AWS Solutions Architect Associate Certification
Services Storage
EFS
In this lesson, we cover file system storage with a focus on Amazon's Elastic File System (EFS). Amazon EFS is one of the two primary file system storage services provided by AWS—the other being Amazon FSx. It supports the Network File System (NFS) protocol, allowing any NFS-dependent application to work seamlessly with the EFS service.
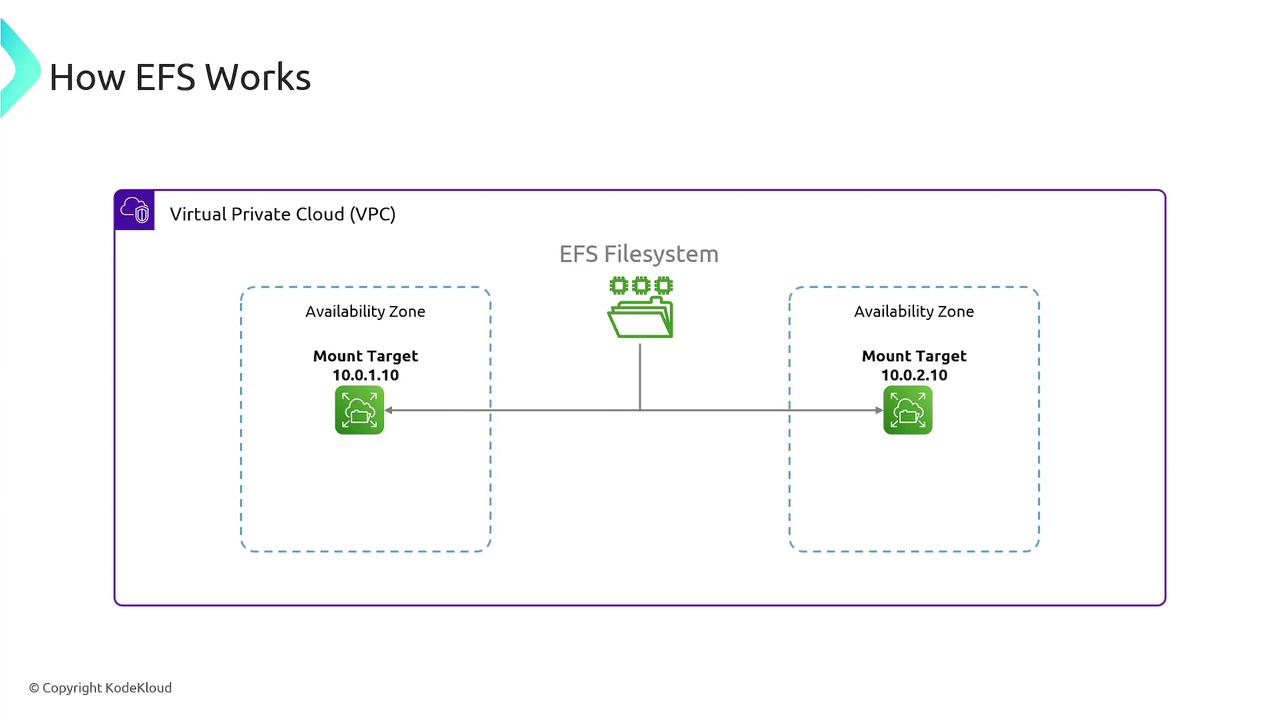
Once you create an EFS file system within your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), your Linux-based EC2 instances and other compute services can mount it remotely. Note that EFS is not supported on Windows-based EC2 instances.
Key Benefit
One of the major advantages of EFS is its ability to be mounted on multiple EC2 instances simultaneously. This feature allows efficient data sharing across instances.
When deploying EFS, you associate it with your VPC by creating mount targets in selected subnets. A mount target is assigned its own IP address, which EC2 instances use to connect to the file system. For high availability, it is highly recommended to create mount targets in multiple availability zones. This ensures that if one mount target becomes unavailable, an alternative is readily available.
EFS Storage Classes
Amazon EFS offers different storage classes to address a variety of use cases:
Standard Storage Classes:
- EFS Standard
- EFS Standard Infrequent Access
These storage classes provide multi-AZ resilience with high durability and availability.
One Zone Storage Classes:
- EFS One Zone
- EFS One Zone Infrequent Access
These options help reduce costs by storing data in a single availability zone.

Performance Modes in EFS
EFS provides various performance modes tailored to different throughput, IOPS, and latency requirements:
General Purpose Performance Mode:
Ideal for latency-sensitive environments such as web applications, content management systems, home directories, and typical file serving operations.Elastic Throughput Mode:
Automatically adjusts throughput performance based on your workload requirements.Max I/O Performance Mode:
Supports extremely high aggregate throughput and a large number of operations per second, though it may exhibit higher latencies for certain operations.Provisioned Throughput Mode:
Allows specification of a throughput level independent of the file system size.Bursting Throughput Mode:
Scales throughput with the amount of storage and supports burst performance for up to 12 hours per day.
Setting Up EFS on an EC2 Linux Instance
This section outlines the process for mounting an EFS file system on an Amazon EC2 Linux instance.
Step 1: Install Amazon EFS Utilities
Depending on your package manager, install the Amazon EFS utilities using one of the following commands:
For systems that use DNF:
sudo dnf -y install amazon-efs-utils
For systems using APT:
sudo apt install amazon-efs-utils
For systems using YUM:
sudo yum install amazon-efs-utils
Tip
Ensure that you have appropriate permissions for installing packages on your EC2 instance.
Step 2: Mount the EFS File System
After installing the utilities, mount your EFS file system to a directory. Replace efs:id with your actual EFS file system ID (available from the AWS Console) and /directory with your chosen mount point:
sudo mount.efs efs:id /directory
This command mounts the EFS file system similarly to other file system types, with the configuration necessary for EFS connectivity.
Summary
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| File System Service | Managed service provided by AWS |
| Protocol | Supports NFS for seamless integration with NFS-based applications |
| Supported Instances | Linux-based EC2 instances only |
| Multi-Instance Mounting | Can be mounted on multiple EC2 instances simultaneously |
| Mount Targets | Provide an IP address for connecting to the EFS file system within a VPC |
| Storage Classes | - Standard (multi-AZ resilience)<br>- One Zone (cost-saving, single-AZ option) |
| Performance Modes | General Purpose, Elastic Throughput, Max I/O, Provisioned Throughput, and Bursting Throughput |
| Boot Storage Limitation | Cannot be used as boot storage for operating systems; EBS is recommended for boot volumes |

Important
Remember, EFS is ideal for shared file systems used by Linux-based applications but is not a substitute for block storage solutions like EBS, especially when used for booting operating systems.
Watch Video
Watch video content