Core Security Pillars
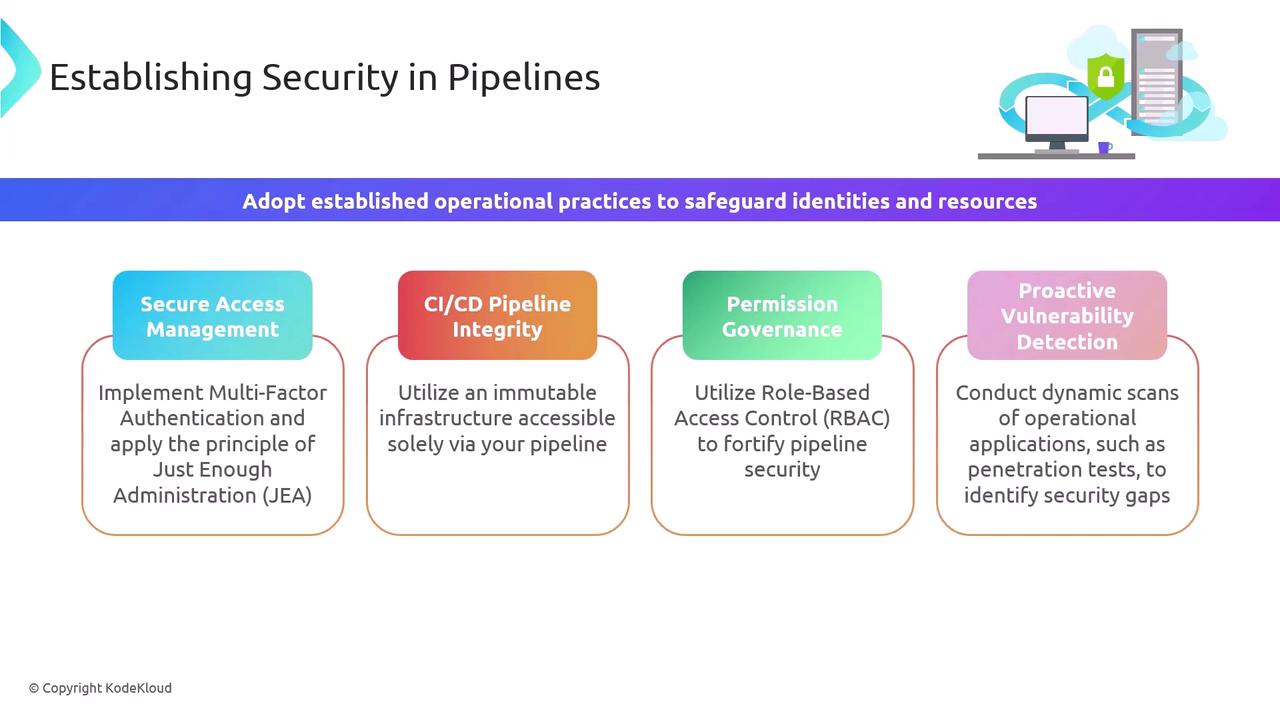
Below are the four fundamental areas you must address to lock down your development pipeline:| Security Pillar | Goal | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Secure Access Management | Ensure only authenticated and authorized users can interact with your pipeline | Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Just-Enough Administration |
| CI/CD Pipeline Integrity | Prevent unauthorized changes to production environments | Adopt immutable infrastructure and restrict direct SSH/RDP access |
| Permission Governance | Define and enforce granular permissions | Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to limit actions per user/group |
| Proactive Vulnerability Detection | Identify and remediate security issues early | Integrate Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) and regular penetration tests |
Regularly review and rotate credentials, secrets, and tokens. Leverage secret management solutions like Azure Key Vault or HashiCorp Vault to avoid hard-coding sensitive data.
Advanced Deployment Pipeline Strategies
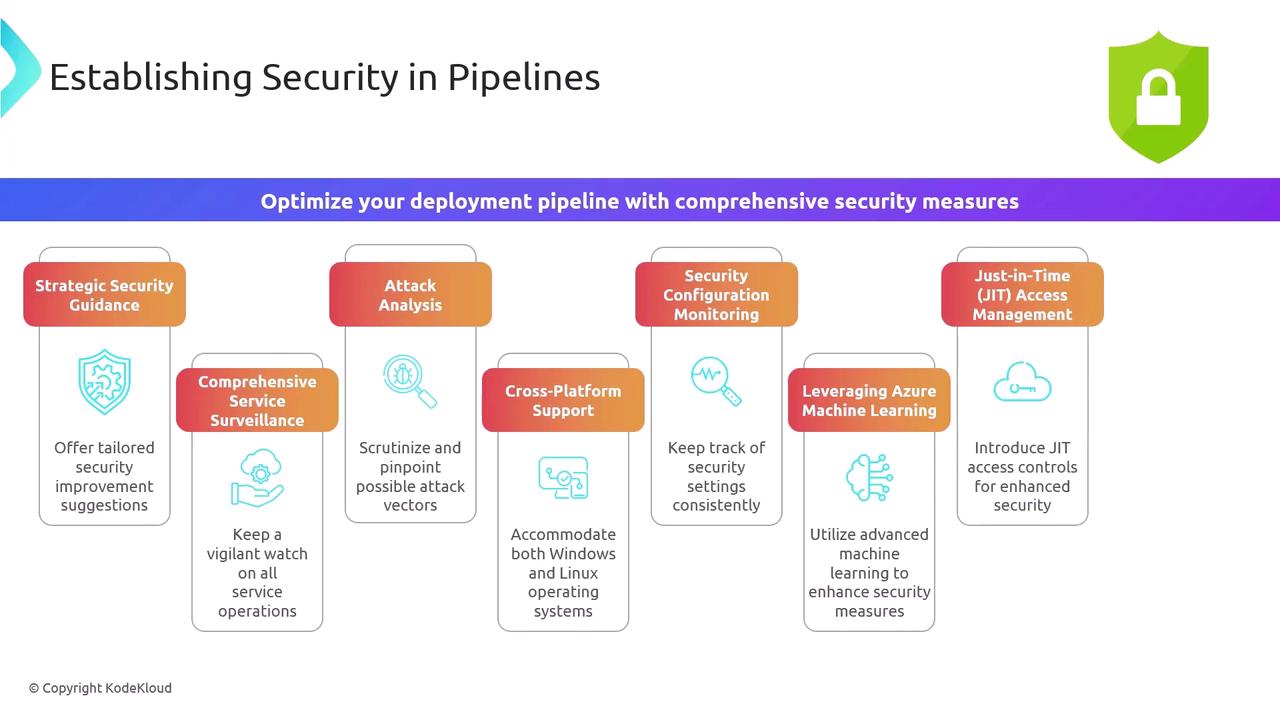
To further enhance your security posture, incorporate these eight practices into your release process:-
Strategic Security Guidance
Automate policy-as-code and compliance verifications that reflect your organizational requirements. -
Comprehensive Service Surveillance
Continuously monitor microservices and infrastructure events for anomalous behavior. -
Attack Analysis & Threat Modeling
Map out attack vectors and incorporate threat modeling to prioritize risk mitigation. -
Cross-Platform Support
Ensure security tooling works seamlessly on both Windows and Linux build agents. -
Configuration Drift Detection
Use continuous configuration monitoring to enforce secure baselines and identify unauthorized changes. -
Leveraging Azure Machine Learning
Apply Azure Machine Learning to analyze logs, detect anomalies, and automate responses. -
Just-In-Time Access Management
Grant elevated privileges only when needed and for a limited time frame. -
Flexible Pricing Options
Select the Azure security tier that aligns cost with your compliance and risk tolerance.
When enabling Just-In-Time access, always define strict time windows and approval workflows. Uncontrolled privileged sessions increase your attack surface.