Defining Stages and Dependencies in Azure Pipelines
Stages represent the major phases of your pipeline (for example, Build, Test, and Deploy). By default, these stages run in the order they’re defined, but you can customize their execution sequence with thedependsOn keyword. In the example below, the Deploy stage waits for both Build and Test to finish before starting:
build_app, run_tests, and deploy_app) that run in parallel or sequence according to your configuration.
Using Conditions for Conditional Execution
Conditions add intelligence to your pipeline by allowing stages, jobs, or steps to run—or be skipped—based on branches, variables, or the outcomes of previous tasks. You define these checks using thecondition keyword. For example, you may want to deploy to production only when the pipeline runs on the main branch and every prior stage has succeeded.
Use conditions to optimize build time and resource usage by skipping unnecessary stages.
For more details, see Variables in Azure Pipelines.
For more details, see Variables in Azure Pipelines.
Example: Branch-Aware Multi-Stage Pipeline
Below is a sample YAML that combines sequential stages with branch-based conditions. The Build stage compiles your code and runs unit tests, with an extra check to decide whether to proceed. The Deploy stage only triggers onrefs/heads/main.
main. Otherwise, the deployment stage is skipped.
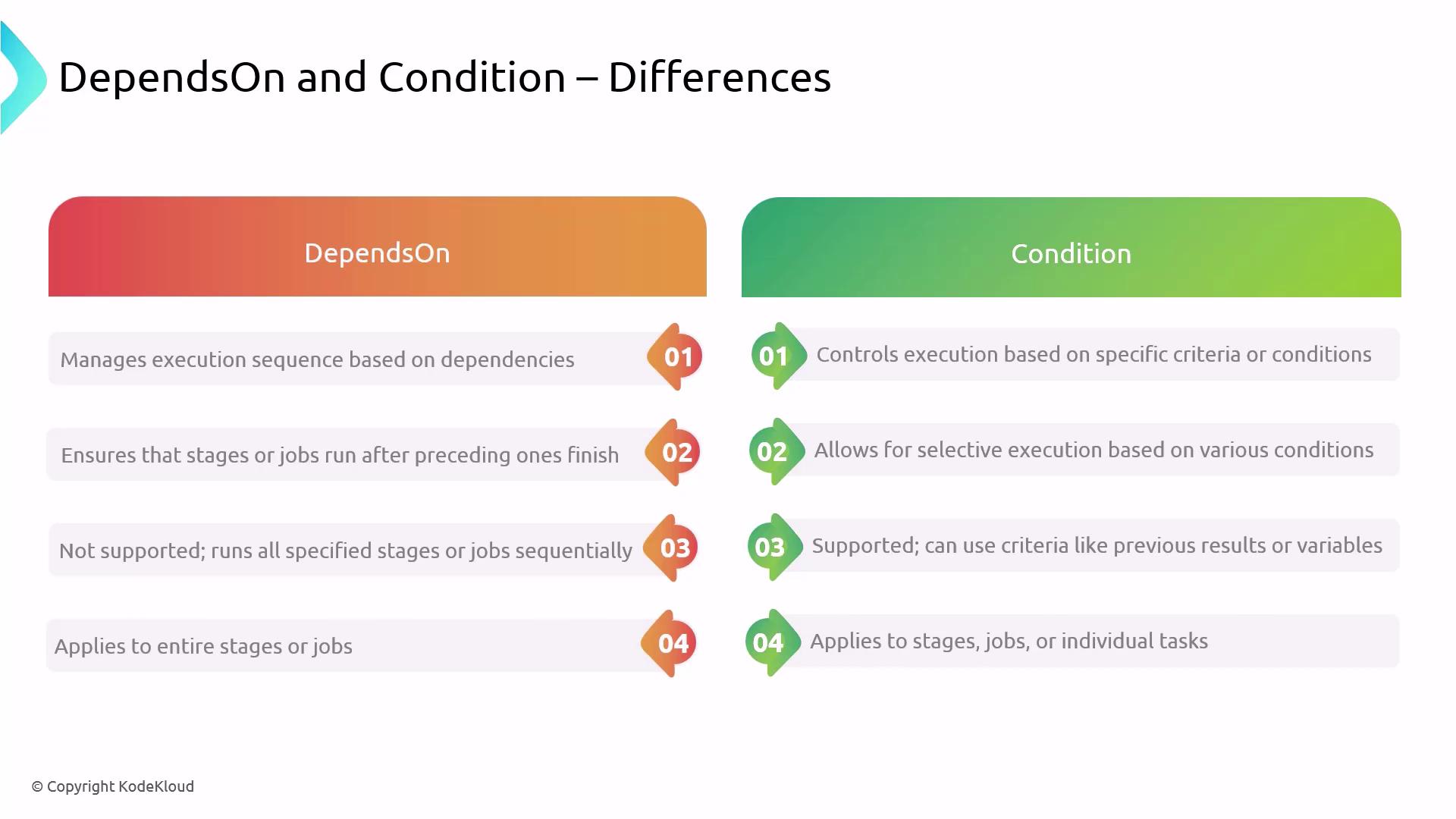
dependsOn vs condition: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Aspect | dependsOn | condition |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Control | Enforces order or parallelism based on stages | Evaluates expressions (branches, variables, results) |
| Criteria | Completion status of specified predecessors | Custom criteria (e.g., branch name, variable values) |
| Application Scope | Stage or job level | Stage, job, or individual step level |
| Parallel Execution | Supports parallel runs when no dependencies | Skips or runs tasks based on evaluated expressions |
Best Practices for Stages, Dependencies, and Conditions
- Align stages with your development lifecycle (e.g., Build → Test → Deploy).
- Use
dependsOnto enforce critical order or allow safe parallelism. - Apply
conditionto skip unnecessary runs and save resources.
Overly complex dependencies and conditions can make pipelines hard to maintain. Keep configurations as clear and simple as possible.