQS, Amazon MQ is tailored for scenarios where industry-standard messaging protocols (such as MQTT) and classic broker functionalities are required. Amazon MQ ensures security using KMS for encryption at rest and supports encrypted data in transit.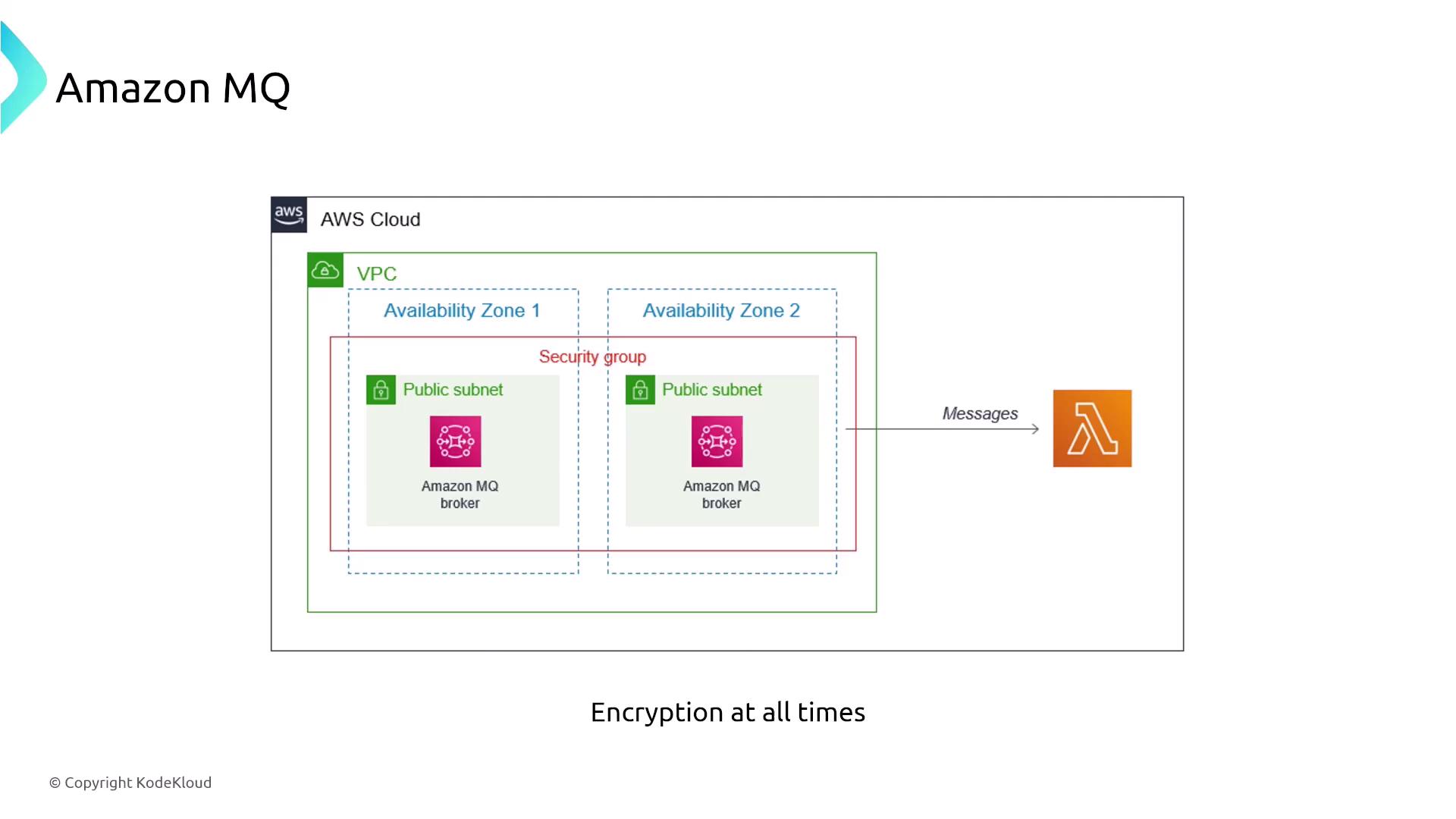
Amazon EventBridge
Amazon EventBridge is a fully managed event bus that efficiently routes events based on defined rules. It encrypts data by default using the AES-256 algorithm and provides a seamless connection between applications without acting as a traditional broker, streaming service, or managed workflow service. To monitor EventBridge, leverage CloudWatch metrics and CloudTrail, along with optional tools such as AWS X-Ray and AWS Config.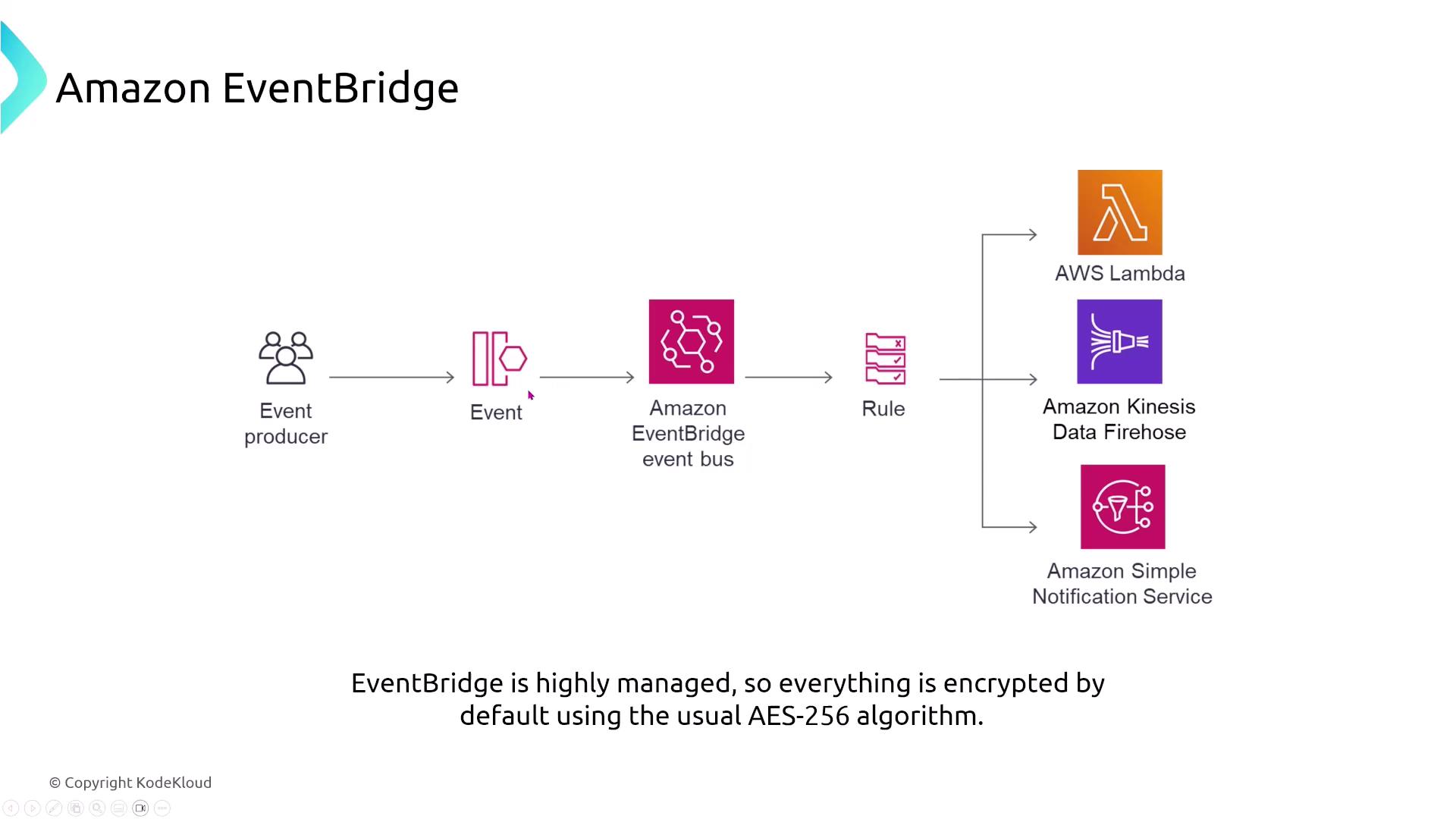

Amazon Simple Email Service (SES)
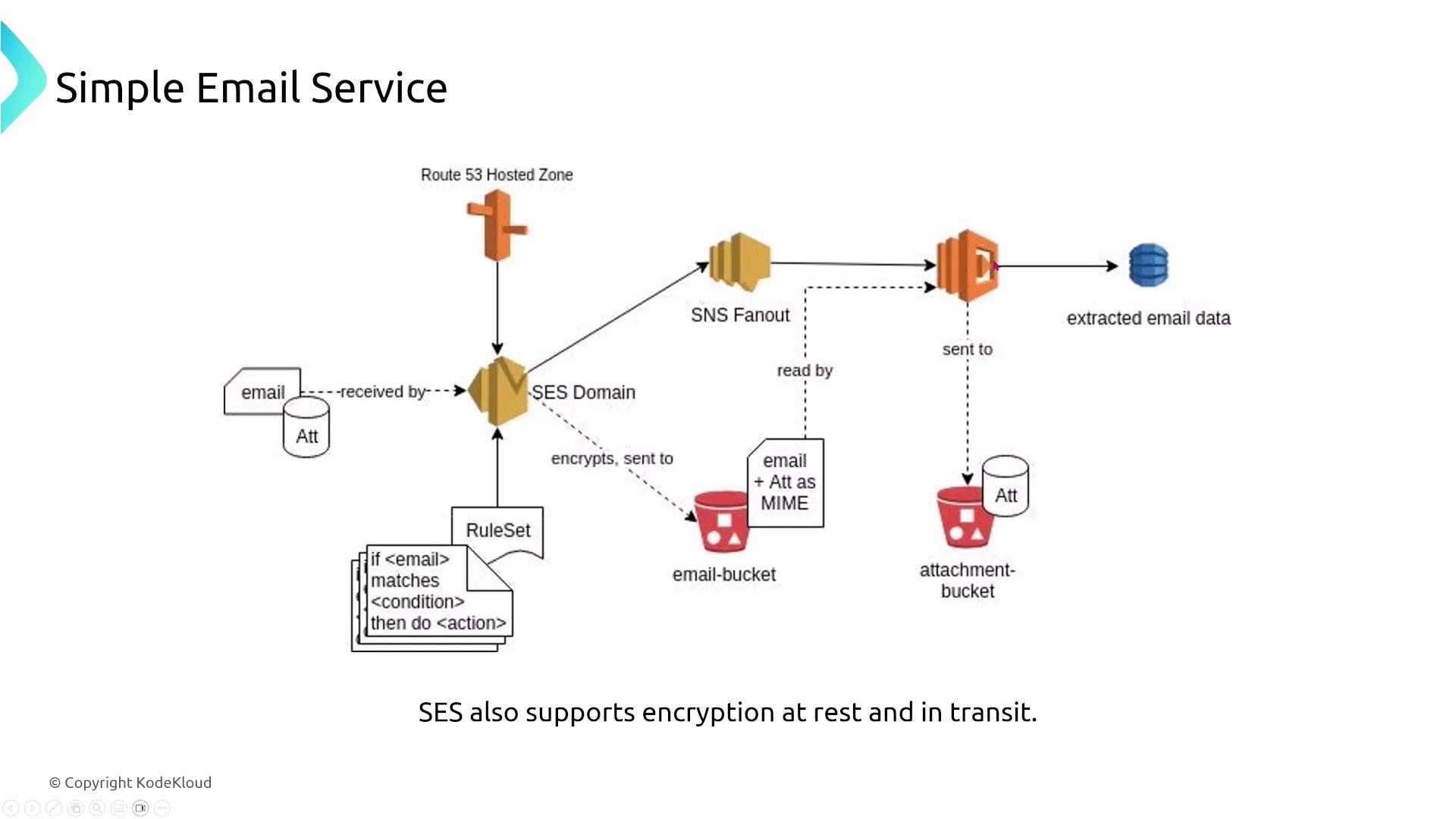
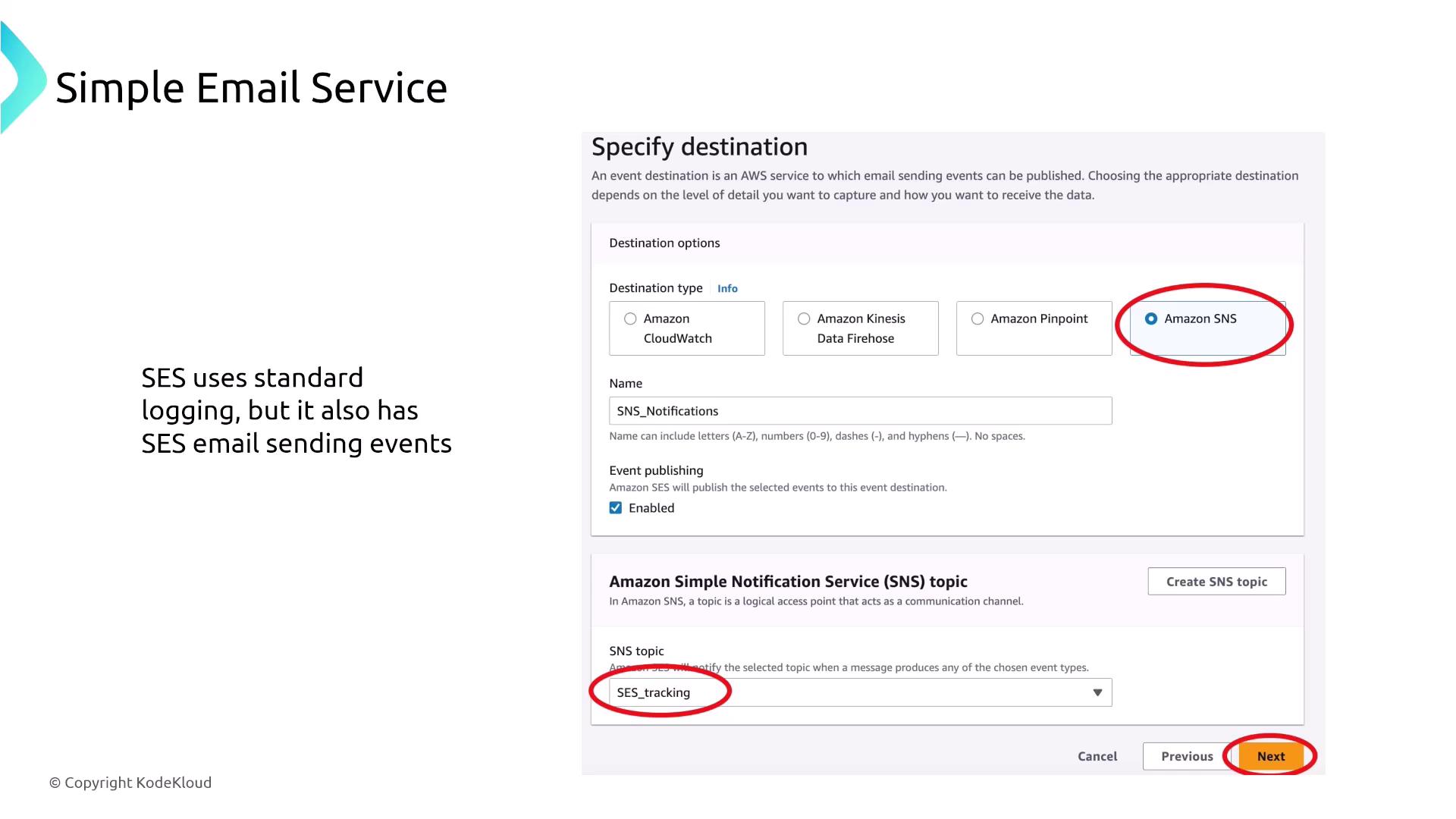
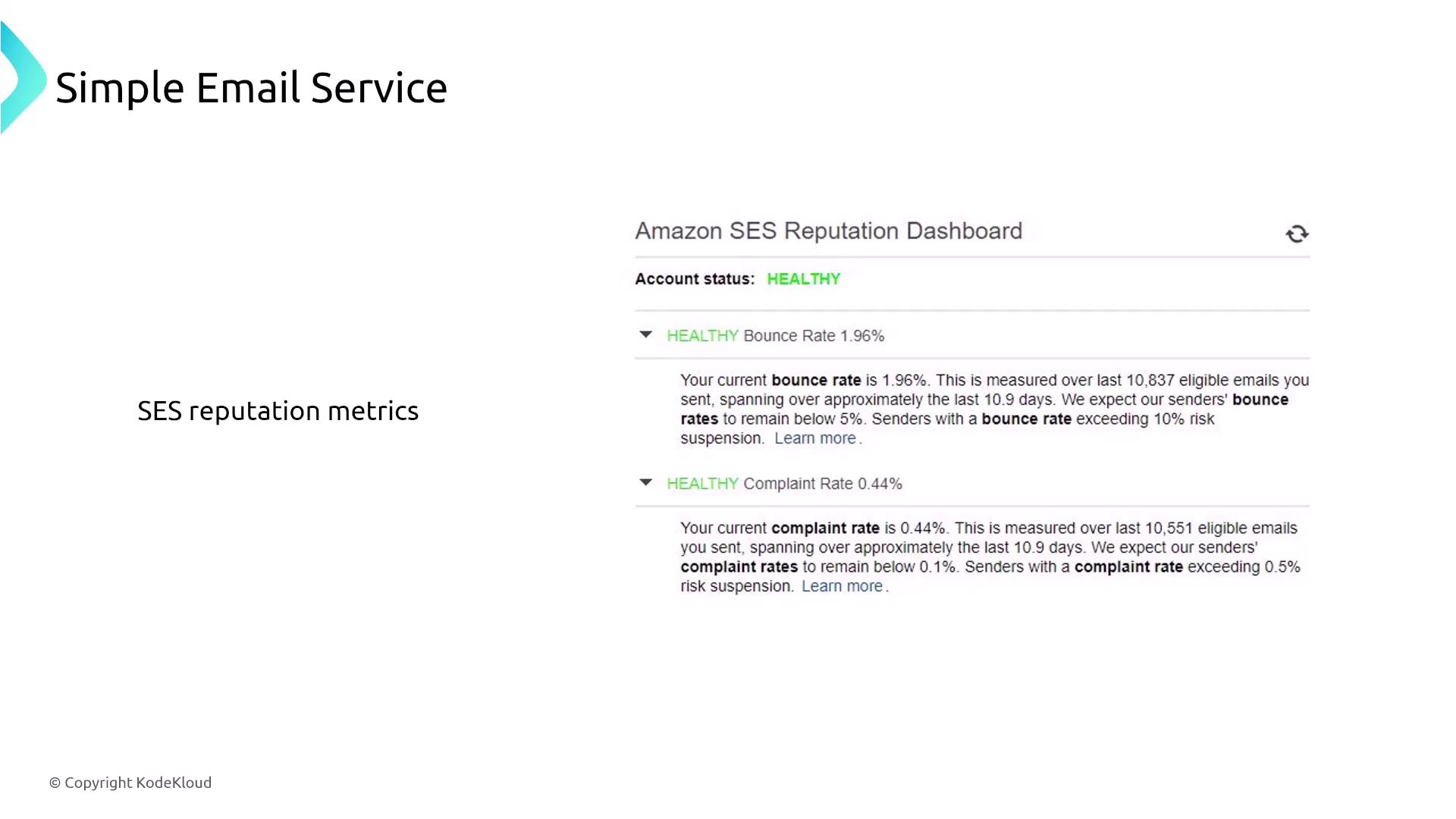
Amazon Simple Email Service (SES) differs from SNS in its focus on sending bulk emails. SES supports multiple actions such as sending emails, storing them on S3, and processing content via Lambda (for tasks like language detection before resending). SES applies AES-256 encryption by default for data in transit and supports encryption at rest. Its standard logging capabilities are available through CloudWatch or Kinesis Data Firehose, and event notifications can be configured with SNS.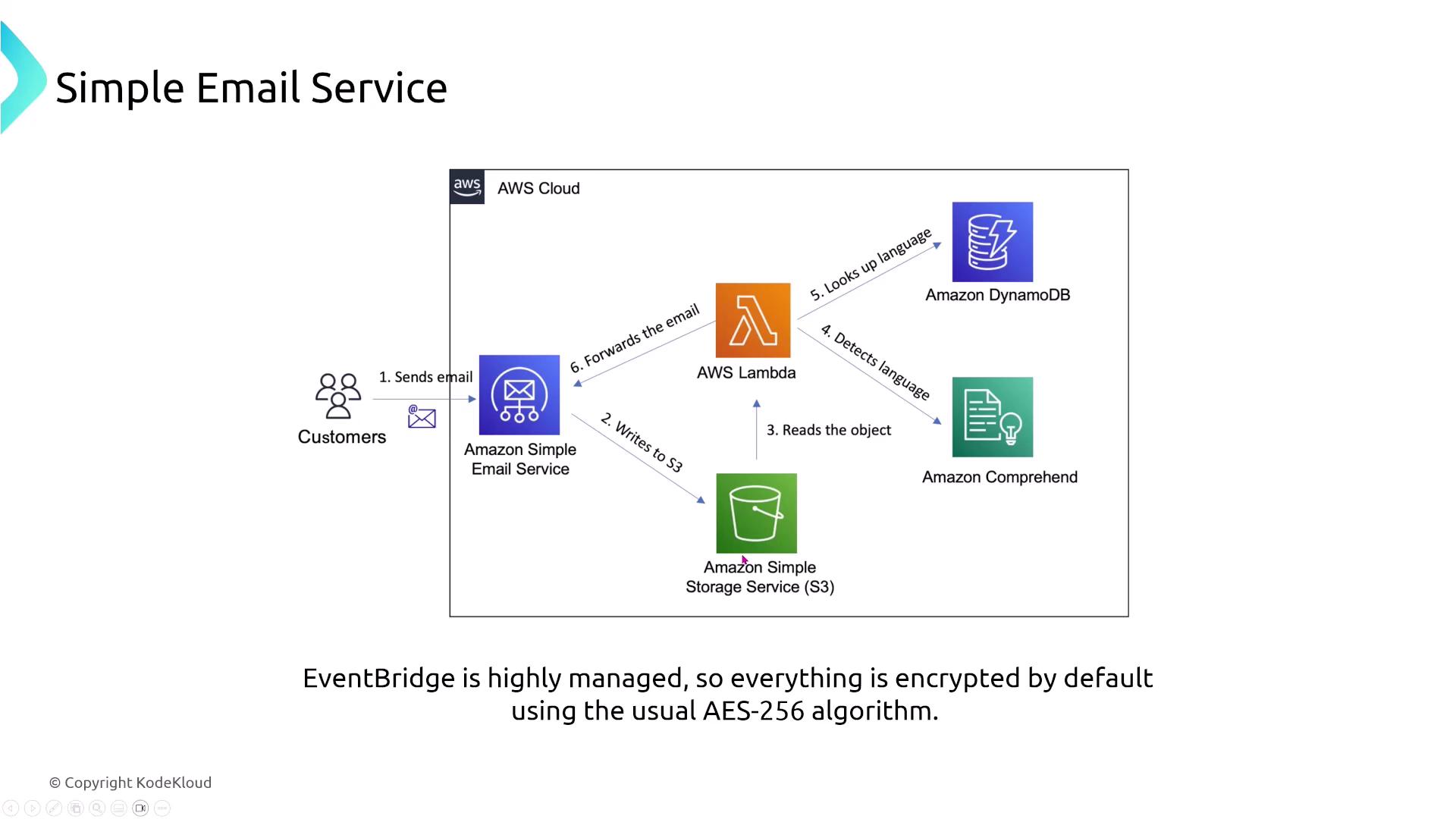

Workflows and Orchestration
AWS Step Functions
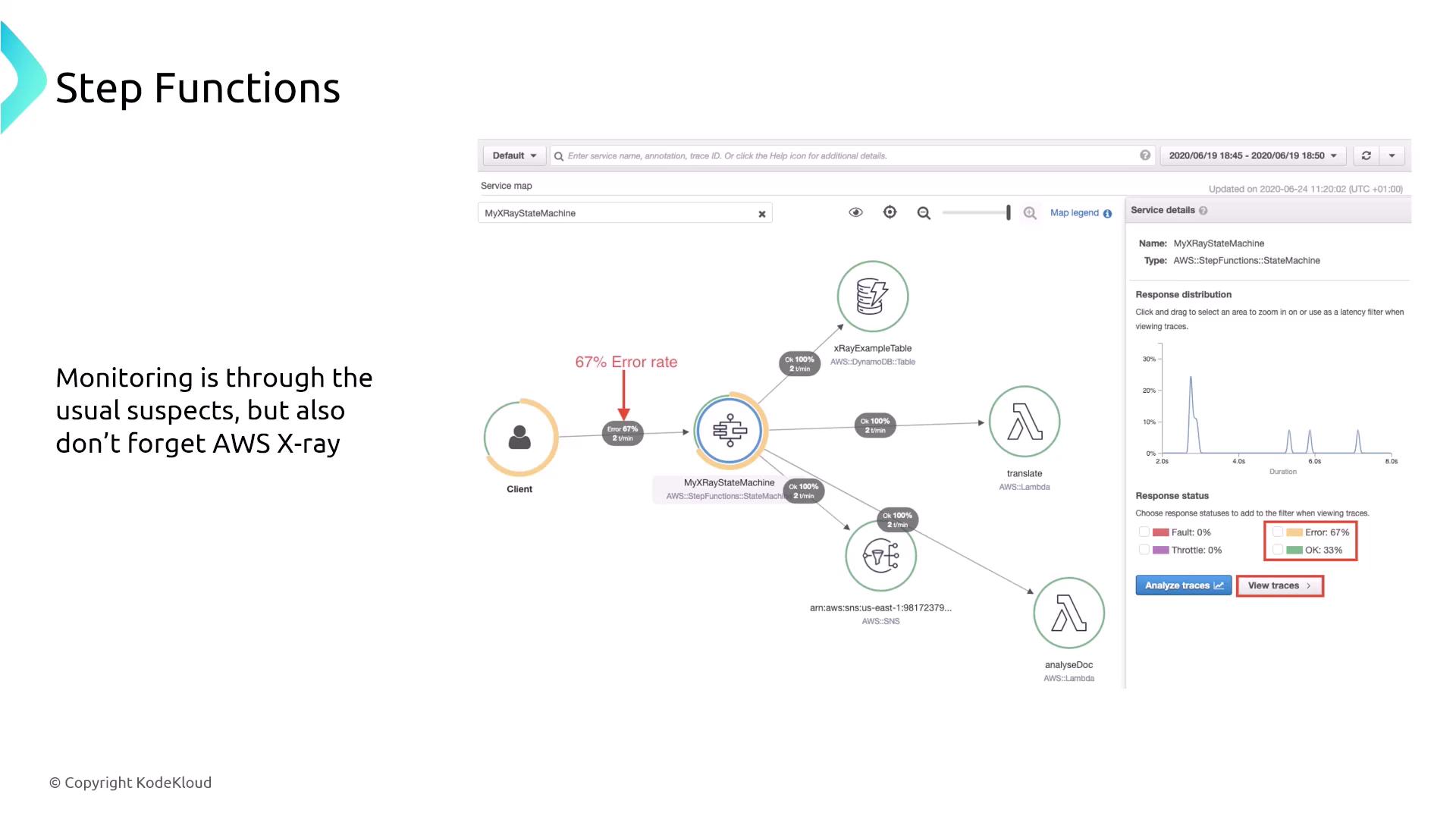
AWS Step Functions serves as an orchestrator and state machine for coordinating tasks, often managing multiple Lambda functions. Security is primarily enforced through IAM policies that restrict both invocation and execution rights, thereby preventing runaway workflows. Monitoring is achieved via CloudWatch, CloudTrail, and AWS X-Ray, while integration with SNS provides timely notifications to users.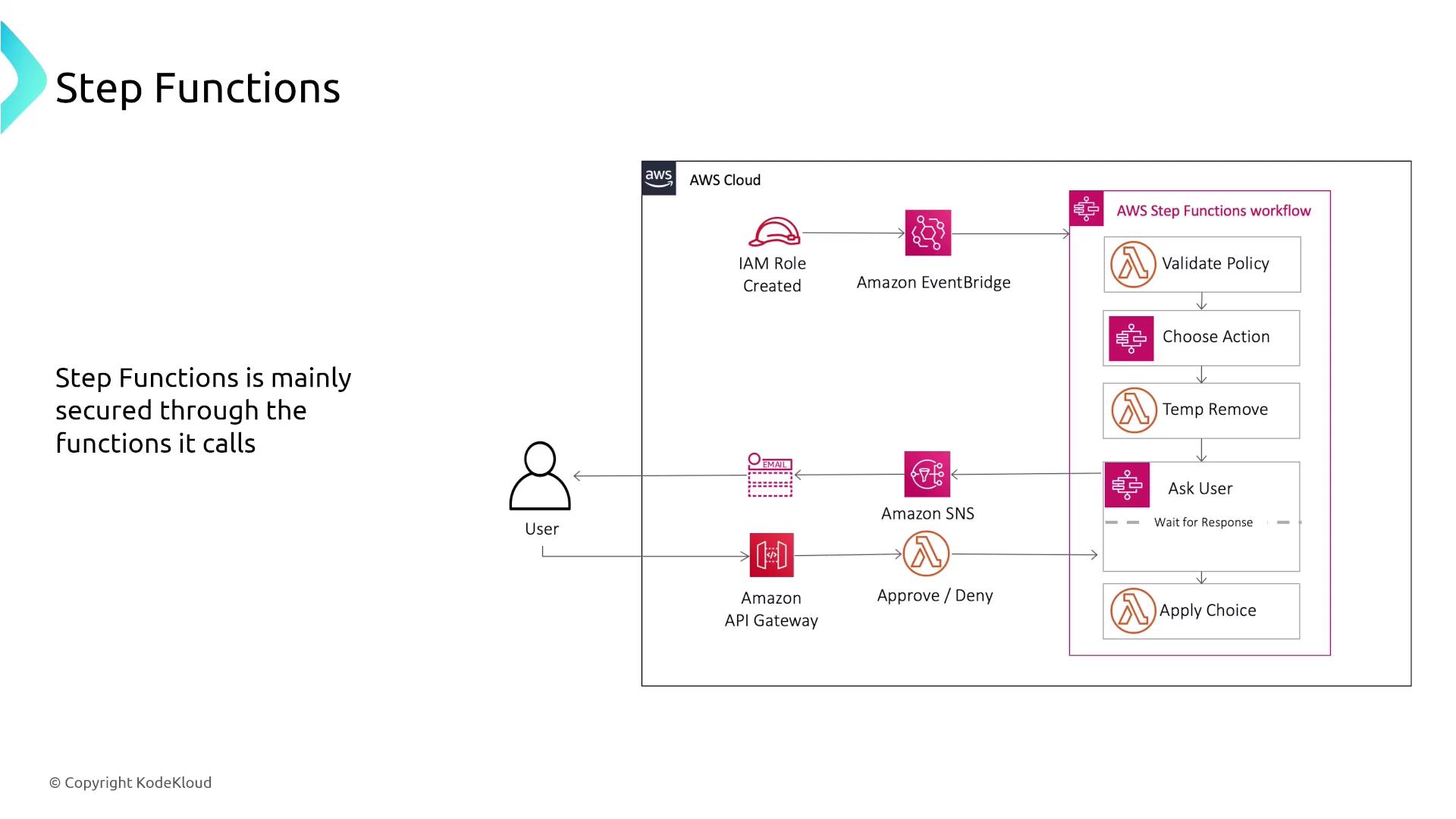
Amazon Simple Workflow Service (SWF)
An older orchestration service, Amazon SWF, is used for coordinating complex tasks (such as credit card processing or order management) through both sequential and parallel steps. SWF requires the invocation of underlying resources, and similar to other AWS services, it supports standard encryption and logging via CloudWatch and CloudTrail.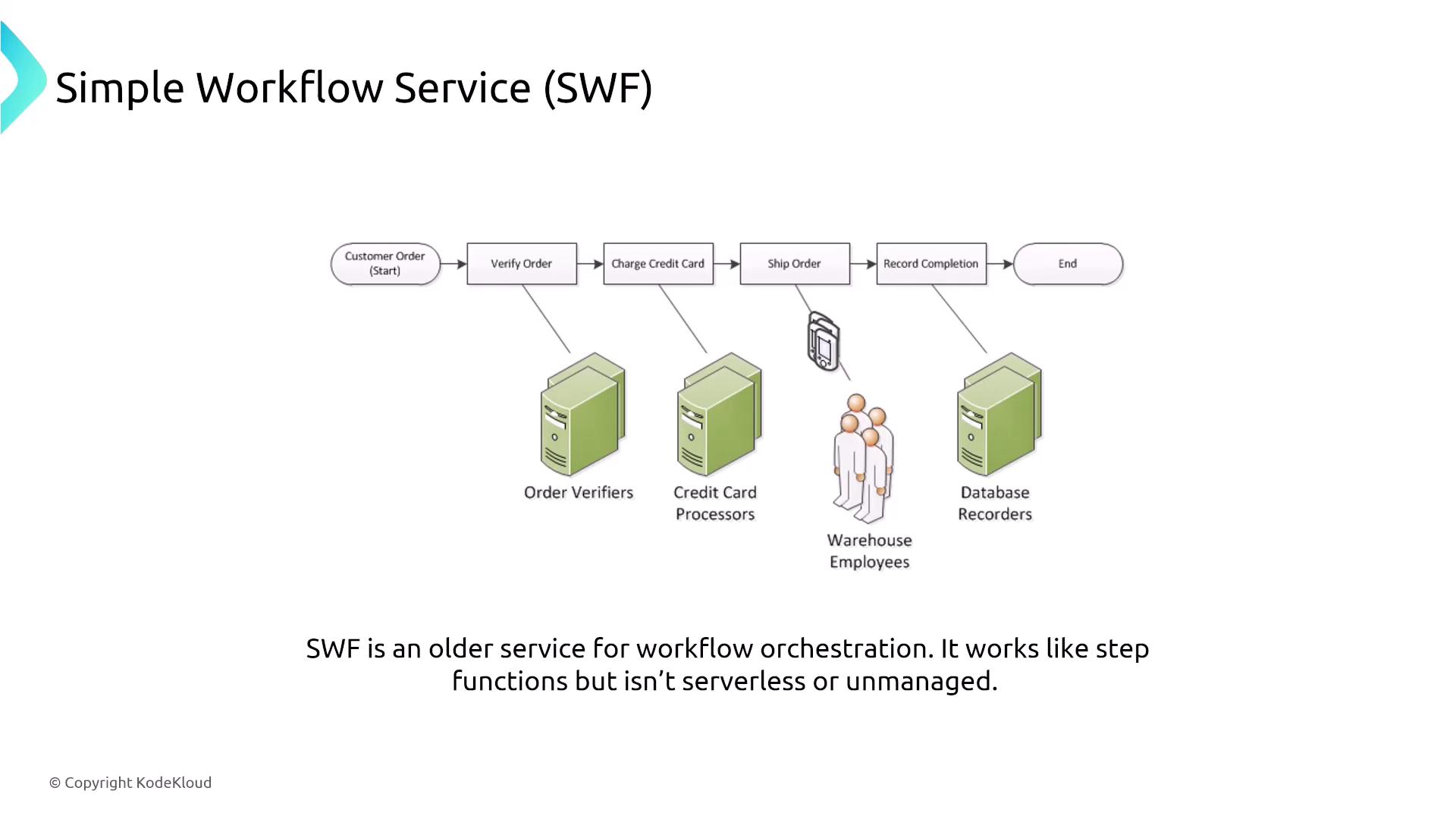



AWS Managed Workflows for Apache Airflow (MWAA)
The final service covered in this lesson is AWS Managed Workflows for Apache Airflow (MWAA). This fully managed solution abstracts away the complexities of managing Apache Airflow components (such as schedulers, workers, and the metadata database), enabling you to focus on designing and running complex ETL workflows. MWAA leverages Amazon Aurora for metadata storage and integrates seamlessly with AWS services for logging and security via CloudWatch and IAM.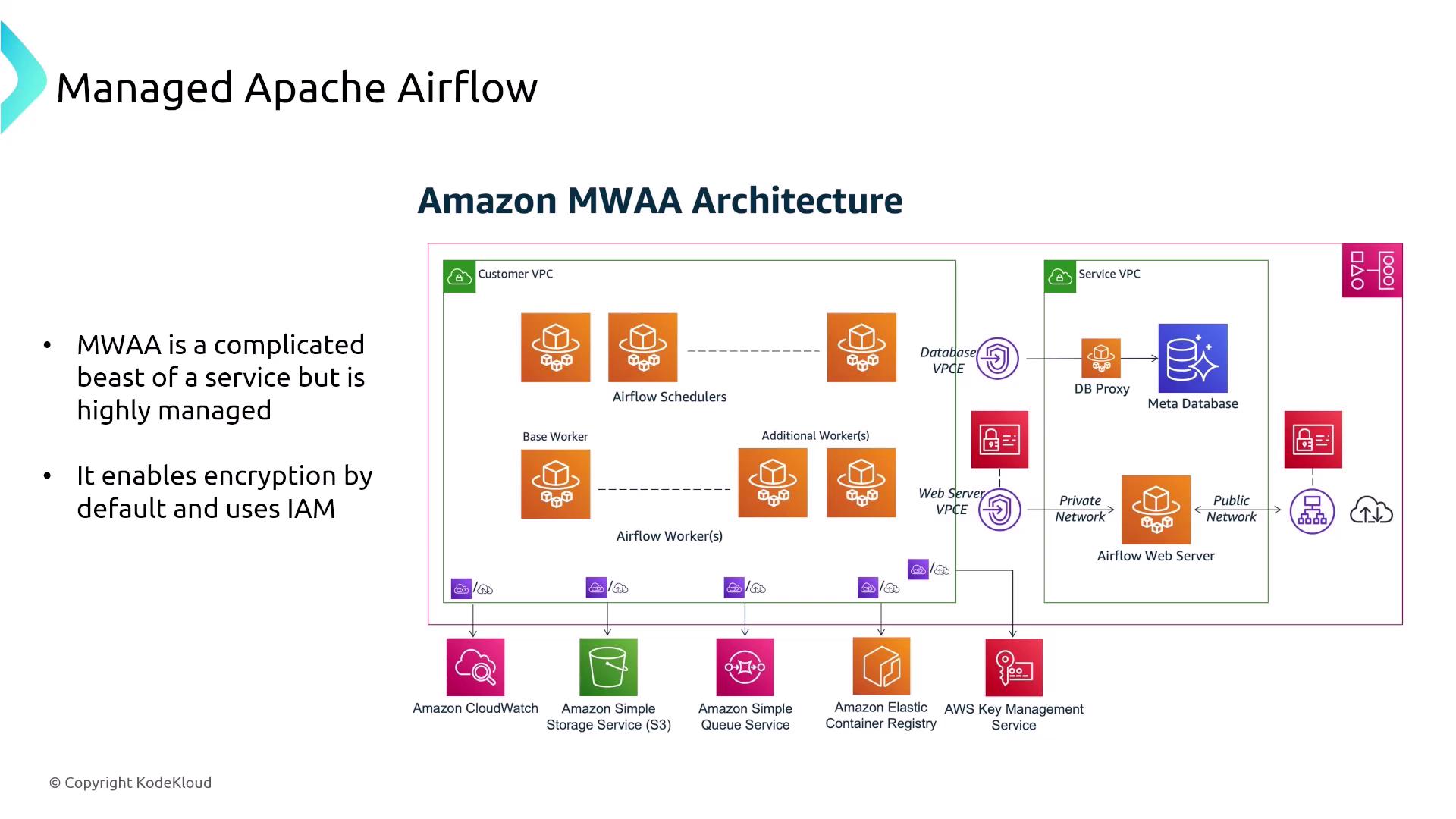


Summary
In this lesson, we covered various AWS application integration services designed to enhance operational scaling by serving as intermediaries between compute and data storage. Key takeaways include:- Built-In Encryption: Most managed services offer encryption by default for data at rest and in transit.
- Robust Logging and Monitoring: CloudWatch and CloudTrail are typically used for logging and monitoring. In some cases, AWS X-Ray and AWS Config provide deeper insights.
- Managed and Secure Integration: These services reduce the need for manual configuration while ensuring strong security and operational oversight.