AWS Solutions Architect Associate Certification
Services Storage
AWS Backup
Delve into disaster recovery and learn about AWS Backup—a crucial service for safeguarding your data and ensuring business continuity. This guide covers the essentials of disaster recovery, examines its benefits, and explains how various AWS services work together to create robust and cost-effective disaster recovery strategies.
Understanding Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery is the systematic process of preparing for and responding to events that could result in data loss or system downtime. Disasters can be natural events like earthquakes or floods, or man-made events such as hardware failures and cyber attacks. The impact of downtime and data loss can be severe, often causing financial loss, reputational damage, and legal complications. A well-designed disaster recovery plan is vital for maintaining data integrity and ensuring continuous business operations.

Backup vs. Disaster Recovery
Although "backup" and "disaster recovery" are sometimes used interchangeably, they address different aspects of data protection.
- Backups involve creating copies of data to enable restoration after data loss.
- Disaster recovery encompasses backups along with the broader strategies, planning, and processes required for full system and application restoration.
AWS and Disaster Recovery
Amazon Web Services provides a suite of tools designed to build flexible, scalable, and cost-effective disaster recovery solutions. Two standout services are Amazon S3 and Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS).
Amazon S3
Amazon S3 offers scalable, durable, and highly available object storage, making it ideal for storing backup data. With an impressive 11 nines of data durability, S3 is engineered to handle the loss of multiple data centers. Its support for data replication between availability zones and cross-region replication makes it a reliable choice for disaster recovery.
Amazon EBS and Snapshots
Amazon EBS features snapshots—point-in-time copies of your EBS volumes—to safeguard your EC2 instances and data. Snapshots can be executed manually or scheduled automatically (e.g., every five minutes) to ensure continuous data protection. As these snapshots are incremental, they only capture changes since the previous snapshot, which optimizes storage usage and reduces costs. Additionally, snapshots can be used to create new EBS volumes during the recovery process.
Introducing AWS Backup
AWS Backup centralizes and automates data protection across multiple AWS services via a unified console. The service streamlines backup processes by automating scheduling, retention policies, and cross-region backups—significantly reducing manual effort and enhancing reliability.
Key Components of AWS Backup
AWS Backup revolves around three core components:
Backup Vault:
A secure container that stores all your backups. You can classify and organize backups by creating multiple vaults across different regions and accounts, tailoring your disaster recovery strategy to your application's specific needs.Backup Plan:
This component defines the backup process, including scheduling frequency, retention policies, and the designated backup vault where the backups will be stored.Recovery Point:
A recovery point marks the specific point in time from which your data can be restored. It serves as a snapshot of your data, enabling efficient and reliable recovery in the event of an incident.
![]()
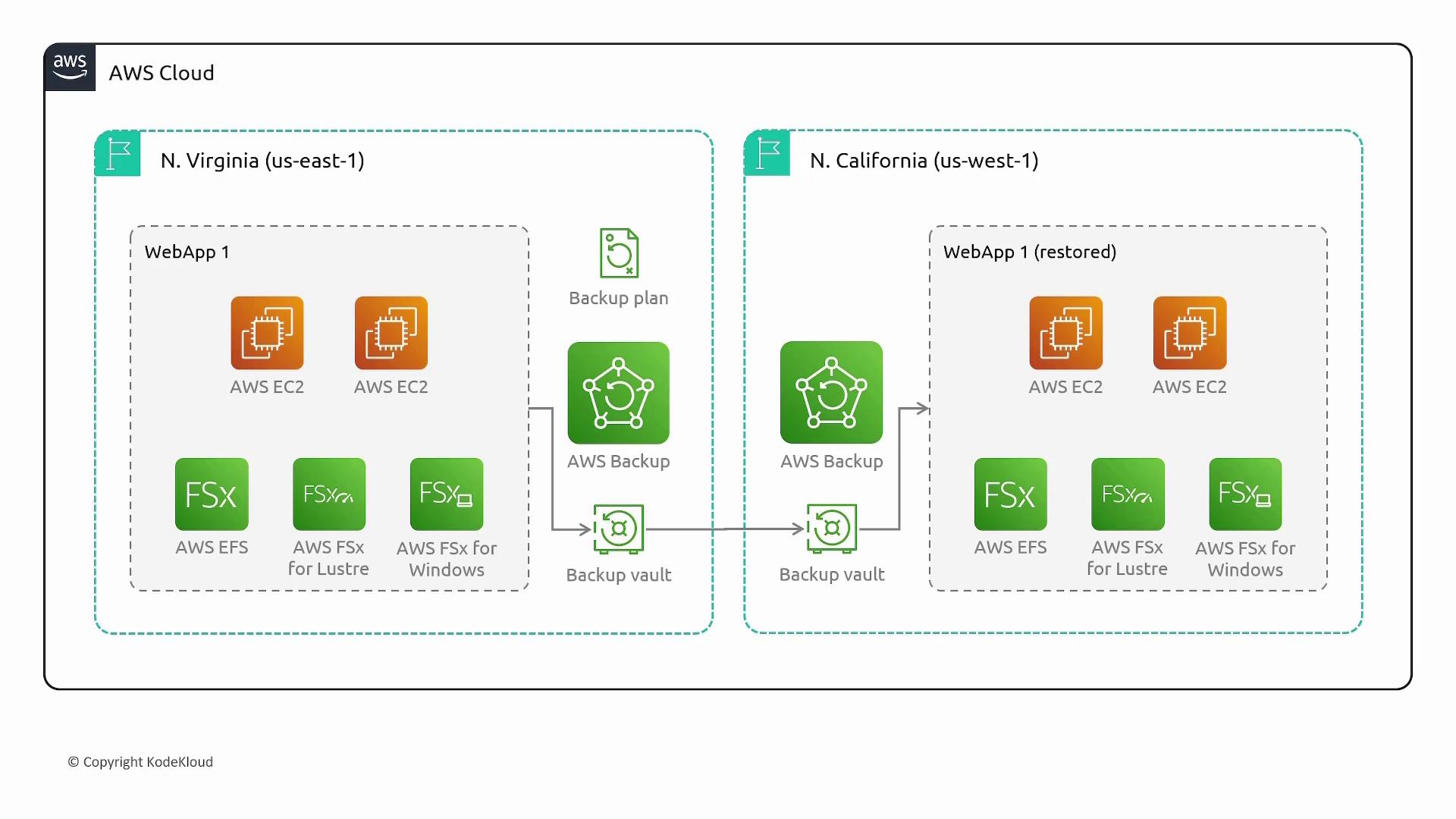
Example Scenario: Using AWS Backup
Consider an application deployed in the US East (N. Virginia) region that consists of multiple EC2 instances, along with associated EFS and EBS volumes and a RDS instance. To implement AWS Backup effectively:
- Create a backup vault in the same region as your application to securely store the backups.
- Define a backup plan that specifies which resources (for example, resources for App One) will be backed up, along with the scheduling and retention policies.
- Optionally, set up another vault in a different region or AWS account and configure a copy job to transfer backups from US East 1 to US West 1. This configuration ensures that resources can be recovered in either region in case of an incident.
AWS Backup Integrations and Monitoring
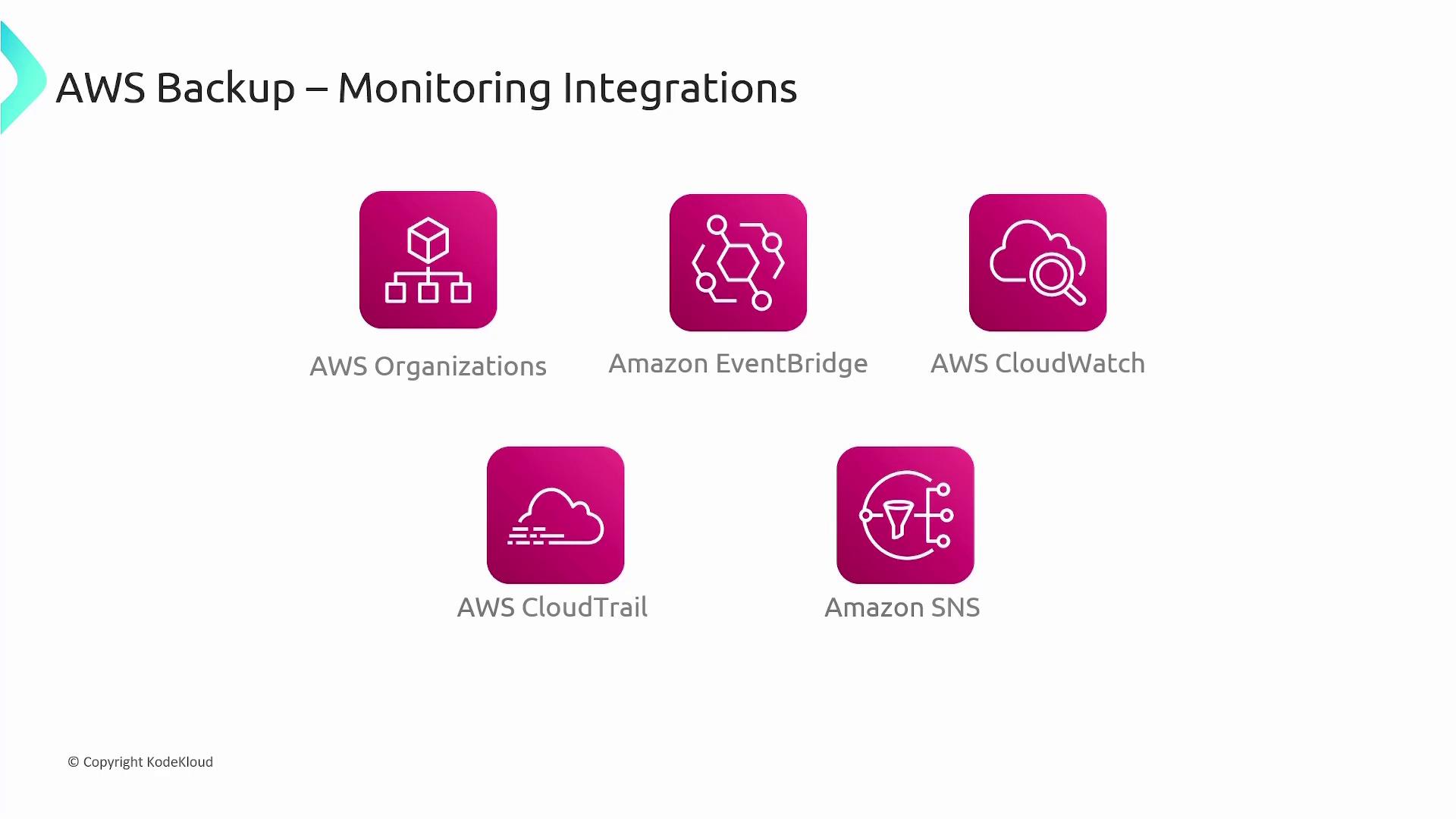
AWS Backup integrates seamlessly with a wide range of AWS services, including EC2, EBS, EFS, and RDS, among others. To keep track of your backups and monitor events, AWS provides several useful services:
- Amazon EventBridge: Monitors backup events and triggers automated responses.
- Amazon CloudWatch: Tracks metrics, creates alarms, and provides dashboards for real-time monitoring.
- Amazon SNS and AWS CloudTrail: SNS delivers notifications, while CloudTrail logs and monitors AWS Backup API calls for comprehensive audit trails.
Summary
Disaster recovery is about preparing for and promptly responding to events that could lead to data loss or system failures. A well-crafted disaster recovery plan minimizes downtime, maintains data integrity, and supports continuous business operations. Unlike simple backups, disaster recovery encompasses a broader strategy that includes the entire system and application restoration process.
AWS delivers a suite of advanced services—such as Amazon S3, EBS snapshots, and AWS Backup—to help you build a resilient disaster recovery strategy. Specifically, AWS Backup centralizes and automates the backup process using three fundamental components: the backup vault, the backup plan, and the recovery point. Together, these components provide a scalable, flexible, and reliable solution for data management and recovery in any disaster scenario.
Note
For more detailed information on AWS Backup and disaster recovery planning, visit the AWS Documentation.
Watch Video
Watch video content