AZ-400: Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps Solutions
Implement Security and Validate Code Bases for Compliance
Exploring Use Cases for Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a cloud-native security solution that strengthens your Azure environment by combining proactive recommendations with reactive incident management. In this guide, we’ll cover its two primary use cases—Incident Management and Security Optimization—along with core components that power these scenarios.
Key Use Cases
- Incident Management: A structured response cycle to detect, assess, and remediate threats.
- Security Optimization: Continuous policy enforcement and actionable recommendations to harden your environment.
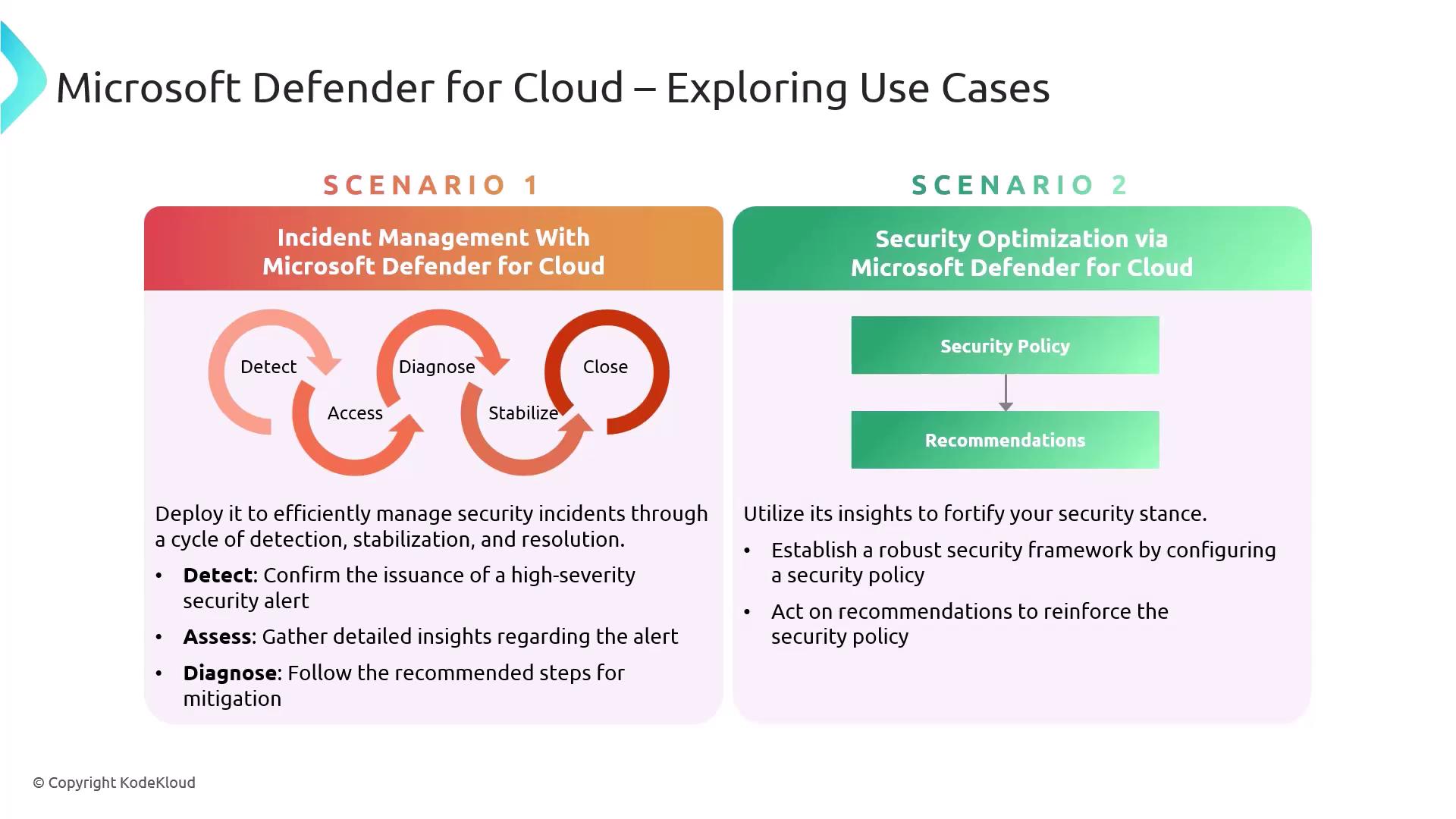
1. Incident Management
Microsoft Defender for Cloud provides a repeatable cycle to handle security incidents from detection to closure.
1.1 Detect
Verify that a high-severity security alert has been generated in the Azure portal or exported to your SIEM.
1.2 Assess
Collect detailed information about the alert, including affected resources, timeline, and potential impact.
1.3 Diagnose
Follow the remediation steps recommended by the alert. Common actions include isolating compromised resources, rotating credentials, and applying patches.
1.4 Stabilize and Close
Confirm that the threat has been neutralized, apply any remaining mitigations, then officially close the incident.
Note
Enable continuous export of security alerts to integrate Defender for Cloud with your SIEM or ITSM workflows.
2. Security Optimization
Security Optimization in Defender for Cloud helps you establish a strong security baseline and continuously reinforce it:
- Configure Security Policies
Define your desired security posture by assigning built-in or custom policies at subscription or resource group scope. - Review Recommendations
Defender for Cloud analyzes your configuration and generates prioritized recommendations. - Remediate
Accept or automate fixes using Azure Policy, Azure Blueprints, or your favorite IaC tool.
This diagram illustrates how Defender for Cloud continuously monitors Azure resources, collects security telemetry, and surfaces actionable insights to maintain a strong cloud security posture.
Continuous Monitoring & Analysis
Defender for Cloud uses built-in sensors and services to collect logs, network traffic data, and threat intelligence. It then correlates events to detect sophisticated attacks, compromised accounts, and lateral movement.
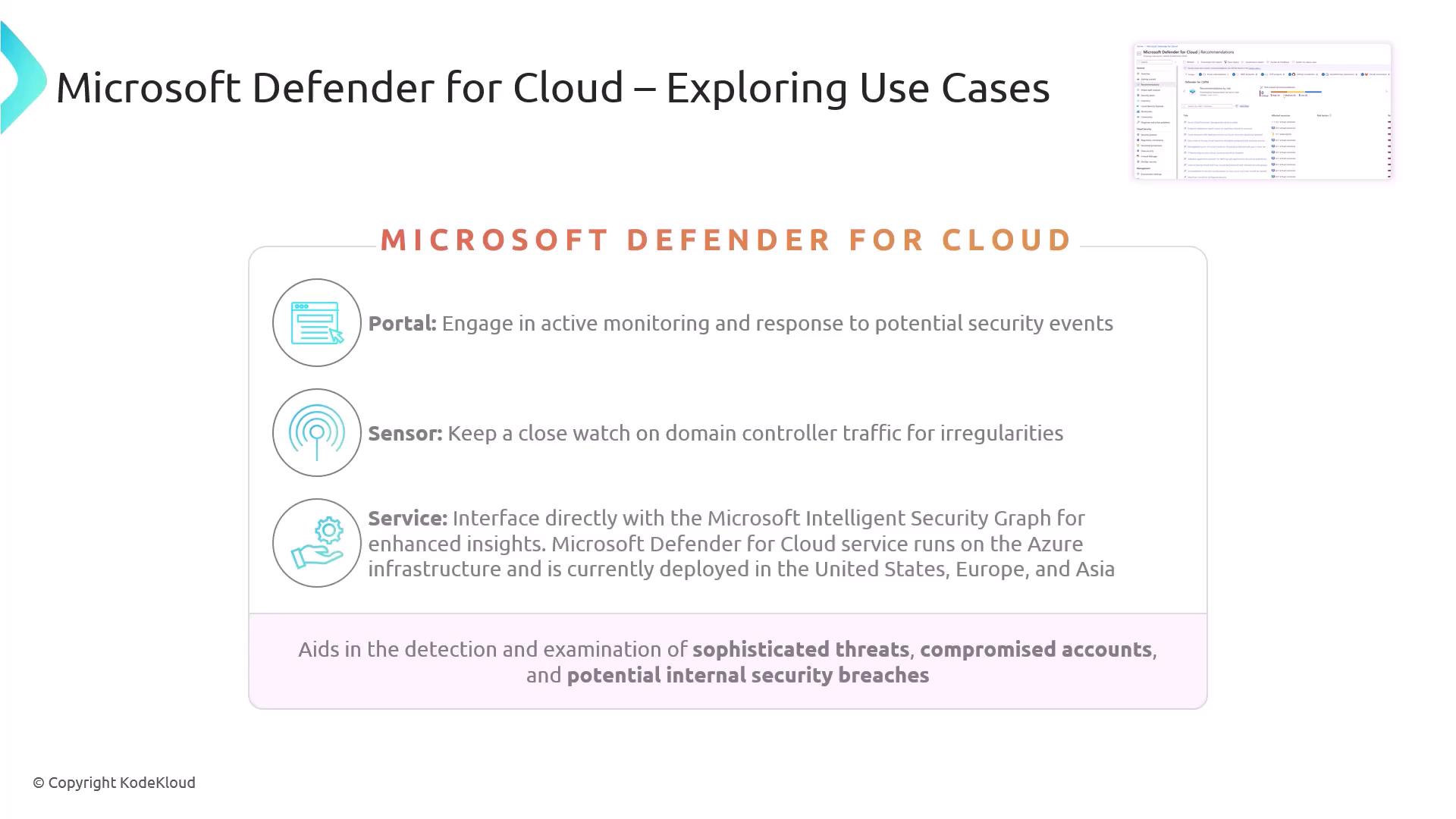
Core Components of Microsoft Defender for Cloud
| Component | Description | Deployment Regions |
|---|---|---|
| Portal | Central console for managing alerts, policies, and recommendations. | Global |
| Sensor | Monitors domain controller traffic and resource logs for anomalous activity. | Global |
| Service | Leverages the Microsoft Intelligent Security Graph for threat intelligence and advanced analytics. | US, Europe, Asia |
Warning
Enabling all recommendations at once may increase your operational costs. Review priority and impact before remediation.
By combining these components, Defender for Cloud helps you:
- Detect and investigate advanced threats
- Respond rapidly with guided remediation
- Continuously enforce security best practices
References
- Microsoft Defender for Cloud Documentation
- Azure Security Center Overview
- Azure Policy in Practice
- Microsoft Intelligent Security Graph
Watch Video
Watch video content