AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
Design and Implement Deployments
Design a hotfix path plan
In this guide, we’ll walk through creating a streamlined hotfix deployment plan in Azure DevOps. A well-defined hotfix strategy is critical for maintaining production stability, meeting Service Level Objectives (SLOs), and succeeding on the [AZ-400 Exam]. Hotfixes address urgent bugs and security vulnerabilities—think of them as emergency patches that keep your application running under pressure.

Why You Need a Hotfix Path Plan
Having a pre-approved hotfix workflow delivers two major benefits:
- Rapid, controlled deployment
Eliminate improvisation during high-pressure incidents by following a documented process. - Minimal service disruption
Apply fixes swiftly without compromising system reliability.
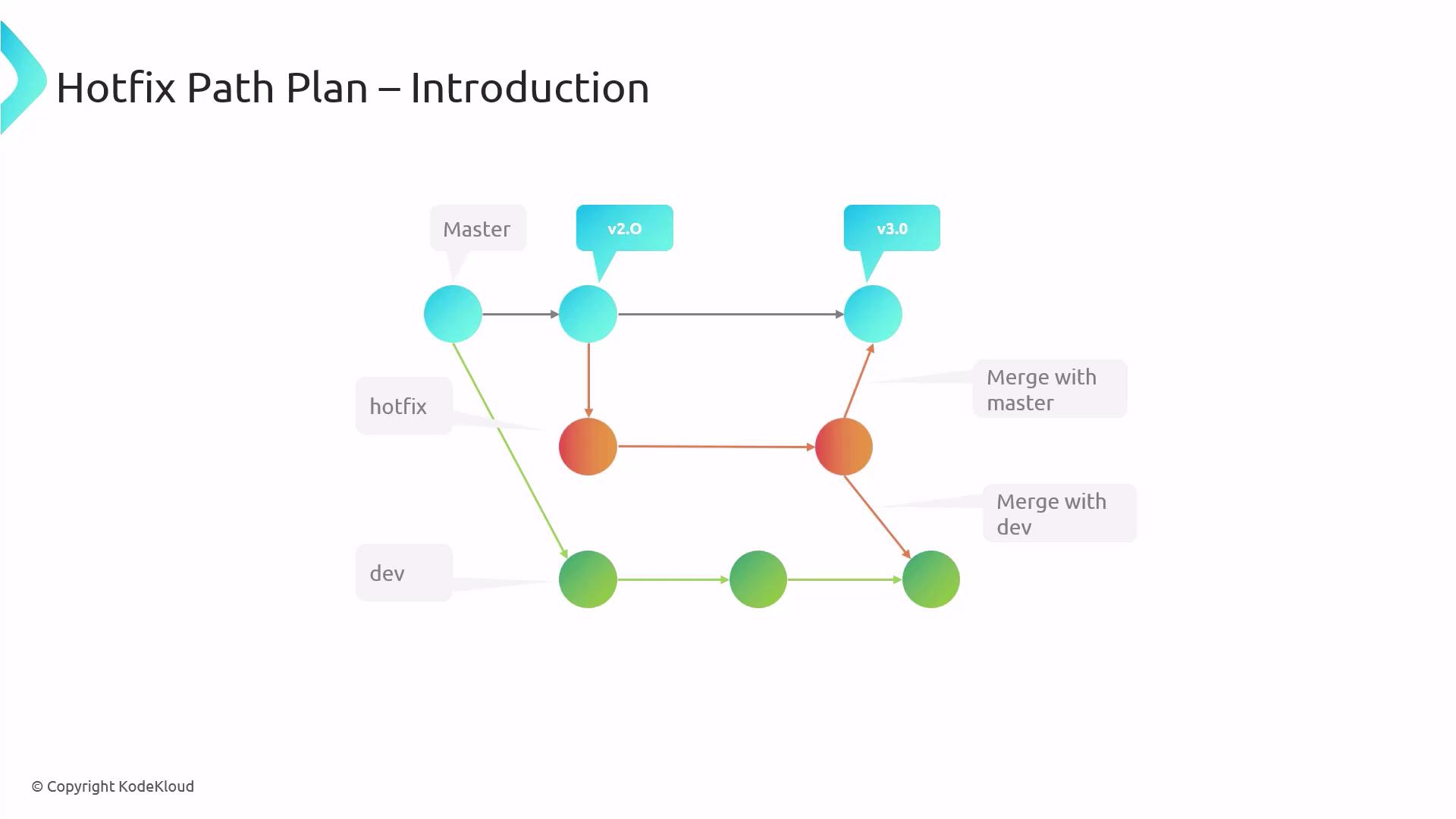
Hotfix Branching Strategy
Adopt a clear branching model to isolate and track urgent fixes:
| Branch | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| master | Production-ready code | v2.0 |
| hotfix | Temporary branch for critical repairs | hotfix/issue-123 |
| dev | Active development and feature integration | dev |
Note
Use consistent naming conventions for hotfix branches (for example, hotfix/{ticket-number}) to simplify tracking and rollbacks.
- Create a hotfix branch from master.
- Implement and test the fix in the hotfix branch.
- Merge changes back into both master and dev to keep all branches up to date.
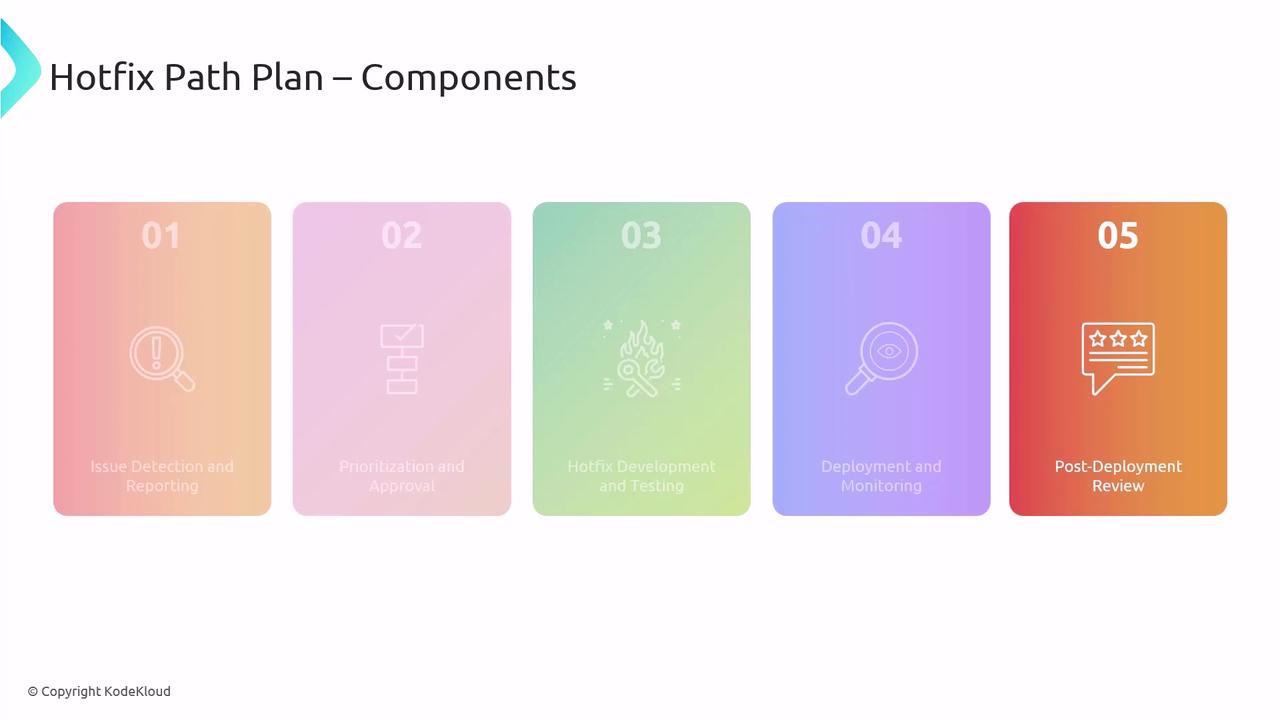
Five Steps of a Hotfix Path Plan
Follow these structured stages to ensure a smooth hotfix rollout:
- Issue Detection & Reporting
Quick logging of errors or security alerts into your tracking system. - Prioritization & Approval
Fast decision-making based on impact and risk. - Hotfix Development & Testing
Code the fix, execute automated and manual tests to prevent regressions. - Deployment & Monitoring
Roll out updates and immediately validate success metrics. - Post-Deployment Review
Document outcomes, identify improvements, and update runbooks.
Deep Dive: Prioritization & Approval
Prioritizing a hotfix is time-sensitive. Evaluate:
- System availability: Is the service down?
- Security impact: Are customers at risk of data loss?
- Business impact: What is the revenue or reputation cost?
Warning
Ensure that decision authority (Dev Lead, Product Owner, or Ops Manager) is clearly defined to avoid delays during incident response.
Automating with Azure DevOps
Leverage [Azure DevOps] to automate builds and tests when hotfix branches are updated. For instance, include a simple YAML trigger:
trigger:
branches:
include:
- hotfix/*
This configuration runs unit and integration tests on each push, catching regressions before deployment.

Automation reduces manual steps and speeds up your hotfix delivery.
Deployment Strategies
Choose the right rollout plan based on risk and urgency:
| Strategy | Description | Pros & Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Phased Rollout | Deploy to a subset of users or environments | Safer but slower |
| Full Rollout | Release to all users at once | Faster but riskier |
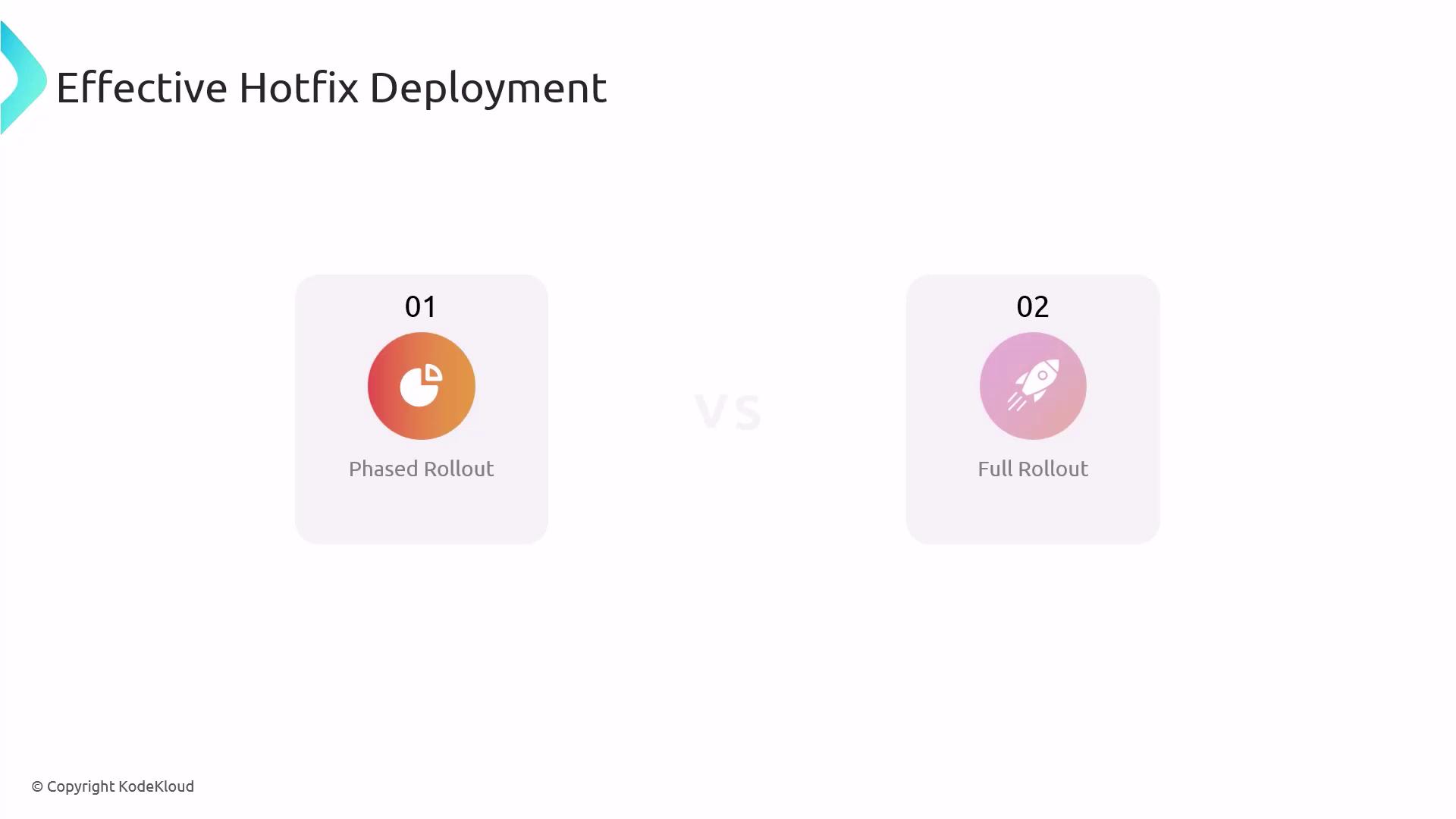
Balance the criticality of the fix against potential side effects to select the optimal approach.
Monitoring & Verification
Monitor your hotfix in two phases:
- Immediate Monitoring
Review logs and alerts right after deployment. - Long-Term Monitoring
Track performance trends over days or weeks to confirm stability.
This layered monitoring ensures both rapid detection and sustained performance.
Post-Deployment Review
After stabilization, schedule a post-mortem meeting to:
- Record successes and failures.
- Update your hotfix runbooks.
- Share insights with the team for continuous improvement.
Whether you’re preparing for the [AZ-400 Exam] or handling live incidents, a structured hotfix path plan is essential. By codifying each step—from branch strategy to post-deployment review—you’ll reduce downtime and maintain high system reliability.
References
Watch Video
Watch video content