| Trigger Type | Description | YAML Keyword |
|---|---|---|
| CI | Start a build when code is pushed | trigger |
| PR | Validate pull requests before merging | pr |
| Scheduled | Run pipelines at defined times (nightly, weekly) | schedules |
| Manual | Launch pipelines on demand via UI or CLI | N/A |
Continuous Integration (CI) Triggers
Continuous Integration (CI) triggers automatically queue a pipeline run whenever new commits are pushed to selected branches. This immediate feedback loop helps catch build failures or integration errors early.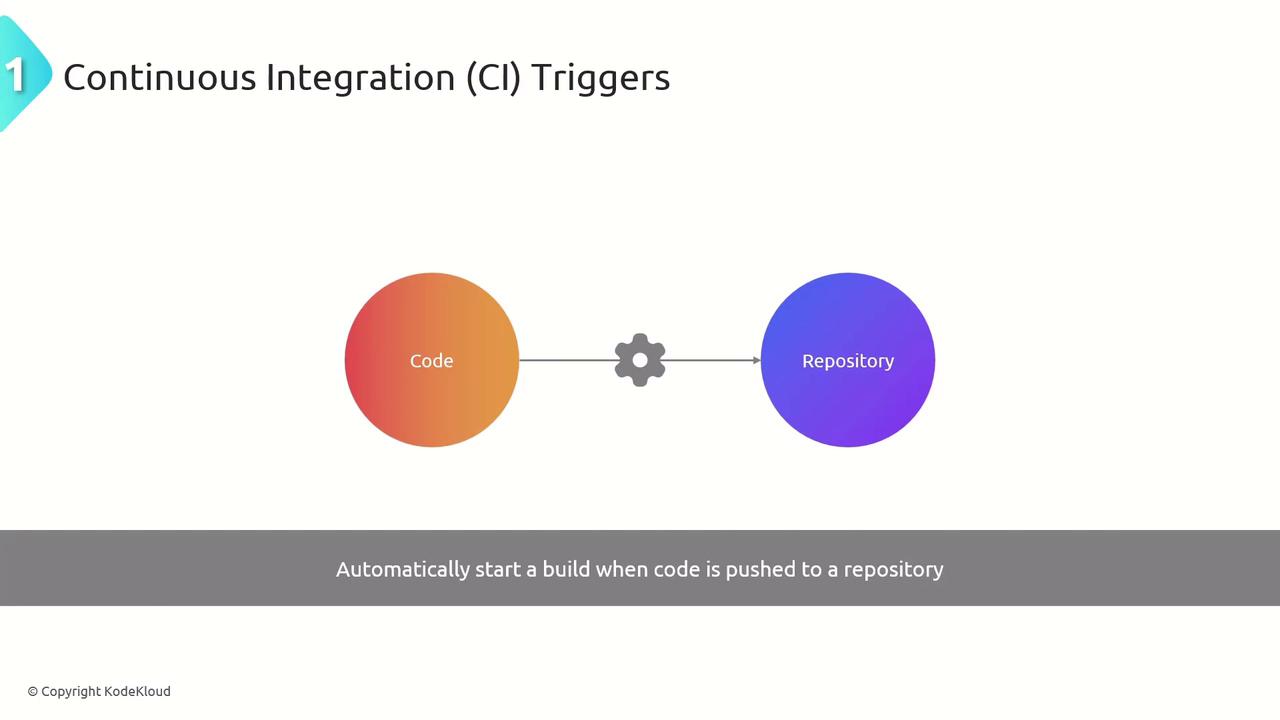
trigger section:
trigger:activates CI-based runsbranches.include:lists branch patterns to watchmainbuilds production coderelease/*handles hotfix or release branchesfeature/*catches ongoing development work
Wildcards (
*) help you include entire branch families. To exclude specific branches, use exclude: under branches.Scheduled Triggers
Scheduled triggers run pipelines at specified intervals or cron schedules—ideal for nightly builds, periodic tests, or routine deployments.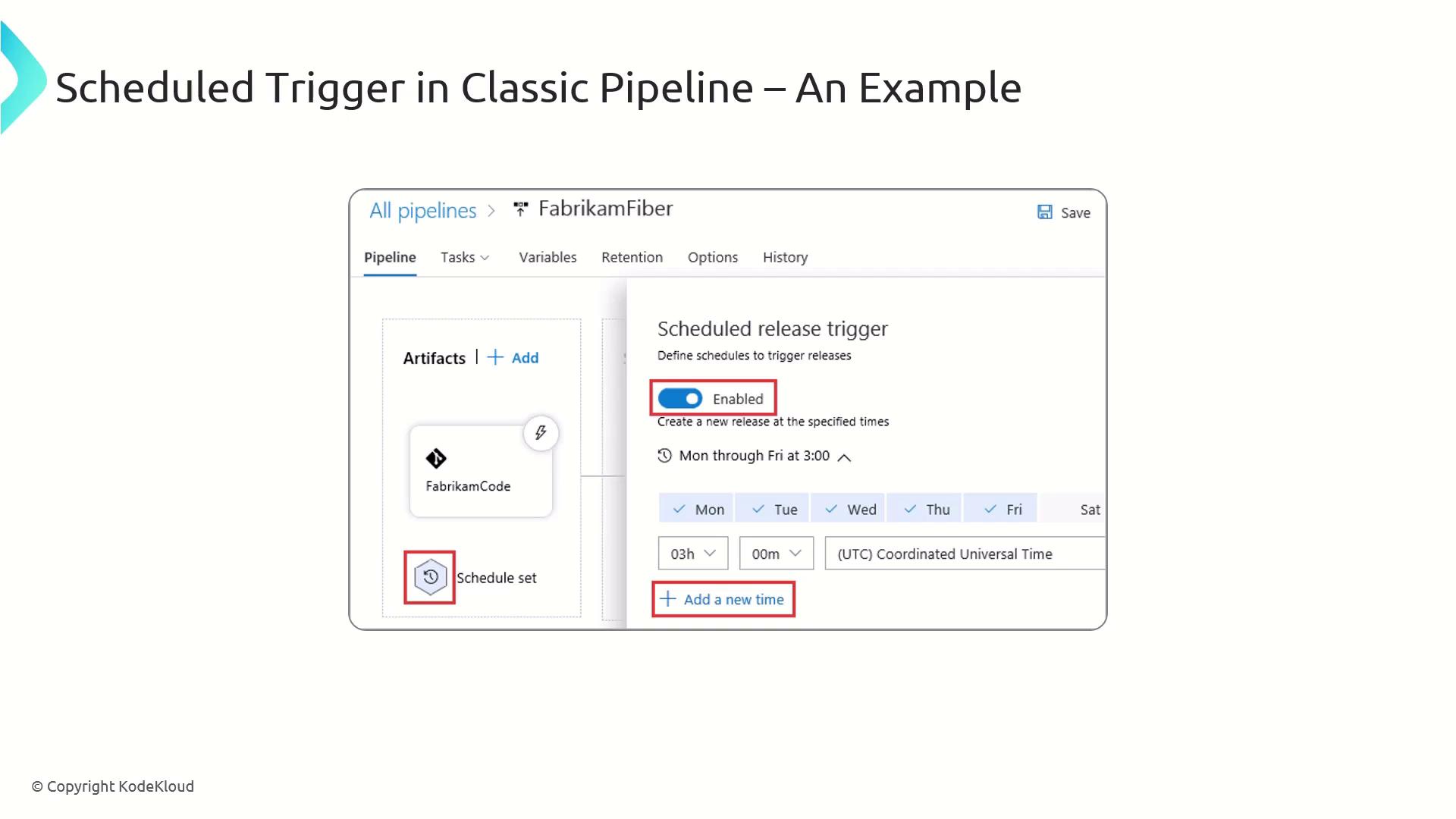
trigger: noneensures only scheduled runs occurcron:follows standard cron syntax (min, hour, dom, mon, dow)always: trueruns the job regardless of changes
Cron schedules in Azure Pipelines are evaluated in UTC. Adjust your
cron expression if your team operates in other time zones.Pull Request (PR) Triggers
PR triggers automatically validate code changes when a pull request is opened or updated. This enforces quality gates before merging to protected branches.
pr:defines pull request validation triggersbranches.include:lists target branches for PR checkspaths.exclude:skips runs when only documentation changes
Manual Triggers
Manual triggers allow teams to start pipelines on demand for production rollouts, hotfix deployments, or ad hoc testing.
- Azure DevOps UI: Click Run pipeline and select parameters
- Azure CLI:
Manual deployments bypass automated gates. Ensure you have approvals or checks in place for sensitive environments.
Best Practices
Adopt these recommendations to keep your pipelines efficient and reliable:- Be selective with branch filters to reduce unnecessary runs.
- Use path and tag filters to scope triggers precisely.
- Combine CI, PR, and scheduled triggers for comprehensive coverage.
- Implement manual approvals for production or compliance-sensitive deployments.
- Regularly review and clean up stale schedules or branch patterns.