- Ensuring proper configuration and hardening.
- Deploying in a highly available, fault-tolerant manner.
- Scaling resources dynamically to meet fluctuating workloads.
- Monitoring health and performance continuously.
- Enforcing strict security to prevent unauthorized access.
Neglecting regular backups or software patches can expose your database to security vulnerabilities and potential data loss.

- Offloading administrative tasks to AWS.
- Ensuring high availability via multi-AZ deployments.
- Enhancing disaster recovery with automated backups and read replicas.
- Adhering to industry-standard security practices.
Instance Types
Amazon RDS offers two main types of instances:-
General Purpose (M Family):
Combines a balanced mix of computing power, memory, and network resources. This option is cost-effective and suitable for a variety of workloads. -
Memory Optimized:
Provides increased memory capacity for workloads that require handling large, in-memory datasets.

Deployment Models
Amazon RDS offers several deployment models to cater to different use cases:Single Availability Zone (AZ) Deployment
In a single-AZ deployment, your RDS instance is launched within one availability zone. This option is more cost-effective, making it suitable for development or staging environments; however, it does not offer high availability since all data is stored in one location. A failure in that AZ can lead to data loss.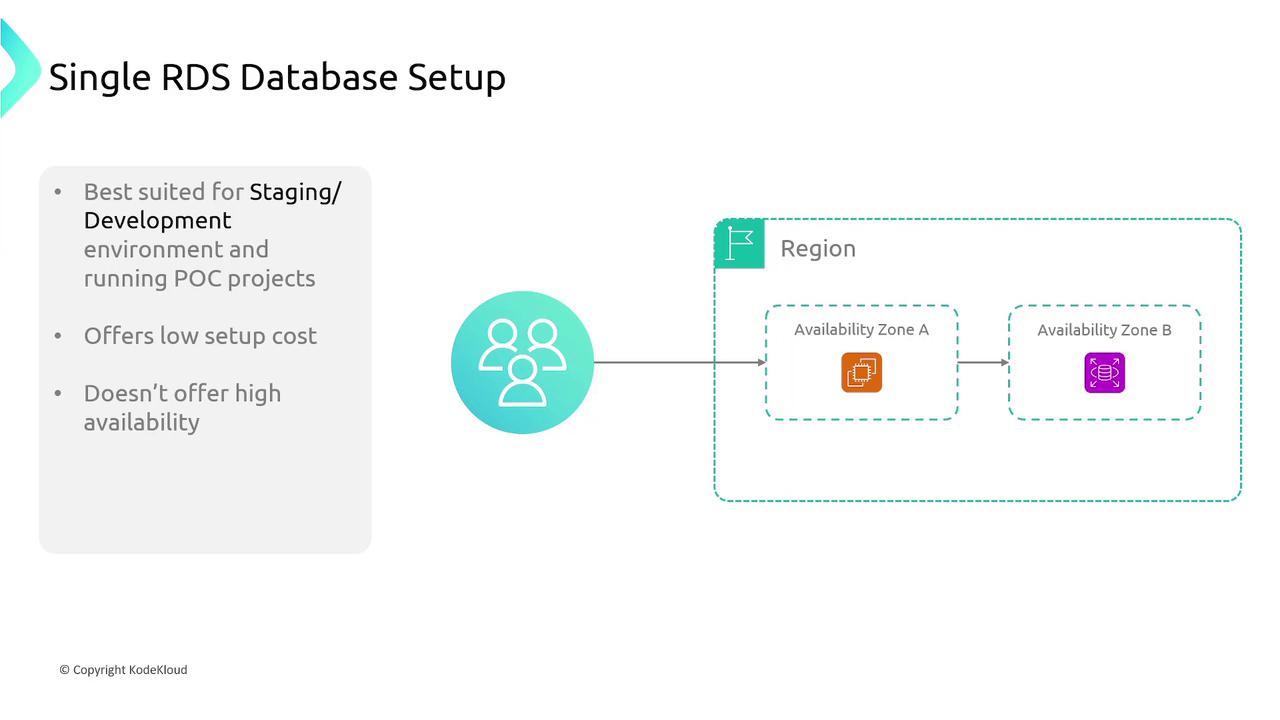
Multi-AZ Deployment
In a Multi-AZ deployment, AWS automatically replicates your primary database instance to a standby instance in a different availability zone. If the primary instance fails, an automatic failover ensures continuity, offering enhanced redundancy and high availability.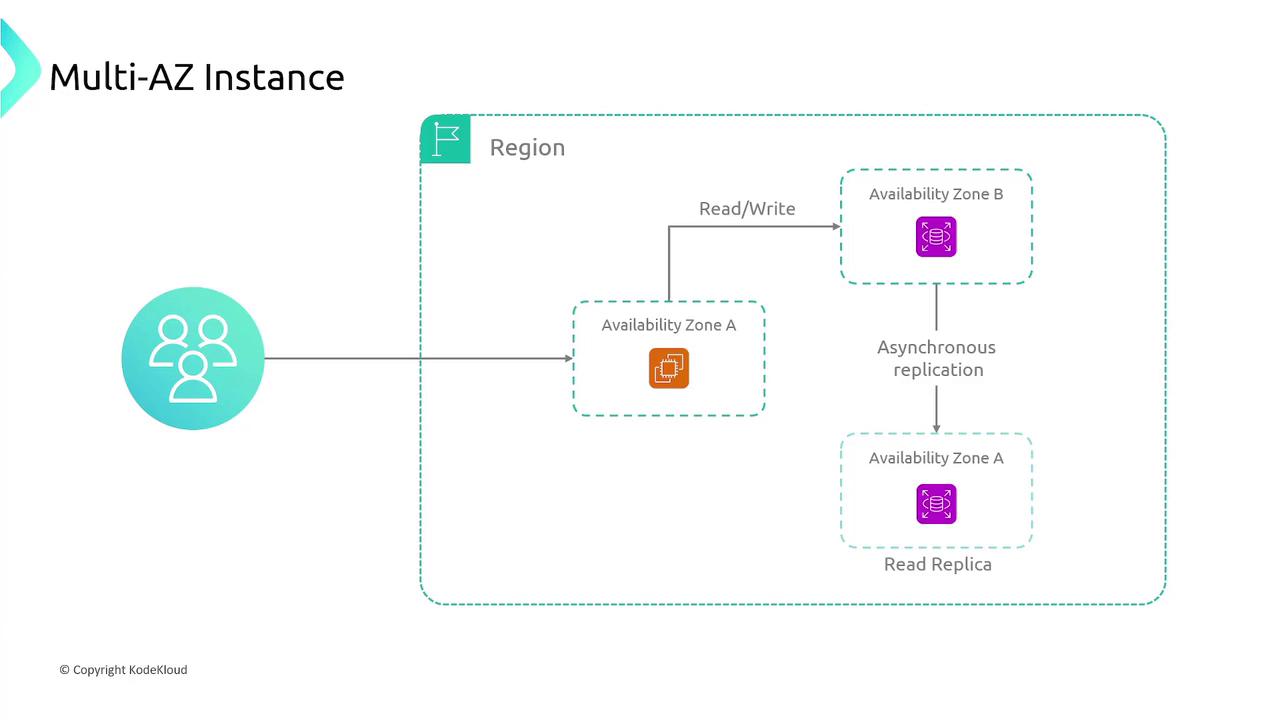
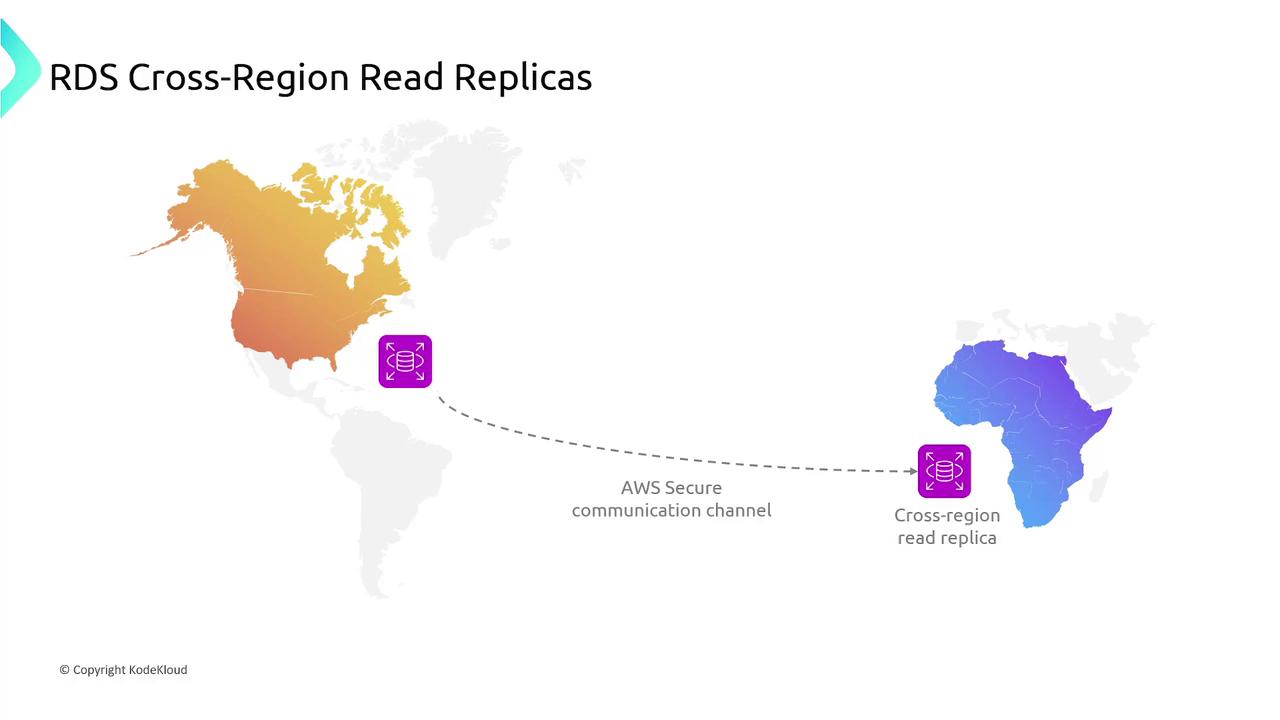
Read Replicas
Read replicas provide additional copies of your primary database instance to distribute and balance read traffic. These replicas are read-only, ensuring that write operations are processed solely by the primary instance. They also serve as a disaster recovery option by enabling promotion to a standalone instance if necessary.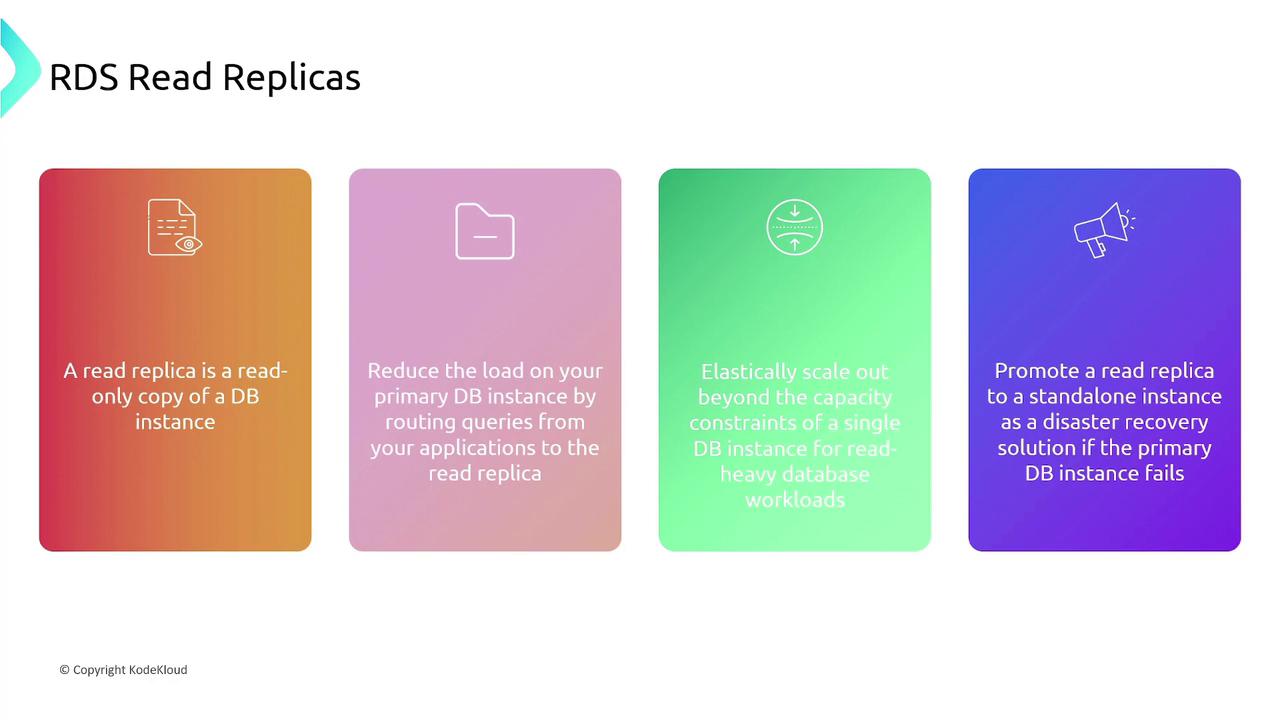
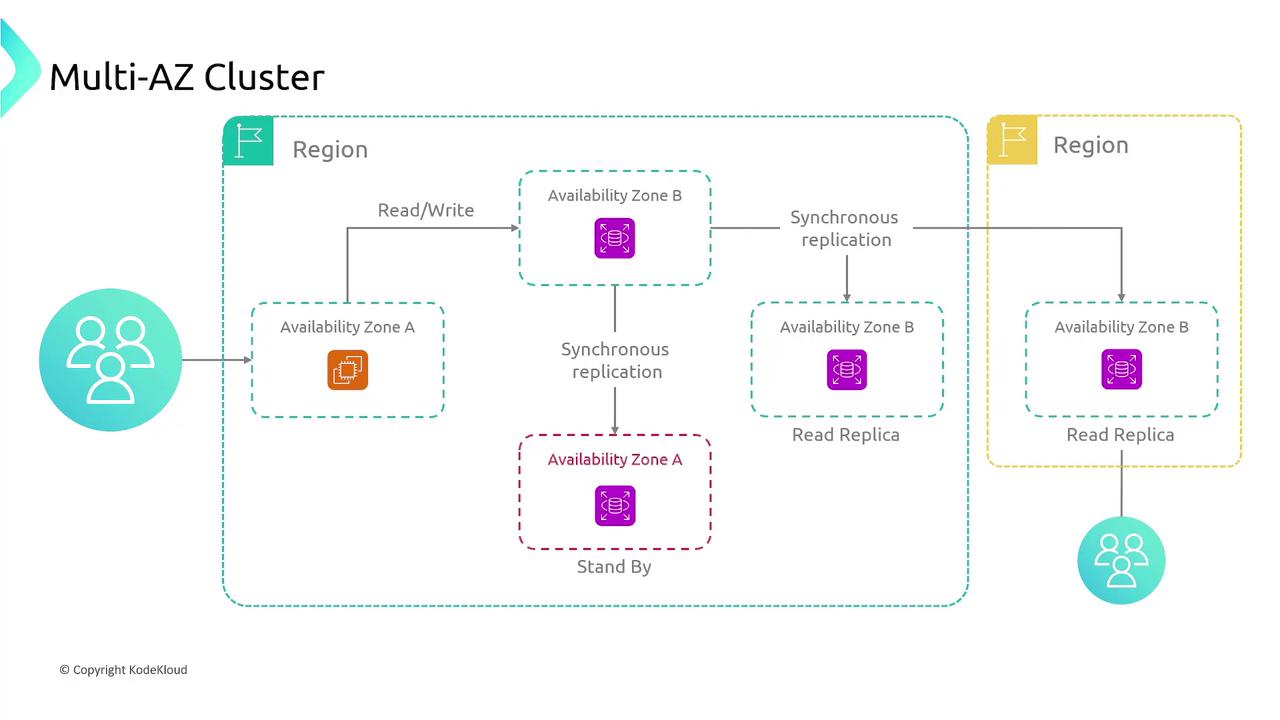
Multi-AZ Cluster
A Multi-AZ cluster combines multiple strategies to enhance resilience:- Primary nodes handle read and write operations.
- Data is replicated across read replicas to distribute read traffic.
- A standby server in another availability zone provides backup.
- In some configurations, data is also replicated to an additional region for rapid disaster recovery.
Blue-Green Deployments
Blue-green deployments involve maintaining two distinct database environments:- The blue environment is live and handles production traffic.
- The green environment is used to test changes and new deployments.


Storage Types
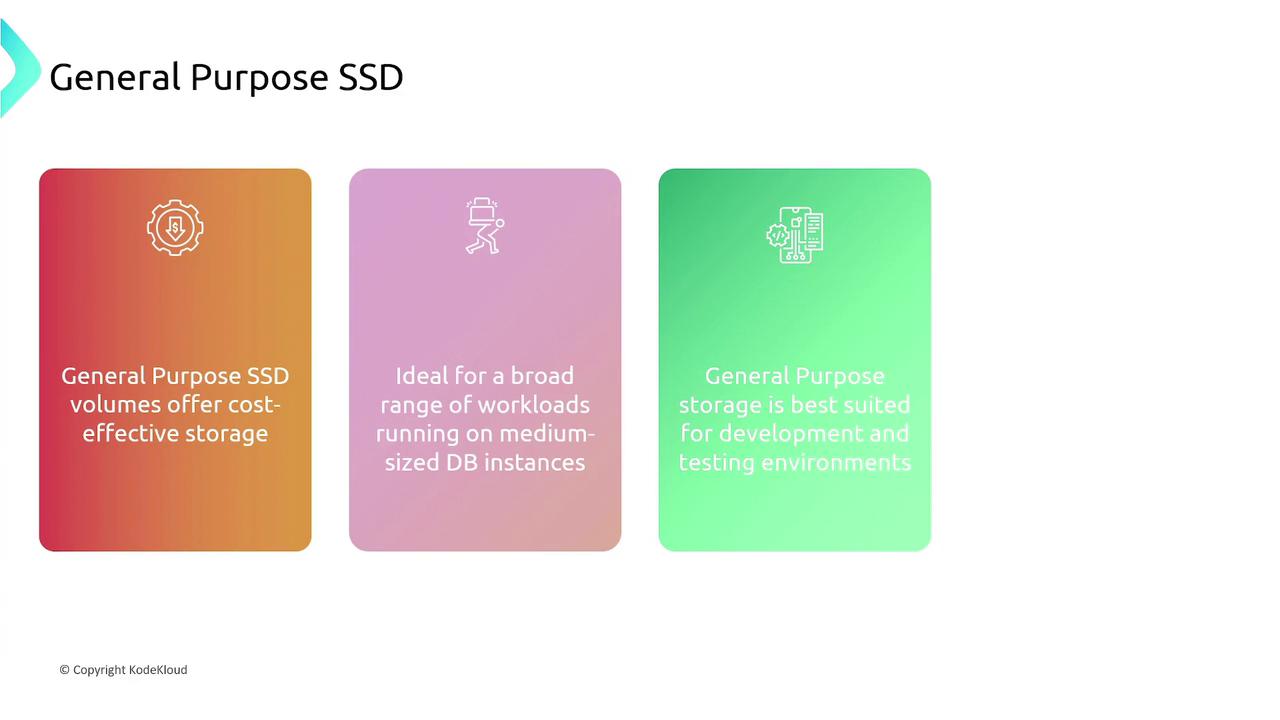
Amazon RDS supports different storage options to meet varying performance requirements:- General Purpose SSD:
Cost-effective storage ideal for a wide range of workloads on medium-sized database instances. Best suited for development and testing environments, this option offers three IOPS per gigabyte with the ability to burst up to 3000 IOPS.
- Provisioned IOPS SSD:
Designed for I/O-intensive workloads that demand low latency and consistent throughput. This storage type is ideal for production environments requiring high performance.

- Magnetic Storage:
An older option based on traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). This storage type offers slower performance compared to SSDs and is being phased out for newer database engine versions.
RDS Configuration Options
When configuring RDS instances, several parameters and groups help you tailor the behavior of your database:-
Database Parameter Groups:
Collections of parameters that control the behavior of your database engine, including performance, security, and resource allocation. -
Database Option Groups:
Manage extra features such as encryption and performance enhancements. These options can be attached to database instances as needed. -
Subnet Groups:
Specify the subnets within your Amazon VPC to deploy your database instances, ensuring proper network configuration. -
Security Groups:
Control inbound and outbound network traffic to ensure that only authorized IP addresses and ports have access to your database. -
Database Snapshots:
Backup copies of your database instances. You can create manual snapshots or configure automated daily backups, allowing restoration to a specific point in time.
- Parameter Store:
Securely stores configuration data and sensitive information. - Performance Insights:
Provides visual representations of database load and query execution patterns. - Enhanced Monitoring:
Collects detailed performance metrics for troubleshooting and optimization. - Audit and Log Data:
Tracks database activities and security events. - Encryption:
Supports encryption at rest and in transit, safeguarding sensitive data.

Key Features and Benefits
AWS RDS provides several essential advantages:-
Quick Deployment:
Launch a production-ready relational database within minutes using the AWS Console, SDK, or API. Pre-configured optimal parameters allow immediate connection to your application. -
Managed Administration:
AWS handles patching, backups, provisioning, and maintenance, significantly reducing the administrative burden. -
Built-in Monitoring:
Integrates with CloudWatch and the RDS Console to provide real-time insights into compute, memory, storage capacity, I/O activity, and connections. -
Blue-Green Deployment:
Enables safer and faster updates with minimal downtime and zero data loss. -
High Availability and Durability:
Automated backups and Multi-AZ deployments allow restoration to any specific point in time (up to the last five minutes) during your retention period. -
Versatile Use Cases:
Ideal for web and mobile applications, AWS RDS lets you focus on innovation by shifting database management to AWS. It also simplifies migration from legacy databases by delivering scalability, performance, and reliability cost-effectively.