Table of Contents
- Basic Trigger Types
- Refining CI Triggers with Branch & Path Filters
- Example: Updating
launchsettings.json - Pull Request Triggers
- Scheduled Triggers
- Tag-Based Triggers
- Pipeline Resource Triggers
- Managing YAML in Azure Repos
- Summary
- Links and References
Basic Trigger Types
Azure Pipelines supports several trigger rules to automate builds and deployments. The key types are:| Trigger Type | Purpose | Example Snippet |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Integration (CI) | Run on every code push | trigger: - master |
| Pull Request (PR) | Validate PRs before merging | pr: branches: include: - master |
| Scheduled | Run on a defined cron schedule | schedules: - cron: "0 2 * * *" |
| Tag-Based | Trigger when a version tag is pushed | trigger: tags: include: - 'v*' |
| Pipeline Resource | Run after another pipeline completes | resources: pipelines: ... |
1. Continuous Integration (CI)
A CI trigger automatically starts a build when code is pushed to specified branches.2. Pull Request (PR)
PR triggers validate changes in pull requests before they’re merged into the target branch.3. Scheduled
Schedule pipelines using cron syntax to run at regular intervals.4. Tag-Based
Trigger builds when Git tags matching a pattern are pushed.5. Pipeline Resource
Chain pipelines by triggering one when another succeeds.Refining CI Triggers with Branch & Path Filters
By default, a CI trigger onmaster fires for any change. You can target multiple branches and restrict file paths:
master or any feature/* branch only when files under Properties/ change (ignoring Markdown updates).
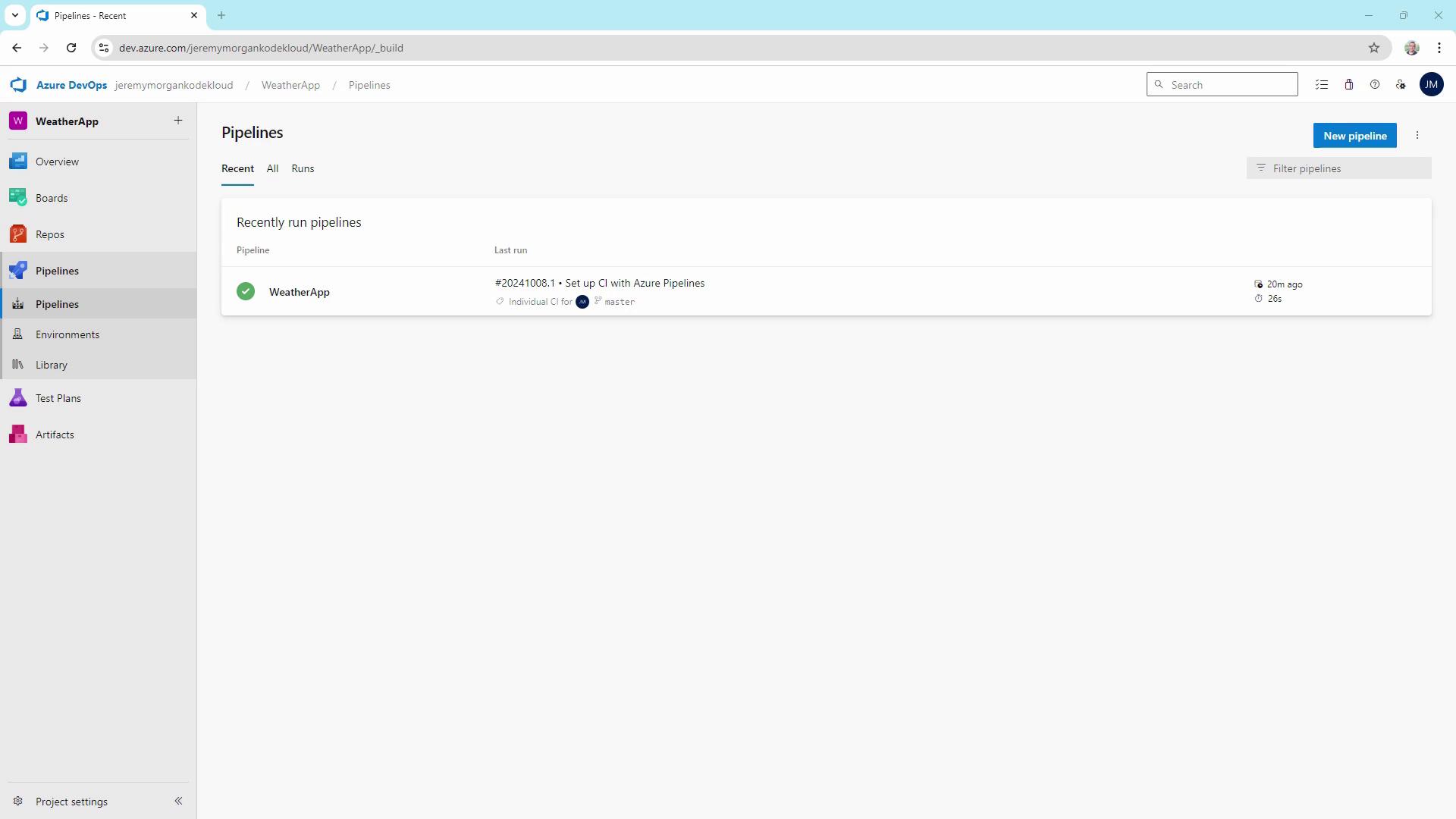
Example: Updating launchsettings.json
Let’s make a change inside the monitored Properties folder:
Properties/, the CI pipeline triggers again.
Pull Request Triggers
To enforce code quality before merging, add a PR trigger in your YAML:Testing Feature Branch Builds
Validating Pull Requests
When you open a PR againstmaster in Azure Repos, the pipeline runs against the merged commit, ensuring no regressions slip through.
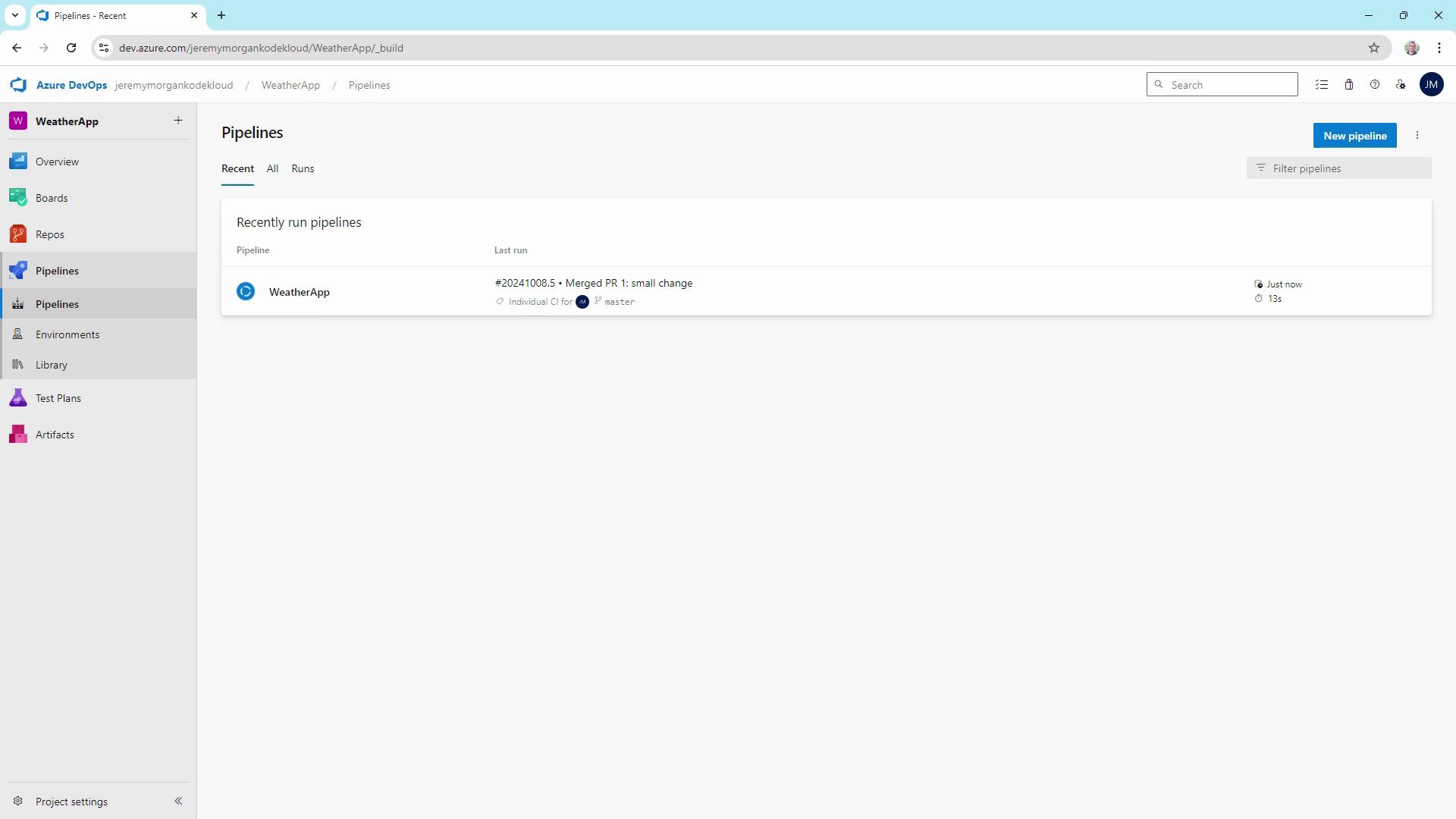
Use PR triggers to run tests, deploy to staging, or produce artifacts before merging.
Scheduled Triggers
Nightly or hourly builds help catch issues that arise over time:The setting
always: true ensures the pipeline runs regardless of code changes.Tag-Based Triggers
Create a build when you tag a release (e.g.,v1.0.0), but only if source or test files changed:
Pipeline Resource Triggers
Connect pipelines to build downstream artifacts automatically:Managing YAML in Azure Repos
Maintainingazure-pipelines.yaml in source control provides:
- Versioned build definitions
- Easier peer review and auditing
- Consistent CI/CD behavior across environments
Summary
By configuring CI, PR, scheduled, tag-based, and pipeline-resource triggers, you can:- Accelerate feedback loops
- Enforce quality gates before merges
- Automate nightly or periodic builds
- Trigger releases on semantic version tags
- Orchestrate multi-pipeline workflows