- Key features and benefits of Classic Pipelines
- Step-by-step creation of a pipeline
- How to decide between Classic and YAML models
- Best practices for maintaining a robust CI/CD process
Why Choose Classic Pipelines?
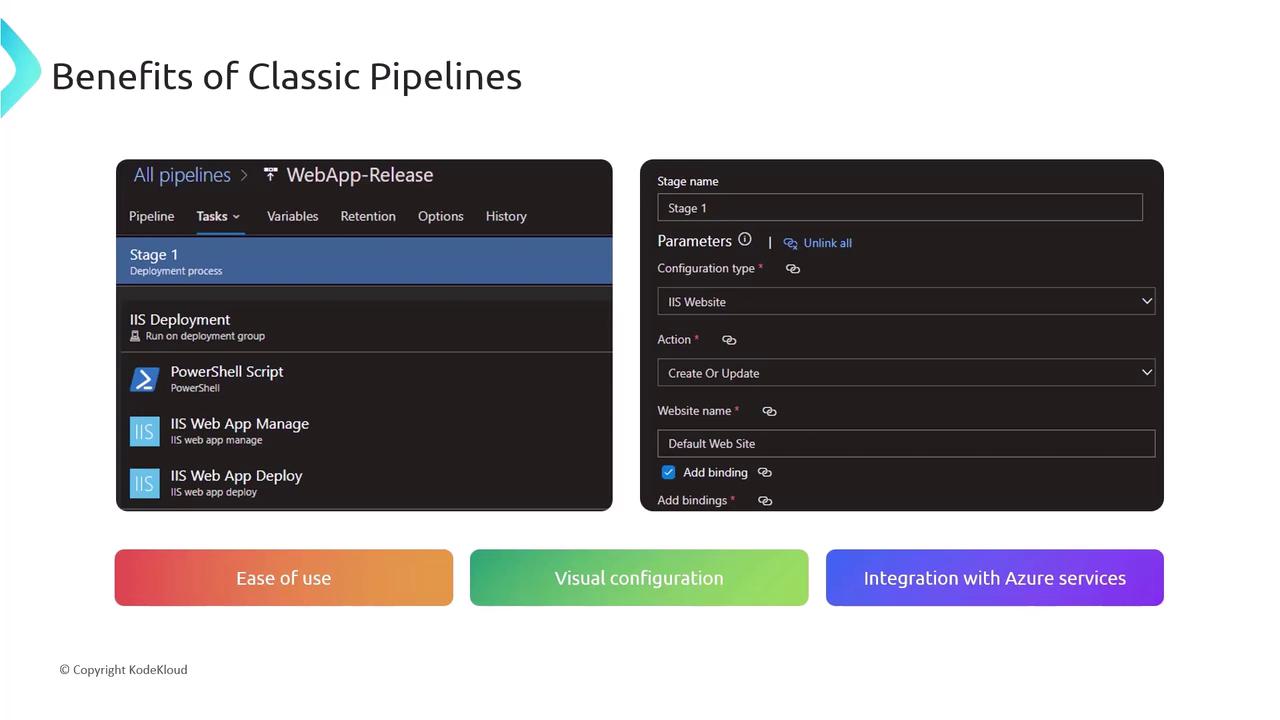
Classic Pipelines excel at lowering the barrier to entry for continuous integration and delivery:- Visual Configuration
Configure build and release tasks in a wizard-style editor. - Rapid Setup
Leverage prebuilt templates for .NET, Java, Docker, and more. - Seamless Azure Integration
Connect to Azure services like App Service, AKS, and Key Vault with a few clicks.
Classic Pipelines are perfect for teams that need a fast, low-code approach. For long-term maintainability, consider storing pipeline definitions in source control via YAML.
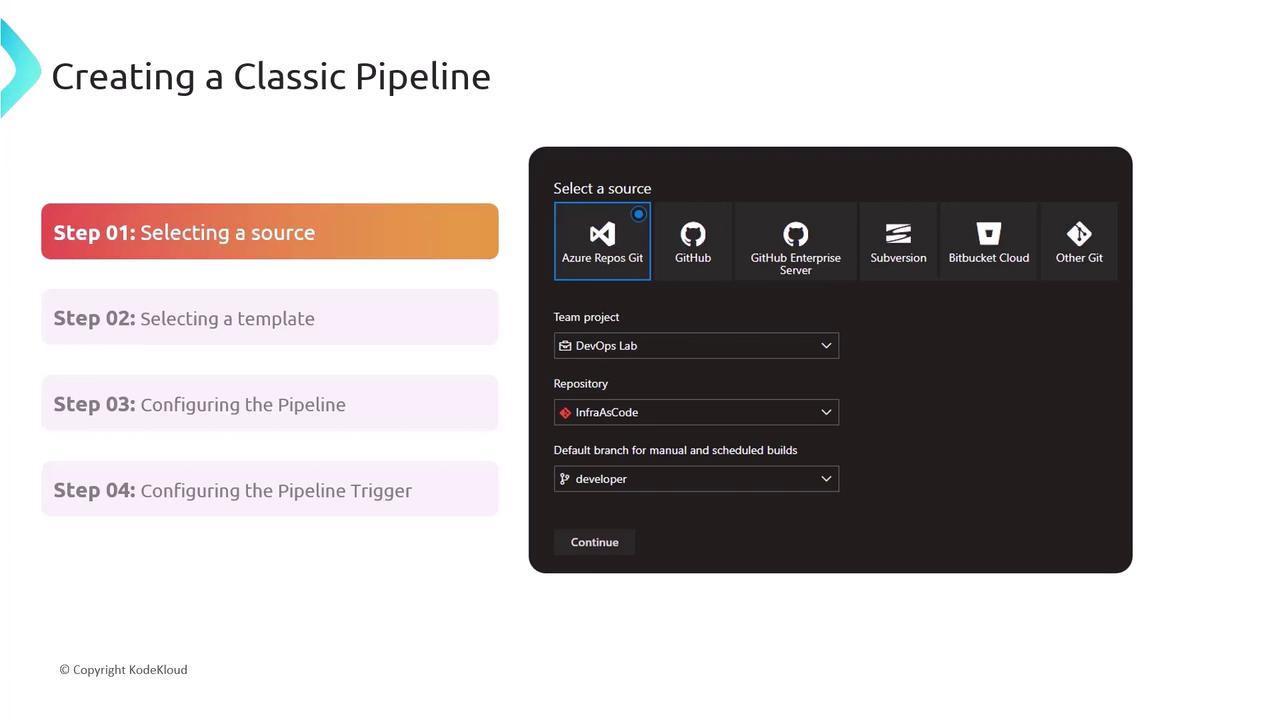
Step 1: Selecting Your Source Repository
- Open your Azure DevOps project and navigate to Pipelines > Releases (or Builds).
- Click New pipeline and choose Classic Editor.
- Select your source: Azure Repos Git, GitHub, Bitbucket, or other supported repositories.
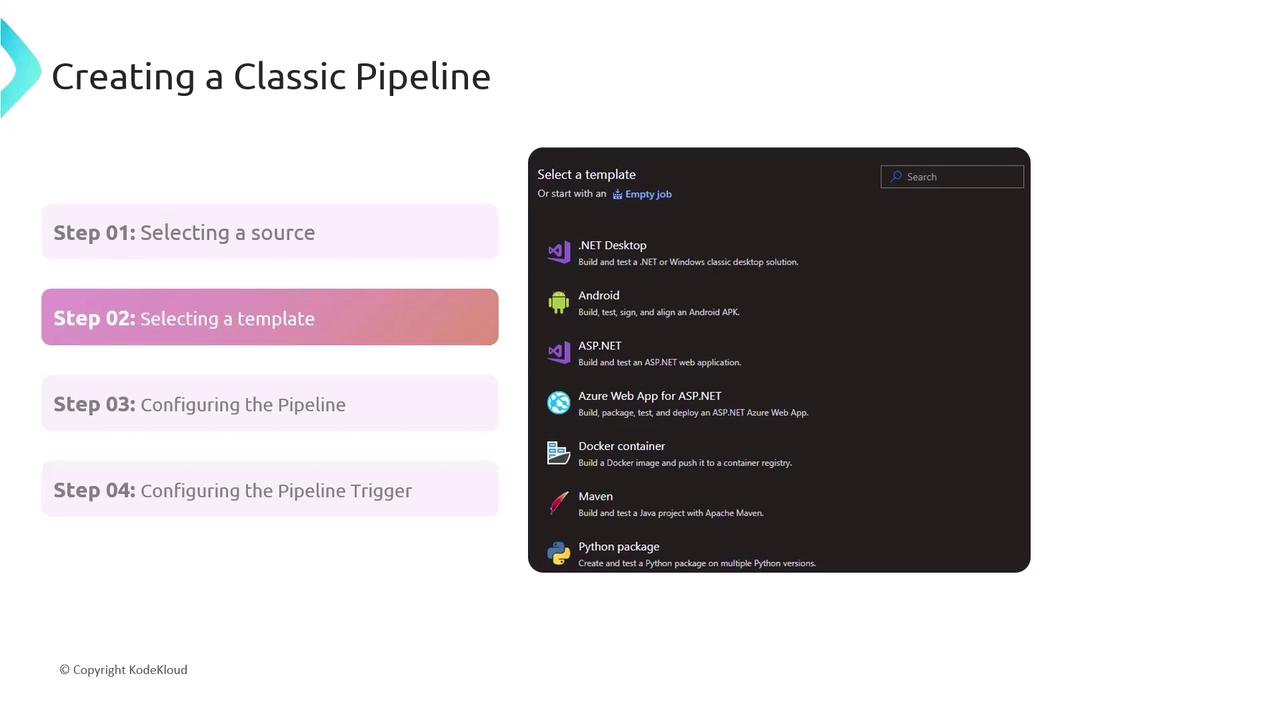
Step 2: Picking a Template
Azure DevOps ships with starter templates to kick-start your pipeline:- .NET Desktop
- Android
- Docker Container
- Node.js
Step 3: Configuring Tasks and Environments
Drag and drop tasks to define your build and release process:- Compile or build artifacts
- Run unit/integration tests
- Package outputs (ZIP, WAR, Docker image)
- Deploy to environments (Dev, QA, Production)
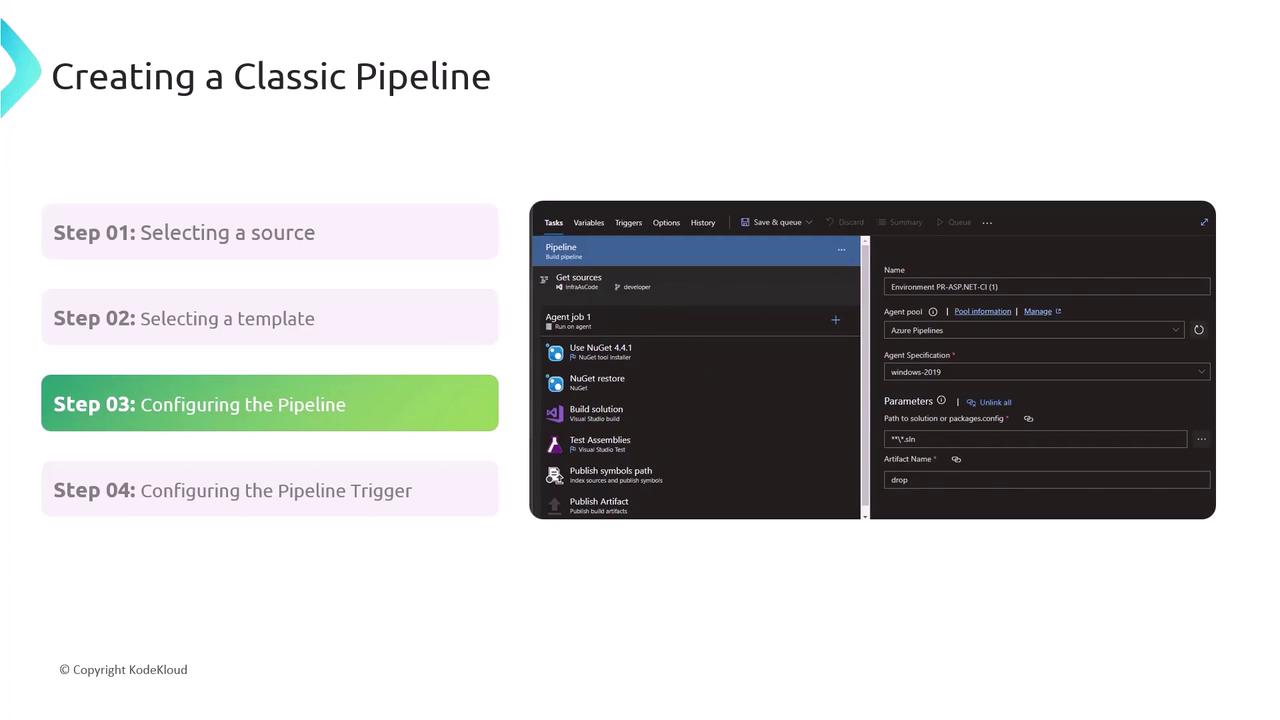
Step 4: Defining Triggers
Set triggers to automate your pipeline runs:- CI Trigger: Automatically start the build on each commit.
- Scheduled Trigger: Run nightly or at specific intervals.
- Manual Release: Deploy on demand to any environment.
Classic vs. YAML Pipelines
Azure DevOps offers two pipeline models—choose the one that aligns with your team’s workflow:| Feature | Classic Pipelines | YAML Pipelines |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | GUI-driven visual editor | Code-defined in a YAML file |
| Version Control | Configuration stored in the portal | Pipeline as code stored alongside your app |
| Flexibility | Quick setup with standard templates | Full control over branching and reuse |
| Best for | Teams new to CI/CD, non-technical users | Complex workflows, infrastructure as code |
Classic Pipelines offer ease of use, but for advanced scenarios and full traceability, YAML pipelines provide better versioning, branching, and reuse across projects.
Best Practices for Classic Pipelines
- Modular Design
Group related tasks into task groups or reusable templates. - Regular Updates & Testing
Keep tasks and agents up to date to leverage security patches and new features. - Security & Compliance
Audit pipeline permissions, enforce branch policies, and scan for vulnerabilities.
