In this guide, you’ll learn how to automate token replacement in your Kubernetes manifests using GitHub Actions. We will cover:
Defining repository-level variables for namespace, replicas, and image
Installing and configuring the cschleiden/replace-tokens@v1 action
Dynamically fetching the Ingress controller’s external IP
Applying placeholder replacement in kubernetes/development/*.yaml
Verifying the transformed manifests before deployment
Placeholder tokens in your manifests Under kubernetes/development/, manifests contain tokens like {_NAMESPACE_}, {_REPLICAS_}, {_IMAGE_}, and {_INGRESS_IP_}:
# kubernetes/development/deployment.yaml apiVersion : apps/v1 kind : Deployment metadata : name : solar-system namespace : { _NAMESPACE_ } spec : replicas : { _REPLICAS_ } selector : matchLabels : app : solar-system template : metadata : labels : app : solar-system spec : containers : - name : solar-system image : { _IMAGE_ } imagePullPolicy : Always ports : - containerPort : 3000 name : http
# kubernetes/development/service.yaml apiVersion : v1 kind : Service metadata : name : solar-system namespace : { _NAMESPACE_ } spec : ports : - port : 3000 targetPort : 3000 selector : app : solar-system
# kubernetes/development/ingress.yaml apiVersion : networking.k8s.io/v1 kind : Ingress metadata : name : solar-system namespace : { _NAMESPACE_ } annotations : kubernetes.io/tls-acme : "true" spec : rules : - host : solar-system-{_NAMESPACE_}.{_INGRESS_IP_}.nip.io http : paths : - path : / pathType : Prefix backend : service : name : solar-system port : number : 3000 tls : - hosts : - solar-system-{_NAMESPACE_}.{_INGRESS_IP_}.nip.io secretName : solar-system
All tokens must be replaced before applying these files to the cluster.
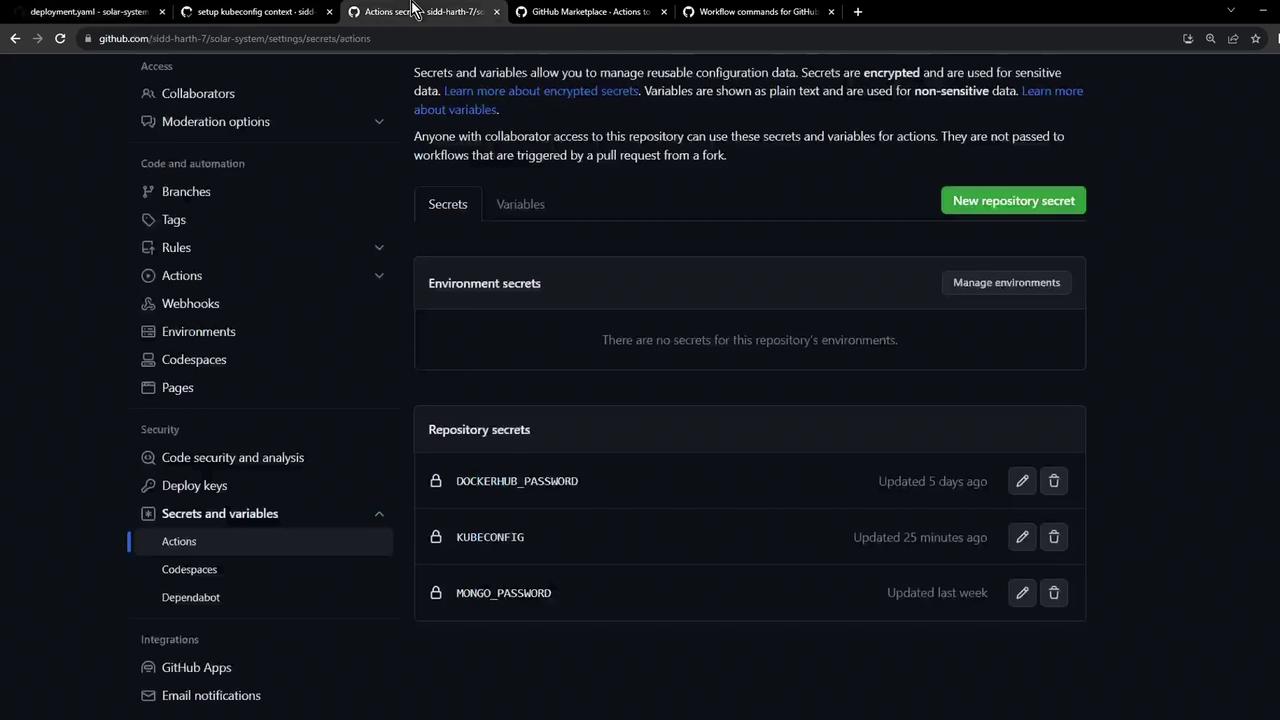
1. Define repository variables Navigate to Settings > Secrets and variables > Actions in your GitHub repository. Here you can add both non-secret variables and secrets.
Use Variables for non-sensitive configuration (e.g., NAMESPACE, REPLICAS) and Secrets for credentials (KUBECONFIG, DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD).
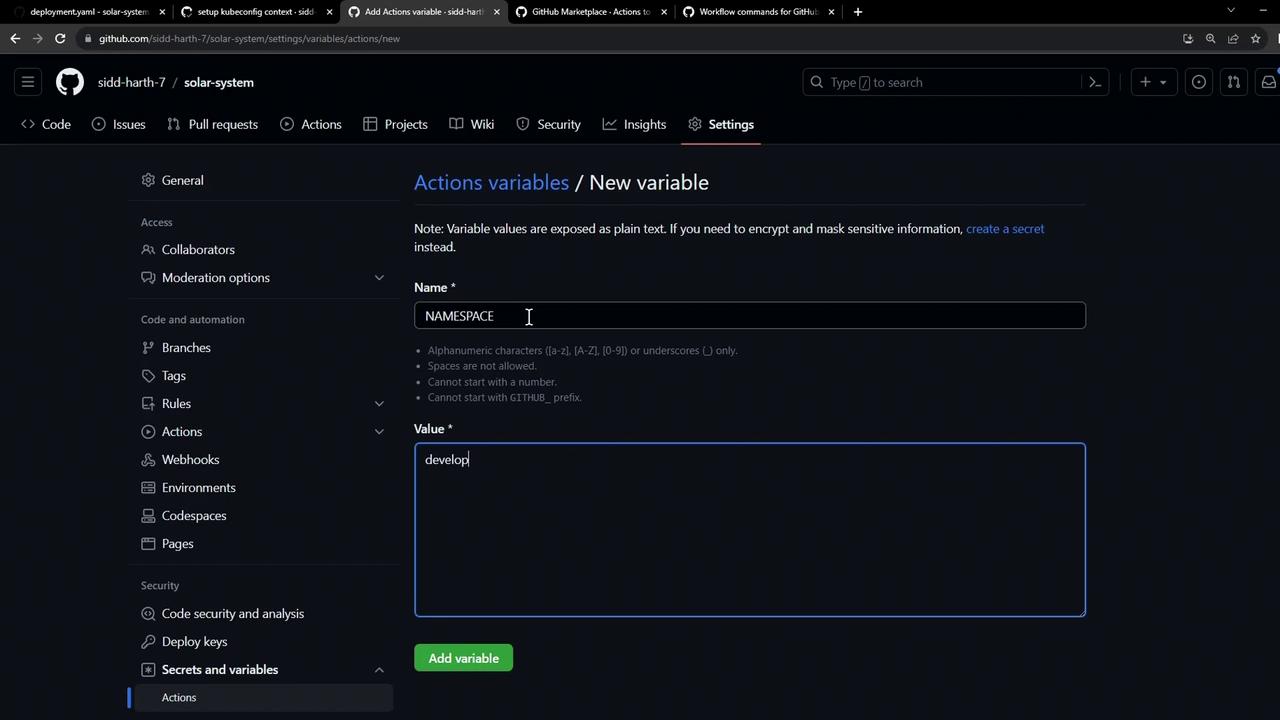
Add the following repository variables:
Name Value Description NAMESPACE development Kubernetes namespace for development REPLICAS 2 Number of replicas to deploy
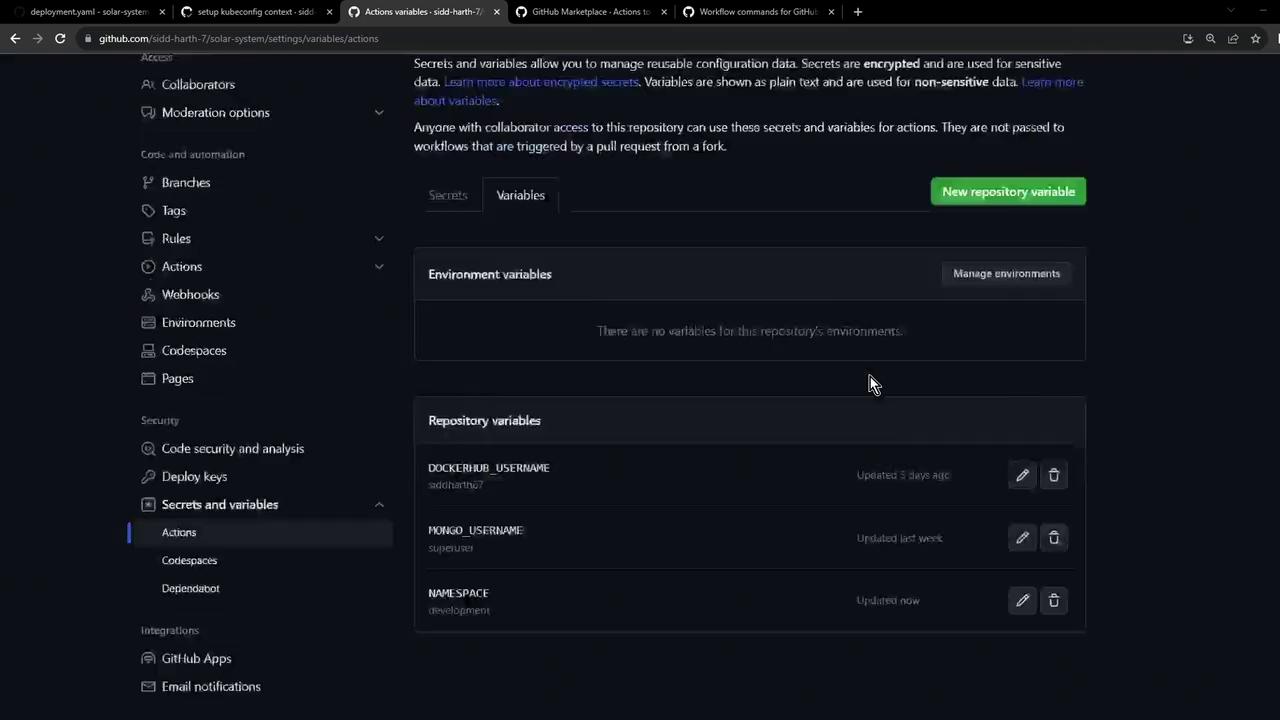
Once added, your list should look like this:
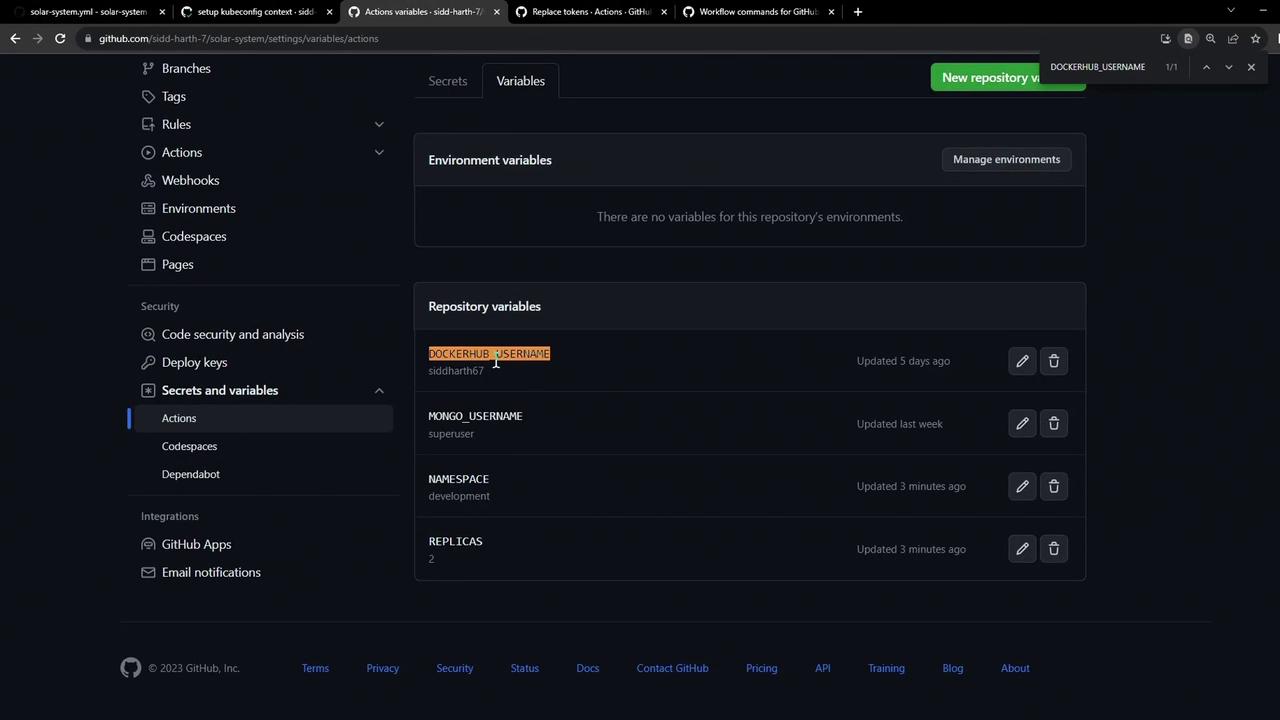
Ensure you also have DOCKERHUB_USERNAME defined for constructing the container image reference:
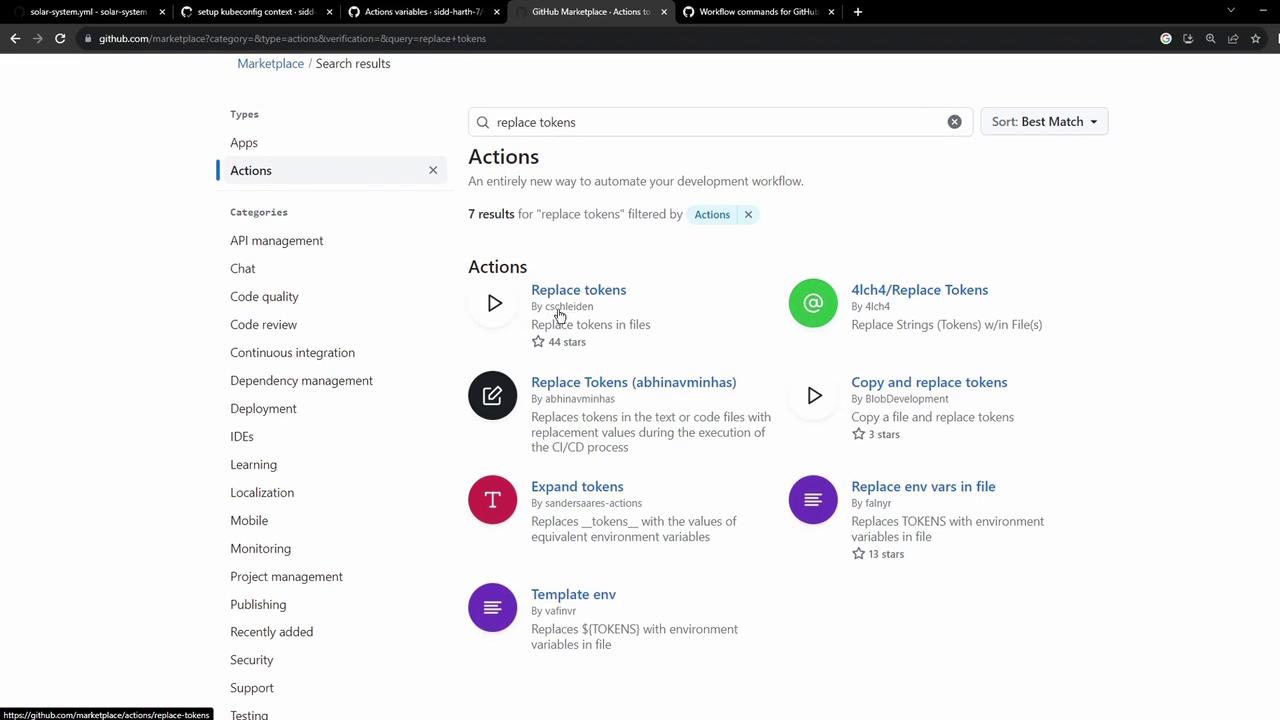
2. Choose a token-replacement action From the GitHub Marketplace, install cschleiden/replace-tokens@v1 . This action will scan files and replace tokens based on your specified prefix and suffix.
Example configuration:
- uses : cschleiden/replace-tokens@v1 with : tokenPrefix : '{_' tokenSuffix : '_}' files : 'kubernetes/development/*.yaml' env : NAMESPACE : ${{ vars.NAMESPACE }} REPLICAS : ${{ vars.REPLICAS }} IMAGE : ${{ vars.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}/solar-system:${{ github.sha }} INGRESS_IP : ${{ env.INGRESS_IP }}
3. Fetch the Ingress IP dynamically Hard-coding the external IP limits flexibility. Instead, retrieve it at runtime using kubectl and store it in GITHUB_ENV:
kubectl -n ingress-nginx get svc ingress-nginx-controller \ -o jsonpath="{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}"
In your workflow, you’ll capture this value:
- name : Save NGINX Ingress Controller IP id : save_ingress_ip run : | echo "INGRESS_IP=$(kubectl -n ingress-nginx \ get svc ingress-nginx-controller \ -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')" >> $GITHUB_ENV
4. Complete GitHub Actions workflow Below is a full example workflow that ties everything together:
name : Dev Deploy on : push : branches : [ main ] jobs : deploy : runs-on : ubuntu-latest steps : - name : Checkout repository uses : actions/checkout@v3 - name : Set Kubeconfig uses : azure/k8s-set-context@v3 with : method : kubeconfig kubeconfig : ${{ secrets.KUBECONFIG }} - name : Fetch Kubernetes cluster details run : | kubectl version --short echo "----------------------------------------------" kubectl get nodes - name : Save NGINX Ingress Controller IP id : save_ingress_ip run : | echo "INGRESS_IP=$(kubectl -n ingress-nginx \ get svc ingress-nginx-controller \ -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')" >> $GITHUB_ENV - name : Replace tokens in Kubernetes manifests uses : cschleiden/replace-tokens@v1 with : tokenPrefix : '{_' tokenSuffix : '_}' files : 'kubernetes/development/*.yaml' env : NAMESPACE : ${{ vars.NAMESPACE }} REPLICAS : ${{ vars.REPLICAS }} IMAGE : ${{ vars.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}/solar-system:${{ github.sha }} INGRESS_IP : ${{ env.INGRESS_IP }} - name : Verify token replacement run : | echo "=== deployment.yaml ===" cat kubernetes/development/deployment.yaml echo "=== service.yaml ===" cat kubernetes/development/service.yaml echo "=== ingress.yaml ===" cat kubernetes/development/ingress.yaml
5. Outcome After the workflow completes:
namespace will be set to developmentreplicas updated to 2image resolved as <your-dockerhub-username>/solar-system:<commit-sha>Ingress host entries generated with the actual load balancer IP
This pattern can be replicated for other environments (e.g., kubernetes/production/) by adjusting repository variables and glob patterns in the workflow.
Links and References